Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Summary of Reaction Mechanisms
Загружено:
'Aqilah ZulkifliИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Summary of Reaction Mechanisms
Загружено:
'Aqilah ZulkifliАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Summary of Reaction Mechanisms Required for A2 Chemistry
Module 3 Introduction to Organic Chemistry
Electrophilic addition symmetrical alkenes with HBr, Br2 and H2SO4.
Nucleophilic substitution primary haloalkanes with OH, CN and NH3. Formation of alkenes from alcohols (elimination reaction in terms of the loss of a proton from a carbonium ion generated from the protonated alcohol). Concurrent displacement and elimination 2 haloalkanes with potassium hydroxide Free radical substitution methane + chlorine (initiation, propagation and termination steps).
Module 4 Further Physical and Organic Chemistry
Electrophilic addition asymmetrical alkenes with HBr and H2SO4.
Electrophilic substitution nitration, alkylation and acylation of benzene. Nucleophilic addition-elimination acyl chlorides with water, alcohols, ammonia and 1 amines. Nucleophilic substitution haloalkanes with ammonia and amines to form 1, 2 and 3 amines and 4 ammonium salts. Elimination reactions alkenes from haloalkanes (and alcohols see CHM03).
Generation of the nitronium ion, NO2+ (below): HNO3 + H2SO4 H2NO3+ H2NO3+ + HSO4 (formation of protonated nitric acid) (decomposition to form nitronium ion)
NO2+ + H2O H3O+ + HSO4
H2O + H2SO4
Overall: HNO3 + 2H2SO4 NO2+ + H3O+ + 2HSO4
Page 1 of 4
Copyright 2003 Nigel Saunders N-ch4-04
Electrophilic addition e.g. of HBr, BrBr, H2SO4 (view as HOSO2OH) X C C + X
+
X C + +
:Y
C Y
Nucleophilic addition i.e. of carbonyl compounds with HCN to make hydroxynitriles
+ C
H+
CN
C CN
O ..
H+
C CN
OH
Nucleophilic substitution e.g. of haloalkanes with OH and CN + C X +
Elimination in alcohols to form alkenes H R C H H C H H H C H + O H H R C H + H2O C H
.. O ..
H H+
C H
Elimination in haloalkanes to form alkenes (favoured by using alcoholic solutions of concentrated alkali) X R C H H H C H H
C H
C H
+ H2O + X
OH
Page 2 of 4
Copyright 2003 Nigel Saunders N-ch4-04
Nucleophilic addition-elimination e.g. acyl chlorides with water, alcohols, ammonia and amines R H O+ R' R C Cl O H O+ + Cl R' R + C O
.. R'OH ..
Cl
R C OR' O + HCl
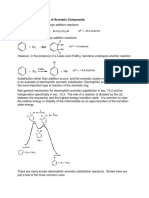
Electrophilic substitution
(nitration of benzene)
Remember the reactions involved in production of the nitronium ion (see first page). H
+
NO2 + H+
NO2
NO2
Electrophilic substitution e.g. FriedelCrafts alkylation of benzene Generation of the electrophile, e.g. as a carbocation complex: RCl + AlCl3 = R+ AlCl4 then H R+AlCl4 R R
+ AlCl4
+ AlCl3 + HCl
Page 3 of 4
Copyright 2003 Nigel Saunders N-ch4-04
Electrophilic substitution e.g. Friedel-Crafts acylation of benzene Generation of the electrophile, e.g. as an acyl cation complex: RCOCl + AlCl3 = RC+O AlCl4 then H RC+O AlCl4 COR COR
+ AlCl4
+ AlCl3 + HCl
Chlorination of methane (free radical substitution) Initiation Homolysis of the ClCl bond using energy from absorbed light or heat supplied: Cl2 2Cl Note: Homolysis of the CH bond is also possible, but less energy is needed to break the ClCl bond (bond energy terms are 435 kJ mol1 and 242 kJ mol1 respectively). Propagation Cl + CH4 HCl + CH3 CH3 + Cl2 CH3Cl + Cl Termination Cl + Cl Cl2 CH3 + CH3 C2H6 Cl + CH3 CH3Cl Other reactions are possible.
Page 4 of 4
Copyright 2003 Nigel Saunders N-ch4-04
Вам также может понравиться
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- AP Chem Test - Chapter 10,11,13 - Gases, Solutions, Solids, Liquids, Inter Forces (2010-2011)Документ12 страницAP Chem Test - Chapter 10,11,13 - Gases, Solutions, Solids, Liquids, Inter Forces (2010-2011)dlloyd63050% (2)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Stereochemistry Basic Concepts, Useful Notes For StudentsДокумент26 страницStereochemistry Basic Concepts, Useful Notes For StudentsATUL R BENDALE89% (45)
- Solution Manual For Organic Chemistry Mechanistic Patterns 1st Edition by Ogilvie PDFДокумент27 страницSolution Manual For Organic Chemistry Mechanistic Patterns 1st Edition by Ogilvie PDFa48880872867% (6)
- Sol. Man. - Chapter 3 Bonds Payable & Other ConceptsДокумент23 страницыSol. Man. - Chapter 3 Bonds Payable & Other ConceptsMiguel Amihan100% (1)
- Grade 9 SecondДокумент3 страницыGrade 9 SecondGelCess ParoanОценок пока нет
- Quiz 2Документ2 страницыQuiz 2JОценок пока нет
- Class IX Chemistry Chapter 05Документ10 страницClass IX Chemistry Chapter 05Sam FisherОценок пока нет
- CFA Chapter 15 Problems SolutionsДокумент5 страницCFA Chapter 15 Problems SolutionsFagbola Oluwatobi OmolajaОценок пока нет
- WorldCom Bond IssuanceДокумент9 страницWorldCom Bond IssuanceAniket DubeyОценок пока нет
- Bond and Stock ValutionsДокумент23 страницыBond and Stock ValutionsNikhil TurkarОценок пока нет
- Chapter 14 Carboxylic Ester Amides PDFДокумент22 страницыChapter 14 Carboxylic Ester Amides PDFMADANОценок пока нет
- Chapter 05Документ6 страницChapter 05Nguyễn Ngọc Hoài ThươngОценок пока нет
- 007 Cheat Codes (Nightfire GC)Документ4 страницы007 Cheat Codes (Nightfire GC)Ian HanlonОценок пока нет
- Chapter 15Документ7 страницChapter 15Rafid InamОценок пока нет
- Idx Monthly February 2021Документ200 страницIdx Monthly February 2021mamanОценок пока нет
- 12a Alkena Dan Reaksinya Bagian 2Документ91 страница12a Alkena Dan Reaksinya Bagian 2ElisОценок пока нет
- Friedländer Synthesis Forms Quinolines from KetonesДокумент1 страницаFriedländer Synthesis Forms Quinolines from Ketonesbad_414Оценок пока нет
- BONDS PAYABLE sample probsДокумент2 страницыBONDS PAYABLE sample probsStephen Jay RioОценок пока нет
- Bank Alpha Inventory Aaa Rated 15 Year Zero Coupon Bonds Fac Chapter 15 Problem 9qp Solution 9781259717772 ExcДокумент1 страницаBank Alpha Inventory Aaa Rated 15 Year Zero Coupon Bonds Fac Chapter 15 Problem 9qp Solution 9781259717772 ExcArihant patilОценок пока нет
- Square planar substitution reactions and trans effectДокумент21 страницаSquare planar substitution reactions and trans effectYoga Rizky 'Muhammad Yusuf'71% (7)
- (Career Endeavour) IIT JAM CHEMISTRY PDFДокумент88 страниц(Career Endeavour) IIT JAM CHEMISTRY PDFKiran Mandal100% (1)
- Simulation BondingДокумент12 страницSimulation BondingCristina Nicomedes Aguinaldo0% (2)
- Lecture No. (4) Elastomer MaterialsДокумент18 страницLecture No. (4) Elastomer MaterialsKhalid AbeedОценок пока нет
- Activity #3Документ2 страницыActivity #3Chryshelle Anne Marie LontokОценок пока нет
- Abdel-Magid, A. F., Maryanoff, C. A., & Carson, K. G. (1990) - Reductive Amination of Aldehydes and Ketones by Using Sodium Triacetoxyborohydride. Tetrahedron Letters, 31 (39), 5595-5598Документ4 страницыAbdel-Magid, A. F., Maryanoff, C. A., & Carson, K. G. (1990) - Reductive Amination of Aldehydes and Ketones by Using Sodium Triacetoxyborohydride. Tetrahedron Letters, 31 (39), 5595-5598de paloОценок пока нет
- Inorganic Solids 2020Документ6 страницInorganic Solids 2020Joseph NyabugaОценок пока нет
- Royal College Chemistry MCQ PracticeДокумент15 страницRoyal College Chemistry MCQ PracticeFarhanОценок пока нет
- Multiple Choice Questions 1 A Company That Uses A MinimumДокумент2 страницыMultiple Choice Questions 1 A Company That Uses A Minimumtrilocksp SinghОценок пока нет
- Bond journal entriesДокумент3 страницыBond journal entriesAsuna SanОценок пока нет
- Bond Portfolio Construction: Chapter SummaryДокумент31 страницаBond Portfolio Construction: Chapter Summarys yanОценок пока нет