Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Innovation Electrostatics
Загружено:
api-3703227Исходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Innovation Electrostatics
Загружено:
api-3703227Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Electrostatics
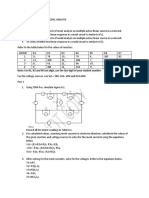
1. Two concentric spherical shell of
radius a and 2a carry charges Qo and (a) (b)
−Qo. The switch S is closed at t = 0.
The charge on the inner shell at time
t is :
t
(a) Q e 8 0 aR
o
t (c) (d)
(b) Q e 4 0 aR
o
t
(c) Q e 2 0 aR
o
(d) zero
5. Two similar conducting plates are
2. In the above question, heat produced in the connecting given equal and opposite charge and
wire is given by : placed as shown in figure. Which of
Q02 Q20 the following diagram best represent
(a) (b)
8 0 a 4 0 a the electric lines of forces :
Q02 Q20
(c) (d) (a) (b)
16 0 a 2 0 a
3. A nonconducting rod carries
charge Q uniformly distributed (c) (d)
over half of its length. The rod
has mass m and length L. It can
rotate about one of its ends O.
Assuming gravity free space, the
angular velocity of rod when it becomes vertical is : 6. A light conducting sphere
QE 9QE suspended by an insulating
(a) (b)
ML 2ML thread is in contact with an
uncharged metal sphere B,
QE
(c) (d) zero which is fixed on an insulating
2ML stand. If a negatively charged
sphere C is through very close
to B without touching it, then :
4. The figure shows three concentric (a) A will remain in same position
conducting shells of radius R, 2R (b) A will move away from B
and 3R. The innermost shell is (c) A will be attracted more strongly by B
earthed and the middle shell is (d) None
given a charge Q. The outer shell
can be earthed by switch S. If 7. In above question, if C is touched with B and removed
radially outwards is taken positive away then :
then variation of electric field with distance x from (a) A will remain in same position
centre is best represented by : (b) A will move away from B
(c) A will be attracted more strongly by B
(d) None
INNOVATIONS, by Er Sunil Kumar Singh. www.physicswithsunilsingh.blogspot.com
2
Qq Qq
8. The figure shows a infinitely (c) (d)
2 0 mr 0 mr
long linear charge distribution
of density λ C/m along y−axis. 12. In the above question if:
A point charge q of m is tied to (a) = 0, path will be straight line
a thread which other end is (b) = 90o, path will be parabolic but particle will not
fixed at x = 2L. What should escape
be minimum velocity v so that (c) = 90o path will be parabolic and particle will
the charge may complete a escape
circle about O in x−y plane. (d) 0o < < 90o will be parabolic and particle will
Assume gravity free space. escape
q 1 2l n3 q
(a) (b) 13. What should be the value of the velocity of charge q
2 0 m 2 0 m
(say v2) and , so that the kinetic energy of the particle
ql n3 ql n3 does not change?
(c) (d)
0 m 2 0 m Qq Qq
(a) , 60o (b) ,90o
4 0 mr 4 0 mr
Qq Qq
9. A ring with charge Q (c) ,90o (d) , 0o
uniformly distributed 2 0 mr 2 0 mr
over it, is fixed in yz
plane with its centre at 14. If the particle is projected with velocity smaller than v2
origin. A charge particle and = 90o, the path of the particle will be represented
is projected from x = 3 by :
R along xaxis. When
(a) (b)
the particle reached Q, its minimum possible speed will
be :
Qq Qq
(a) (b)
0 mR 4 0 mR
3Qq 3Qq (c) (d)
(c) (d)
4 0 mR 0 mR
10. A nonconducting semicircular
ring of radius R, contains 15. If the particle is projected with velocity greater than v 2
charge Q and Q as shown in but smaller than v1 with =900, then the path of the
figure. What work is required particle will be represented by:
to rotate the semiring surviving slowly by an angle /2.
(a) (b)
4QRE
(a) 4QRE (b)
2QRE
(c) (d) 2QRE
11. A point charge ‘Q’ is fixed
at a point and another (c) (d)
point charge ‘q’ of mass
‘m’ is projected with
velocity v at angle with 16. The semicircular nonconducting
the line joining them. With what minimum velocity (say ring of radius R containing +ve
v1) should the charge be projected so that it may escape and negative charge as shown are
from attraction field of Q? joined in two perpendicular
planes. The magnitude of linear
Qq 2Qq charge densities is . The electric
(a) (b)
4 0 mr 0 mr field at O will be :
INNOVATIONS, by Er Sunil Kumar Singh. www.physicswithsunilsingh.blogspot.com
3
2
(a) (b) (c) (d)
2 0 R 0 R
(c) (d) zero
2 0 R
r 22. The diagram shows an
17. In above question if an electric field E E 0 ˆi exists, arrangement of four evenly
then net force on the loop will be : spaced parallel metal plates.
(a) RE (b) 2RE Which of following graph
(c) 2RE (d) zero best represent the variation of
potential V with position r ?
18. In above question, the magnitude of torque acting on the
(a) (b)
loop will be :
(a) R2E (b) 2R2E
(c) 2R 2 E (d) 2 2R 2 E
19. Charge Q is uniformly distributed over volume of a non
conducting sphere of radius R and dielectric constant (c) (d)
k. The variation of electric field with the distance x
from the center of sphere is correctly represented by :
(a) (b) 23. The variation of electric field strength E with position r
is best represented by :
(a) (b)
(c) (d)
(c) (d)
20. The diagram shows two fixed
spheres P and Q which carry equal
but opposite charges. A third
charged sphere R is moved with a
constant velocity in the shown 24. Two infinitely long and
direction. The variation of y uniformly charged wires
component of force as a function (with linear charge
of time varies as : density ) are fixed in x
y plane at x = a as
(a) (b) shown in figure. Another
similar wire is hanging
freely in the symmetric
plane between the wires.
The maximum possible linear mass density of this wire
(c) (d) will be:
2 2
(a) (b)
0 ag 2 0 ag
2 2
(c) (d)
21. In above question variation of xcomponent of force as 0 ag 2 0 ag
a function of time varies as :
(a) (b)
INNOVATIONS, by Er Sunil Kumar Singh. www.physicswithsunilsingh.blogspot.com
4
25. A point charge is placed at the center of a non−
conducting sphere of radius R and of dielectric constant
k. Which of the following plot best represents the
variation of electric field with distance r from the point
charge.
(a) (b)
(c) (d)
Answers
1.A 2.C 3.B 4.A 5.C 6.B 7.B 8.A 9.B 10.B 11.C 12.A,C,D
13.B 14.B 15.C 16.C 17.D 18.B 19.D 20.D 21.C 22.B 23.C 24.B 25.C
INNOVATIONS is a series of topic wise fresh problems framed exclusively by
Er Sunil Kumar Singh for students preparing for IITJEE.
INNOVATIONS, by Er Sunil Kumar Singh. www.physicswithsunilsingh.blogspot.com
Вам также может понравиться
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Measuring Charge On A CapacitorДокумент3 страницыMeasuring Charge On A CapacitorPrasunkali BhattacharyyaОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5795)
- Physics Current Electricity MCQДокумент7 страницPhysics Current Electricity MCQHimanshu VasisthaОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan 7 DynamicsДокумент4 страницыLesson Plan 7 DynamicsGift TanОценок пока нет
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- RESISTORSДокумент3 страницыRESISTORSFaizal Usop PatikamanОценок пока нет
- Application Note: Connection Between Gate Driver and ControllerДокумент4 страницыApplication Note: Connection Between Gate Driver and ControllerEdsonОценок пока нет
- Firing Pin Impact StudiesДокумент3 страницыFiring Pin Impact Studiesblowmeasshole1911Оценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- (Electric Cable Pulling and Termination Work ITP) FINAL Rev1Документ25 страниц(Electric Cable Pulling and Termination Work ITP) FINAL Rev1Aous HОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Electrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsДокумент6 страницElectrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsAhmad Bin Ismail KhanОценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Efields PDFДокумент73 страницыEfields PDFsydonai416Оценок пока нет
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- 2 Chapter 2 - A Student AnsДокумент87 страниц2 Chapter 2 - A Student Ansfullmetal Aesir100% (1)
- Short-Circuit Current Calculations: Basic Point-to-Point Calculation ProcedureДокумент1 страницаShort-Circuit Current Calculations: Basic Point-to-Point Calculation Procedurebalbeloanna7Оценок пока нет
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- ELEQ GSA Broschyr enДокумент4 страницыELEQ GSA Broschyr enJaime Salazar ArayaОценок пока нет
- Suction Cups/grippers: BFF40P, BFF60P, BFF80P, BFF110PДокумент2 страницыSuction Cups/grippers: BFF40P, BFF60P, BFF80P, BFF110PBe HappyОценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Orbits of The Planets in Our Solar SystemДокумент2 страницыThe Orbits of The Planets in Our Solar SystemMarko ŠtimacОценок пока нет
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Experiment 6 ProcedureДокумент4 страницыExperiment 6 ProcedureNathaniel EsguerraОценок пока нет
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- 4.1 Simple Harmonic Motion: 1a. (4 Marks)Документ21 страница4.1 Simple Harmonic Motion: 1a. (4 Marks)xОценок пока нет
- Acoustic PDFДокумент42 страницыAcoustic PDFBùi Trường GiangОценок пока нет
- Closed Loop Speed Control of 3-Phase Induction MotorДокумент27 страницClosed Loop Speed Control of 3-Phase Induction MotorRajesh kumar yadavОценок пока нет
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Lessons in Electric Circuits - Volume IIДокумент16 страницLessons in Electric Circuits - Volume IIartleaderОценок пока нет
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Verification of Thevenin's Theorem.Документ3 страницыVerification of Thevenin's Theorem.Sharmin83% (6)
- Electrical-Engineering FormulasДокумент19 страницElectrical-Engineering FormulasShara Lorraine EstiponaОценок пока нет
- Statics Assgnmnt)Документ20 страницStatics Assgnmnt)Mohammed AdemОценок пока нет
- Design Thrust Restraint For IRON PIPE LINESДокумент23 страницыDesign Thrust Restraint For IRON PIPE LINESAlberto AguilarОценок пока нет
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- SSC JE Electrical SyllabusДокумент4 страницыSSC JE Electrical SyllabusHarpal SainiОценок пока нет
- EE405 Electrical System Design PDFДокумент2 страницыEE405 Electrical System Design PDFSudev S0% (1)
- Solved Problems in Electrical & Safety Engineering 2014Документ28 страницSolved Problems in Electrical & Safety Engineering 2014hshshdhdОценок пока нет
- Malla Reddy Engineering College: B. Tech. Iv Semester (Mr15) Regular End ExaminationsДокумент2 страницыMalla Reddy Engineering College: B. Tech. Iv Semester (Mr15) Regular End ExaminationsNaresh KumarОценок пока нет
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Resonant TestДокумент4 страницыResonant TestL AdlyОценок пока нет
- MST 2Документ4 страницыMST 2Neha Prashant VermaОценок пока нет
- Ial WPH04 01 Oct19Документ28 страницIal WPH04 01 Oct19Happy AyichОценок пока нет