Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Vital Signs Terms
Загружено:
Mix AmericaИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Vital Signs Terms
Загружено:
Mix AmericaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Apnea - Absence of breathing. Arrhythmia - Loss or abnormality of rhythm, denoting especially an irregularity of the heartbeat.
Axilla - (or armpit, underarm, or oxter) is the area on the human body directly under the joint where the arm connects to the shoulder. BMR Basal Metabolic Rate is the rate of energy utilization in the body required to maintain essential activities such as breathing. Bradycardia Slow heart rate Bradypnea - refers to an abnormally slow breathing rate. Centigrade (Celsius) - is a scale and unit of measurement for temperature. Cyanosis - is the appearance of a blue or purple coloration of the skin or mucous membranes due to the tissues near the skin surface being low on oxygen Diaphoresis - is excessive sweating commonly associated with shock and other medical emergency conditions. Dyspnea Shortness of breath. Eupnea is normal, good, unlabored ventilation, sometimes known as quiet breathing or resting respiration. Evaporation is a type of vaporization of a liquid that occurs only on the surface of a liquid. The other type of vaporization is boiling, which, instead, occurs on the entire mass of the liquid. Exhalation (or expiration) is the movement of air out of the bronchial tubes, through the airways, to the external environment during breathing. Fahrenheit is the temperature scale proposed in 1724 by, and named after, the Dutch-German-Polish physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit Febrile - having or showing the symptoms of a fever. Hyperpyrexia Abnormally high fever. Hypothermia is a condition in which core temperature drops below the required temperature for normal metabolism and body functions which is defined as 35.0 C (95.0 F).
Inhalation (also known as inspiration) is the movement of air from the external environment, through the air ways, and into the alveoli. Oral by mouth Orthopnea is shortness of breath (dyspnea) which occurs when lying flat,[1] causing the person to have to sleep propped up in bed or sitting in a chair. It is the opposite of platypnea. Pulse represents the tactile arterial palpation of the heartbeat by trained fingertips. Pulse pressure is most easily defined as being the amount of pressure required to create the feeling of a pulse. Pulse rate a person's heart rate as it is felt in various places throughout the body. Pyrexia (also known as fever or controlled hyperthermia[1]) is a common medical sign characterized by an elevation of temperature above the normal range of 36.537.5 C (98100 F) due to an increase in the body temperature regulatory set-point. Respiration the act of breathing. Rhythm refers to the regularity. Stethoscope is an acoustic medical device for auscultation, or listening to the internal sounds of an animal body. Stridor is a high pitched wheezing sound resulting from turbulent air flow in the upper airway. Stridor is a physical sign which is produced by narrow or obstructed airway path. Systolic pressure The blood pressure when the heart is contracting. It is specifically the maximum arterial pressure during contraction of the left ventricle of the heart Tachycardia omes from the Greek words tachys (rapid or accelerated) and kardia (of the heart). Tachycardia typically refers to a heart rate that exceeds the normal range for a resting heart rate (heart rate in an inactive or sleeping individual). It can be dangerous depending on the speed and type of rhythm.
Tachypnea - (or "tachypnoea") (Greek: "rapid breathing") means rapid breathing. Any rate between 12-20 breaths per minute is normal. Tachypnea is a respiration rate greater than 20 breaths per minute. Thermometer is a device that measures temperature or temperature gradient using a variety of different principles. Wheezing (formally called "sibilant rhonchi" in medical terminology) is a continuous, coarse, whistling sound produced in the respiratory airways during breathing.
Вам также может понравиться
- DefinitionДокумент1 страницаDefinitionAnonymous IXBLDPrОценок пока нет
- NCM 101 Vital Signs PPT BSN 1a Group 1Документ138 страницNCM 101 Vital Signs PPT BSN 1a Group 1Brian Anthony100% (1)
- vital signsДокумент29 страницvital signsGLAIZA PALATINOОценок пока нет
- BHC RevДокумент14 страницBHC RevShaine CababatОценок пока нет
- Abnormalities of Vital SignsДокумент3 страницыAbnormalities of Vital SignsAbigail BascoОценок пока нет
- Vital Signs BrochureДокумент6 страницVital Signs Brochureapi-527956594Оценок пока нет
- Medterm July 20Документ11 страницMedterm July 20sandra seguienteОценок пока нет
- Publication 2Документ2 страницыPublication 2api-527903914Оценок пока нет
- Vitalsignslecturenewbatch 160211000037Документ8 страницVitalsignslecturenewbatch 160211000037faityneoОценок пока нет
- Vital Signs: Body Temperature, Pulse, Respiration & Blood PressureДокумент10 страницVital Signs: Body Temperature, Pulse, Respiration & Blood PressureEdelou Alegria JumawanОценок пока нет
- Vital Signs: Understanding Body Temperature, Pulse, Respiration Rate & Blood PressureДокумент69 страницVital Signs: Understanding Body Temperature, Pulse, Respiration Rate & Blood PressureSamantha SunglaoОценок пока нет
- Vital Signs Guide for Detecting Medical ProblemsДокумент3 страницыVital Signs Guide for Detecting Medical ProblemsNicole NipasОценок пока нет
- Vital Signs: Carol Mitchell, RN, MSNДокумент56 страницVital Signs: Carol Mitchell, RN, MSNokaciaОценок пока нет
- Shortness of Breath: ER Perspective Shaesta TabassumДокумент46 страницShortness of Breath: ER Perspective Shaesta TabassumAjay DherwaniОценок пока нет
- Terminologies FNДокумент3 страницыTerminologies FNMonaОценок пока нет
- Vital Signs and Oxygen AdministrationДокумент11 страницVital Signs and Oxygen AdministrationCrisha Shane BoticarioОценок пока нет
- Hyperventilation Syndrome: Dr. Shahbaz Ahmad PTДокумент19 страницHyperventilation Syndrome: Dr. Shahbaz Ahmad PTMuhammadОценок пока нет
- The Vital SignsДокумент5 страницThe Vital SignsKhalid EppingОценок пока нет
- Assignment 1Документ2 страницыAssignment 1Pam ArienzaОценок пока нет
- Signos VitalesДокумент5 страницSignos VitalesAndrea Correa OrtegaОценок пока нет
- HEALTH ASSESSMENT (Week 4)Документ8 страницHEALTH ASSESSMENT (Week 4)CHELSEA MAE SAULOОценок пока нет
- Question 2 FundamentalsДокумент7 страницQuestion 2 FundamentalsJess Fernandez BorgaОценок пока нет
- Vital Sign 1Документ34 страницыVital Sign 1wowila6489Оценок пока нет
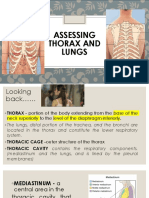
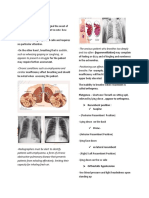
- ASSESSING THORAX and LUNGSДокумент25 страницASSESSING THORAX and LUNGSPrincess AñabezaОценок пока нет
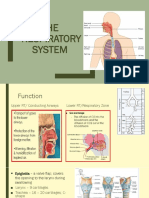
- RespirationДокумент29 страницRespirationbemina jaОценок пока нет
- Advanced Resuscitation TechniquesДокумент20 страницAdvanced Resuscitation TechniquesCharlieFAY100% (1)
- Thorax and Lung - LectureДокумент60 страницThorax and Lung - LectureТаншолпан ШохбутоваОценок пока нет
- Respiratory System Assessment: Other SystemsДокумент4 страницыRespiratory System Assessment: Other SystemsChetan KumarОценок пока нет
- Platypnea - Shortness F Breath On Sitting Up0Документ4 страницыPlatypnea - Shortness F Breath On Sitting Up0Charie MaeОценок пока нет
- Assessment of Vital SignsДокумент7 страницAssessment of Vital SignsFloriza de LeonОценок пока нет
- Lung ExaminationДокумент14 страницLung Examinationსალომე მუმლაძე “Slay” TMAОценок пока нет
- Vital Signs: (Temperature)Документ43 страницыVital Signs: (Temperature)Aehra Josh PascualОценок пока нет
- Circulatory System AssessmentДокумент7 страницCirculatory System AssessmentGeraldine EslavaОценок пока нет
- Risk Factors and Signs of Pulmonary DiseaseДокумент3 страницыRisk Factors and Signs of Pulmonary DiseaseAnonymous b4P7PDОценок пока нет
- 6 Vital Signs 1Документ78 страниц6 Vital Signs 1Arissa Jamelia Lofranco AldeanoОценок пока нет
- Collapsed LungsДокумент3 страницыCollapsed LungsJayson MontemayorОценок пока нет
- Physical Diagnoses: Respiratory SystemДокумент72 страницыPhysical Diagnoses: Respiratory SystemAmanuel MaruОценок пока нет
- Module 2 Full SlidesДокумент69 страницModule 2 Full SlidesMaria Du-PastoralОценок пока нет
- Dart Bls CPR With Aed 2018 1Документ33 страницыDart Bls CPR With Aed 2018 1NivekОценок пока нет
- Final Death Note - Compre NotesДокумент1 550 страницFinal Death Note - Compre NotesSteph TabasaОценок пока нет
- Medical Terminology - Sheet1Документ3 страницыMedical Terminology - Sheet1Connor McNamaraОценок пока нет
- Nursing Skills (Vital Signs) PDFДокумент48 страницNursing Skills (Vital Signs) PDFkhizer hayatОценок пока нет
- Basic Clinical SkillsДокумент6 страницBasic Clinical SkillsBlake KamminОценок пока нет
- Kuliah Pengantar PF ParuДокумент62 страницыKuliah Pengantar PF Parugagah152Оценок пока нет
- Vital-Signs (Quiz Nalang Kulang)Документ51 страницаVital-Signs (Quiz Nalang Kulang)Hannah TollenoОценок пока нет
- Respiratory ExamДокумент9 страницRespiratory Examjoelh9Оценок пока нет
- Vital Signs PDFДокумент69 страницVital Signs PDFrenz bartolomeОценок пока нет
- Unit Human Respiratory & Circulatory System Class NotesДокумент4 страницыUnit Human Respiratory & Circulatory System Class NotesAiza SulemanОценок пока нет
- Module 7-11 The Respiratory SystemДокумент52 страницыModule 7-11 The Respiratory SystemAlfred James SorianoОценок пока нет
- PND Exposicion EnglishДокумент3 страницыPND Exposicion EnglishEmanuelMCОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular Physical Examination GuideДокумент59 страницCardiovascular Physical Examination GuideSheila Jessica AndavaniaОценок пока нет
- Review NotesДокумент9 страницReview NotesKhaskie Geneva DumaguinОценок пока нет
- Assessment of Respiratory System: Group 3Документ33 страницыAssessment of Respiratory System: Group 3ChicieMonalisaОценок пока нет
- DR Amsalu Bekele Ass - Professor of Medicine Head of Chest Unit Department of Internal Medicine Addis Ababa University, School of Medicine Addis Ababa, EthiopiaДокумент81 страницаDR Amsalu Bekele Ass - Professor of Medicine Head of Chest Unit Department of Internal Medicine Addis Ababa University, School of Medicine Addis Ababa, EthiopiaBethelhem BirhanuОценок пока нет
- Respiratory ExaminationДокумент19 страницRespiratory ExaminationMohini33% (3)
- RESPIRATIONДокумент7 страницRESPIRATIONnjayrestОценок пока нет
- Importance of Oxygen for the BodyДокумент68 страницImportance of Oxygen for the BodyYehezkiel RizalОценок пока нет
- Respiratory Exam: Lungs, Breathing, CyanosisДокумент81 страницаRespiratory Exam: Lungs, Breathing, CyanosisashuОценок пока нет
- Periodic ClassificationДокумент4 страницыPeriodic ClassificationtusharОценок пока нет
- Understanding Oscilloscope BasicsДокумент29 страницUnderstanding Oscilloscope BasicsRidima AhmedОценок пока нет
- General Separator 1636422026Документ55 страницGeneral Separator 1636422026mohamed abdelazizОценок пока нет
- Childrens Ideas Science0Документ7 страницChildrens Ideas Science0Kurtis HarperОценок пока нет
- ĐỀ SỐ 3Документ5 страницĐỀ SỐ 3Thanhh TrúcОценок пока нет
- Kahveci: OzkanДокумент2 страницыKahveci: OzkanVictor SmithОценок пока нет
- Lady Allen On Froebel Training School, Emdrup, CopenhagenДокумент5 страницLady Allen On Froebel Training School, Emdrup, CopenhagenLifeinthemix_FroebelОценок пока нет
- Statement of Compulsory Winding Up As On 30 SEPTEMBER, 2008Документ4 страницыStatement of Compulsory Winding Up As On 30 SEPTEMBER, 2008abchavhan20Оценок пока нет
- Post Marketing SurveillanceДокумент19 страницPost Marketing SurveillanceRamanjeet SinghОценок пока нет
- TransistorДокумент1 страницаTransistorXhaОценок пока нет
- Yanmar America publication listing for engine parts, service, and operation manualsДокумент602 страницыYanmar America publication listing for engine parts, service, and operation manualsEnrique Murgia50% (2)
- Ramdump Memshare GPS 2019-04-01 09-39-17 PropsДокумент11 страницRamdump Memshare GPS 2019-04-01 09-39-17 PropsArdillaОценок пока нет
- Course Tutorial ASP - Net TrainingДокумент67 страницCourse Tutorial ASP - Net Traininglanka.rkОценок пока нет
- Jazan Refinery and Terminal ProjectДокумент3 страницыJazan Refinery and Terminal ProjectkhsaeedОценок пока нет
- Factsheet B2B PunchOut en 140623Документ2 страницыFactsheet B2B PunchOut en 140623Curtis GibsonОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1: Newton Forward and Backward Interpolation: M R Mishra May 9, 2022Документ10 страницLecture 1: Newton Forward and Backward Interpolation: M R Mishra May 9, 2022MANAS RANJAN MISHRAОценок пока нет
- Cold Forging Process TutorialДокумент28 страницCold Forging Process TutorialpanyamnrОценок пока нет
- Create a seat booking form with Google Forms, Google Sheets and Google Apps Script - Yagisanatode - AppsScriptPulseДокумент3 страницыCreate a seat booking form with Google Forms, Google Sheets and Google Apps Script - Yagisanatode - AppsScriptPulsebrandy57279Оценок пока нет
- Give Five Examples Each of Nature Having Reflection Symmetry and Radial Symmetry Reflection Symmetry Radial Symmetry Butterfly StarfishДокумент12 страницGive Five Examples Each of Nature Having Reflection Symmetry and Radial Symmetry Reflection Symmetry Radial Symmetry Butterfly StarfishANNA MARY GINTOROОценок пока нет
- Control SystemsДокумент269 страницControl SystemsAntonis SiderisОценок пока нет
- Cianura Pentru Un Suras de Rodica OjogДокумент1 страницаCianura Pentru Un Suras de Rodica OjogMaier MariaОценок пока нет
- Reflection Paper #1 - Introduction To Action ResearchДокумент1 страницаReflection Paper #1 - Introduction To Action Researchronan.villagonzaloОценок пока нет
- Feasibility StudyДокумент47 страницFeasibility StudyCyril Fragata100% (1)
- Suband Coding in MatlabДокумент5 страницSuband Coding in MatlabZoro Roronoa0% (1)
- C Exam13Документ4 страницыC Exam13gauravsoni1991Оценок пока нет
- Domingo V People (Estafa)Документ16 страницDomingo V People (Estafa)Kim EscosiaОценок пока нет
- Diemberger CV 2015Документ6 страницDiemberger CV 2015TimОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1: The Critical Role of Classroom Management DescriptionДокумент2 страницыChapter 1: The Critical Role of Classroom Management DescriptionJoyce Ann May BautistaОценок пока нет
- Installation Instruction XALM IndoorДокумент37 страницInstallation Instruction XALM IndoorVanek505Оценок пока нет
- April 2017 Jacksonville ReviewДокумент40 страницApril 2017 Jacksonville ReviewThe Jacksonville ReviewОценок пока нет