Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Water and Its Solutions
Загружено:
karendbrooksИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Water and Its Solutions
Загружено:
karendbrooksАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Double Certificate GCSE Science Pack 3
Unit 2
The structures of atoms
There are only about 109 different kinds of atoms which make up the entire universe (see Unit 3). Every atom has the same basic structure and is in two parts:
Nucleus
Electron cloud containing orbiting electrons
Chemical reactions involve interactions between the electron clouds of different atoms. The cloud is made up of shells like the inside of an onion.
eThe first shell can hold up to two electrons The second shell can hold up to eight electrons The third shell can hold up to eight electrons eee- eeeeeeeeeeee- eeNucleus
The three innermost electron shells e- represents one electron Since electrons have almost no mass, practically all the mass of an atom is made up of the protons and neutrons in its nucleus. However, the nucleus of an atom has no influence on chemical activity. The nucleus is made up of a cluster of protons and neutrons. Each proton has one positive (+) charge; each neutron has no charge. The units of mass for atoms are atomic mass units (amu). The mass number of an atom = the number of protons + neutrons in the nucleus. The atomic number of an atom = the number of protons in the nucleus. The mass number - the atomic number = the number of neutrons in the nucleus.
Particle proton (p) neutron (n) electron (e) Mass (amu) 1 1 almost nil Charge 1 0 -1
Proton
Neutron
The nucleus of an atom of sodium contains 11 protons and 12 neutrons. There are 11 electrons in its shells 2 in the first, 8 in the second and 1 in the outer. The atom of sodium can be represented by the symbol 23 Na where 11 is the atomic number and 23 is the atomic mass. 11 The total number of (-) electron charges in the cloud exactly equals the number of (+) proton charges in the nucleus. So there is no overall charge on an atom it is neutral. When different kinds of atoms react with each other, they upset this neutral condition by exchanging or sharing electrons from their clouds see Units 12 and 13.
Pearson Publishing, Chesterton Mill, Frenchs Road, Cambridge CB4 3NP
Double Certificate GCSE Science Pack 3
Unit 2
Questions
Tick the box next to the correct answer. 1 Atoms of elements: A B C D have an overall positive charge are neutral overall have an overall negative charge are always charged either positive or negative
5 Atoms of different elements can join together to form chemical compounds. To do this the atoms:
n n n n
A B C D
join their nuclei together share their outer electrons exchange nuclei bond protons with their partners electrons
n n n n
6 Atoms of different elements must have: 2 The atomic number of an element tells you: A B C D the number of protons in its nucleus the number of neutrons in its nucleus the number of electrons in its nucleus the number of electrons in its shells
n n n n
3 An atom of aluminium can be represented by the symbol 27 Al. Which line in the table 13 gives the correct number of protons, neutrons and electrons in an atom of aluminium?
Protons A B C D 13 14 13 14 Neutrons 14 13 13 27 Electrons 13 27 14 13
A different mass numbers B the same number of neutrons in their nuclei C different numbers of electrons in their shells D different numbers of protons in their nuclei
n n n n
7 How many neutrons are there in an atom of fluorine 19 F? 9 A B C D 9 19 10 28
n n n n
8 If a neutral atom of an element has 14 electrons and 19 neutrons, its atomic number is: A B C D 5 14 19 33
4 The mass number of an atom is the number of: A B C D protons in the nucleus neutrons in the nucleus all the particles in the atom the number of protons and neutrons together
n n n n
n n n n
Pearson Publishing, Chesterton Mill, Frenchs Road, Cambridge CB4 3NP
Double Certificate GCSE Science Pack 3
Unit 9
Water and solutions
Three-quarters of the Earths surface is covered by water. Water is sometimes called a universal solvent because so many substances can be dissolved in it. Almost all chemical reactions in biological systems take place in solution in water (in aqueous solution (aq)). Water also has great importance as a solvent and as a coolant in industry.
The water cycle
The water cycle is what keeps an approximately constant amount of water available for us to use.
Rain, hail and snow return water to the surface Plants transpire Used in factories and homes Water table
Water evaporates from sea and land
Some water enters the ground, forming a saturated layer of rock Where the water table intersects the surface springs occur Water treatment plant
Hardness in water
As water cycles through the soil, in particular, it dissolves minerals and salts and causes hardness; this makes it difficult for soap to form a lather and also produces a scum.
SO42ClCa2+ Mg2+ HCO3-
Permanent hardness Softened by: A Adding washing soda (Na2CO3) (cheap and convenient) B Using ion exchange resins (eg Permutit and others) which remove Ca2+ and Mg2+ (inexpensive but tedious) C Distillation (very expensive)
Temporary hardness Softened by boiling Ca(HCO3)2 (aq) CaCO3 (s) + H2O(l) + CO2 (g) Scale
Salts and minerals in the soil
Advantages and disadvantages of hard water
Both types of hardness are found in most water supplies to varying degrees. Hard water causes problems with scaling, which narrows pipes and reduces the efficiency of immersion heaters, and with poor lather formation from the use of soaps and detergents. Hard water tastes nicer, however, and is healthier in several ways since it contains minerals which are good for the body.
Pearson Publishing, Chesterton Mill, Frenchs Road, Cambridge CB4 3NP
33
Double Certificate GCSE Science Pack 3
Unit 9
Questions
Tick the box next to the correct answer. 1 The water cycle shows: A the network of rivers and canals in the UK B how water is purified C the steps in recycling water over the Earth D how climates change due to sea breezes 6 Permanently hard water: A can be softened by adding washing soda B can never be softened C must be boiled to remove hardness D means that there are impurities in the water
n n n n
n n n n
7 Hardness in water is caused by: A calcium and magnesium ions dissolved in the water B isotopes of oxygen in the water molecules C bacteria in the water D the presence of any metal ions in the water
n n n n
2 What percentage of the Earths surface is covered by water? A B C D 25% 50% 75% 100%
n n n n
3 Water is sometimes called a universal solvent because: A the human body is over 90% water B so many substances can be dissolved in it C so much of the Earths surface is covered by it D it is essential for all plant and animal life
8 Hard water has some advantages over soft water. One of these is that hard water:
n n n n
A dissolves substances more quickly than soft water B is more efficient in central heating systems C boils quicker than soft water D contains minerals useful to the body
n n n n
4 Water is said to be hard when it: A can be easily compressed B is not easy to find in drought conditions C contains many impurities D makes it difficult to get lather with soap
9 Which of the following statements is not correct?
n n n n
A Using soft water is cheaper than using hard water B Temporarily hard water can be softened by boiling C Scum is the result of using soap with hard water D Soft water is better for plants than hard water
n n n n
5 Temporarily hard water is caused by calcium and magnesium ions and also: A B C D hydrogencarbonate ions other metal ions minerals which cause scale sulphate and chloride ions
n n n n
34
Pearson Publishing, Chesterton Mill, Frenchs Road, Cambridge CB4 3NP
Вам также может понравиться
- Acid ReactionsДокумент1 страницаAcid ReactionskarendbrooksОценок пока нет
- Magnesium WsДокумент2 страницыMagnesium WskarendbrooksОценок пока нет
- B3 Life On Earth WorkbookДокумент43 страницыB3 Life On Earth WorkbookkarendbrooksОценок пока нет
- Igcse Revision BookДокумент18 страницIgcse Revision BookkarendbrooksОценок пока нет
- Pressure IgcseДокумент2 страницыPressure IgcsekarendbrooksОценок пока нет
- C6 Chemical Synthesis SOWДокумент87 страницC6 Chemical Synthesis SOWkarendbrooksОценок пока нет
- Radioactivity Booklet1Документ36 страницRadioactivity Booklet1karendbrooksОценок пока нет
- Y9 Science Transition Test Teacher GuideДокумент30 страницY9 Science Transition Test Teacher Guidekarendbrooks0% (1)
- Fuels To Make ElectricityДокумент1 страницаFuels To Make ElectricitykarendbrooksОценок пока нет
- Stoichiometry With Solutions PracticeДокумент1 страницаStoichiometry With Solutions PracticekarendbrooksОценок пока нет
- GCSE P2 2.1.4 Forces and Terminal VelocityДокумент7 страницGCSE P2 2.1.4 Forces and Terminal VelocitykarendbrooksОценок пока нет
- Igcse Physics (7) - Pressure PDFДокумент6 страницIgcse Physics (7) - Pressure PDFkarendbrooksОценок пока нет
- 1.1 Diet and ExerciseДокумент2 страницы1.1 Diet and ExercisekarendbrooksОценок пока нет
- IGCSE Specification Questions - Life ProcessesДокумент3 страницыIGCSE Specification Questions - Life ProcesseskarendbrooksОценок пока нет
- Igcse Revision Book (To Print)Документ66 страницIgcse Revision Book (To Print)Andreea Maria PavelОценок пока нет
- Unesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Chemical Laboratory TechniquesДокумент0 страницUnesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Chemical Laboratory Techniquesmasruri123Оценок пока нет
- Plot Vi GraphДокумент1 страницаPlot Vi GraphkarendbrooksОценок пока нет
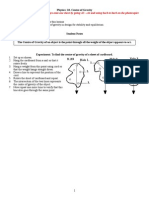
- Centre of GravityДокумент4 страницыCentre of GravityAvish GunnuckОценок пока нет
- Biology Workbook SampleДокумент13 страницBiology Workbook SamplekarendbrooksОценок пока нет
- 1.1 Diet and ExerciseДокумент2 страницы1.1 Diet and ExercisekarendbrooksОценок пока нет
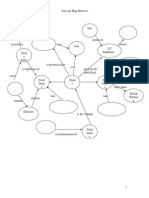
- Concept Map ExerciseДокумент3 страницыConcept Map ExercisekarendbrooksОценок пока нет
- f214 Kidneys and ExcretionДокумент4 страницыf214 Kidneys and ExcretionkarendbrooksОценок пока нет
- GreenChemistryTeacher SpackДокумент122 страницыGreenChemistryTeacher Spackilias1973Оценок пока нет
- ChemistryДокумент78 страницChemistryShabnam Fatima SiddiquiОценок пока нет
- Immune Responses QuestionsДокумент2 страницыImmune Responses QuestionskarendbrooksОценок пока нет
- Worksheet 15Документ2 страницыWorksheet 15karendbrooksОценок пока нет
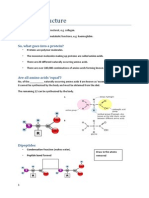
- Protein Structure WorksheetДокумент7 страницProtein Structure WorksheetkarendbrooksОценок пока нет
- Bdol5 2Документ1 страницаBdol5 2karendbrooksОценок пока нет
- ChromatographyДокумент44 страницыChromatographyAravind KanthОценок пока нет
- Change Through TimeДокумент2 страницыChange Through TimekarendbrooksОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Nso Sample Paper Class-4Документ3 страницыNso Sample Paper Class-4Ashish100% (2)
- Consolidation (2) - 4th SEMДокумент3 страницыConsolidation (2) - 4th SEMDipankar NathОценок пока нет
- Jürgen Breuste - The Green City - Urban Nature As An Ideal, Provider of Services and Conceptual Urban Design Approach-Springer (2022)Документ393 страницыJürgen Breuste - The Green City - Urban Nature As An Ideal, Provider of Services and Conceptual Urban Design Approach-Springer (2022)Rafaela TeodoraОценок пока нет
- Lesson-Plan-in-Science-8 - Human ImpactДокумент13 страницLesson-Plan-in-Science-8 - Human ImpactMaricris RanaraОценок пока нет
- Atoms and Elements ExplainedДокумент10 страницAtoms and Elements ExplainedsleepyanyaОценок пока нет
- STAIF-2003-118 Technologies To Improve Ion Propulsion System Performance, Life and EfficiencyДокумент11 страницSTAIF-2003-118 Technologies To Improve Ion Propulsion System Performance, Life and EfficiencyDr. Shahin IqbalОценок пока нет
- An Educational Guide To Extract The Parameters of Heavy Duty Gas Turbines Model in Dynamic Studies Based On Operational Data PDFДокумент9 страницAn Educational Guide To Extract The Parameters of Heavy Duty Gas Turbines Model in Dynamic Studies Based On Operational Data PDFAlozie OgechukwuОценок пока нет
- Diffusion of Helium Through QuartzДокумент5 страницDiffusion of Helium Through QuartzElenaОценок пока нет
- Climate of PakistanДокумент43 страницыClimate of Pakistansatayish75% (4)
- Nitin Ventures Gas Suppression SystemsДокумент2 страницыNitin Ventures Gas Suppression Systemsshreeket3953Оценок пока нет
- IGA Quarterly Newsletter Highlights Geothermal DevelopmentsДокумент16 страницIGA Quarterly Newsletter Highlights Geothermal DevelopmentsWillianОценок пока нет
- 2018 JC2 H2 Physics SA2 Temasek Junior CollegeДокумент8 страниц2018 JC2 H2 Physics SA2 Temasek Junior CollegeaarnaОценок пока нет
- Lecture Note Hilly Region Planning by IslamДокумент9 страницLecture Note Hilly Region Planning by IslamK. M. Ashraful IslamОценок пока нет
- The Centenary of Einstein's First Scientific PaperДокумент6 страницThe Centenary of Einstein's First Scientific PaperMCarbajalОценок пока нет
- Climatic Design of BuildingsДокумент22 страницыClimatic Design of BuildingspatОценок пока нет
- Hydrogenics Annual ReportДокумент81 страницаHydrogenics Annual ReportseboestОценок пока нет
- Problems and Concerning Soil and LandДокумент8 страницProblems and Concerning Soil and LandLove Borja0% (1)
- Performance Test (PT)Документ17 страницPerformance Test (PT)mohammad imron100% (1)
- A.zerrouki Et El The Natural Circulation Solar Water Heater ModelДокумент11 страницA.zerrouki Et El The Natural Circulation Solar Water Heater ModelJuan-Pierre HerbothОценок пока нет
- Binti Daud, N.K., PHD Thesis Final Copy - 2Документ236 страницBinti Daud, N.K., PHD Thesis Final Copy - 2yasin kocaboğaОценок пока нет
- Miscarea Soarelui Pe CerДокумент3 страницыMiscarea Soarelui Pe CerwexlerОценок пока нет
- Tokamax Parts A and B (Rev)Документ4 страницыTokamax Parts A and B (Rev)Shahroze MirzaОценок пока нет
- Chapt 6 Quiz Notes For Quiz On Primary and Secondary SuccessionДокумент8 страницChapt 6 Quiz Notes For Quiz On Primary and Secondary Successionicemaniceman1111100% (5)
- Iee Unbalanced PDFДокумент5 страницIee Unbalanced PDFDery TriОценок пока нет
- RPH Kimia 2Документ62 страницыRPH Kimia 2aisyaomeiraОценок пока нет
- Jena 2019Документ68 страницJena 2019Amir MahmudОценок пока нет
- HW 01Документ2 страницыHW 01Icy45Оценок пока нет
- WavelengthPeriodFrequency QuestionsДокумент2 страницыWavelengthPeriodFrequency QuestionssalmasomaОценок пока нет
- Second Law of ThermofluidДокумент29 страницSecond Law of ThermofluidMichael ElliottОценок пока нет
- Starter: How Might These Things Be Involved in The Carbon Cycle?Документ11 страницStarter: How Might These Things Be Involved in The Carbon Cycle?fatima al neyadiОценок пока нет