Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Waves
Загружено:
Mark ProchaskaИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Waves
Загружено:
Mark ProchaskaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
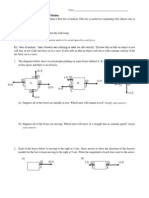
Physics POGIL: Waves When oscillators, be they pendulums, masses vibrating on springs, or electrons in an atom, are linked together,
the motion of one affects the motions of the others. We say that the oscillators are coupled. When this is the case, we often see a repeated pattern that moves through the oscillators. We call this pattern a wave. Waves permit us to transmit oscillations over large distances and obtain information about objects that we cannot reach otherwise. Transverse Waves The picture below shows some transverse waves on a slinky and some of the terms we use to describe them.
amplitude
crest
wavelength
trough
The waves are initiated by the hand shown and travel to the right. You can use a slinky to see these waves in action. Shown below are some additional terms we use to describe transverse waves. frequency: the number of waves that pass by a point per unit of time period: the time it takes for one wave to pass by a point wave speed: how fast the wave moves, measured by a distance per unit of time.
1. Describe, in words, the following terms as they apply to transverse waves. (a) crest
(b) trough
(c) wavelength
2. Study the picture of the transverse wave below, traveling to the right. An observer notes that 5 waves pass by the point P in 10 s.
4m
3m
Physics (a) What is the amplitude of the wave?
(b) What is the wavelength of the wave?
(c) What is the frequency of the wave?
(d) What is the period of the wave?
(e) How far does the wave travel during the time you found in (d)?
(f) What is the speed of the wave?
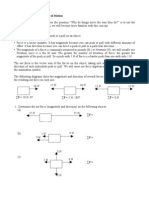
Longitudinal Waves The picture below shows some longitudinal waves on a slinky and some of the terms we use to describe them.
compression
rarefaction
wavelength
The waves are initiated by the hand shown and travel to the right. You can use a slinky to see these waves in action. Most of the terms we use to describe transverse waves, such as frequency, period, and amplitude, apply to longitudinal waves as well. 3. Describe, in words, the following terms as they apply to longitudinal waves. (a) compressions
(b) rarefactions
(c) wavelength
4. Compare and contrast transverse and longitudinal waves. (a) What do they have in common?
Physics (b) What is different about them?
5. Study the picture of the longitudinal wave below. As it is travels to the right, an observer notes that it takes 0.4 s for one wave to pass by point P.
1.5 m
P
(a) What is the wavelength of the wave?
(b) What is the frequency of the wave?
(c) What is the period of the wave?
(d) How far does the wave travel during one period?
(e) What is the speed of the wave?
Problem Solving 6. On the shores of Lake Maxinkuckee, 12 waves roll in to shore in 20 seconds. The distance between successive wave crests is 2 m. (a) In the space below, draw a picture of the waves and label the crests, troughs, and wavelength.
Physics (b) Is this a transverse or longitudinal wave?
(c) What is the wavelength of the waves?
(d) What is the frequency of the waves?
(e) What is the period of the waves?
(f) How far do the waves travel in 20 s?
(g) What is the speed of the waves?
(h) How far do the waves travel in: i. one minute?
ii.
two minutes?
iii.
five minutes?
Вам также может понравиться
- WavesДокумент4 страницыWavesMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- Wave C11Документ8 страницWave C11Wajira Sanjaya PereraОценок пока нет
- Waves: Presented By: Ms. Evalyn Suyat-CapindingДокумент72 страницыWaves: Presented By: Ms. Evalyn Suyat-CapindingKristina C IbonОценок пока нет
- Wavelength and How It Compares To A SlinkyДокумент3 страницыWavelength and How It Compares To A Slinkyapi-262586446100% (1)
- Tutorial 5 Projectile Motion Circular MotionДокумент2 страницыTutorial 5 Projectile Motion Circular Motionapi-3827354100% (4)
- Work and PowerДокумент3 страницыWork and PowerMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- Wave ActionsДокумент2 страницыWave Actionsapi-263830904Оценок пока нет
- POGIL - Universal Gravitation ANWERSДокумент3 страницыPOGIL - Universal Gravitation ANWERSSharmet SolarzОценок пока нет
- Newton's Third LawДокумент3 страницыNewton's Third LawMark Prochaska100% (1)
- Lesson10 Universal Wave Equation WorksheetДокумент2 страницыLesson10 Universal Wave Equation WorksheetJep Val0% (1)
- IB PHYSICS HL MULTIPLE CHOICE REVIEW ON WAVES & VIBRATIONSДокумент20 страницIB PHYSICS HL MULTIPLE CHOICE REVIEW ON WAVES & VIBRATIONSshammi nathanОценок пока нет
- Newton's Second LawДокумент5 страницNewton's Second LawMark Prochaska100% (1)
- Speed and VelocityДокумент4 страницыSpeed and VelocityMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- WavesДокумент4 страницыWavesusman3686Оценок пока нет
- Position, Displacement, VelocityДокумент3 страницыPosition, Displacement, VelocityMark Prochaska0% (1)
- Relativistic EnergyДокумент4 страницыRelativistic EnergyMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- 4.1 Conceptual Questions: Chapter 4 Dynamics: Newton's Laws of MotionДокумент18 страниц4.1 Conceptual Questions: Chapter 4 Dynamics: Newton's Laws of MotionnourОценок пока нет
- Velocity Acceleration Lab PDFДокумент6 страницVelocity Acceleration Lab PDFUltramixОценок пока нет
- Seismic Waves-2Документ3 страницыSeismic Waves-2api-251874912Оценок пока нет
- GB Atoms Pogil 2014-2015Документ2 страницыGB Atoms Pogil 2014-2015api-261277442Оценок пока нет
- Ionic Bonding WorksheetДокумент2 страницыIonic Bonding WorksheetAnbiya FathimaОценок пока нет
- Science Worksheet Grade7 Q3Документ9 страницScience Worksheet Grade7 Q3Evelyn Apostol100% (1)
- Lesson plan on waves in physicsДокумент7 страницLesson plan on waves in physicsAly SobosoboОценок пока нет
- Working and PowerДокумент4 страницыWorking and PowerMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- Atomic Structure PowerpointДокумент13 страницAtomic Structure PowerpointMary TaklaОценок пока нет
- General Physics 1 q1 Week 3Документ24 страницыGeneral Physics 1 q1 Week 3Chool Cydrick B. BascosОценок пока нет
- Temperature, Thermal Energy, and HeatingДокумент3 страницыTemperature, Thermal Energy, and HeatingMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- Examview Waves and Sound Practice Test4Документ9 страницExamview Waves and Sound Practice Test4Tajay Billings100% (1)
- Light Notes 1Документ31 страницаLight Notes 1api-233194737Оценок пока нет
- Newton's First LawДокумент3 страницыNewton's First LawMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- EnergyДокумент3 страницыEnergyMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- Voltage and ResistanceДокумент4 страницыVoltage and ResistanceMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- Waves Chapter 1 Form 5Документ33 страницыWaves Chapter 1 Form 5Nurul SyahirahОценок пока нет
- q3 Module 2 Waves Around You PDFДокумент18 страницq3 Module 2 Waves Around You PDFRoman Andrew ManaliliОценок пока нет
- CP Spring Scale POGIL 2012 2013Документ4 страницыCP Spring Scale POGIL 2012 2013Anthony ButlerОценок пока нет
- 8.5 Final Review Key PDFДокумент4 страницы8.5 Final Review Key PDFAlex VongОценок пока нет
- 101science WavelengthДокумент53 страницы101science Wavelengthnm9536766Оценок пока нет
- Work Power EnergyДокумент28 страницWork Power Energymarife gupaalОценок пока нет
- Sound WavesДокумент91 страницаSound WavesSarah Mae Lequin ManzanasОценок пока нет
- Long Quiz Physics 1 Newton Laws of MotionДокумент1 страницаLong Quiz Physics 1 Newton Laws of MotionK-Cube MorongОценок пока нет
- 01 Static ElectricityДокумент31 страница01 Static ElectricitySkyZz CSGOОценок пока нет
- Quarter 1: Week 4.2: LightsДокумент2 страницыQuarter 1: Week 4.2: LightsLougene Castro100% (1)
- Slinky Wave LabДокумент5 страницSlinky Wave Labapi-2847529120% (2)
- CIRCULAR MOTION JEE PracticeДокумент21 страницаCIRCULAR MOTION JEE PracticeDev PatelОценок пока нет
- Power, Work and Force IIДокумент4 страницыPower, Work and Force IIchpwalkerОценок пока нет
- Unit: FORCES Law of Universal Gravitation: Variables WorkДокумент4 страницыUnit: FORCES Law of Universal Gravitation: Variables WorkeenamorataОценок пока нет
- Ch 15: Wave Properties and BehaviorДокумент26 страницCh 15: Wave Properties and BehaviorAhmed El-Lithi100% (1)
- Waves and CurrentsДокумент1 страницаWaves and Currentsapi-254428474100% (1)
- Em SpectrumДокумент3 страницыEm SpectrumMark Prochaska100% (1)
- Electric PowerДокумент4 страницыElectric PowerMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- Scalars and Vector DiscoveryДокумент3 страницыScalars and Vector DiscoveryBen Sirolly100% (1)
- POGIL - Heat Transfer ModesДокумент4 страницыPOGIL - Heat Transfer ModesDon SekarОценок пока нет
- Distance and DisplacementДокумент5 страницDistance and DisplacementzandejuanicaОценок пока нет
- Heating and Phase ChangesДокумент4 страницыHeating and Phase ChangesMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- Temperature and HeatingДокумент4 страницыTemperature and HeatingMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- Sound PDFДокумент4 страницыSound PDFB.VОценок пока нет
- Electric ForceДокумент4 страницыElectric ForceMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- Waves Quarter 3 Week 4Документ6 страницWaves Quarter 3 Week 4marieleempuriheheОценок пока нет
- Properties of WavesДокумент4 страницыProperties of WavesrohmawatiОценок пока нет
- WavesДокумент31 страницаWavesShauna Prettygyol HamilОценок пока нет
- Time DilationДокумент3 страницыTime DilationMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- Mass Defect and Binding EnergyДокумент3 страницыMass Defect and Binding EnergyMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- Work and PowerДокумент3 страницыWork and PowerMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- Voltage and ResistanceДокумент4 страницыVoltage and ResistanceMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- POGIL: Length ContractionДокумент3 страницыPOGIL: Length ContractionMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- VectorsДокумент2 страницыVectorsMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- Nuclear Fission and FusionДокумент4 страницыNuclear Fission and FusionMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- Relativistic EnergyДокумент4 страницыRelativistic EnergyMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- Position, Displacement, VelocityДокумент3 страницыPosition, Displacement, VelocityMark Prochaska0% (1)
- Vector ComponentsДокумент4 страницыVector ComponentsMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- Newton's Second LawДокумент3 страницыNewton's Second LawMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- Free Body DiagramsДокумент4 страницыFree Body DiagramsMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- Newton's Third LawДокумент3 страницыNewton's Third LawMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- Newton's First LawДокумент3 страницыNewton's First LawMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- Motion in Two Dimensions 2Документ3 страницыMotion in Two Dimensions 2Mark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- Motion in Two Dimensions 1Документ4 страницыMotion in Two Dimensions 1Mark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- Electric ForcesДокумент4 страницыElectric ForcesMark Prochaska100% (1)
- EnergyДокумент3 страницыEnergyMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- Electric PowerДокумент4 страницыElectric PowerMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- Electric CurrentДокумент2 страницыElectric CurrentMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- Magnetic ForcesДокумент3 страницыMagnetic ForcesMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic InductionДокумент4 страницыElectromagnetic InductionMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- Atomic NucleiДокумент4 страницыAtomic NucleiMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- AccelerationДокумент2 страницыAccelerationMark Prochaska0% (1)
- Working and PowerДокумент4 страницыWorking and PowerMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- Work and PowerДокумент4 страницыWork and PowerMark Prochaska100% (1)
- VelocityДокумент4 страницыVelocityMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- Temperature and HeatingДокумент4 страницыTemperature and HeatingMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- Universal GravitationДокумент3 страницыUniversal GravitationMark ProchaskaОценок пока нет
- States of Matter Questions For Test PaperДокумент5 страницStates of Matter Questions For Test PaperNevin ShajiОценок пока нет
- Lecture Notes in Statistical Mechanics and Mesoscopics: Doron CohenДокумент139 страницLecture Notes in Statistical Mechanics and Mesoscopics: Doron CohenMiguel AngelОценок пока нет
- Marcos Rosenbaum, Michael P. Ryan, Jr. and Sukanya Sinha - A Nonlinear Model of A Quantum Minisuperspace System With Back ReactionДокумент29 страницMarcos Rosenbaum, Michael P. Ryan, Jr. and Sukanya Sinha - A Nonlinear Model of A Quantum Minisuperspace System With Back ReactionMremefОценок пока нет
- (Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering 292) Jacob Scharcanski, Hugo Proenà A, Eliza Du (Eds.) - Signal and Image Processing For BiometricsДокумент336 страниц(Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering 292) Jacob Scharcanski, Hugo Proenà A, Eliza Du (Eds.) - Signal and Image Processing For Biometricsjosefiel29Оценок пока нет
- Exercise 2 For Solution ThermodynamicsДокумент4 страницыExercise 2 For Solution ThermodynamicsShane MillenaОценок пока нет
- Behaviour of Gases - PDFДокумент7 страницBehaviour of Gases - PDFNasih AhmadОценок пока нет
- Revision Phase EquilibriumДокумент19 страницRevision Phase EquilibriumJeshurun DavidОценок пока нет
- CH 02Документ6 страницCH 02Janmejay GoenkaОценок пока нет
- NCS21 - 03 - Describing Function Analysis - 01Документ10 страницNCS21 - 03 - Describing Function Analysis - 01zain khuramОценок пока нет
- Iso Plate Bending StiffnessДокумент29 страницIso Plate Bending StiffnesslapuОценок пока нет
- STEAM TABLE FORMULATION AND VERIFICATIONДокумент8 страницSTEAM TABLE FORMULATION AND VERIFICATIONcemal gümrükçüoğluОценок пока нет
- 07 DifferentiationДокумент47 страниц07 DifferentiationryanphillbsОценок пока нет
- Gas Phase Fugacity Coefficient CalculationsДокумент15 страницGas Phase Fugacity Coefficient CalculationsayushОценок пока нет
- E106 - AgustinДокумент20 страницE106 - AgustinSeth Jarl G. AgustinОценок пока нет
- Heat Transfer: The Conduction Rate EquationДокумент6 страницHeat Transfer: The Conduction Rate EquationOmer Ghassan Abdulkareem Hassan AlsultanОценок пока нет
- SET 3 MODUL CEMERLANG FIZIK F4B4 2018 Skema PDFДокумент15 страницSET 3 MODUL CEMERLANG FIZIK F4B4 2018 Skema PDFCooKiEs YuMmyОценок пока нет
- Chaos in Delay Differential Equations WithДокумент13 страницChaos in Delay Differential Equations WithMDARQUAMОценок пока нет
- 04 Frequency Domain Analysis of Continuous Time Signals and SystemsДокумент51 страница04 Frequency Domain Analysis of Continuous Time Signals and SystemsHanan ShayiboОценок пока нет
- 2016-2-Joh-Batu Pahat-AДокумент9 страниц2016-2-Joh-Batu Pahat-ANur B TapriОценок пока нет
- Math 2004 NotesДокумент79 страницMath 2004 NotesAliОценок пока нет
- Lesson 6 MatricesДокумент4 страницыLesson 6 MatricesAbdihakim MohamedОценок пока нет
- Medio Continuo 6Документ210 страницMedio Continuo 6Alexander Humpire ColquehuancaОценок пока нет
- Photoelectric EffectДокумент3 страницыPhotoelectric EffectBIALIGYОценок пока нет
- Chapter Four Forced Convection: Parallel Flow Over Flat PlatesДокумент6 страницChapter Four Forced Convection: Parallel Flow Over Flat PlatesprasanthiОценок пока нет
- 6-4-Partial Fugacity in Liquid MixturesДокумент8 страниц6-4-Partial Fugacity in Liquid MixturesIkОценок пока нет
- Sol T4Документ7 страницSol T4Sohini RoyОценок пока нет
- MATH136: Linear Algebra 1 Written Assignment 3 Solutions Winter 2023Документ8 страницMATH136: Linear Algebra 1 Written Assignment 3 Solutions Winter 2023yasin pakzatОценок пока нет
- 2.3 Properties of Determinants CramersДокумент4 страницы2.3 Properties of Determinants CramersChloeОценок пока нет
- Finite Element Modeling of Vibration of BarsДокумент32 страницыFinite Element Modeling of Vibration of BarsrasoolОценок пока нет
- 809 Books Doubtnut Question BankДокумент256 страниц809 Books Doubtnut Question BankgurujalamaheshwariОценок пока нет
- Quantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishОт EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (18)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessОт EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (6)
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsОт EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldОт EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (8)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingОт EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismОт EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (500)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterОт EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (409)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesОт EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (2193)
- The Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceОт EverandThe Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (23)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidОт EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1395)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)От EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (155)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceОт EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayОт EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (125)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowОт EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (48)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeОт EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeОценок пока нет
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsОт EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (94)
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityОт EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (75)
- What is Life?: With Mind and Matter and Autobiographical SketchesОт EverandWhat is Life?: With Mind and Matter and Autobiographical SketchesРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (139)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldОт EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (60)
- Starry Messenger: Cosmic Perspectives on CivilizationОт EverandStarry Messenger: Cosmic Perspectives on CivilizationРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (158)
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseОт EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (13)
- The Sounds of Life: How Digital Technology Is Bringing Us Closer to the Worlds of Animals and PlantsОт EverandThe Sounds of Life: How Digital Technology Is Bringing Us Closer to the Worlds of Animals and PlantsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldОт EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (53)