Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Transformers Yesterday, Today & Tomorrow
Загружено:
Faiz AhmedИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Transformers Yesterday, Today & Tomorrow
Загружено:
Faiz AhmedАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
TRANSFORMERS YESTERDAY, TODAY & TOMORROW
: VK Lakhiani Crompton Greaves Ltd.
TRANSFORMER IS 117 YEARS OLD !
FIRST TRANSFORMER OF THE WORLD
60 W, 4.3 / 46.5 V, 18 Hz,
Single phase, Shell type, Dry type by 3 Hungarian Engineers working in GANZ, Budapest. * Karoly Zipernowsky * Titusz Otto Blathy * Miksa Deri
2
Patented in 1985
Blathy coined the tame Transformer
HOW IT ALL BEGAN !
1831 - Faradays law of Electromagnetic Induction discovered
1864 - Maxwells equations for mathematical models of electromagnetic apparatus formulated.
1885 - First real Transformer (single phase) Patented.
1893 - First three phase Transformer was used in Hellsjon 9.6
kV Transmission System in Sweden (Dry type 3 phase
transformers manufactured by ASEA)
1900 - Oil Immersed Transformer was born.
3
GROWTH OF LARGE POWER RATING TRANSFORMERS
World Scenario
15 MVA 45 MVA 120 MVA 1300 MVA 3-phase (Brown Boveri, 400 kV) 550 MVA, 1-phase (1650 MVA Bank) (Alsthom-France) 775 MVA, 230 kV 60 Hz, SC Tested (ABB)
4
1920s :
1930s :
1940s :
1960s :
1970s :
1998 :
GROWTH OF EHV TRANSFORMERS
World Scenario
220 kV 400 kV 765 kV 1150 kV (USSR)
1930s :
1950s :
1960s :
1960s :
Experimental Transformer - 1785 kV / 1850 kV Class 1200 kV (Japan, Italy, Canada, Brazil, USA)
2000s :
GROWTH OF TRANSMISSION VOLTAGES Indian Scene :
1902:
Worlds first 78 kV, longest high rated voltage transmission line on commercial basis in Mysore State made operational Sivasamudram-Kankanhalli (about 150 km)
1931:
132 kV Introduced
1959:
First 220 kV line become operative between Bhakra to Delhi
(300 km approx.)
1977:
First 400 kV line commissioned between Obra- Lucknow
(370 km approx.)
1988:
HVDC Systems Introduced
6
2005(?): 800 kV AC
LARGEST TRANSFORMERS (INDIA)
1968:
250 MVA 220 kV GT
1977:
240 MVA 400 kV GT
1980:
315 MVA 400 kV AT
1980:
600 MVA 400 kV Bank
1990:
315 MVA 1-phase HVDC Transformer
1995:
315 MVA 220 kV GT
2000:
320 MVA 275 kV GT
(Largest rating exported from India (CGL)
7
CORE MATERIAL DEVELOPMENT
Year
Core Material
1885
Soft magnetic
1900
Non-oriented silicon steel
1935
Grain Oriented silicon steel
(Developed by Armco, USA)
1968
Hi-B (Developed by Nippon Steel Corpn.)
1980
Laser Scribed Hi-B
1990
Mechanically Scribed Hi-B
GRADES & LOSSES OF ELECTRICAL STEELS Grade (Typical)
35 - M6 27 - M4 30 M2H 30 M0H 27 M0H 27 ZH 100 23 M0H 27 ZDkH 23 ZDkH 27 ZDMH 23 ZDMH 1.44 1.26 1.13 1.04 1.03 1.00 0.94 0.92 0.85 0.92 0.85
9
Type
Loss w / kg at 1.7 T 50 Hz
Conventional
Hi-B
Laser Scribed Hi-B
Mechanically Scribed
DEVELOPMENT IN CORE
Reduction of core losses - Design & technology
- Mitred Joints (1960s) - 2 x 2 blading - 10 mm over lap - Minimum air gaps at joints - Minimum burr level - Yoke-less building - Stepped lap core construction
10
DEVELOPMENT IN CORE
Bolt-less legs
- Banding with resi-glass tapes.
- Skin stressed cylinder.
- Semi conducting tape
Bolt-less yokes
- Bolts outside the yokes.
- Resiglass bands with pressure buckles.
Stainless steel clamp plate for stray-loss reduction or,
laminated CRGO clamp plates or, epoxy bonded legs.
Optimum cross section or utility factor.
Hotspot calculations and positioning of oil ducts.
Realisation of oil ducts with button spacers or dimple sheets
11
FUTURE OUTLOOK ON CORE STEEL
Two needs :Reduced Iron Loss Reduced Noise
Energy Saving
Environmental Problem
Latest Trends :
1) More outstanding grain oriented electrical steels by optimising
Electrical Resistivity
Steel thickness
Domain width
Grain Orientation alignment
12
Roughness of the substrate steel & coating film interface
FUTURE OUTLOOK ON CORE STEEL (Contd.)
2) Gap between calculated values and measured values to bridge - 6 sigma tools
3) Stepped lap core construction shall be the order of the Day !
13
DEVELOPMENT IN WINDINGS
Windings Subjected to :
Dielectric steady state stresses upto system highest voltage conditions
Dielectric stresses under one minute power frequency induced over voltages.
Non Linear Transient Voltage Distribution
Under Lightning and Switching Conditions
Corona Discharges
Thermal Stresses
Short Circuit / Mechanical Stresses
Vibrations
14
Stray losses
DEVELOPMENT OF INSULATING OIL
Fire resistant, non-flammable silicon based liquid. High grade mineral oil, with exceptional oxidation stability and
improved electrical properties
Opticool fluids with low viscosity for better cooling properties
Thermally upgraded oils for operation upto 150oC
Super biodegradable eco-fluid made from vegetable seed oils
for environmentally sensitive locations.
15
DEVELOPMENT IN WINDING CONDUCTORS
Thermally upgraded paper insulated conductors Enamel insulated conductor Bunched conductors Epoxy bonded bunched conductors Continuously transposed cables (CTC) Epoxy bonded CTC Foil (and sheet) conductors
16
DEVELOPMENT OF INSULATING MATERIALS
Softer Pressboard
Pre-compressed Pressboard in 1960
Moulded Angle rings, angle caps
Special Insulation at ends of windings to match electrostatic
field plots
Low permitivity pressboard (permitivity equal to that of oil)
- Futuristic
17
DEVELOPMENT IN WINDINGS
Design and Technological Development
Use of interleaved / PID winding / contra shield winding
Optimisation of radial clearances on stress distribution concepts
Optimisation of axial clearances and use of moulded components
Reduction in solid pressboard insulation in sub-divided barrier arrangement
Optimum winding placement
Use of guided oil flow
Use of yoke shunt / wall shunt / flux trap to control stray losses
Improvement in short circuit withstand capability
Stressed oil volume concept for lead clearances
18
Wave shape sensitivity analysis and part winding resonance
DEVELOPMENT IN WINDINGS
Ongoing and Futuristics Trends
T50 concept for withstand of transient voltage
Behaviour of steep fronted nanosecond waves in GIS operation
Winding noise & vibrations
Focus on winding manufacturing process to stay within the given tolerances.
Focus also on achieving the measured losses as calculated.
19
DEVELOPMENT IN WINDINGS
Requirement of low deviations between measured and calculated winding temperature and thereby need to control manufacturing process.
Increased demand for short circuit test in developing countries
20
DEVELOPMENT IN PROCESSING
Vapour phase drying system developed which ahs following
advantages over the conventional Heat / Vacuum System
- Uniform heating of entire mass
- Less heat up time
- Removal of dust and dirt
- More effective extraction of moisture
- Shorter drying time cycle
21
DEVELOPMENT IN PROCESSING (CONTD.)
Dew Point method of monitoring of dryness of the insulation is
developed - particularly useful at site after repair
Low frequency induction heating technique
Current areas of improvement
- RVM (Recovery Voltage Measurement)
- PDC
( Polarisation Depolarisation Current)
22
DEVELOPMENT IN STRUCTURAL DESIGN
Clamping Structure for core and coil should be capable or withstanding the forces of short circuit apart from lifting and clamping the core
- Use of HTS at the appropriate places e.g. flitch plate is desirable
in large capacity transformers.
- Better coil clamping methods e.g. use of dash pots, coil clamping
jack screws etc.
- Flat end frames to reduce stray losses.
23
DEVELOPMENT IN STRUCTURAL DESIGN (CONTD)
Tank is subjected to complex loading
Lifting - Vacuum - Pressure - Transport - Vibration
- Stress analysis is possible based on FEM
Simplified rectangular tank construction with box type
vertical stiffeners is the trend.
Bell shaped construction developed for ease of site inspection
Welded curb flanges
Gaskets in machined grooves
24
DEVELOPMENT IN MFG. TECHNIQUES
High degree of automation is employed to achieve high dimensional accuracy for lamination for reducing air gaps and to improve efficiency.
Vertical winding machine for winding large capacity transformer coil.
Pressurised chambers used for windings and insulating parts to protect against pollution and dirt.
High frequency brazed joints / Improved crimping joints
Vapour phase drying for effective and fast cleaning of core and windings.
25
Particle count for oil contamination
IMPROVEMENTS IN BUSHING TECHNOLOGY
`SRBP to `OIP to `RIP to SF6 Practically Non-existent Upto 800 kV Upto 500 kV Upto 1000 Kv
SRBP OIP RIP SF6
RIP with Silicon rubber sheds composite insulated for heavily polluted atmosphere (Futuristic trends)
26
IMPROVEMENTS IN BUSHING TECHNOLOGY (CONTD)
Condition Monitoring of Bushings (on-going developments) - Online infra-red scanning for hot spots - Dissolved gas analysis - Particle count of oil - RIV Measurement to detect corona - Tan Monitoring - Capacitance Monitoring - PD
27
IMPROVEMENTS IN OLTC
Reactor type switching OLTC patented 1905 & 1906 (still popular in USA) High speed resistor type OLTC developed based on Dr. Jansens patent (1926) (used in large scales) Improvement in construction features to increase reliability of operation
28
IMPROVEMENTS IN OLTC (CONTD.)
FUTURISTIC
Maintenance free OLTC
Use of semiconductors and vacuum for switching
Dry type OLTC
Condition Monitoring of OLTC
29
OIL PRESERVATION SYSTEMS
Isolation of oil from moisture and oxygen result in slower deterioration
of oil
Popular preservation systems are :
Nitrogen Sealing - Inert dry atmosphere of N2 is created over the oil in conservator
Atmoseal System - Rubber pouch placed inside the conservator inflates or deflates with contraction / expansion of oil
Diaphragm System - Rubber diaphragm creates a partition between oil and outside air
Thermosyphon System - Part of the oil circulated through an absorbent sieve of Alumina by thermosyphon action
30
NEW ADDITIONS TO FAMILY OF TRANSFORMERS
AMORPHOUS METAL TRANSFORMERS (AMT)
Amorphous metal has a non-crystalline structure (like glass)
with molecules in random pattern - results from rapid solidification of molten alloy @ one Million Degrees celsius per second.
Gives 80% reduction in no-load losses compared to conventional
CRGO.
Substantial reduction in magnetisation current and hence low
reactive VAR consumption.
31
AMORPHOUS METAL TRANSFORMERS (AMT) (CONTD.)
Low harmonic losses
Present limitation - distribution range upto 5 MVA.
(Futuristic) energy efficient cast resin transformers
32
DRY TYPE TRANSFORMERS
Two types (i) Conventional (ii) Cast Resin or Resin Impregnated
Class `C or `F
Suitable for indoor application with low fire hazard
Nomex paper / board used has temperature withstand capability
of 2200C
Vacuum pressure impregnation (VPI) with polyestermide
resin ensures high mechanical strength
Initial higher cost than that of oil cooled
Maintenance free
Future trends - ratings beyond 33 kV
33
Problems related to PD and UV radiation
SF6 GAS INSULATED TRANSFORMERS
Technology more popular in USA and Japan.
Conductor Insulation is PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate (No reaction with SF6 and has high temperature withstand)
20% reduced weight, 15% reduced size compared to oil immersed transformers.
Suitable for installation in high fire risk elimination of fire hazards and explosion that exist with transformer oil.
Cooled by Gas to liquid heat exchangers.
Pressured SF6 Gas provides dielectric strength during the startup period.
34
SF6 GAS INSULATED TRANSFORMERS
Liquid fluorocarbon is dispersed over the magnetic circuit and the windings. When the transformer is loaded where it is vapourised. The vapours increase the dielectric strength and also provide cooling.
GIS is the trend, right upto 1200 kV
Environmental concerns, sealing problems and high cost of manufacture may restrict the growth of SF6 transformers
35
CONDITION MONITORING TECHNIQUES
Online Off-line --------x x x ---------Fields of application -----------------------------
Diagnostic methods &
Measuring Quantities Core & coil assly - Thermal faults and elect.discharges Winding hot-spots - loading capability x x x Dryness of insulation Healthiness of bushings
--------------------------------
Gas-in-oil analysis
Fibre optic sensors
embedded in wdg. For
hot-spot measurement
RVM, PDC, Tan Delta
C, Tan delta of
bushings
36
CONDITION MONITORING TECHNIQUES (CONTD.)
Online Off-line x x x Fields of application Core & coil assembly, ageing, incipient faults Core & coil assly. Winding displacement, x x x x x x x winding faults
Diagnostic methods &
Measuring Quantities
PD measurement
and location
Transfer function
PPM
Active part dryness Arcing and contact wear Winding displacement during transport, short circuit RLA
37
OLTC monitoring
FRA,LV1,HV1
Furfural Content
TRANSFORMERS FOR TOMORROW
Power-former
High voltage Electric Generators employing XLPE cable are being developed upto 400 kV
First Power-former : a hydro machine rated at 11 MVA, 45 kV commissioned at the Porjus Hydro Power Centre in Northern Sweden in 1998.
38
TRANSFORMERS FOR TOMORROW
DRYFORMER - LATEST BREAKTHROUGH First patent filed in February 1997 : 10 MVA, 52/17 kV First commercial installation in 1999 : 2 x 20 MVA, 140/6.6 kV at Birka Energis Lottefors Hydropower Station Result of marriage of high voltage cable technology and transformer technology It is oil free, dry type transformer which is a complement to, and an extension of existing range of conventional high voltage transformers using XLPE cable as winding conductors. Claimed advantages: positive environ-mental impact, enhanced safety, flexible placement, higher reliability; hence suitable for placement in densely populated urban areas and environmen39 tally sensitive areas
DRYFORMER (CONTD.)
Better short-circuit strength as windings are held in a place in
a cage like structure that provides both axial and radial
supports
Windings are self supported (not clamped from yoke / frame)
Mechanical behaviour of XLPE changes especially at high
temperatures (upper temperature limit 900C)
New dry type OLTC and new cable to air terminations are
under development
40
HIGH TEMPERATURE SUPER CONDUCTING TRANSFORMERS (HTS)
TRANSFORMER FOR NEAR FUTURE (Next 5-10 Years)
Reduces energy losses by approx. 50%
Reduces weight and size as much as 50%
Elimination of oil
Used with non-flammable liquid N2 as a coolant and dielectric
About 100 compounds now classified as HTS, some of them becomes
super conducting at temperature as high as 1350C
Two important types : YBCO - Yttrium barium Copper Oxide BSCCO - Bismuth Strontium Calcium Copper Oxide
41
HIGH TEMPERATURE SUPER CONDUCTING TRANSFORMERS (HTS)
Worlds First Operational HTS Distribution Transformer
630 kVA, 18.7 kV / 420 V Commissioned in Geneva, Switzerland in
March 97, using BSCCO-2223 PIT windings cooled in liquid N2.
42
DISTINCT TRENDS AT THIS TIME
The continued interest and emphasis on improved reliability for
both transformers and accessories
Research and Development of condition monitoring techniques
to ensure trouble free service
Estimation of remnant life of transformers and accessories
Diagnostic methods for fault locations
Microprocessor based monitors
Electronic instrumentation for controls and protection
Future is for dry technology
- Dryformer
43
- Dry bushings
- Dry static tapchangers
BUSINESS TRENDS AT THIS JUNCTURE
Business around aging population of transformers shall increase
- Consultation business to grow to help utilities plan for
replacement or refurbishment
- RLA will have good business potential
Upgrading will be a large business
- New windings and new insulating material can increase the
rating upto 50%
Site repair, site refurbishment, site dry out and site testing may
develop as good business
44
BUSINESS TRENDS AT THIS JUNCTURE(CONTD.)
Trend towards specialisation and segmentaion to achieve high quality and stay competitive and concentrate on Niche Products
Focus on efficient and fast manufacturing.
45
( TODAY )
TRANSFORMER INDUSTRY IS NOW
COMPLETELY GLOBALISED LIKE
AIRCRAFT OR AUTOMOBILE OR IT
INDUSTRYOF TODAY
46
( TOMORROW )
TRANSFORMER WILL CONTINUE
TO SERVE MANKIND SELFLESSLY
47
48
Вам также может понравиться
- Temperature Correction Factors - Power Grid IndiaДокумент6 страницTemperature Correction Factors - Power Grid IndiaAMIT BISWASОценок пока нет
- Sri RamachandranДокумент7 страницSri RamachandranNavaneethakrishnan MurugesanОценок пока нет
- Design of High Voltage Filter For Power Transformer TestingДокумент6 страницDesign of High Voltage Filter For Power Transformer TestingmayureshОценок пока нет
- 24/30 MVA Transformer SpecsДокумент1 страница24/30 MVA Transformer Specsram krishnanОценок пока нет
- Analysis of Residual Life Estimation Methods for Power TransformersДокумент19 страницAnalysis of Residual Life Estimation Methods for Power TransformersJicheng PiaoОценок пока нет
- Instrument Transformers 2016Документ24 страницыInstrument Transformers 2016sogetsu kazamaОценок пока нет
- TRANSFORMERS FOR FUTURE: Optimized Solutions for Power NetworksДокумент8 страницTRANSFORMERS FOR FUTURE: Optimized Solutions for Power NetworksMohd Ghazali JPMM100% (1)
- DRM of OltcДокумент4 страницыDRM of OltcBestwick Braveen SylvesterОценок пока нет
- Impulse Voltage Distribution in Intershield Disk Winding VS Interleaved and Continuous Disk Winding in Power TransformerДокумент6 страницImpulse Voltage Distribution in Intershield Disk Winding VS Interleaved and Continuous Disk Winding in Power TransformerrendraОценок пока нет
- Upptcl Training (Ee)Документ27 страницUpptcl Training (Ee)AakashОценок пока нет
- Singapore Seminar 14.05.2020Документ96 страницSingapore Seminar 14.05.2020HafiziAhmadОценок пока нет
- Bushing Power Factor Training PPTДокумент44 страницыBushing Power Factor Training PPTMiguel Zuñiga100% (1)
- CCVT Products l3 Otcf Ansi 71508 v1 enДокумент8 страницCCVT Products l3 Otcf Ansi 71508 v1 enZeeshan HayatОценок пока нет
- How To Select The Suitable OLTCДокумент23 страницыHow To Select The Suitable OLTCTarun BhatejaОценок пока нет
- Wall Bushings: STB Series: 40.5 252 KV Combined Wall Bushings With Current Transformer: STB-L Series: 40.5 252kVДокумент4 страницыWall Bushings: STB Series: 40.5 252 KV Combined Wall Bushings With Current Transformer: STB-L Series: 40.5 252kVRamesh PatelОценок пока нет
- S2-6-Calculating Circulating Currents in Clamping Strucure and Preventing Gassing Problem - Manan Pandya-Siemens - Rev1Документ3 страницыS2-6-Calculating Circulating Currents in Clamping Strucure and Preventing Gassing Problem - Manan Pandya-Siemens - Rev1MallikarjunОценок пока нет
- CSP SystemДокумент23 страницыCSP Systemvinay kumarОценок пока нет
- Online Drying Systems With MoistureДокумент51 страницаOnline Drying Systems With MoisturePrasanna MohandossОценок пока нет
- High Voltage Testing Techniques and EquipmentДокумент16 страницHigh Voltage Testing Techniques and Equipmenthadrien100% (1)
- Ethiopia EEPCOTransmission Substations Mobile Transformer SpecsДокумент9 страницEthiopia EEPCOTransmission Substations Mobile Transformer SpecsNavneeth100% (1)
- Methodology and Methods for Assessing Transformer ConditionДокумент47 страницMethodology and Methods for Assessing Transformer ConditionAshroof Abdo50% (2)
- Partial Discharge Monitoring On Rotating Machines Using A Modular Instrument ApproachДокумент26 страницPartial Discharge Monitoring On Rotating Machines Using A Modular Instrument Approachreza515heiОценок пока нет
- Four Types of High Voltage Current TransformersДокумент3 страницыFour Types of High Voltage Current TransformersSudhakar KethireddyОценок пока нет
- 25.insulation Testing M4000Документ86 страниц25.insulation Testing M4000rashid rahmanОценок пока нет
- Transformer Winding Layer Vs DiskДокумент33 страницыTransformer Winding Layer Vs Diskbibhoo100% (1)
- Qualitrol - Low Frequency Vs High Frequency Partial Discharge DetectionДокумент20 страницQualitrol - Low Frequency Vs High Frequency Partial Discharge DetectionDennis MendozaОценок пока нет
- 24 66 11 KV 5 MVA Transformer With Amendment PDFДокумент100 страниц24 66 11 KV 5 MVA Transformer With Amendment PDFNirmal mehtaОценок пока нет
- UTP MKII Product Training SlidesДокумент65 страницUTP MKII Product Training Slidesberkahharian100% (1)
- Transposition in Transformer WindingsДокумент29 страницTransposition in Transformer WindingsM V Ravindra Mutyala100% (1)
- Power Transformer Condition Monitoring and Remanent Life AssessmentДокумент5 страницPower Transformer Condition Monitoring and Remanent Life AssessmentAmarinder DhimanОценок пока нет
- SFRA White PaperДокумент4 страницыSFRA White Paperykh92167Оценок пока нет
- CRGOДокумент15 страницCRGOipraoОценок пока нет
- Optical Current & Voltage Sensors: Eric Langford, Langford & Associates John Swindlehurst, P.Eng, Nxtphase T&D CorpДокумент38 страницOptical Current & Voltage Sensors: Eric Langford, Langford & Associates John Swindlehurst, P.Eng, Nxtphase T&D CorpKrishna Venkataraman100% (1)
- Doble Lemke Power Transformer Advanced PD Monitoring UHF 2009Документ21 страницаDoble Lemke Power Transformer Advanced PD Monitoring UHF 2009taufiqishak09Оценок пока нет
- Controlled Shunt Reactors BrochureДокумент13 страницControlled Shunt Reactors BrochureFeras KharmaОценок пока нет
- A Calculation Method For Impulse Voltage Distribution in TransformerДокумент10 страницA Calculation Method For Impulse Voltage Distribution in Transformerrajfab86% (7)
- HV CB For SubstationДокумент28 страницHV CB For SubstationjokotsОценок пока нет
- VCB Switching Furnace LoadДокумент8 страницVCB Switching Furnace LoadkrcdewanewОценок пока нет
- Dielectric Analysis of High Voltage Power TransformersДокумент13 страницDielectric Analysis of High Voltage Power Transformersykh92167Оценок пока нет
- Dead Tank Circuit-Breakers Brochure GEA31987Документ12 страницDead Tank Circuit-Breakers Brochure GEA31987sani priadiОценок пока нет
- Gapped Core Current Transformer Characteristics and PerformanceДокумент9 страницGapped Core Current Transformer Characteristics and PerformanceBalajiОценок пока нет
- Power Transformer by PT. UNINDOДокумент78 страницPower Transformer by PT. UNINDOCharles AbbetОценок пока нет
- WETI Brochure - ElectrInsulPaperДокумент28 страницWETI Brochure - ElectrInsulPaperSharin Bin Ab GhaniОценок пока нет
- Instrument Transformers PDFДокумент39 страницInstrument Transformers PDFJuan Sebastián GómezОценок пока нет
- Power Transformer Construction CoreДокумент4 страницыPower Transformer Construction CoreJayadevDamodaran0% (1)
- DGA Oil SamplingДокумент6 страницDGA Oil Samplinghino_kaguОценок пока нет
- 2 - 14 Experiences EuroDoble MeetingsДокумент22 страницы2 - 14 Experiences EuroDoble Meetingsbcqbao100% (1)
- Harnonics in TransformerДокумент11 страницHarnonics in Transformeranon_831041953Оценок пока нет
- On Transformer ManufacturingДокумент25 страницOn Transformer ManufacturingThakur Dhananjay Singh Gaur100% (1)
- 7.arteche Combined HV - Ka72Документ8 страниц7.arteche Combined HV - Ka72Luis Blas100% (1)
- Instrument Transformer Testing Brochure ENUДокумент36 страницInstrument Transformer Testing Brochure ENUJayakumar JОценок пока нет
- Thoshiba Power TransformerДокумент28 страницThoshiba Power TransformerGabyña QuispeОценок пока нет
- MIDEL 7131 Dielectric Insulating Fluid OverviewДокумент2 страницыMIDEL 7131 Dielectric Insulating Fluid Overviewvzimak2355Оценок пока нет
- Method Statement For Partial Discharge Measurement: Application NoteДокумент13 страницMethod Statement For Partial Discharge Measurement: Application Notejmrs7322Оценок пока нет
- IEEMA-Basics of Dual Ratio TransformersДокумент3 страницыIEEMA-Basics of Dual Ratio TransformersHari Krishna.MОценок пока нет
- Spectra Engineering Brochure - TransformerДокумент4 страницыSpectra Engineering Brochure - TransformerAkash VermaОценок пока нет
- Impulse Voltage Testing of Power TransformersДокумент10 страницImpulse Voltage Testing of Power TransformerssameekОценок пока нет
- Pre-Commissioning Format For Reactor: I. General DetailsДокумент27 страницPre-Commissioning Format For Reactor: I. General Detailsmayur dhandeОценок пока нет
- Candlesticks Analysis For Forex Beginners PDFДокумент22 страницыCandlesticks Analysis For Forex Beginners PDFFaiz AhmedОценок пока нет
- 0625 w03 ErДокумент14 страниц0625 w03 ErFaiz AhmedОценок пока нет
- Mean of Grouped DataДокумент3 страницыMean of Grouped Dataim_nabeelОценок пока нет
- Geometric Proof: GCSE HigherДокумент4 страницыGeometric Proof: GCSE HigherFaiz AhmedОценок пока нет
- Directed Number: Using Negative NumbersДокумент31 страницаDirected Number: Using Negative Numbersfarah-ain-8485Оценок пока нет
- Circle TheoremsДокумент19 страницCircle TheoremsFaiz Ahmed0% (1)
- Speed, Distance, Time, and Density Measures ExplainedДокумент16 страницSpeed, Distance, Time, and Density Measures ExplainedFaiz AhmedОценок пока нет
- Enlargement: OCR Stage 6Документ5 страницEnlargement: OCR Stage 6Faiz AhmedОценок пока нет
- 3D Coordinates: OCR Stage 7Документ7 страниц3D Coordinates: OCR Stage 7Faiz AhmedОценок пока нет
- Brackets & Factors ExplainedДокумент14 страницBrackets & Factors ExplainedFaiz AhmedОценок пока нет
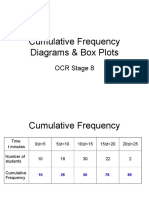
- Cumulative Frequency DiagramsДокумент8 страницCumulative Frequency DiagramsFaiz AhmedОценок пока нет
- 2016 2018 Syllabus PDFДокумент45 страниц2016 2018 Syllabus PDFPepz SupitchaОценок пока нет
- Algebraic FractionsДокумент12 страницAlgebraic FractionsHui Ying YingОценок пока нет
- Pressure Conversion and Torque TableДокумент3 страницыPressure Conversion and Torque TableFaiz AhmedОценок пока нет
- ST TLE Agri. Crop Production 7 NO. 1Документ3 страницыST TLE Agri. Crop Production 7 NO. 1Vince Zoi Galvan100% (1)
- Predampening Benefits Shotcrete Quality and SafetyДокумент3 страницыPredampening Benefits Shotcrete Quality and SafetySantosh UpadhyayОценок пока нет
- 3D Printing of Structured Electrodes For Rechargeable BatteriesДокумент22 страницы3D Printing of Structured Electrodes For Rechargeable Batterieskhue tranОценок пока нет
- Irganox® 1010 Sds en SGДокумент10 страницIrganox® 1010 Sds en SGPrototypeОценок пока нет
- UPSEE Full-Paper 2006Документ40 страницUPSEE Full-Paper 2006AditiBhatnagar1100% (1)
- Lecture 2 - Clinical and Lab Steps - Preliminary Impression-Preliminary Cast (3.03)Документ42 страницыLecture 2 - Clinical and Lab Steps - Preliminary Impression-Preliminary Cast (3.03)Ioachim FriedmannОценок пока нет
- Rotamat® Rok 4 Pumping Stations Screen: WasteДокумент4 страницыRotamat® Rok 4 Pumping Stations Screen: WastecrvenicajОценок пока нет
- Evaluation of Steam Jet EjectorsДокумент11 страницEvaluation of Steam Jet EjectorsRajeh Somrani100% (3)
- Cyanide-Free Gold Ore Dressing Agent PDFДокумент13 страницCyanide-Free Gold Ore Dressing Agent PDFAldemar Arciniegas100% (1)
- SDS - Penguard Topcoat - Comp. A With LC - Marine - Protective - English (Uk) - United KingdomДокумент8 страницSDS - Penguard Topcoat - Comp. A With LC - Marine - Protective - English (Uk) - United KingdomNPTОценок пока нет
- Extra BMP Unit 1Документ40 страницExtra BMP Unit 1V R SrinivasanОценок пока нет
- Dust Collection ChecklistДокумент4 страницыDust Collection ChecklistbroedenОценок пока нет
- Beto 18 Peer Review 2021 Feedstk KlingerДокумент23 страницыBeto 18 Peer Review 2021 Feedstk KlingerNanasaheb PatilОценок пока нет
- Pop-up and Starter Fertilizers for Corn: Rates, Placement and Nutrient RemovalДокумент5 страницPop-up and Starter Fertilizers for Corn: Rates, Placement and Nutrient RemovaluserОценок пока нет
- Mooring Line Management SNAME 1994Документ8 страницMooring Line Management SNAME 1994Peyman MznОценок пока нет
- 1 s2.0 S1319610311002407 MainДокумент14 страниц1 s2.0 S1319610311002407 Mainspanu oanaОценок пока нет
- ReasoningДокумент43 страницыReasoningrajkh0786Оценок пока нет
- 6 Ways To Make Candle Making EasyДокумент17 страниц6 Ways To Make Candle Making Easyelcuco2011100% (1)
- Bbe ProductДокумент9 страницBbe Productbackkomster6439Оценок пока нет
- Bricks PDFДокумент86 страницBricks PDFSai DasaradharamОценок пока нет
- Martin Flexible Couplings CatalogДокумент37 страницMartin Flexible Couplings CatalogJean CarlosОценок пока нет
- 1584Документ6 страниц1584malsttarОценок пока нет
- Cambridge IGCSE Physics Coursebook Second Edition (Cambridge University Press) - Pages-DeletedДокумент22 страницыCambridge IGCSE Physics Coursebook Second Edition (Cambridge University Press) - Pages-DeletedMariam ShehabОценок пока нет
- Screw Gluing Pressure Distribution and Bond StrengthДокумент10 страницScrew Gluing Pressure Distribution and Bond Strengthm2auОценок пока нет
- Grammar Files b2 Unit 1Документ7 страницGrammar Files b2 Unit 1Irina Shopova100% (1)
- EndocrineДокумент3 страницыEndocrinePotato HeadОценок пока нет
- 01Документ97 страниц01cheery1Оценок пока нет
- Dow Corning 3145 RTV Adhesive-SealantДокумент8 страницDow Corning 3145 RTV Adhesive-SealantEdgarОценок пока нет
- Module 2: Problem Set CH148/A32: Camacho, Ocampo, Patuto, Rodenas, TizonДокумент5 страницModule 2: Problem Set CH148/A32: Camacho, Ocampo, Patuto, Rodenas, TizonZhane TizonОценок пока нет
- Thermal Conductivity Meter: Guarded Heat Flow Test MethodДокумент2 страницыThermal Conductivity Meter: Guarded Heat Flow Test Methodrajesh_rbpОценок пока нет