Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Female Pelvis
Загружено:
api-3742802Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Female Pelvis
Загружено:
api-3742802Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Page 1 of 1
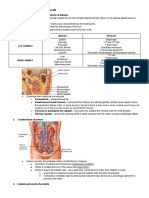
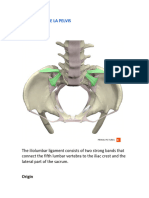
FEMALE PELVIS
Peritoneal Covering Covers/Relations Others
Recto-uterine pouch Fundus, uterus (posterior surface of body), upper 1/3 rectum Covering also used as
(cul-de-sac of Douglas) serosa of these organs
Vesiculo-uterine Fold inserted between upper 1/3 uterus & superior surface of
pouch bladder
Broad ligament Below FT, sides of uterus and cervix Double layered fold
Fixed by infundibulo-pelvic ligament to sacro-iliac joint Encloses parametrium
Parametrium Supports uterine vessels and nerves and distal ends of ureters Abundant endopelvic fascia
Mesosalphinx Covers fallopian tubes
Mesovarium Enfolds ovaries; includes true ovarian ligament
True ovarian ligament Supero-lateral angle of uterus below utero-tubal jxn tubal pole
False suspensory lig. Tubal pole lateral pelvic wall at sacro-iliac joint; ovarian vsls. Blends with infundibulo-
pelvic ligament
Infundibulo-pelvic lig. Thickening at sacro-iliac joint; encloses ovarian vessels
Cardinal Thickennings at sides of cervix, extended to lateral pelvic walls Maintains cervix and uterus
(Mckenrodt’s) lig. Uterine arteries along its superior border in place
Utero-Sacral ligament Back of cervix recto-uterine fold and last segments of sacrum Prevents forward
displacement of cervis
Round ligament Superior angles of uterus anterior to utero-tubal jxn inguinal Remnants of Wolffian ducts
canal fibrous tissue beneath labia majora
Pubo-vesical ligament From pelvic surface of symphysis pubis to neck of bladder Normal position of uterus
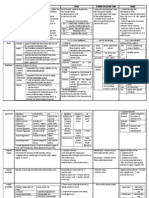
Organ Definition
Ovaries Size of almond seed Fossa ovarica of Waldeyer – where it lodges; below
age, scarring (corpora lutea and albicans) bifurcation of ext and int iliac vessels
Mesovarium – covering of ovaries Superior or tubal pole – directed postero-laterally
Inferior or uterine pole – antero-medially
Fallopian Muscular tubes in lateral pelvic wall Below bifurcation of common iliac vessels
Tubes Vicinity of sacro-iliac joint 10-12 cms long, enveloped by mesosalphinx
Intramural Shortest, narrowest, most fixed part Embedded in uterus at superior lateral angle of
segment Opening: 1 mm in diameter uterus
Isthmus 2.5 cms From uterine wall and extended laterally
Ampulla Gradual widening; longest part Dilated ends curved downwards near tubal pole
Infundibulum Expanded end with finger-like extensions (fimbriae)
Abdominal opening (ostium abdominale) – potential but direct communication with ext env’t via utero-tubal
and vaginal passages
Ovarian fimbria – longer fimbria; facilitates entry of ovum through ostium into ampulla
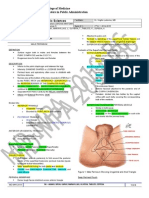
Uterus Hollow muscular organ
Diameter: 7-8 cm (0-1 pregnancy), 9-10 (multi), 3-4 (menopause)
Fundus Slightly arching superior border anove utero-tubal junctions
Directed forwards towards symphysis pubis
Body Main part; Broadened below fundus
(corpus) Narrows inferiorly (isthmus)
Cervix Invaginated into upper end of vaginal Intravaginal portion – enclosed by vaginal fornices
canal Ant. fornix – nicest area to palpate for tumor; shallowest
Internal os – in isthmus of cervix Lateral fornices – BV
External os – rounded or narrow slit Post. fornix – largest and deepest; receptaculum seminis
Supravaginal portion – upper segment - rises above pelvic diaphragm into pelvic cavity contact
with cul-de-sac of Douglas
Cavity Triangular; lined by endometrium Intrauterine openings – at superior angles of cavity
Plica palmatae – characteristic palm-leaf-like folds After deliver: involution; 8-12 weeks to recover
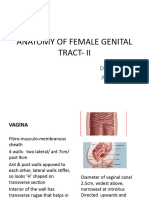
Vagina Upper end – distended for lower half of cervix Lower 1/3 of vaginal canal – surrounded by:
Fornices – pouches produced by walls at upper end Pubo-coccygeus (of levator ani)
Anterior vaginal wall – shorter, rough (due to rugae) Sphincter urethra and deep TP muscles
- related to neck of bladder and urethra Bulbo-cvernoss and superficial TP muscles
Posterior wall – longer , smoother; from rectal wall by Musculo-membranous tube; 7-8 cms long
thin fascial septum Opens into vestibule of perineum
NVS Origin Course End
Uterine a. Internal iliac Down, forwards, medially to lateral border of isthmus Anastomose with tubal
Enveloped by cardinal ligament branch of ovarian artery
Side of isthmus: Gives off vaginal branch
Ascends on lateral border of uterus utero-tubal jxn
Ovarian a. Abdominal Oblique course down crossing over the ureter Anastomose with uterine
aorta Pelvic brim: enters fold of infundibulo-pelvic ligament artery
Below origins Mesovarian border hilus of ovary
of renal a. Gives tubal branch mesosalphinx utero-tubal jxn
Vaginal a. Int. iliac Gives branches to lowest part of bladder and rectum Anastomose to form median
Vaginal wall: gives off anterior and posterior branches longitudinal azygos artery
Veins Vaginal plexuses along sides of vagina uterine plexuses other pelvic plexuses
Lymphatic Sides of uterus and vagina + urethral, ovarian, and tubal channels nodules along vein int & ext iliac vsls
Efferent vsls lumbar, aortic, and other nodes; some into femoral nodes
Sym Sacral Joins perivascular plexus (hemorrhoidal arteries, branches Innervate smooth muscles
nerves ganglia from inf hypogastric plexus) and glands (uterus &
PS nerves S2, 3, 4 Conveyed by pelvic splancnic nerve + above plexuses oviducts)
2006
Вам также может понравиться
- Anthony Robbins - Time of Your Life - Summary CardsДокумент23 страницыAnthony Robbins - Time of Your Life - Summary CardsWineZen97% (58)
- Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemДокумент12 страницAnatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemSyed Isamil100% (1)
- ZOO 4733 - Exam 3 ReviewДокумент21 страницаZOO 4733 - Exam 3 ReviewDaniel PóoОценок пока нет
- Nature of Science-Worksheet - The Amoeba Sisters HWДокумент2 страницыNature of Science-Worksheet - The Amoeba Sisters HWTiara Daniel25% (4)
- Roland Fantom s88Документ51 страницаRoland Fantom s88harryoliff2672100% (1)
- Anatomy of The Female ReproductionДокумент108 страницAnatomy of The Female ReproductionDaisy HamdaliОценок пока нет
- Female Genital SystemДокумент29 страницFemale Genital SystemMuna MОценок пока нет
- Female Reproductive OrgansДокумент32 страницыFemale Reproductive Organsapi-19916399100% (1)
- Anatomy of Female Reproductive Organs: Dr.M.Mahalakshmi Assistant Professor Government Chengalpattu Medical CollegeДокумент20 страницAnatomy of Female Reproductive Organs: Dr.M.Mahalakshmi Assistant Professor Government Chengalpattu Medical Collegepranu6789Оценок пока нет
- Female Pelvic VisceraДокумент73 страницыFemale Pelvic VisceraAnania EmmanuelОценок пока нет
- Anaesthesia and Analgesia in Labour: Brett Johnson Vadewattie Ramnarine Anna Singh Gabrielle de Nobrega Bhavanie SinghДокумент188 страницAnaesthesia and Analgesia in Labour: Brett Johnson Vadewattie Ramnarine Anna Singh Gabrielle de Nobrega Bhavanie SinghRochelle BaileyОценок пока нет
- Final Module in M101Документ56 страницFinal Module in M101J. TSОценок пока нет
- Final Module in M101 1Документ54 страницыFinal Module in M101 1J. TSОценок пока нет
- Female Reproductive SystemДокумент46 страницFemale Reproductive SystemAzza100% (11)
- Anatomy of The Female Reproductive SystemДокумент62 страницыAnatomy of The Female Reproductive SystemBibek GajmerОценок пока нет
- Session 4 Lecture 1 Part 1Документ25 страницSession 4 Lecture 1 Part 1avin xsroОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент7 страницUntitledDania Ibraheem100% (1)
- Anterior Posterior: o Posterior Renal Fascia Is Also Known As Zuckerkandl's Fascia)Документ4 страницыAnterior Posterior: o Posterior Renal Fascia Is Also Known As Zuckerkandl's Fascia)Lester AldridgeОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of Fallopian Tube & OvaryДокумент89 страницAnatomy of Fallopian Tube & OvaryAsma AijazОценок пока нет
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreДокумент28 страницOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreabctutorОценок пока нет
- ANATOMY Trans PELVIS POST ABDOMINAL WALL PERINEUMДокумент8 страницANATOMY Trans PELVIS POST ABDOMINAL WALL PERINEUMSan LapuhapuОценок пока нет
- CBL 2Документ20 страницCBL 2Hammad AkramОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology of Female ReproductiveДокумент6 страницAnatomy and Physiology of Female ReproductiveChryst Louise SaavedraОценок пока нет
- ANATOMIДокумент43 страницыANATOMIWidayuОценок пока нет
- Perineum 180922120553 PDFДокумент45 страницPerineum 180922120553 PDFFazle RabbiОценок пока нет
- Anterior Abdominal Wall and Inguinal CanalДокумент35 страницAnterior Abdominal Wall and Inguinal Canalapi-3698357100% (3)
- GynaДокумент22 страницыGynaIGA ABRAHAMОценок пока нет
- 17 Inguinal CanalДокумент17 страниц17 Inguinal CanalgeorgefrombaОценок пока нет
- Trans Male ReproДокумент4 страницыTrans Male ReproJames MaravillasОценок пока нет
- (DR - Romi) Female Reprod System2022Документ74 страницы(DR - Romi) Female Reprod System2022Audio TechnicaОценок пока нет
- Anatomy Lec 22 (FGOs)Документ49 страницAnatomy Lec 22 (FGOs)Humraz100% (1)
- Peritoneum & Peritoneal Cavity PresentationДокумент59 страницPeritoneum & Peritoneal Cavity Presentationsaint thuggerОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of Female Reproductive SystemДокумент25 страницAnatomy of Female Reproductive SystemQurat-ul-ain IrfanОценок пока нет
- Female Reproductive System-AnatomyДокумент57 страницFemale Reproductive System-AnatomyEstellaОценок пока нет
- External Structure: Common Positions of Uterus Inside Female PelvisДокумент2 страницыExternal Structure: Common Positions of Uterus Inside Female PelvisHerne BalberdeОценок пока нет
- Abdominal Wall: Muh. Iqbal Basri Anatomy Department Hasanuddin UniversityДокумент33 страницыAbdominal Wall: Muh. Iqbal Basri Anatomy Department Hasanuddin UniversityDavid ChristianОценок пока нет
- 41 Female Reproductive AnatomyДокумент14 страниц41 Female Reproductive Anatomyruaa firasОценок пока нет
- Ureters Urinary Bladder UrethraДокумент20 страницUreters Urinary Bladder UrethraFlora PopaОценок пока нет
- OB - TransesДокумент112 страницOB - TransesAldwin BagtasОценок пока нет
- Intro Lab Anatomi Rps (2024)Документ117 страницIntro Lab Anatomi Rps (2024)Jason Maxwell mcguireОценок пока нет
- M1207: Gastrointestinal System Embryology Lecture 01: Dr. Sampath PaththinigeДокумент30 страницM1207: Gastrointestinal System Embryology Lecture 01: Dr. Sampath Paththinigekavinduherath2000Оценок пока нет
- Abdomen CavityДокумент55 страницAbdomen CavitySrisalma LasamaОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of Female Genital Tract - IiДокумент44 страницыAnatomy of Female Genital Tract - Iigksah711Оценок пока нет
- Overview of Female Reproductive System ResearchДокумент21 страницаOverview of Female Reproductive System ResearchOmar Ali AyoubkhanОценок пока нет
- Anatomia TrabajoДокумент60 страницAnatomia TrabajoFelipe Domínguez FigueroaОценок пока нет
- Female Reproductive OrgansДокумент7 страницFemale Reproductive OrgansAnastasia KasapiОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of Female GenitaliaДокумент3 страницыAnatomy of Female GenitaliaameerabestОценок пока нет
- 2.1 Male and Female Repro IntroductionДокумент11 страниц2.1 Male and Female Repro IntroductionTrisha Mae BalladОценок пока нет
- Physio OB Maternal Anatomy External and Internal Generative Organs PPT 2Документ67 страницPhysio OB Maternal Anatomy External and Internal Generative Organs PPT 2Janine SergioОценок пока нет
- Pelvis Anatomy AnswersДокумент15 страницPelvis Anatomy AnswersAvi C100% (1)
- Female GenitaliavДокумент39 страницFemale GenitaliavKathlyn PactorananОценок пока нет
- Abdomen Dan PelvisДокумент64 страницыAbdomen Dan PelvisRachmad RasidinОценок пока нет
- Male Reproductive SystemДокумент15 страницMale Reproductive SystemCharisse Dizon EstocadoОценок пока нет
- The AbdomenДокумент3 страницыThe AbdomenotaОценок пока нет
- 07 - Uterus, Uterine Tubes, OvariesДокумент52 страницы07 - Uterus, Uterine Tubes, Ovariesck4realОценок пока нет
- Dr. Reynaldo V. Lopez Senior Lecturer Department of AnatomyДокумент55 страницDr. Reynaldo V. Lopez Senior Lecturer Department of AnatomyMohammad AliОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of The Female Genital OrganДокумент19 страницAnatomy of The Female Genital Organaachal dhitalОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2 - Embryology of The Female Genital Tract & Anatomy of Female Pelvis & Fetal SkullДокумент11 страницLecture 2 - Embryology of The Female Genital Tract & Anatomy of Female Pelvis & Fetal SkullBrandonRyanF.MosidinОценок пока нет
- Maternal Anatomy ReportДокумент89 страницMaternal Anatomy ReportWildelyn JaoОценок пока нет
- Maternal Anatomy ReportДокумент52 страницыMaternal Anatomy Reportlovelots1234Оценок пока нет
- Maternal Notes 1Документ34 страницыMaternal Notes 1Mica Campoy CabinongОценок пока нет
- Sistema Reproductor FemeninoДокумент28 страницSistema Reproductor FemeninoChavok JjОценок пока нет
- USTNG2010 Brain ModelДокумент13 страницUSTNG2010 Brain Modelapi-3742802Оценок пока нет
- Chok Biochem 4th Shift Reviewer Nutritional DisordersДокумент2 страницыChok Biochem 4th Shift Reviewer Nutritional Disordersapi-3742802Оценок пока нет
- Water Soluble 1Документ1 страницаWater Soluble 1api-3742802Оценок пока нет
- Trace Elements 2Документ1 страницаTrace Elements 2api-3742802Оценок пока нет
- Trace Elements 1Документ1 страницаTrace Elements 1api-3742802Оценок пока нет
- Neuroanatomy Practical 2nd ShiftДокумент2 страницыNeuroanatomy Practical 2nd Shiftapi-3742802Оценок пока нет
- Rin Case StudyДокумент4 страницыRin Case StudyReha Nayyar100% (1)
- Investigative JournalismДокумент8 страницInvestigative JournalismMitchie LlagasОценок пока нет
- Carpentry Grade 8 Week 1 2Документ20 страницCarpentry Grade 8 Week 1 2SANTIAGO ALVISОценок пока нет
- Vintage Airplane - May 1982Документ24 страницыVintage Airplane - May 1982Aviation/Space History LibraryОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Designing An Active Directory InfrastructureДокумент18 страницIntroduction To Designing An Active Directory InfrastructurepablodoeОценок пока нет
- UBMM1011 Unit Plan 201501Документ12 страницUBMM1011 Unit Plan 201501摩羯座Оценок пока нет
- Nse 2Документ5 страницNse 2dhaval gohelОценок пока нет
- O'Dell v. Medallia, Inc. Et Al, 1 - 21-cv-07475, No. 1 (S.D.N.Y. Sep. 7, 2021)Документ15 страницO'Dell v. Medallia, Inc. Et Al, 1 - 21-cv-07475, No. 1 (S.D.N.Y. Sep. 7, 2021)yehuditgoldbergОценок пока нет
- Chunking Chunking Chunking: Stator Service IssuesДокумент1 страницаChunking Chunking Chunking: Stator Service IssuesGina Vanessa Quintero CruzОценок пока нет
- Dept & Sem: Subject Name: Course Code: Unit: Prepared byДокумент75 страницDept & Sem: Subject Name: Course Code: Unit: Prepared by474 likithkumarreddy1Оценок пока нет
- Taxation Law 1Документ7 страницTaxation Law 1jalefaye abapoОценок пока нет
- Dash 3000/4000 Patient Monitor: Service ManualДокумент292 страницыDash 3000/4000 Patient Monitor: Service ManualYair CarreraОценок пока нет
- ProjectДокумент33 страницыProjectPiyush PatelОценок пока нет
- Risk Analysis and Assessment Methodologies in Work SitesДокумент49 страницRisk Analysis and Assessment Methodologies in Work SitesNhut NguyenОценок пока нет
- Strategic Audit of VodafoneДокумент35 страницStrategic Audit of VodafoneArun Guleria89% (9)
- Angelo (Patrick) Complaint PDFДокумент2 страницыAngelo (Patrick) Complaint PDFPatLohmannОценок пока нет
- Thesis On Retail Management of The Brand 'Sleepwell'Документ62 страницыThesis On Retail Management of The Brand 'Sleepwell'Sajid Lodha100% (1)
- A Brief Tutorial On Interval Type-2 Fuzzy Sets and SystemsДокумент10 страницA Brief Tutorial On Interval Type-2 Fuzzy Sets and SystemstarekeeeОценок пока нет
- 2432 - Test Solutions - Tsol - 2432 - 21702Документ5 страниц2432 - Test Solutions - Tsol - 2432 - 21702Anmol PanchalОценок пока нет
- ISO-3046-4-2009 (Gobernador de Velocidad)Документ8 страницISO-3046-4-2009 (Gobernador de Velocidad)David GastelumОценок пока нет
- Process Description of Function For Every Unit OperationДокумент3 страницыProcess Description of Function For Every Unit OperationMauliduni M. AuniОценок пока нет
- Operational Readiness and Airport TransferДокумент2 страницыOperational Readiness and Airport TransferochweriОценок пока нет
- Community Resource MobilizationДокумент17 страницCommunity Resource Mobilizationerikka june forosueloОценок пока нет
- Generator ControllerДокумент21 страницаGenerator ControllerBrianHazeОценок пока нет
- Comparitive Study of Fifty Cases of Open Pyelolithotomy and Ureterolithotomy With or Without Double J Stent InsertionДокумент4 страницыComparitive Study of Fifty Cases of Open Pyelolithotomy and Ureterolithotomy With or Without Double J Stent InsertionSuril VithalaniОценок пока нет
- Guidelines For Plenipotentiary - 1Документ6 страницGuidelines For Plenipotentiary - 1Oladimeji Ibukun IjaodolaОценок пока нет
- Sample Interview Questions For Planning EngineersДокумент16 страницSample Interview Questions For Planning EngineersPooja PawarОценок пока нет