Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
TIK - Chapter 4 System Software
Загружено:
Aska NoveliaИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
TIK - Chapter 4 System Software
Загружено:
Aska NoveliaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Using Information Technology Chapter 4 System Software
System Software : The Power behind the Power 4.1 The Components of System Software 4.2 The Operating System: What It Does 4.3 Other System Software: Device Drivers & Utility Programs 4.4 Common Operating Systems 4.5 The OS of the Future
4.1 The Components of System Software
Operating system = the principal component of system software Device drivers = help the computer control peripheral devices Utility programs = support, enhance, or expand existing programs
4.2 The Operating System: What It Does
Booting = the process of loading an operating system into a computers main memory 1. When you turn on the computer 2. The processor (CPU) automatically begins 3. Executing the part of the operating systems start-up system (BIOS) located in ROM 4. These instructions help load the operating system from the hard disk into RAM 5. They pass control to the OS User interface = user-controllable display screen that allows one to communicate, or interact, with a computer CPU Management Supervisor (kernel) = program which remains in main memory while the computer is running, and directs other nonresident programs to perform tasks that support application programs File Management and Formatting The operating systems file system arranges files in hierarchical fashion Formatting or initializing a disk is the process of preparing that disk for use
Task Management Number of Users Multi-tasking Multi-programming Time sharing Multi-processing One Multiple Multiple One or more Number of Processors One One One Two or more Order of Processing Concurrently Concurrently Round robin Simultaneously
Processing of two or more programs
4.3 Other System Software: Device Drivers & Utility Programs
Device drivers = specialized software programs that allow input and output devices to communicate with the rest of the computer system Utilities = Service Programs Backup utility = program which makes a duplicate copy of the information on your hard disk Data-recovery utility = program which restores data that has been physically damaged or corrupted Antivirus software = program that scans hard disks, floppy disks, and memory to detect viruses Data compression utility = program which removes redundant elements, gaps, and unnecessary data from a computers storage space so that less space (fewer bits) is required to store or transmit data Fragmentation = the scattering of portions of files about the disk in nonadjacent areas, thus greatly slowing access to the files Defragmenter utility = program that finds all the scattered files on a hard disk and reorganizes them as contiguous files Disk scanner and disk cleanup utilities: o Detect & remove unnecessary files o Detect & correct disk problems
4.4 Common Operating Systems
Desktop & Laptop Operating Systems Platform - a particular processor model and operating system on which a computer system is based Disk Operating System (DOS) = the original operating system produced by Microsoft, which had a hard-to-use command-driven user interface Mac OS = operating system which runs only on Apple Macintosh computers Microsoft Windows 3.X - released in 1992; simply a layer over DOS Microsoft Windows 95/98 - successors to 3.X Plug and Play = the ability of a computer to automatically configure a new hardware component that is added to it Microsoft Windows Me (WinMe) = Millennium Edition
Network Operating Systems Novells Netware = a popular network operating system for coordinating microcomputer-based local area networks (LANs) Windows NT = Microsofts multitasking OS which allows multiple users to share resources such as data and programs Windows 2000 = successor to Windows NT Windows XP = Microsofts newest OS, which combines elements of Windows 2000 and Windows Me UNIX = a multitasking operating system for multiple users with built-in networking capability and versions that can run on all kinds of computers Sun Microsystems Solaris Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD) Linux = a free version of UNIX, with continual improvements resulting from the efforts of tens of thousands of volunteer programmers Linux-ppen-source software = software which any programmer can download from the Internet for free and modify with suggested improvements Microsoft .NET A set of Microsoft software technologies for connecting information, people, and systems through the use of special building block web service programs. Web services programs are created using XML a web-document tagging format. Operating Systems for Handhelds Palm OS = the dominant OS for handhelds, which runs the Palm and Handspring Visor, and is licensed to other companies Windows CE (now Pocket PC) = slimmed-down version of Windows for handhelds Embedded Systems An embedded system is any electronic system that uses CPU chip It is a specialized computer system that is a part of a larger system Used extensively in cars, space vehicles, cell phones, PDAs, and robots Many companies have formed the non-profit, vendor neutral Embedded Linux Consortium to make Linux a top OS of choice
4.5 The OS of the Future: Web Services Platform
Web services allow describing, identifying, and communicating data over the WWW in a consistent fashion that can be read by many different types of machines Microsoft .NET delivers web services Competitors concentrating on middleware as an answer
Open Source Computing Distributed system = a non-centralized network consisting of several computers and other devices that can communicate with one another Gaining ground in foreign countries, small companies, and schools Concept check 1. What is the latest version of Microsoft Windows? o XP 2. What is the term for software which can be downloaded from the Internet for free and modified with suggested improvements? o Open-source software 3. Which Microsoft OS runs on handheld computers? o Windows CE/Pocket PC 4. What is the term for a non-centralized network consisting of several computers and other devices that can communicate with one another? o Distributed system 5. What is the name of the popular open-source version of UNIX? o Linux 6. What was the first OS released by Microsoft? o DOS (Disk Operating System) 7. What is the process of loading an operating system into a computers main memory called? o Booting 8. What is the term for the execution of two or more programs by one user at the same time on the same computer with one central processor? o Multitasking 9. What is the term for a single computer processing the tasks of several users of different stations in round-robin fashion? o Time-sharing 10. What is the term for the scattering of portions of files about the disk in nonadjacent areas, thus greatly slowing access to the files? o Fragmentation 11. What kind of utility program is used to restore data that has been physically damaged or corrupted? o A data-recovery program 12. What kind of utility program is used to remove redundant elements, gaps, and unnecessary data from a computers storage space so that less space is required to store or transmit data? o A data compression program 13. What is the term for the particular processor model and operating system on which a computer system is based? o Platform 14. Which OS, first introduced in 1984, set the standard for icon-oriented, easy-to-use graphical user interfaces?
o Macintosh OS 15. What is the process of preparing a floppy disk so that it can store data or programs called? o Formatting or initializing 16. What is the name for the component of system software that allows input and output devices to communicate with the rest of the computer system? o Device drivers 17. What kind of utility program eliminates disk fragmentation? o Defragmentation utility or defragger
Вам также может понравиться
- Microbial Enhanced Oil Recovery (Meor)Документ7 страницMicrobial Enhanced Oil Recovery (Meor)Yomel RamziОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Bombas Pentax SAДокумент48 страницBombas Pentax SAAgustin CahuanaОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- April 2016Документ68 страницApril 2016Treatment Plant Operator MagazineОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- LN3 Geng2340Документ61 страницаLN3 Geng2340Seth VineetОценок пока нет
- Anna University:: Chennai - 600025. Office of The Controller of Examinations Provisional Results of Nov. / Dec. Examination, 2020. Page 1/4Документ4 страницыAnna University:: Chennai - 600025. Office of The Controller of Examinations Provisional Results of Nov. / Dec. Examination, 2020. Page 1/4Muthu KumarОценок пока нет
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
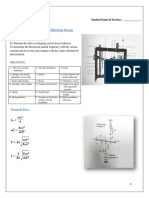
- Student Manual of Damped & Un DampedДокумент3 страницыStudent Manual of Damped & Un DampedaqibОценок пока нет
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- University of Mumbai: Syllabus For Sem V & VI Program: B.Sc. Course: PhysicsДокумент18 страницUniversity of Mumbai: Syllabus For Sem V & VI Program: B.Sc. Course: Physicsdbhansali57Оценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Project Presentation SurveyingДокумент14 страницProject Presentation SurveyingSACHIN MEENAОценок пока нет
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- RTE Online Application Form For Admission Year 2018 19Документ6 страницRTE Online Application Form For Admission Year 2018 19sudheer singhОценок пока нет
- SunstarДокумент189 страницSunstarSarvesh Chandra SaxenaОценок пока нет
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- TT2223 Week 12a Z-TransformДокумент39 страницTT2223 Week 12a Z-TransformAjiMaulanaОценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- FINAL ITP 2024 CompressedДокумент388 страницFINAL ITP 2024 Compressedhamidjumat77Оценок пока нет
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Rev2 Service Manual Apollo PDFДокумент370 страницRev2 Service Manual Apollo PDFJordi Vaquero RamirezОценок пока нет
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- TRCM Safe Parking: Technical InformationДокумент2 страницыTRCM Safe Parking: Technical InformationMirek BudaОценок пока нет
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- DualityДокумент27 страницDualitySuprabhat TiwariОценок пока нет
- Splunk 7 Essentials Third EditionДокумент388 страницSplunk 7 Essentials Third EditionHaripriya100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- 01-19 Diagnostic Trouble Code Table PDFДокумент40 страниц01-19 Diagnostic Trouble Code Table PDFmefisto06cОценок пока нет
- ANSYS Mechanical Basic Structural NonlinearitiesДокумент41 страницаANSYS Mechanical Basic Structural NonlinearitiesalexОценок пока нет
- On-Farm Composting Methods 2003 BOOKДокумент51 страницаOn-Farm Composting Methods 2003 BOOKlalibОценок пока нет
- SuperOhm 3754 (3748-11) - Technical Data Sheet - ECC - Rev 2 - 2016-09Документ2 страницыSuperOhm 3754 (3748-11) - Technical Data Sheet - ECC - Rev 2 - 2016-09igor brocaОценок пока нет
- Properties of Building Materials and Their Importance in ConstructionДокумент5 страницProperties of Building Materials and Their Importance in ConstructionDaisy Jane LulabОценок пока нет
- Quotation 98665Документ5 страницQuotation 98665Reda IsmailОценок пока нет
- RT120 ManualДокумент161 страницаRT120 ManualPawełОценок пока нет
- MCB 12V-8A MCB 24V-5A Battery ChargerДокумент2 страницыMCB 12V-8A MCB 24V-5A Battery ChargerJosé Wilton AlvesОценок пока нет
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Op Amp TesterДокумент2 страницыOp Amp TesterPhay KhamОценок пока нет
- PT 0817 Cebu Room Assignment PDFДокумент16 страницPT 0817 Cebu Room Assignment PDFPhilBoardResultsОценок пока нет
- Mumbai BylawsДокумент110 страницMumbai BylawsLokesh SharmaОценок пока нет
- Tailless AircraftДокумент17 страницTailless AircraftVikasVickyОценок пока нет
- Excel CatДокумент132 страницыExcel Catjuanf_scribdОценок пока нет
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Software TestingДокумент4 страницыSoftware TestingX DevilXОценок пока нет