Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
How The Body Heals Itself - Immune System
Загружено:
SyncOrSwimОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
How The Body Heals Itself - Immune System
Загружено:
SyncOrSwimАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
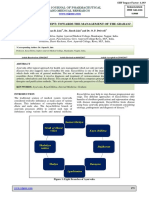
HOW THE BODY HEALS ITSELF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
Cellular damage occurs repeatedly every day
Sunlight, toxins, chemicals, infections and other irritants damage cells every day Cuts, scrapes, blows and other minor injuries cause damage to millions of cells and tissues that must be regenerated and replaced Even exercise and exertion can damage cells, causing tenderness (strain) and muscle aches
How does the body recognize damage?
When cells are damaged the natural balanced chemistry inside the cell is disturbed, causing a shift in healthy metabolism and oxidative stress results Oxidative Stress is the natural build-up of oxidant molecules, including free radicals, in the liquid environment inside cells Oxidative stress is the condition that sends up red flags to neighboring healthy cells that cells have been damaged in their neighborhood
How does the body repair damage?
The immune system is activated by oxidative stress to kill the harmful invading organisms The immune system also kills and dissolves damaged cells that cannot be repaired (swelling and redness mark this stage) damaged cells and foreign materials
How does the body regenerate tissues?
Healthy balanced chemistry is restored after all invading organisms are dead and damage is cleaned up (the red flags are turned off) Restoration of this chemical balance turns off swelling and redness and stimulates neighboring healthy cells to divide and fill in the missing cells and tissue Healthy cells still continue to divide and multiply until the gap has been filled in with healthy new cells
How does the body maintain a healthy chemical balance?
Anti protect healthy cells Antioxidants keep excess oxidants in check, neutralizing them and maintaining correct chemical balance Cells produce antioxidants and deploy them to protect vulnerable areas inside and outside of the cell
How are Reductants and oxidants made?
Reduct formed naturally in the cell, made from the simple atoms in the salt water that fill and surround the cells The Mitochondria inside the cells produce these reactive molecules both oxidants and Reductants and also produce the fuel used to energize the cell (ATP) The Reductants pair up with anti-oxidants to protect the cell from excess reactive oxygen and toxins The oxidants are the weapon of choice used by the immune system to destroy invading organisms
attack
Why is a healthy chemical balance
important?
Too many oxidants in the cells or blood causes damage and aging to all tissues An incorrect balance of Reductants and oxidants can cause the immune system to attack healthy cells , inflame tissues and slows down the healing process Too few oxidants will infected and malfunctioning cells (those that should be flagged and destroyed by the immune system) to thrive, divide and spread the damage
How can I help maintain a healthy chemical balance?
Supplement the raw materials the body needs to support the immune system
Raw, green vegetables, juices and herbs Or, anti-oxidants and vitamin supplements
Use products that have the correct balance of Reductants that enhance the action of the anti-oxidants Maintain a proactive and healthy attitude mental attitude measurably helps balance chemistry
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. H. Kiura, et al., "Bactericidal activity of electrolyzed acid water from solution containing sodium chloride at low concentration, in comparison with that at high concentration", J. Microbio. Methods, v49, p285-93 (2002) I.J. Wilk, RS Altmann an p191-197, Elsevier Science Pub (1987) d with reference to the -651 (2003) -68 (1978) Sung-Hoon Lee and Bong-22 (Aug 2006) -53 (1 Nov 2004) H. Tanaka, et al., "Antimicrobial activity of superoxidized water", J. Hospital Infection, v34(1), p43-49 (Sep 1996) for J of Bio Chem v281,52 p39860-69 (29 Dec 2006) y -82 (Jan 2004) 1307-1313 (2001) Research Comm, v234(1), p269-74 (May 8,1997)
-195 (1984)
p571-574 (2003) 14. -438 (2003) 15. S. Roy, et al., "Dermal wound healing is subject to redox control", Mol Ther., v13(1), p211-220 (Jan 2006) 16. -induced oxidative stress in endInternational v62(2), p704-14 (Aug 2003) 17. th Chloride-7 (1980) 18. Oxygen Radicals in Biology and Medicine, Plenum Press, ed. Michael G. Simic, et al. (1987) [Book based on papers presented at the ld June 27 July 3, 1987 at the University of California, La Jolla.] 19. Oxygen Radicals in Biology and Medicine, Plenum Press, ed. Michael G. Simic, et al. (1987) [Book based on papers presented at the -ICO July 3, 1987 at the University of California, La Jolla.] 20. troduction to Peroxidation and 21. or Dioxygen Species (O2, O2-*, HOO*, HOOH and HOO-) and Monooxygen species (O, O-*, *OH and OH22. r Protection Against Damage by 23. Vol I,II, CRC Press (1989) 24. The Biology and Chemistry of Active Oxygen, Elsevier, Volume 26, ed. J.V. and W.H. Bannister, (1984) 25. 26. Superoxide Dismutase Activi Pg. 146 27. 28. 29. Antioxidant and Redox Regulation of Genes, Academic Press, ed. Chandan K. Sen (2000) 30. Lars-Oliver Klotz, et al., "Signaling by Singlet Oxygen in Biological Systems", Pg. 3
31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46.
Crawford, Suzuki and Davies, "Redox Regulation of Gene Expression", Pg. 21 Giron-Calle and Forman, "Cell Ca2+ in Signal Transduction: Modulation in Oxidative Stress", Pg. 106 P.A. Baeuerle, "Reactive Oxygen Species as Costimulatory Signals of Cytokine-Induced NF-kappaB Activation Pathways", Pg. 181 V.Goossens, et al., "Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in Tumor Necrosis Factor Toxicity", Pg. 245 S. Roy, C.K. Sen, et al., "Redox Regulation of Cell Adhesion Processes", Pg. 266 N. Maulic and D.K. Das, "Redox Regulation of Ischemic Adaptation", Pg. 492 W.C. Orr and R.S. Sohal, "Oxidative Stress as a Governing Factor in Physiological Aging", Pg. 517 L.S. Terada, "Specificity in reactive oxidant signaling: think globally, act locally (mini review)", J. of Cell Biology, v174(5), p615-23 (Aug 2006) 75 pC1-C24 (1998) H.T.F. Facundo, et al., "Mitochondrial ATP-sensitive K+ channels are redox-sensitive pathways that control reactive oxygen species production", Free Radical Biology and Medicine, v42(7), p1039-48 (Apr 2007) -64 (2005) [http://www.protein.bio.msu.ru/biokhimiya/contents/v70/pdf/bcm_0200.pdf] A.F. Jalbout, X.H. Li and M Solimannejad, "Thermochemical stability of the HO2-HOCl complex", Chem. Phys. Letters, v420 (1-3), p 20408 (Mar 2006) M. Solimannejad, I. Alkorta, J. Elguero, "Stabilities and Properties of O3-HOCl complexes; A computational study", Chem. Phys. Letters, v449, p 23-27 (2007) D.C. Phillips, et al., "Sphingosine-Induced Apoptosis in Rhabdomyosarcoma Cell Lines Is Dependent on Pre-Mitochondrial Bax Activation and Post-Mitochondrial Caspases", Cancer Res, v67(2), p756-64 (Jan 2007) C.M. Cruz, et al., "ATP Activates a ROS-dependent Oxidative Stress Response and Secretion of Proinflammatory Cytokines in Macrophages", The J. or Bio. Chem., v282(5), p2871-79 (Feb 2007) B.J. Hawkins, M. Madesh, C.J. Kirkpatrick, A.B. Fisher, "Superoxide Flux in Endothelial Cells via the Chloride Channel-3 Mediates Intracellular Signaling", Molec. Bio. of the Cell, v18, p2002-2012 (Jun 2007)
Вам также может понравиться
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Book of EnochДокумент137 страницThe Book of EnochSyncOrSwim100% (19)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Thyroid Reset Diet 3 ChaptersДокумент71 страницаThe Thyroid Reset Diet 3 ChaptersjovaneticОценок пока нет
- Pattern For The Second Coming.Документ1 страницаPattern For The Second Coming.SyncOrSwimОценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- In Need of A Revelation About The Book of RevelationДокумент7 страницIn Need of A Revelation About The Book of RevelationSyncOrSwim100% (1)
- True PDFДокумент459 страницTrue PDFAmna MmfОценок пока нет
- 04 - Typhoid FeverДокумент35 страниц04 - Typhoid Feversoheil100% (1)
- Micp211 - Lecture: Introduction To MicrobiologyДокумент23 страницыMicp211 - Lecture: Introduction To MicrobiologyAngelica LegaspiОценок пока нет
- Laparoscopic Anatomy of The Abdominal CavityДокумент14 страницLaparoscopic Anatomy of The Abdominal CavityUffie-Isabela GheОценок пока нет
- Primary Graduation Certificate TemplateДокумент2 страницыPrimary Graduation Certificate TemplateSyncOrSwimОценок пока нет
- Paul's Journey To Rome, SimplifiedДокумент1 страницаPaul's Journey To Rome, SimplifiedSyncOrSwimОценок пока нет
- At Peace With GodДокумент175 страницAt Peace With GodSyncOrSwimОценок пока нет
- The Brass Plates Story - Book On A PageДокумент2 страницыThe Brass Plates Story - Book On A PageSyncOrSwimОценок пока нет
- David Albert Whitmer Interview 11-15-95Документ26 страницDavid Albert Whitmer Interview 11-15-95SyncOrSwimОценок пока нет
- 'Messiah' in Hebrew and GreekДокумент4 страницы'Messiah' in Hebrew and GreekSyncOrSwimОценок пока нет
- David Albert Whitmer Interview 11-18-93Документ27 страницDavid Albert Whitmer Interview 11-18-93SyncOrSwimОценок пока нет
- Eve Handout - 4 UpДокумент1 страницаEve Handout - 4 UpSyncOrSwimОценок пока нет
- Elijah Map - Letter SizeДокумент1 страницаElijah Map - Letter SizeSyncOrSwimОценок пока нет
- 3 Nephi Chapter 17 - Book-On-A-page, InstructionsДокумент2 страницы3 Nephi Chapter 17 - Book-On-A-page, InstructionsSyncOrSwimОценок пока нет
- Ruth 1:16-17 - Book On A PageДокумент2 страницыRuth 1:16-17 - Book On A PageSyncOrSwimОценок пока нет
- Bednar Quote On Repentance - 4 UpДокумент1 страницаBednar Quote On Repentance - 4 UpSyncOrSwimОценок пока нет
- Abraham's Journeys - 12 X 18Документ1 страницаAbraham's Journeys - 12 X 18SyncOrSwimОценок пока нет
- The Idols We WorshipДокумент1 страницаThe Idols We WorshipSyncOrSwimОценок пока нет
- Mormon Missouri Timeline MapДокумент1 страницаMormon Missouri Timeline MapSyncOrSwimОценок пока нет
- Christmas Message 2013Документ4 страницыChristmas Message 2013SyncOrSwimОценок пока нет
- Suggested Steps For Responsible RevelationДокумент1 страницаSuggested Steps For Responsible RevelationSyncOrSwim0% (1)
- Stewardship Title CardsДокумент2 страницыStewardship Title CardsAnthony HermanОценок пока нет
- Alma's 50 QuestionsДокумент2 страницыAlma's 50 QuestionsSyncOrSwimОценок пока нет
- Who're You Calling A Luddite?Документ5 страницWho're You Calling A Luddite?SyncOrSwimОценок пока нет
- Jesus Loves Me-Everbody CardsДокумент2 страницыJesus Loves Me-Everbody CardsSyncOrSwimОценок пока нет
- The Arizona Center For Law in The Public Interest Slices and Dices The F-35A DEISДокумент13 страницThe Arizona Center For Law in The Public Interest Slices and Dices The F-35A DEISSyncOrSwimОценок пока нет
- Juliet Buck: Planet PentagonДокумент8 страницJuliet Buck: Planet PentagonSyncOrSwimОценок пока нет
- Away in A Manger - The Word Among UsДокумент4 страницыAway in A Manger - The Word Among UsSyncOrSwimОценок пока нет
- A Private Business That Has Become A Form of Permanent GovernmentДокумент29 страницA Private Business That Has Become A Form of Permanent GovernmentSyncOrSwimОценок пока нет
- GAO Report On The Growing Financial Crisis of The F-35 Joint Strike Fighter ProgramДокумент25 страницGAO Report On The Growing Financial Crisis of The F-35 Joint Strike Fighter ProgramSyncOrSwimОценок пока нет
- The Militarization of America - at What Cost?Документ93 страницыThe Militarization of America - at What Cost?SyncOrSwimОценок пока нет
- Personality DisordersДокумент51 страницаPersonality DisordersMary Jo LegaspiОценок пока нет
- Lynch Syndrome For The Gynaecologist, TOG-2021Документ12 страницLynch Syndrome For The Gynaecologist, TOG-2021saeed hasan saeedОценок пока нет
- Nejmoa1708566 PDFДокумент10 страницNejmoa1708566 PDFAhmad SahidОценок пока нет
- Modern Treatment Planning Approach Facing A Failure of Conventional Treatment. Part I: Analysis of Treatment OptionsДокумент11 страницModern Treatment Planning Approach Facing A Failure of Conventional Treatment. Part I: Analysis of Treatment OptionscdoskarОценок пока нет
- Munchies BrochureДокумент28 страницMunchies BrochureIbrahim Diaz LazoОценок пока нет
- Lipids Review QuestionsДокумент10 страницLipids Review QuestionsDavid TamayoОценок пока нет
- Primary HyperparathyroidismДокумент9 страницPrimary HyperparathyroidismJamesОценок пока нет
- Cerebrovascular DiseaseДокумент29 страницCerebrovascular DiseaseKamsha UyОценок пока нет
- Pylorus Preservation Pancreatectomy or Not: Ulla Klaiber, Pascal Probst, Markus W. Büchler, Thilo HackertДокумент8 страницPylorus Preservation Pancreatectomy or Not: Ulla Klaiber, Pascal Probst, Markus W. Büchler, Thilo HackertHiroj BagdeОценок пока нет
- Activ One Policy WordingДокумент55 страницActiv One Policy WordingAditya SinghОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ36 страницChapter 1ayush aggarwalОценок пока нет
- NRNP 6568 Week 8 Comprehensive Practice REVISED 2023-2024Документ14 страницNRNP 6568 Week 8 Comprehensive Practice REVISED 2023-2024mary011danielОценок пока нет
- BPM-1200 (PATRON) /1010 (MATRON) : Operation ManualДокумент76 страницBPM-1200 (PATRON) /1010 (MATRON) : Operation ManualMd ShitolОценок пока нет
- Craniopharyngioma Management Principles and Recent AdvancesДокумент34 страницыCraniopharyngioma Management Principles and Recent Advanceszuzaki sharafuddinОценок пока нет
- EEG - Basic Principles and Application in EpilepsyДокумент19 страницEEG - Basic Principles and Application in Epilepsyemilio9fernandez9gatОценок пока нет
- Siwak Perkolasi PDFДокумент8 страницSiwak Perkolasi PDFdwi fitrianaОценок пока нет
- Daftar PustakaДокумент5 страницDaftar PustakaBobby Febri KrisdiyantoОценок пока нет
- D-37/1, TTC MIDC, Turbhe, Navi Mumbai-400 703: ThyrocareДокумент2 страницыD-37/1, TTC MIDC, Turbhe, Navi Mumbai-400 703: ThyrocareGurushantayya SwamiОценок пока нет
- Commercial Essential Oils As Potential Antimicrobials To Treat Skin DiseasesДокумент92 страницыCommercial Essential Oils As Potential Antimicrobials To Treat Skin DiseasesxiuhtlaltzinОценок пока нет
- Grahani Rog PDFДокумент3 страницыGrahani Rog PDFAnkit SainiОценок пока нет
- PATIENT CASE HPI J.O. Is A 5 Yo Girl Who Is Brought To The PediatricДокумент5 страницPATIENT CASE HPI J.O. Is A 5 Yo Girl Who Is Brought To The PediatricKyla ValenciaОценок пока нет
- d10 The Host-Parasite RelationshipДокумент4 страницыd10 The Host-Parasite RelationshipMuhammad Bilal SaifulhaqОценок пока нет
- Annatomy Notes For Bpe StudДокумент14 страницAnnatomy Notes For Bpe StudYoga KalyanamОценок пока нет
- Horizontal Guided Bone Regeneration On Knife Edge Ridges: A Retrospective Case-Control Pilot Study Comparing Two Surgical TechniquesДокумент12 страницHorizontal Guided Bone Regeneration On Knife Edge Ridges: A Retrospective Case-Control Pilot Study Comparing Two Surgical TechniquesFelix SchweppeОценок пока нет
- 1115 3209 1 PBДокумент9 страниц1115 3209 1 PBMaria SuyantiОценок пока нет