Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
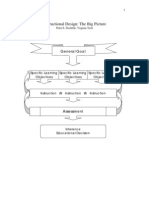
Instructional Delivery Methods
Загружено:
api-3770163Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Instructional Delivery Methods
Загружено:
api-3770163Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Instructional Delivery Methods
Comparison Chart: Selection Criteria
Instructor-Led Virtual Web-Based/
Feature Print-Based
Classroom-Based Classroom-Based Computer-Based
Interactivity Depending on the style of the Activities delivered by print that Depending on the instructional If designed effectively, CBT and
instructor and the instructional design are most conducive to interactivity design quality and the instructor’s WBT can provide a very high level
quality, the level of interactivity can include problem-based learning, style, the level of interactivity can of interactivity through the use of
be extremely high. Consistency games, simulations and case be very high. The instructor’s various learning activities,
among different instructors is a studies. comfort level with the software simulations and games and mouse-
concern. features may be a concern. overs.
Flexibility By design, this format is instructor- Materials can be written for self- By design, this format is largely A multi-purpose program can be
dependent. With some adaptation, it study, small group on-the job instructor-dependent. Virtual suited for individuals or small
may also be suitable for synchronous training, or classroom delivery. classroom sessions can be groups.
distance learning delivery. They can also accompany other “blended” with other self-study
training delivery methods such as formats or recorded for later
video- and computer-based. viewing.
Individualized Individualization can be difficult, and A programmed learning approach Individualization can be difficult This format can provide self-paced
Instruction depends on the size of the class and using testing and remediation can and depends on the size of the instruction with a high degree of
homogeneity of learning needs and result in high degrees of class, learning needs and styles. individualized learning.
styles. individualization.
Performance Feedback is provided by the Measurement can occur through Feedback may be provided by the It is possible to provide immediate
Measurement instructor(s) and by other learners. self-checking, use of scannable instructor or other learners. scoring and feedback to learners,
answer forms, or by submitting Immediate scoring and feedback as track each learner’s overall effort
assignments for instructor check well as tracking of scores are also and scores, and analyze collective
and feedback. possible. learner performance.
Customization Depending on what learning aids are Changes and updates are easy to Changes are easy to make. Most The design may enable easy access
and Modification used, modifications might be easy to make, but they require a classroom material can be easily to areas where modifications are
make. coordinated effort. modified for virtual classroom. needed.
Instructional A good instructor will provide Development costs are relatively Provides the benefits of live Feedback to the learners is
Benefit/Strength immediate feedback and recognize low. Learning is self-paced and instruction and interaction in a immediate. Learners can work at
when learners need coaching and/or location independent. location-independent setting. their own pace and receive training
remediation. just in time.
Disadvantages It is location-dependent. Feedback is not optimal. Tracking Interactivity must be well planned Development is expensive and
Individualized instruction is a the overall effort of each learner and coordinated, individualized centered around constantly
challenge, and having poor can be difficult. Duplication and instruction is limited and poor changing technology. Users must
instructors could be worse than dissemination costs are usually instructors will doom a session. be computer literate.
having no training at all. high.
© 2004 Deloitte Development LLC. All rights reserved. 1
Selecting Delivery Methods for Effective Learning
Use classroom for: • Changing behavior, building culture, or demonstrating skills
• Encouraging veteran staff to work in teams or brainstorm together
• Subjects that need role modeling and/or skills practice
• Training that requires demonstration of complex procedures
• Presentation, feedback and question and answer session (Q&A) with expert speaker
• Training that requires hands-on participation and immediate feedback
• Training that requires direct interaction with complex software applications, which typically need for individualized coaching from
an onsite facilitator
• Encouraging new staff to network and receive orientation
Use virtual classroom for: • Synchronous training on the use of non-complex technology tools, systems or business processes
• Synchronous training that requires remote users to brainstorm or analyze and solve problems in small groups
• Synchronous training that requires immediate feedback and active participation
Use web-based self-study for: • Content that is largely knowledge-sharing such as reading to understand methodologies, business processes and product information
• Content that is shelf stable (current for three or more years)
• Audiences that are large (100+) and geographically disbursed
• Training that requires learning mathematical formulas, solving problems and completing forms
• Training that uses case studies to apply concepts to real life situations
• Training that includes simulations of real life situations
• Training that requires access of online resources or external web sites
Use CD-ROM for: • Programs requiring extensive use of video and audio
• Courses that are too large to be downloaded onto learners’ laptops
Blended Learning Courses combine elements of more than one type of delivery method in the same course. Some examples of these include:
1. Learners complete online or CD-ROM-based pre-work to cover the basic principles and procedures, read background information, and pass quizzes to ensure
mastery of foundation level concepts. Then learners attend fewer days in traditional classroom to complete team activities, role-plays, and question and
answer sessions (Q&A).
2. Learners participate in virtual classroom session to cover basic concepts and receive their assignments. Then learners go to online self-study course to
complete assignment, prepare presentation, collect information or complete exams. Finally learners return to virtual classroom session to debrief, present
findings, and participate in final Q&A.
© 2004 Deloitte Development LLC. All rights reserved. 2
3. Learners take online self-study course to complete course exercises, case studies or simulations, or access information in web sites. Then learners attend a
virtual classroom session to debrief and participate in Q&A.
© 2004 Deloitte Development LLC. All rights reserved. 3
Вам также может понравиться
- Fundamentals of Blended LearningДокумент38 страницFundamentals of Blended LearningGatot SandyОценок пока нет
- Learning Management Systems A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionОт EverandLearning Management Systems A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionОценок пока нет
- Edu 371 Udl Unit PlanДокумент18 страницEdu 371 Udl Unit Planapi-359110943Оценок пока нет
- Progressive Education In Nepal: The Community Is the CurriculumОт EverandProgressive Education In Nepal: The Community Is the CurriculumОценок пока нет
- Instructional Design FormatДокумент3 страницыInstructional Design FormatRizwana Baig100% (1)
- Student Teacher's Perceptions of the Pre-Service Mathematics Programme in a Primary Teachers' College in ZimbabweОт EverandStudent Teacher's Perceptions of the Pre-Service Mathematics Programme in a Primary Teachers' College in ZimbabweРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Trainers-Module SWAYДокумент15 страницTrainers-Module SWAYJOHN67% (3)
- Trainer Agenda For Coaching Effective Teaching Strategies1Документ6 страницTrainer Agenda For Coaching Effective Teaching Strategies1api-159966168Оценок пока нет
- Steps in Process of Curriculum DevelopmentДокумент10 страницSteps in Process of Curriculum DevelopmentTulika BansalОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan GagneДокумент2 страницыLesson Plan Gagnechiew gin siongОценок пока нет
- Instructional Design Tips For Online LearningДокумент8 страницInstructional Design Tips For Online Learningapi-3860347100% (3)
- 06 Async Artefacts M3 NicholasChee 24102020Документ95 страниц06 Async Artefacts M3 NicholasChee 24102020iAnodisedОценок пока нет
- Backward Design: 1. Teachers Are Designers 2. Why Backwards Is Best. 3. The 3 StagesДокумент5 страницBackward Design: 1. Teachers Are Designers 2. Why Backwards Is Best. 3. The 3 StagesMariana SuarezОценок пока нет
- 84 Tips New Id For New ItДокумент34 страницы84 Tips New Id For New ItAlexander ÁlvarezОценок пока нет
- Rapid Instructional Design TemplateДокумент2 страницыRapid Instructional Design Templateiaindoherty100% (1)
- WCE Appendix A: Cover Page TemplateДокумент1 страницаWCE Appendix A: Cover Page TemplatePWU Graduate Studies100% (1)
- Topic 2 Learning Design SequenceДокумент36 страницTopic 2 Learning Design SequenceSEA ServerОценок пока нет
- Final Instructional Design ProjectДокумент37 страницFinal Instructional Design ProjectJennifer Oestreich-FrostОценок пока нет
- InstructionalDesign ManualДокумент204 страницыInstructionalDesign ManualFasika Mekete100% (1)
- ADDIE TemplateДокумент7 страницADDIE TemplatefaОценок пока нет
- Edt 688 - Backward Design LP 3Документ2 страницыEdt 688 - Backward Design LP 3api-285156839Оценок пока нет
- Instructional DesignДокумент46 страницInstructional DesignMarvion Ang100% (1)
- Lesson Plan For AdultsДокумент9 страницLesson Plan For AdultsHeba OthmanОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan DemoДокумент2 страницыLesson Plan DemoJuana Arapan ArvesuОценок пока нет
- Betty Final Draft Assignment 2 - 04Документ13 страницBetty Final Draft Assignment 2 - 04Sei ChanОценок пока нет
- Appendix: Sample 6-Page TemplateДокумент6 страницAppendix: Sample 6-Page Templateoptionality458Оценок пока нет
- AECT StandardsДокумент3 страницыAECT StandardsDavina SmalleyОценок пока нет
- 21ST Century Classroom Facilitation SkillsДокумент8 страниц21ST Century Classroom Facilitation SkillsMora, Aileen Joy R.100% (2)
- Moodle Exemplary Course Rubric 2021-22Документ6 страницMoodle Exemplary Course Rubric 2021-22JiaXinLim100% (1)
- Learning Theory and Instructional Design Research PaperДокумент14 страницLearning Theory and Instructional Design Research PaperVertoria Lagroon AndersonОценок пока нет
- UDL Lesson Plan TemplateДокумент2 страницыUDL Lesson Plan TemplatePsiho LoguseОценок пока нет
- Instructional Design in E-LearningДокумент9 страницInstructional Design in E-Learningapi-3860347100% (1)
- Teacher Development and LeadershipДокумент12 страницTeacher Development and LeadershipRobert TsuiОценок пока нет
- Digital Citizenship ReflectionДокумент8 страницDigital Citizenship Reflectionapi-520658920100% (1)
- Microlearning A Strategy For Ongoing Professional Development.Документ15 страницMicrolearning A Strategy For Ongoing Professional Development.ibuchemОценок пока нет
- Edrd6150 UnitДокумент12 страницEdrd6150 Unitapi-519502575Оценок пока нет
- 10 Lesson Unit Plan Assignment and RubricДокумент4 страницы10 Lesson Unit Plan Assignment and Rubriccom682Оценок пока нет
- Instructional Design Models - Instructional Design Central (IDC)Документ10 страницInstructional Design Models - Instructional Design Central (IDC)Anggie Paola CaocОценок пока нет
- 5 Instructional Design Principles You Can't Do WithoutДокумент4 страницы5 Instructional Design Principles You Can't Do Withoutmohiyul2751Оценок пока нет
- Elearning Developer Instructional Designer in New York NY Resume Michael ForbesДокумент2 страницыElearning Developer Instructional Designer in New York NY Resume Michael ForbesMichaelForbesОценок пока нет
- Addie Presentation - Sharin 1Документ15 страницAddie Presentation - Sharin 1api-510028688Оценок пока нет
- E-Learning Benefits and ApplicationДокумент31 страницаE-Learning Benefits and ApplicationAbu temitopeОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals Course DesignДокумент17 страницFundamentals Course Designstorkj50% (2)
- ADDIE ModelДокумент11 страницADDIE ModelSampada Sawant100% (2)
- Technolgy Education in Elementary EducationДокумент22 страницыTechnolgy Education in Elementary EducationRose Ann GumabongОценок пока нет
- Experiential LearningДокумент31 страницаExperiential Learningapi-659802423Оценок пока нет
- Us 2 Observation Lesson PlanДокумент12 страницUs 2 Observation Lesson Planapi-363732356Оценок пока нет
- Blended Learning ResourcesДокумент7 страницBlended Learning ResourcesPedro C. C. PimentaОценок пока нет
- Storyboard Designing Interview QuestionsДокумент8 страницStoryboard Designing Interview QuestionsvijayakumarvarmaОценок пока нет
- Teacher EvaluationДокумент12 страницTeacher EvaluationNyeinTunОценок пока нет
- Choice BoardДокумент2 страницыChoice Boardapi-317273644Оценок пока нет
- Why Are Instructors Flipping Their Class?: Students Learn More DeeplyДокумент4 страницыWhy Are Instructors Flipping Their Class?: Students Learn More DeeplyLoRe MedRaОценок пока нет
- Marzano Teacher Evaluation Model All 8 QuestionsДокумент26 страницMarzano Teacher Evaluation Model All 8 Questionskeila mercedes schoolОценок пока нет
- Tracy Ballew Google ClassroomДокумент91 страницаTracy Ballew Google ClassroomYin DavidОценок пока нет
- Backward DesignДокумент29 страницBackward Designapi-312990091Оценок пока нет
- Reflection On Lesson Plan TaughtДокумент1 страницаReflection On Lesson Plan Taughtapi-347973818Оценок пока нет
- ADDIE Lesson PlanДокумент5 страницADDIE Lesson PlanMabell Brigole50% (2)
- Students AS DESIGNERS & MAKERSДокумент16 страницStudents AS DESIGNERS & MAKERSWilmie Joy Dela Torre100% (1)
- Blended Learning - Standards ToolkitДокумент9 страницBlended Learning - Standards ToolkitHuong QuachОценок пока нет
- SMART Goals & Conducting Performance DiscussionДокумент8 страницSMART Goals & Conducting Performance Discussionapi-3770163100% (1)
- Water TherapyДокумент14 страницWater Therapyapi-3770163Оценок пока нет
- Aetna Case StudyДокумент8 страницAetna Case StudybucchoОценок пока нет
- Introduction Investment PlanningДокумент5 страницIntroduction Investment Planningapi-3770163Оценок пока нет
- Talent ManagementДокумент6 страницTalent Managementapi-3770163Оценок пока нет
- The Extrasensory Potentials of The Mind - by Shriram Sharma AcharyaДокумент222 страницыThe Extrasensory Potentials of The Mind - by Shriram Sharma AcharyaGuiding Thoughts- Books by Pandit Shriram Sharma Acharya100% (4)
- Introduction To Mutual FundsДокумент5 страницIntroduction To Mutual Fundsapi-3722617Оценок пока нет
- PDC Men Tee ExpectationsДокумент1 страницаPDC Men Tee Expectationsapi-3770163Оценок пока нет
- Practice Consulting..7.12Документ2 страницыPractice Consulting..7.12api-3770163Оценок пока нет
- Teachers Manual - Moodle1.5Документ151 страницаTeachers Manual - Moodle1.5api-3770163Оценок пока нет
- On EducationДокумент6 страницOn Educationapi-3770163Оценок пока нет
- PDC Mentee GuidebookДокумент23 страницыPDC Mentee Guidebookapi-3770163Оценок пока нет
- Creative Thinking Methods MDG.7.12Документ2 страницыCreative Thinking Methods MDG.7.12api-3770163Оценок пока нет
- Establish The Foundation.7.12Документ2 страницыEstablish The Foundation.7.12api-3770163Оценок пока нет
- HarwarLearningBPO WP 02Документ3 страницыHarwarLearningBPO WP 02api-3770163Оценок пока нет
- Good To GreatДокумент1 страницаGood To Greatapi-3770163Оценок пока нет
- Writing File 4 - Teacher's Notes: Learning Objectives in This LessonДокумент1 страницаWriting File 4 - Teacher's Notes: Learning Objectives in This LessonМикола КрушинОценок пока нет
- Research Proposal On BehaviourismДокумент3 страницыResearch Proposal On BehaviourismAmm AR100% (1)
- Internship Plan SampleДокумент2 страницыInternship Plan SampleLily Antonette AgustinОценок пока нет
- Nat G12 Reviewer in Reading and WritingДокумент5 страницNat G12 Reviewer in Reading and WritingDebbie VisitacionОценок пока нет
- Week 30 SB - Supergirl Isay (Supergirl Isay)Документ24 страницыWeek 30 SB - Supergirl Isay (Supergirl Isay)Yu NaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9 - MAslowДокумент26 страницChapter 9 - MAslowHONEY VEB PORRASОценок пока нет
- Team Management: By:-Akshara Saxena B.A.S.L.P Second YearДокумент18 страницTeam Management: By:-Akshara Saxena B.A.S.L.P Second YearAkshara SaxenaОценок пока нет
- Professional Education Drill 9 - Part 1Документ5 страницProfessional Education Drill 9 - Part 1Seph TorresОценок пока нет
- Purpose Statment PDFДокумент2 страницыPurpose Statment PDFZohaibShoukatBalochОценок пока нет
- New Year'S ResolutionsДокумент10 страницNew Year'S ResolutionsChiaraMazzoleniОценок пока нет
- Image Captioning Research PaperДокумент59 страницImage Captioning Research PaperabhishekОценок пока нет
- The DIR Model (Developmental, Individual Difference, Relationship Based) : A Parent Mediated Mental Health Approach To Autism Spectrum DisordersДокумент11 страницThe DIR Model (Developmental, Individual Difference, Relationship Based) : A Parent Mediated Mental Health Approach To Autism Spectrum DisordersLaisy LimeiraОценок пока нет
- Samantha Maldonado: Contact Related ExperienceДокумент1 страницаSamantha Maldonado: Contact Related ExperienceSamantha MaldonadoОценок пока нет
- Final Examination - Short Story (Pelecio, Jhaia)Документ3 страницыFinal Examination - Short Story (Pelecio, Jhaia)elianaОценок пока нет
- Child Friendly School System (CFSS) ChecklistДокумент4 страницыChild Friendly School System (CFSS) ChecklistDivine Grace Samortin91% (45)
- All Report Writing Lectures All Report Writing LecturesДокумент98 страницAll Report Writing Lectures All Report Writing LecturesAhmed ButtОценок пока нет
- PORTFOLIO Opinion Essays ClassДокумент5 страницPORTFOLIO Opinion Essays ClassCalin Chelcea100% (1)
- Letting Go of Shame and GuiltДокумент7 страницLetting Go of Shame and Guilteng.tahasuliman100% (2)
- UHB40102/40202: English For Occupational Purposes: Chapter Two: Job Seeking SkillsДокумент27 страницUHB40102/40202: English For Occupational Purposes: Chapter Two: Job Seeking SkillsSabrina AzharОценок пока нет
- FS1-Learning Episode 3 Activity 3.1Документ13 страницFS1-Learning Episode 3 Activity 3.1RUBY ANN SISONОценок пока нет
- Panmure Maths Lesson Plan MultiplicationДокумент5 страницPanmure Maths Lesson Plan Multiplicationapi-454406266Оценок пока нет
- Cognitive Training For Agility The Integration Between Perception and ActionДокумент8 страницCognitive Training For Agility The Integration Between Perception and ActionSamuelОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 LinguisticДокумент6 страницUnit 1 LinguisticMelissa Monsalve PabónОценок пока нет
- Zapf 1999Документ32 страницыZapf 1999Kashif Munir IdreesiОценок пока нет
- Differential Evolution in Search of Solutions by Vitaliy Feoktistov PDFДокумент200 страницDifferential Evolution in Search of Solutions by Vitaliy Feoktistov PDFMaroua HamlaouiОценок пока нет
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayДокумент3 страницыGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayReciel De VillaОценок пока нет
- Grade 8 - Archimedes: Pigcarangan Integrated School Weekly Home Learning PlanДокумент4 страницыGrade 8 - Archimedes: Pigcarangan Integrated School Weekly Home Learning PlanMarize RondillasОценок пока нет
- WLP#28 English8 2019-2020Документ4 страницыWLP#28 English8 2019-2020Anonymous FNahcfОценок пока нет
- From Motivation To Engagement: The Role of Effort Regulation of Virtual High School Students in Mathematics CoursesДокумент12 страницFrom Motivation To Engagement: The Role of Effort Regulation of Virtual High School Students in Mathematics CoursesRea MirandillaОценок пока нет
- Learning Module II - Teaching Profession Lesson 3 - The Demands of Society From The Teacher As A ProfessionalДокумент8 страницLearning Module II - Teaching Profession Lesson 3 - The Demands of Society From The Teacher As A ProfessionalWincel Ann GoОценок пока нет