Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Texture
Загружено:
Achord ZhuangИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Texture
Загружено:
Achord ZhuangАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Texture Definition -In the visual arts, texture is the perceived surface quality of a work of art.
It is an element of two-dimensional and three-dimensional design and is distinguished by its perceived visual and physical properties. Use of texture, along with other elements of design, can convey a variety of messages and emotions. - Texture in painting is the look and feel of the canvas. It is based on the paint, and its application, or the addition of materials such as ribbon, metal, wood, lace, leather and sand. The concept of 'painterliness' also has bearing on texture. The texture stimulates two different senses; sight and touch. There are four types of texture in art: actual texture, simulated texture, abstract texture, and invented texture. -texture (plural textures) 1. The feel or shape of a surface or substance; the smoothness, roughness, softness, etc. of something. -The word texture means: what things are made of and how they feel. Textures can be described as rough, smooth, hard, soft, liquid, solid, lumpy, gritty etc. The word texture is used for many different things. It can even be used in abstract senses, e.g. for music and poetry. Definition: 1. [noun] the feel of a surface or a fabric; "the wall had a smooth texture" 2. [noun] the essential quality of something; "the texture of Neapolitan life" 3. [noun] the musical pattern created by parts being played or sung together; "then another melodic line is added to the texture" 4. [noun] the characteristic appearance of a surface having a tactile quality -Texture Texture creates the feeling of an object. Physical Physical texture, also known as actual texture or tactile texture, are the actual variations upon a surface. This can include, but is not limited to, fur, wood grain, sand, smooth surface of canvas or metal, , glass, and leather. It differentiates itself from visual texture by having a physical quality that can be felt by touch. Specific use of a texture can effect the smoothness that an artwork conveys. For instance, use of rough surfaces can be visually active, whilst smooth
surfaces can be visually restful. The use of both can give a sense of personality to a design, or utilized to create emphasis, rhythm, contrast, etc.[1] Light is an important factor for physical artwork, because it can affect how a surface is viewed. Strong lights on a smooth surface can obscure the readability of a drawing or photograph, whilst they can create strong contrasts in a highly texture surface such as moose or pigs. Visual Visual texture is the illusion of having physical texture. Every material and every support surface has its own visual texture and needs to be taken into consideration before creating a composition. As such, materials such as canvas and watercolour paper are considerably rougher than, for example, photo-quality computer paper and may not be best suited to creating a flat, smooth texture. Photography, drawings and paintings use visual texture both to portray their subject matter realistically and with interpretation. Texture in these media are generally created by the repetition of shape and line. Implied texture is a visual texture that has no basis in everyday reality.[2] It is most often utilized in works of abstraction. Examples of physical texture
Berlin Green Head, 500BC. Note the smooth texture and mood of the bust.
Animals are often defined by their physical texture, such as a fuzzy kitten or this scaly iguana.
Ralph's Diner, Ralph Goings, 1982. The actual physical texture of this painting is smooth, despite its visual textures.
Examples of visual texture
View From the Window at Le Gras, Nicphore Nipce, 1826. Photography.
Canticle, Mark Tobey, 1954. Note the sandy visual texture.
Cataract 3, Bridget Riley, 1967. Visual texture through repetition of line. Image texture An image texture is a set of metrics calculated in image processing designed to quantify the perceived texture of an image. Image Texture gives us information about the spatial arrangement of color or intensities in an image or selected region of an image.[1] Image textures can be artificially created or found in natural scenes captured in an image. Image textures are one way that can be used to help in Segmentation (image processing) or classification of images. To analyze an image texture in computer graphics, there are two ways to approach the issue: Structured Approach and Statistical Approach. Examples of materials, techniques and tools which can be used with acrylic paint in order to create different textures and surfaces: sugar, tea leaves, salt, pasta, egg shell, candle wax, rice, sand, sandpaper, crepe paper, sponges, sea salt, stenciling, masking tape, collage, clingfilm, drybrush, blotting, gloss and matte mediums, turpentine, plastic wrap, Japanese papers, waxed paper and tissue paper.
Texture Techniques
Several different plaster and texture techniques may be applied to a wall to give relief. Trowel on plaster by hand. Hold the sharp edge of the trowel against the wall at about a 30-degree angle. Move the plaster around the wall with the flat portion of the trowel. Texture may also be rolled on with a paint roller. You can use a large paint roller, but a 3-inch roller is easier to handle and will not feel as heavy once loaded with plaster. Randomly roll the plaster onto the wall. Leave as is, or then knock down the high areas of the plaster with a putty knife or use the trowel.
definition One important element in art is the texture (texture). Texture is something we can see, taste (with fingers) on a surface. For example, as the surface of cloth, rocks, plants and many more. There are two types of textures are 'optical' as seen and 'Tactical' texture that we can feel and touch. If we feel, the texture elements are actually very interesting if we look closely. Especially if we look at from various angles. -Texture or "texture" is one of the art of public significance. As we learned earlier, teksture also divided into two which is a flat (2D) or can be felt, touched, held, transported, etc. (3D). Purpose of the distribution is, we see it looks like there, but when held in fact a piece of paper for example. So only a mere illusion. For example, if you want to buy rubber mats - now come in many varieties. Some even spill each other really do not like the carpet just like when you hold it is only a mat only and you can not feel the thread as the actual carpet.
Вам также может понравиться
- Paintings of Bundelkhand: Some Remembered, Some Forgotten, Some not yet DiscoveredОт EverandPaintings of Bundelkhand: Some Remembered, Some Forgotten, Some not yet DiscoveredОценок пока нет
- sTEVE MccurryДокумент1 страницаsTEVE MccurryJuan Manuel LópezОценок пока нет
- Japanese Garden: Antariksh Agrawal Akash Paradkar Arti Kumari S.Sushrut Shivani Kumari Tara ChandДокумент34 страницыJapanese Garden: Antariksh Agrawal Akash Paradkar Arti Kumari S.Sushrut Shivani Kumari Tara ChandAbhishek AkodiyaОценок пока нет
- Steve MccurryДокумент22 страницыSteve Mccurryapi-525807581Оценок пока нет
- Lady MurasakiДокумент2 страницыLady Murasakidroyeskiivan100% (1)
- Stevemccurry 11Документ9 страницStevemccurry 11api-317091123Оценок пока нет
- Pune Historical MonumentsДокумент13 страницPune Historical Monumentsvaidehi vakilОценок пока нет
- Data Collection - AnthropometryДокумент5 страницData Collection - AnthropometryJudith John100% (1)
- New Stone Age: Neolithic, Also Called New Stone Age, Final Stage of Cultural Evolution orДокумент2 страницыNew Stone Age: Neolithic, Also Called New Stone Age, Final Stage of Cultural Evolution orDaniella GonzalesОценок пока нет
- Allen Solly 1Документ14 страницAllen Solly 1Rohit DhaulaОценок пока нет
- ART APPRECIATION WEEK 2 (Autosaved)Документ50 страницART APPRECIATION WEEK 2 (Autosaved)maria100% (1)
- Jataka Tales of The Buddha: Part III: Ken & Visaka KawasakiДокумент13 страницJataka Tales of The Buddha: Part III: Ken & Visaka KawasakitrungdaongoОценок пока нет
- Turko Mughal and Rajput Period (Ceramics)Документ5 страницTurko Mughal and Rajput Period (Ceramics)shubhangi gargОценок пока нет
- Roman ArtДокумент13 страницRoman ArtDwardita Heisulher100% (1)
- CHINESE Garden and LandscapeДокумент20 страницCHINESE Garden and Landscapenazia zamanОценок пока нет
- Jataka StoriesДокумент2 страницыJataka StoriesShivamОценок пока нет
- Unit-10 Evolution of Early Indian SocietyДокумент25 страницUnit-10 Evolution of Early Indian SocietySaurabh Singh100% (1)
- I P R XI: N Oseidons EichДокумент40 страницI P R XI: N Oseidons EichVladislav UlitinОценок пока нет
- Japanese GardenДокумент57 страницJapanese GardenVanshika DograОценок пока нет
- Astro Book 0 CourseДокумент9 страницAstro Book 0 CourseCMОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1: Prehistoric Art in EuropeДокумент32 страницыChapter 1: Prehistoric Art in Europesuresh sОценок пока нет
- ChineseДокумент17 страницChinesesubash saravananОценок пока нет
- Principle of IdДокумент51 страницаPrinciple of IdPreet100% (1)
- Northern Black Polished Ware in IndiaДокумент19 страницNorthern Black Polished Ware in IndiaMohit Sony100% (1)
- History of Alcohol in IndiaДокумент13 страницHistory of Alcohol in IndiaDaniyaal Ali100% (1)
- 10 MedievalДокумент55 страниц10 MedievalErika Mae LibangОценок пока нет
- Pyramids of Our DaysДокумент9 страницPyramids of Our Daysion durОценок пока нет
- Ancient Greek Pottery: Kevin J. BenoyДокумент30 страницAncient Greek Pottery: Kevin J. BenoyCraig MawsonОценок пока нет
- Renaissance Art - SchalkДокумент102 страницыRenaissance Art - SchalkschalkrvОценок пока нет
- Baroque ArtsДокумент19 страницBaroque ArtsMark Anthony Maquiling100% (1)
- Info Sheet PackagingДокумент16 страницInfo Sheet PackagingArman Santiago100% (1)
- Design TheoryДокумент2 страницыDesign Theoryhamidreza mohseniОценок пока нет
- EOD Class.Документ81 страницаEOD Class.agga11110% (1)
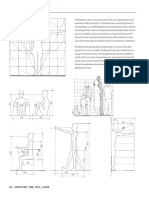
- AnthropometryДокумент4 страницыAnthropometryGeline EsguerraОценок пока нет
- AntrophometryДокумент11 страницAntrophometryCrystal Gaile Padrigao100% (1)
- Hand Made SoapДокумент12 страницHand Made SoapAstra Cloe100% (1)
- Interior Design: History of Furniture'Документ42 страницыInterior Design: History of Furniture'Maria SuhailОценок пока нет
- Is The Ashokan Brahmi Script Derived FroДокумент7 страницIs The Ashokan Brahmi Script Derived FroSubramanian Kannan100% (1)
- Pat Ta ChitraДокумент2 страницыPat Ta ChitraShivani SisodiaОценок пока нет
- Pattachitra WikipediaДокумент3 страницыPattachitra WikipediaxiaoboshiОценок пока нет
- Hoysala Soapstone CarvingДокумент11 страницHoysala Soapstone Carvingsorceress.rsОценок пока нет
- Archaeology Survey of IndiaДокумент6 страницArchaeology Survey of IndiamddhanaОценок пока нет
- Bhirrana To Mehrgarh and Beyond in The C PDFДокумент33 страницыBhirrana To Mehrgarh and Beyond in The C PDFundying100% (2)
- Khurja ReportДокумент18 страницKhurja ReportAayush_Verma_5419Оценок пока нет
- 11 Painting - Fundamentals of Visual Art - Notes and Video LinkДокумент4 страницы11 Painting - Fundamentals of Visual Art - Notes and Video LinksnehaОценок пока нет
- Simbologia en Los BodegonesДокумент4 страницыSimbologia en Los BodegonesEvanthia BinetzisОценок пока нет
- Leonardo Da VinciДокумент12 страницLeonardo Da Vincimuhammad shahadat awanОценок пока нет
- The 7 Principles of Art and DesignДокумент15 страницThe 7 Principles of Art and DesignJustinne CruzОценок пока нет
- 5 Chola DynastyДокумент4 страницы5 Chola DynastyShubham Raut100% (1)
- Art AppreciationДокумент43 страницыArt AppreciationMark Lawrence ReyesОценок пока нет
- The Study of Human MeasurementДокумент23 страницыThe Study of Human Measurementravinaj21Оценок пока нет
- Art App - Fundamentals of Art - Lesson 1Документ50 страницArt App - Fundamentals of Art - Lesson 1William Hallare100% (1)
- No Sanskrit, Hindi, Marathi, Telugu, Gujarati Malayalam TamilДокумент4 страницыNo Sanskrit, Hindi, Marathi, Telugu, Gujarati Malayalam TamilSup_Rao100% (1)
- Renaissance IntroductionДокумент29 страницRenaissance IntroductionMark De GuzmanОценок пока нет
- An Introduction To Indian Art Part IДокумент146 страницAn Introduction To Indian Art Part Isgangwar2005sg100% (3)
- What Is PatternДокумент3 страницыWhat Is PatternIriniОценок пока нет
- Navamsa A Ready ReckonerДокумент4 страницыNavamsa A Ready ReckonerMukesh Bhambhani100% (1)
- Ancient Greece History of HairstylingДокумент2 страницыAncient Greece History of HairstylingMichelleDeGuzman-RunatayОценок пока нет
- Principles of Texture (Visual Art)Документ23 страницыPrinciples of Texture (Visual Art)Arthur PoitrОценок пока нет
- Elementofdesign Texture 130302192544 Phpapp01Документ15 страницElementofdesign Texture 130302192544 Phpapp01NainaОценок пока нет
- Date Name Company WebsiteДокумент10 страницDate Name Company WebsiteJennifer JОценок пока нет
- Furniture Styles: By: Myeisha FoleyДокумент12 страницFurniture Styles: By: Myeisha FoleyAdina BadeaОценок пока нет
- Advanced Photoshop Issue 030Документ83 страницыAdvanced Photoshop Issue 030Dipesh BardoliaОценок пока нет
- Van Der Merwe, LucindaДокумент68 страницVan Der Merwe, LucindaDivyRaj SinghОценок пока нет
- Illustrate With Photoshop Genius Guide Vol. 2Документ180 страницIllustrate With Photoshop Genius Guide Vol. 2Siniša Teofilović100% (6)
- Asian Modernities Appendices John Clark September 2010Документ397 страницAsian Modernities Appendices John Clark September 2010เดินสาย เอกОценок пока нет
- East Asian Art: Quarter 2 - Module 1Документ33 страницыEast Asian Art: Quarter 2 - Module 1SHEILA MAE PERTIMOS50% (2)
- Arvil Group-RevitДокумент6 страницArvil Group-Revitamrabdelazzem3Оценок пока нет
- CV Michelle Gratacós ArillДокумент4 страницыCV Michelle Gratacós ArillMichelle Gratacós-ArillОценок пока нет
- RPH - Spoliarium RiksДокумент4 страницыRPH - Spoliarium RiksMaria Rixa Joyce AtienzaОценок пока нет
- Superhero ProjectДокумент24 страницыSuperhero Projectapi-423105147Оценок пока нет
- Sculptures From The Early AgeДокумент31 страницаSculptures From The Early AgeROXANNE APOSTOLОценок пока нет
- Acting Out: Claude Cahun and Marcel Moore Exhibition, April-July 2005. ChronologyДокумент2 страницыActing Out: Claude Cahun and Marcel Moore Exhibition, April-July 2005. ChronologymagnesmuseumОценок пока нет
- Curriculum Map Mapeh ArtsДокумент8 страницCurriculum Map Mapeh ArtsMaenard TambauanОценок пока нет
- Expressionism 1900 1955Документ60 страницExpressionism 1900 1955enistenebim100% (3)
- Stage Design ProcessДокумент36 страницStage Design ProcessGaurav AgrawalОценок пока нет
- Plein Air Painting: With WatercolorДокумент40 страницPlein Air Painting: With WatercolorAlison De Sando Manzoni100% (1)
- De Stijl Modernism in The Netherlands Van DusburgДокумент37 страницDe Stijl Modernism in The Netherlands Van DusburgЕмануела НачевскаОценок пока нет
- The International StyleДокумент11 страницThe International StyleGeetakshri Jajoria100% (1)
- Teaching Arts in The Elementary Grades: OgdimalantaДокумент8 страницTeaching Arts in The Elementary Grades: OgdimalantaDiana Rose SimbulanОценок пока нет
- Mapeh Arts GR 6 Week 3 4Документ43 страницыMapeh Arts GR 6 Week 3 4Katrina SalasОценок пока нет
- Methodology For Painting WorksДокумент4 страницыMethodology For Painting Worksᜇᜒᜌᜓᜈᜎ᜔ᜇ᜔ ᜊᜒᜇᜓᜌ᜔Оценок пока нет
- GAS Journ14 Web2Документ126 страницGAS Journ14 Web2first lastОценок пока нет
- Asian PaintsДокумент8 страницAsian Paintspragyaa4Оценок пока нет
- Different Art TechniquesДокумент39 страницDifferent Art TechniquesRommel LegaspiОценок пока нет
- Ansel Adams: The American Landscape Through The Lens ofДокумент5 страницAnsel Adams: The American Landscape Through The Lens ofkalendersayaОценок пока нет
- Picture StorybooksДокумент122 страницыPicture StorybooksCeleste Atienza Bawag100% (1)
- Instapdf - in Asian Paints Colour Shade Card 334Документ10 страницInstapdf - in Asian Paints Colour Shade Card 334IamDeathОценок пока нет
- Expressionism Is Very Different From Impressionism: Edvard Munch: The Scream (1893)Документ14 страницExpressionism Is Very Different From Impressionism: Edvard Munch: The Scream (1893)nirvaangОценок пока нет
- The Simultaneity of Robert Delaunay's First DiskДокумент28 страницThe Simultaneity of Robert Delaunay's First DiskIsai Abacuc GómezОценок пока нет
- Drawing and Sketching Portraits: How to Draw Realistic Faces for BeginnersОт EverandDrawing and Sketching Portraits: How to Draw Realistic Faces for BeginnersРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- Beginner's Guide To Procreate: Characters: How to create characters on an iPad ®От EverandBeginner's Guide To Procreate: Characters: How to create characters on an iPad ®3dtotal PublishingРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Swatch This, 3000+ Color Palettes for Success: Perfect for Artists, Designers, MakersОт EverandSwatch This, 3000+ Color Palettes for Success: Perfect for Artists, Designers, MakersРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (3)
- Creative Abstract Watercolor: The beginner's guide to expressive and imaginative paintingОт EverandCreative Abstract Watercolor: The beginner's guide to expressive and imaginative paintingРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)
- Fundamentals of Character Design: How to Create Engaging Characters for Illustration, Animation & Visual DevelopmentОт EverandFundamentals of Character Design: How to Create Engaging Characters for Illustration, Animation & Visual Development3dtotal PublishingРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- The Lost Art of Handwriting: Rediscover the Beauty and Power of PenmanshipОт EverandThe Lost Art of Handwriting: Rediscover the Beauty and Power of PenmanshipРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (14)
- Crochet with London Kaye: Projects and Ideas to Yarn Bomb Your LifeОт EverandCrochet with London Kaye: Projects and Ideas to Yarn Bomb Your LifeРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- Art Models Jesse222: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceОт EverandArt Models Jesse222: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (3)
- Designa: Technical Secrets of the Traditional Visual ArtsОт EverandDesigna: Technical Secrets of the Traditional Visual ArtsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- The Kew Gardens Botanical Artist: Learn to Draw and Paint Flowers in the Style of Pierre-Joseph RedoutéОт EverandThe Kew Gardens Botanical Artist: Learn to Draw and Paint Flowers in the Style of Pierre-Joseph RedoutéОценок пока нет
- Watercolor For The Soul: Simple painting projects for beginners, to calm, soothe and inspireОт EverandWatercolor For The Soul: Simple painting projects for beginners, to calm, soothe and inspireРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (6)
- Art Models SarahAnn031: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceОт EverandArt Models SarahAnn031: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (4)
- Art Models Sam074: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceОт EverandArt Models Sam074: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Art Models Adrina032: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceОт EverandArt Models Adrina032: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- Art Models KatarinaK034: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceОт EverandArt Models KatarinaK034: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (3)
- Ernst Haeckel's Art Forms in Nature: A Visual Masterpiece of the Natural WorldОт EverandErnst Haeckel's Art Forms in Nature: A Visual Masterpiece of the Natural WorldОценок пока нет
- Art Models AnaIv309: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceОт EverandArt Models AnaIv309: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (2)
- Just Draw Botanicals: Beautiful Botanical Art, Contemporary Artists, Modern MaterialsОт EverandJust Draw Botanicals: Beautiful Botanical Art, Contemporary Artists, Modern MaterialsРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (3)
- One Zentangle a Day: A 6-Week Course in Creative Drawing for Relaxation, Inspiration, and FunОт EverandOne Zentangle a Day: A 6-Week Course in Creative Drawing for Relaxation, Inspiration, and FunРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (25)
- Sketch-A-Day Drawing Challenge 2020: 365 pages of Drawing Prompts to inspire Artists, and Incite the imaginationОт EverandSketch-A-Day Drawing Challenge 2020: 365 pages of Drawing Prompts to inspire Artists, and Incite the imaginationРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)