Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Lab 3
Загружено:
bandit1rИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Lab 3
Загружено:
bandit1rАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
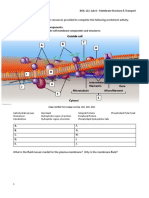
BIO 105
Prof. Fuller Chemical Functions
Lab 3
Information for Lab 3 1. Diffusion:
a.
b. c. d.
Definition: the movement of a substance from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration Selectively (differentially) permeable membrane: a membrane that allows only certain substances to pass (e.g. the cell membrane) Complete the activity demonstrating changes in diffusion rate among a semisolid, a liquid, and gas. Complete the activity demonstrating diffusion across a selectively permeable membrane.
2.
Osmosis:
a.
b.
Definition: the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane Observe the osmosis demonstration at the front of the lab.
3.
Tonicity
a.
b.
Involves a comparison of solute and solvent concentrations between the inside of a cell and the outside Isotonic solution: solute and solvent concentrations are equal Hypertonic solution: greater water concentration on the inside of the cell and greater solute concentration on the outside of the cell (result: cell in this solution would shrivel due to water loss) Hypotonic solution: greater water concentration on the outside of the cell and greater solute concentration on the inside of the cell (result: cell in this solution would gain water and could potentially burst) Complete the activity to compare the properties of hypertonic vs. hypotonic solutions using potato pieces, distilled water, and sodium chloride solution. Answer the questions. Complete the table using the demonstration tubes containing red blood cells and three concentrations of sodium chloride solution at the front of the room to compare the properties of the three types of solutions (You will make slides from each of the three test tubes in addition to viewing your lab manual through each of the tubes.) Complete the activity to compare the properties of hypertonic vs. hypotonic solutions with regard to Elodea cells.
c.
d.
e.
f.
g.
4.
pH
a. b.
concerned with the relative hydrogen ion concentration of a solution pH scale: a range of measurements of hydrogen ion concentration i. ii. iii. acidic levels: 0-6 neutral: 7 basic levels: 8-14
c. d. e.
Buffer: a group of chemicals that can maintain a pH (to a degree). (NOTE: Cytoplasm of cells is a buffered solution.) Complete the activity to practice measuring pH and to compare pH of water, a buffer, and cytoplasm. Fill in the table. Complete the activity to demonstrate the properties of buffers in relation to pH. Complete the table, construct the two graphs, and answer the questions.
Activities:
1.
2.
Complete all procedures assigned. Be able to describe the purpose, outcome, and properties of each procedure.
Вам также может понравиться
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesОт EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- AP Biology Lab Practical Guide A Lab Practical or Exam Tests ...Документ4 страницыAP Biology Lab Practical Guide A Lab Practical or Exam Tests ...marisa corderoОценок пока нет
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Movement of substancesОт EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Movement of substancesОценок пока нет
- Biology 110 Principles of Biology 17 3. Diffusion and OsmosisДокумент10 страницBiology 110 Principles of Biology 17 3. Diffusion and OsmosislauraningsihОценок пока нет
- Osmosis Diffusion Water Potential LabДокумент18 страницOsmosis Diffusion Water Potential Labdrew-163821Оценок пока нет
- 1 - Difussion and OsmosisДокумент11 страниц1 - Difussion and OsmosisLisa Jin100% (1)
- Investigation 4 Diffusion and Osmosis PDFДокумент13 страницInvestigation 4 Diffusion and Osmosis PDFAref DahabrahОценок пока нет
- Physiological Practical 1Документ4 страницыPhysiological Practical 1Khezia ChalweОценок пока нет
- AP Biology Lab Review 1-4Документ59 страницAP Biology Lab Review 1-4swagsurferОценок пока нет
- Cell Water Balance LabДокумент5 страницCell Water Balance LabYa'el CourtneyОценок пока нет
- Diffusion and Osmosis LabsДокумент2 страницыDiffusion and Osmosis Labsgailluna112795Оценок пока нет
- Year 10 Biology Revision BookletsДокумент43 страницыYear 10 Biology Revision BookletsAbdullah SheikhОценок пока нет
- Water Potential Packet 2015 - Student HandoutДокумент7 страницWater Potential Packet 2015 - Student Handoutkanthamneni01Оценок пока нет
- Module 6Документ20 страницModule 6Jan VivienelОценок пока нет
- Osmosis and Diffusion Lab For AP BioДокумент11 страницOsmosis and Diffusion Lab For AP Bioitssabbyx3Оценок пока нет
- Kami Export - Experiment 1Документ9 страницKami Export - Experiment 1MAYNARD E. ABONADORОценок пока нет
- Lab 3 TransportДокумент5 страницLab 3 TransportMark GirasolОценок пока нет
- Bio S2 Exercises NewДокумент7 страницBio S2 Exercises NewNSABIMANA JANVIERОценок пока нет
- Biol-111 - Membrane Structure & Transport WorksheetДокумент11 страницBiol-111 - Membrane Structure & Transport WorksheetKing JoshОценок пока нет
- Bio SummativeДокумент5 страницBio SummativeCarlJesterAMontinoОценок пока нет
- Unit 4 - Review On Basic Principles Applied in Analytical ChemistryДокумент14 страницUnit 4 - Review On Basic Principles Applied in Analytical Chemistryariel egonОценок пока нет
- Neutralization ReactionsДокумент3 страницыNeutralization ReactionsShan Abi keash-1223Оценок пока нет
- Adsorption in Packed Bed: Experiment No-3Документ7 страницAdsorption in Packed Bed: Experiment No-3Harsh DuttaОценок пока нет
- CHM2123 Exp1Документ17 страницCHM2123 Exp1Darimi JohariОценок пока нет
- Lab ReportДокумент7 страницLab ReportJasz Azliey AzzamОценок пока нет
- ACT Biology-Dr. Rehab Final Revision 1Документ10 страницACT Biology-Dr. Rehab Final Revision 1m.mansoor3377Оценок пока нет
- Bio Chem Labbb EditДокумент37 страницBio Chem Labbb EditAlbert Azura100% (1)
- 1 Tonicity KeyДокумент3 страницы1 Tonicity KeygbgbkrishnaОценок пока нет
- Distillation Lab 9.10.2014Документ10 страницDistillation Lab 9.10.2014Ahmed AliОценок пока нет
- Ws1-Membrane Transport WorksheetДокумент3 страницыWs1-Membrane Transport WorksheetTy BakrОценок пока нет
- Exercises Bio f4 c3Документ7 страницExercises Bio f4 c3Azlin ShahОценок пока нет
- Formal Lab Report 2 (Complete)Документ11 страницFormal Lab Report 2 (Complete)the_real_wasabiОценок пока нет
- Chemical Equilibrium Lab 2012Документ4 страницыChemical Equilibrium Lab 2012Untung Ari Wibowo100% (1)
- Lapreport 1Документ9 страницLapreport 1api-282130056Оценок пока нет
- Virtual Lab On Osmosis: Visit The Link Below and Conduct The Experiment SuggestedДокумент1 страницаVirtual Lab On Osmosis: Visit The Link Below and Conduct The Experiment SuggestedVictoria Niño DОценок пока нет
- Puspa Sari Sains (12 12124140007) WS 02Документ6 страницPuspa Sari Sains (12 12124140007) WS 02Phuz-Pha BearwhiteexanfaОценок пока нет
- Properties of Solutions: Electrolytes and Non-Electrolytes: Ionic CompoundsДокумент4 страницыProperties of Solutions: Electrolytes and Non-Electrolytes: Ionic CompoundsArlane M. AbenojaОценок пока нет
- Canossa Academy: ObjectiveДокумент3 страницыCanossa Academy: ObjectiveG10 HUDENCIAL, Mary Margarette M.Оценок пока нет
- Cell BiologyДокумент5 страницCell BiologyPat Dumandan100% (4)
- Inbo13 QuestionДокумент40 страницInbo13 QuestionKalpavriksha1974Оценок пока нет
- Bio 4 OsmosisДокумент8 страницBio 4 OsmosisJustin Damian Malaki MalubayОценок пока нет
- Solubility & MiscibilityДокумент8 страницSolubility & MiscibilityMT20622 Nik Nur Zahidah Binti Nik HassanОценок пока нет
- MO3A - Exercise 5 - Group3Документ13 страницMO3A - Exercise 5 - Group3whyОценок пока нет
- Osmosis Diffusion Lab-1Документ7 страницOsmosis Diffusion Lab-1api-1658690000% (1)
- 101.12 IMF Fa19Документ6 страниц101.12 IMF Fa19Jossmyr NarceОценок пока нет
- Unit 4 - Review On Basic Principles Applied in Analytical ChemistryДокумент12 страницUnit 4 - Review On Basic Principles Applied in Analytical ChemistryJayson PolinarОценок пока нет
- Lab 4 Dialysis ManualДокумент8 страницLab 4 Dialysis Manualassem.assilbekovaОценок пока нет
- Questions-Tonicity - Answer KeyДокумент5 страницQuestions-Tonicity - Answer KeyNd 03Оценок пока нет
- SpectrometerДокумент17 страницSpectrometerMazzel Lou BaelОценок пока нет
- Shayma Chem II Lab Manual.... Petrochemical Engineering DepartmentДокумент55 страницShayma Chem II Lab Manual.... Petrochemical Engineering DepartmentMUHAMMAD AKRAM100% (1)
- Laboratory Exercise Questions: Lab 4 WorksheetДокумент6 страницLaboratory Exercise Questions: Lab 4 WorksheetMadison GreenОценок пока нет
- Diffusion LabДокумент7 страницDiffusion LabtinkerloveОценок пока нет
- Reduced Answer Cell Transport Level Test 2016Документ3 страницыReduced Answer Cell Transport Level Test 2016John Kevin NocheОценок пока нет
- Liquid Liquid Extraction ExperimentДокумент22 страницыLiquid Liquid Extraction ExperimentMohd Sharu Mamat67% (12)
- Holiday Homework Class Xii-AДокумент42 страницыHoliday Homework Class Xii-Ageetanjaliawasthi375Оценок пока нет
- Simple DistillationДокумент48 страницSimple DistillationSundar SkОценок пока нет
- Water Potential by Gravimetric MethodДокумент9 страницWater Potential by Gravimetric Methodsvusantoshkumar100% (1)
- !doctype H P ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Документ4 страницы!doctype H P ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)jenisatrianiОценок пока нет
- First Lab Exam ReviewerДокумент13 страницFirst Lab Exam ReviewerBea Constantino100% (1)
- Predicting Drilling Mud Loss Occurrence While Using Directional Drilling To Install Pipelines Across RiversДокумент20 страницPredicting Drilling Mud Loss Occurrence While Using Directional Drilling To Install Pipelines Across RiversObumse Chukwuebuka MichaelОценок пока нет
- PHD Thesis - Alfonso Palazzo 2015Документ444 страницыPHD Thesis - Alfonso Palazzo 2015johanОценок пока нет
- Exercisesweek 1Документ3 страницыExercisesweek 1api-254818047Оценок пока нет
- Excel Workbook No. 05 Atterberg LimitsДокумент4 страницыExcel Workbook No. 05 Atterberg LimitsEngr Ghulam MustafaОценок пока нет
- Chapter11 - SEISMICALLY ISOLATED STRUCTURESДокумент48 страницChapter11 - SEISMICALLY ISOLATED STRUCTUREScfajardo16Оценок пока нет
- Steen e Ken 1989Документ20 страницSteen e Ken 1989suryakantОценок пока нет
- Hydrology EvaporationДокумент21 страницаHydrology EvaporationMr. Mark B.Оценок пока нет
- Matrix InverseДокумент2 страницыMatrix InverseComFnoОценок пока нет
- For ECT & ECE Board ExamДокумент60 страницFor ECT & ECE Board ExamRalph Alvin Quizon100% (2)
- Self Healing ElectronicsДокумент16 страницSelf Healing ElectronicsVamsiKrishnaОценок пока нет
- Safety and Health at Work: Original ArticleДокумент30 страницSafety and Health at Work: Original ArticlePaul TanuОценок пока нет
- The Little Liste: Lvashington, D.CДокумент5 страницThe Little Liste: Lvashington, D.CNur AgustinusОценок пока нет
- Celesta Ire 2012 CatalogДокумент96 страницCelesta Ire 2012 Catalogjsom1021Оценок пока нет
- Analyses of Fat Oil and Grease in Wastewater or Receiving WaterДокумент26 страницAnalyses of Fat Oil and Grease in Wastewater or Receiving WaterFlorin Sorin Bolboaca100% (1)
- Shin Bunka Shokyu Nihongo 1Документ16 страницShin Bunka Shokyu Nihongo 1Raúl Zúñiga MedinaОценок пока нет
- Mechanism and Degrees of Freedom 2Документ10 страницMechanism and Degrees of Freedom 2Hamza TariqОценок пока нет
- KU To CentiPoiseДокумент4 страницыKU To CentiPoiseUna Si Ndéso100% (1)
- Calculation of Electro Dynamic Forces On Busbars in LV SystemsДокумент4 страницыCalculation of Electro Dynamic Forces On Busbars in LV Systemsgormankung100% (1)
- ASTM D6816-11 (Reapproved 2016)Документ9 страницASTM D6816-11 (Reapproved 2016)anant11235Оценок пока нет
- Partes Del SEMДокумент23 страницыPartes Del SEMFrancisco Javier Escobar MedinaОценок пока нет
- The Mechanism of The Leuckart Reaction PDFДокумент12 страницThe Mechanism of The Leuckart Reaction PDFatomoscoОценок пока нет
- KINEMATICS - Scientific PaperДокумент8 страницKINEMATICS - Scientific PaperDai VenusОценок пока нет
- 0625 m18 Ms 62Документ7 страниц0625 m18 Ms 62Syed AshabОценок пока нет
- Von Karman Collection GuideДокумент130 страницVon Karman Collection GuideKitana Hananda SuhattaОценок пока нет
- Sample of Absract, Tableofcontent, ListoffiguresymboletcДокумент10 страницSample of Absract, Tableofcontent, ListoffiguresymboletcEddy FadleyОценок пока нет
- Equilibrium Stage Processes - Perpindahan MassaДокумент30 страницEquilibrium Stage Processes - Perpindahan Massaj0haNN3sОценок пока нет
- U0/U U Is The Power Frequency Voltage Between Phase and Earth (V RMS)Документ3 страницыU0/U U Is The Power Frequency Voltage Between Phase and Earth (V RMS)ShashidharОценок пока нет
- PVT DaneshДокумент202 страницыPVT Daneshegv2000Оценок пока нет
- 14.4D ExerciseДокумент18 страниц14.4D ExerciseKnyazev DanilОценок пока нет
- Surface Settlement Induced by TunnellingДокумент84 страницыSurface Settlement Induced by Tunnellingyahyashak100% (3)
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseОт EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (52)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldОт EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (597)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityОт EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsОт EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (6)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisОт EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerОт EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (393)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomОт EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (216)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessОт Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (33)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceОт EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (517)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)От EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (411)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceОт EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (18)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesОт EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (397)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedОт EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (11)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainОт EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (110)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionОт EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (812)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainОт EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (65)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorОт EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorОценок пока нет
- Lymph & Longevity: The Untapped Secret to HealthОт EverandLymph & Longevity: The Untapped Secret to HealthРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (13)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildОт EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (44)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindОт EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (93)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemОт EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (115)
- Why We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsОт EverandWhy We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2083)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveОт EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (66)