Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
ps-II, IImid
Загружено:
Gopi Pavan JonnadulaИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
ps-II, IImid
Загружено:
Gopi Pavan JonnadulaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
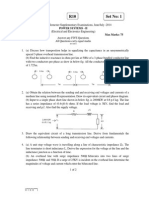
NRI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY PS-II / MID-II QUESTIONS / III-I EEE UNIT-5 1. a)What is ferranti effect?
Prove with mathematical expression the actual
phenomenon that occurs in ferranti effect b) A 3-phase, 220 kV, 50 Hz transmission line has equilateral triangular spacing of side 1.5 m. The conductor diameter is 3.0 cm. The air density factor and irregularity factor are 0.95 and 0.8 respectively. Find the disruptive critical voltage and corona loss per km. Assume any data required. [5+5] 2. a) Explain the skin and proximity effects on transmission system b)A 132kV overhead line conductor of radius 1cm is built so that corona takes place if the line voltage is 210 kV (r.m.s). If the value of voltage gradient at which ionization occurs can be taken as 21.21 kV (r.m.s) per cm, determine the spacing between the conductors. [5+5] 3. What are the disadvantages of corona? Explain how the corona considerations affect The design of a line . And what are the factors that effects on corona. [10] 4. a)Determine the disruptive critical voltage and the visual critical voltages for local and General corona on a 3-phase overhead transmission line consisting of three stranded copper conductors spaced at 2.2 meters apart at the corners of an equilateral triangle. Air temperature and pressure are 210C and 73.5 cm of Hg respectively. Conductor diameter is 1.6 cm, irregularity factor (m0) 0.85, and surface factors (mv) 0.7 for local and general corona 0.7 and 0.8 respectively. Breakdown strength of air is 21.1 kV (r.m.s) / cm. b) ) Define disruptive critical voltage and visual critical voltage? On what factor do they depend? Write equations for calculating these voltages. [10]
UNIT-6
1.a)Define string efficiency. Why is it necessary to have high string efficiency? How can it be achieved? b) Each conductor of a 33 kV, 3-phase system is suspended by a string of 3 similar insulators. The capacitance between each insulator pin and earth is 10% of self capacitance of each insulator. Find (i) The distribution of voltage over three insulators and (ii)String efficiency [5+5] 2. a)Explain different types of insulators used in overhead (OH) line? Give their field of application. b) Each of the three insulators forming a string has a self-capacitance of C Farads. The shunting capacitance of the connecting metal work of each insulator is 0.3 C to earth and 0.1 C to the line. A guard ring increases the capacitance to the line of the metal work of the lowest insulator to 0.3 C. Calculate the string efficiency of this arrangement with the guard ring. [5+5] 3. a) Explain why the potential distribution is not, in general, uniform over the string in suspension type of insulators b) Each conductor of a 3-phase high voltage transmission line is suspended from cross arm of steel tower by a string of 4 suspension type disc insulators. If the voltage across the secondunit is 13.2 kV and that across the third unit is 18 kV. Calculate the voltage between the conductors. [3+7] 4. a) A 3-phase 66kV transmission line is carried by strings of 5 suspension insulators. The capacity of each unit insulator to the capacity relative to earth is 4:1. Calculate the potential across each unit and the string efficiency. Assume that there is no leakage. b) derive the expression for voltage distribution over the units of suspension type insulator string. [5+5]
UNIT-7
1. An overhead line consists of 7 strands of copper, having a cross sectional area of 2.0 cm2 Weight of conductor =1.4kg/m, Ultimate strength =8000kg/cm2 Wind pressure =35 kg/m2 of projected area. Calculate the vertical sag of the time for a span of 250 meters, assuming a factor of safety is 5. b) Obtain an expression for sag of a line supported by towers of equal heights at the ends & when the effect of wind & ice are considered. [7+3] 2. a)What is a stringing chart? How can be it is prepared? What is its use b) A transmission line has a span of 160 m between supports, the supports being at the same level. The conductor has a cross-sectional area of 2 cm2. The ultimate strength is 5,000 kg/cm2. The specific gravity of the material is 8.5 gm/cm3. If the coating of ice is 1.0 cm, calculate the sag at the center of the conductor if factor of safety is 4. [3+7] 3. a) What is a sag template? Explain how this is useful for the location of towers and The stringing of power conductors. b) Determine the sag of an overhead line for the following data: span length 150 meters,conductor diameter 0.9 cm, weight per unit length of the conductor 0.65 kg/meter.Ultimate stress 4250 kg/cm2, wind pressure 40 kg/cm2 of projected area and factor of safety 4. [3+7] 4. a) Obtain an expression for sag of a line supported by towers of different heights at the ends b) A transmission line has a span of 50m between level supports. The cross-sectional area of the conductor is 1.25cm2 and weighs 100 kg per 100 meters if the breaking stress is 4220 kg/cm2.Calculate the factor of safety if the sag of the line is 3.5 m.
Assume a maximum wind pressure of 10 kg/m2. [4+6]
UNIT-8
1. a) Derive the formula for insulation resistance of a cable b) The inner and outer diameters of a cable are 3 cm and 7cm. The cable is insulated with two materials having permittivity of 5 and 3 with corresponding stresses of 35kV/cm and 31kV/cm. Calculate the radial thickness of each insulating layer and the safe working voltage of the cable. [3+7] 2. a)Derive a relation between the conductor radius and inside sheath radius of a single Core cable so that the electric stress of the conductor surface may be minimum b) The capacitance of 3-core cable belted type are measured and found to be as follows: (i) Between three cores bunched together and the sheath is 7F (ii) Between the conductor and the other two connected together to the sheath is 4 F. Calculate the capacitance to neutral and the total charging kVA . [3+7] 3. a) Discuss the methods of grading cables. Why are they not used generally? b) A single core 2 km long cable has a conductor radius of 1.3cm and an insulation thickness of 3.5 mm. If the resistivity of dielectric is 7 1012 ohm-m, determine the insulation resistance of the cable. [4+6] 4. a)What do you understand by grading of cable? Explain why grading is more of Theoretical interest than practical? What is the modern practice adopted to avoid grading b)A 3-phase,66 kV, single core cable of conductor diameter 2.5 cm and lead sheath of diameter 6cm and diameters of two inter sheaths are 3cm and 5cm are introduced in-between the core and lead sheath. If the maximum stress in layers is the same.
Find the voltages on the inter sheaths.
[4+6]
Вам также может понравиться
- ESD Training ModuleДокумент26 страницESD Training ModuleFajar SantosoОценок пока нет
- PsДокумент8 страницPsAlluri Appa RaoОценок пока нет
- Question Bank PS1Документ3 страницыQuestion Bank PS1goyal.167009Оценок пока нет
- FUJITEC CP38 DEBUGGING GUIDEДокумент23 страницыFUJITEC CP38 DEBUGGING GUIDEthành100% (9)
- 9A02502 Transmission of Electric PowerДокумент6 страниц9A02502 Transmission of Electric PowersivabharathamurthyОценок пока нет
- It Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingОт EverandIt Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- MCQ EeeДокумент9 страницMCQ EeeVishal ThakurОценок пока нет
- Poewr System 2Документ4 страницыPoewr System 2కెవి సాయిОценок пока нет
- T&DДокумент5 страницT&DMATHANKUMAR.SОценок пока нет
- Das PDFДокумент527 страницDas PDFMaiChiVu100% (1)
- Frequency Converter Type Vacon NX For Alimak's Hoists and Lifts User's ManualДокумент27 страницFrequency Converter Type Vacon NX For Alimak's Hoists and Lifts User's Manualsulthan1975Оценок пока нет
- Manual Do Operador IL NT 12-2008Документ9 страницManual Do Operador IL NT 12-2008albertooliveira100% (1)
- r05310203 Power Systems IIДокумент8 страницr05310203 Power Systems IISrinivasa Rao G100% (1)
- Nov 2008Документ8 страницNov 2008Viswa ChaitanyaОценок пока нет
- 9A02502 Transmission of Electric PowerДокумент6 страниц9A02502 Transmission of Electric PowersivabharathamurthyОценок пока нет
- R5310203 Power Systems - IIДокумент2 страницыR5310203 Power Systems - IIsivabharathamurthyОценок пока нет
- Power Systems Exam QuestionsДокумент8 страницPower Systems Exam QuestionsShivakrishna MulkaОценок пока нет
- bt3114 Part2 14 11 09rahulДокумент38 страницbt3114 Part2 14 11 09rahulSwathi ChinnuОценок пока нет
- PsiiДокумент8 страницPsiiAlluri Appa RaoОценок пока нет
- Ee335-Transmission and Distribut PDFДокумент2 страницыEe335-Transmission and Distribut PDFPradeep AmmasaikuttiОценок пока нет
- Assignment 1 (Total Marks: 70) EEE 323: Power System IIДокумент2 страницыAssignment 1 (Total Marks: 70) EEE 323: Power System IIShahriar SauravОценок пока нет
- PS PaperДокумент8 страницPS PaperBhavani Chandra UniqueОценок пока нет
- 07a50202 Powersystems IIДокумент8 страниц07a50202 Powersystems IIPaone KalyanОценок пока нет
- 08 r05310203 Power Systems IIДокумент8 страниц08 r05310203 Power Systems IIandhracollegesОценок пока нет
- B.E. 7th Semester EEE Class Test Power SystemsДокумент3 страницыB.E. 7th Semester EEE Class Test Power SystemsRajkumarJhapteОценок пока нет
- 9A02502 Transmission of Electric PowerДокумент2 страницы9A02502 Transmission of Electric PowersivabharathamurthyОценок пока нет
- 31S11020518 Pdf-MergedДокумент2 страницы31S11020518 Pdf-MergedrameshОценок пока нет
- MODEL PAPER Ps-1saquibДокумент3 страницыMODEL PAPER Ps-1saquibKaize JbОценок пока нет
- Tutorial ProblemsДокумент2 страницыTutorial ProblemsIstianaFani33% (3)
- R7310203 Power Systems - IIДокумент1 страницаR7310203 Power Systems - IIsivabharathamurthyОценок пока нет
- Biee 003Документ3 страницыBiee 003Vaibhav SinghОценок пока нет
- Transmission Line Tutorial QuestionsДокумент3 страницыTransmission Line Tutorial QuestionsRomil GargОценок пока нет
- rr310203 Power Systems IIДокумент8 страницrr310203 Power Systems IISRINIVASA RAO GANTAОценок пока нет
- Rr310203 Power Systems IIДокумент8 страницRr310203 Power Systems IISrinivasa Rao G100% (1)
- Fourth Question (Total 15 Marks) 4) Answer The Following QuestionsДокумент10 страницFourth Question (Total 15 Marks) 4) Answer The Following QuestionsRadak RuduОценок пока нет
- Ps-II II MID Question BankДокумент3 страницыPs-II II MID Question Banksrinu247Оценок пока нет
- Model Paper End Semester Examination Power System 1Документ3 страницыModel Paper End Semester Examination Power System 1Stephen BridgesОценок пока нет
- nr310203 Power Systems II Set1Документ2 страницыnr310203 Power Systems II Set1SRINIVASA RAO GANTAОценок пока нет
- PsiiДокумент8 страницPsiiandhracollegesОценок пока нет
- EE3012 Oct2013Документ4 страницыEE3012 Oct2013Amazing ElectricalОценок пока нет
- 31R17021119 Pdf-MergedДокумент3 страницы31R17021119 Pdf-MergedrameshОценок пока нет
- T&D Question Bank Aug 2019Документ15 страницT&D Question Bank Aug 2019thenithyanagrajОценок пока нет
- MICROWAVE MEASUREMENTS AND DEVICESДокумент12 страницMICROWAVE MEASUREMENTS AND DEVICESGajanan Birajdar100% (1)
- WWW - Manaresults.co - In: Code No: R1631021Документ2 страницыWWW - Manaresults.co - In: Code No: R1631021MuraliDhar EswaraОценок пока нет
- BДокумент7 страницBrajbir kaurОценок пока нет
- WWW - Manaresults.co - In: Part-B (50 Marks)Документ2 страницыWWW - Manaresults.co - In: Part-B (50 Marks)Manish KushwahaОценок пока нет
- Eee-503 Elements of Power System 2013-14Документ3 страницыEee-503 Elements of Power System 2013-14Devesh RaiОценок пока нет
- CH 9Документ24 страницыCH 9CaliОценок пока нет
- EE3013 Aug2018Документ3 страницыEE3013 Aug2018Amazing ElectricalОценок пока нет
- Unit Test - 2 QuestionsДокумент1 страницаUnit Test - 2 QuestionsManohar_3020Оценок пока нет
- Probable Questions - EptdДокумент3 страницыProbable Questions - EptdManas ChakrabortyОценок пока нет
- EE301 POWER GENERATION TRANSMISSION AND PROTECTION QUESTION BANKДокумент6 страницEE301 POWER GENERATION TRANSMISSION AND PROTECTION QUESTION BANKMohammed NadheerОценок пока нет
- EE3103 a .3Документ2 страницыEE3103 a .3Charandeep TirkeyОценок пока нет
- Question Bank On T & DДокумент4 страницыQuestion Bank On T & DArpita BanikОценок пока нет
- Transmission Line Corona ProblemsДокумент2 страницыTransmission Line Corona ProblemsDeepak Srinivas YadavОценок пока нет
- Https WWW - Suit.edu - PK Uploads Past Papers Power Transmission Distribution - ELC254Документ1 страницаHttps WWW - Suit.edu - PK Uploads Past Papers Power Transmission Distribution - ELC254GHS Kass Korona MardanОценок пока нет
- Module-1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7.: Question BankДокумент6 страницModule-1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7.: Question BankPreethi SinhaОценок пока нет
- Sample Transmission Line PaperДокумент2 страницыSample Transmission Line PaperAnup PatelОценок пока нет
- Nr310203 Power Systems II Set1Документ2 страницыNr310203 Power Systems II Set1Srinivasa Rao GОценок пока нет
- Calculate Flux Densities and Current for Magnetic CircuitsДокумент22 страницыCalculate Flux Densities and Current for Magnetic CircuitsHari NathОценок пока нет
- Vacuum Nanoelectronic Devices: Novel Electron Sources and ApplicationsОт EverandVacuum Nanoelectronic Devices: Novel Electron Sources and ApplicationsОценок пока нет
- Simulation of Transport in NanodevicesОт EverandSimulation of Transport in NanodevicesFrançois TriozonОценок пока нет
- An Essential Guide to Electronic Material Surfaces and InterfacesОт EverandAn Essential Guide to Electronic Material Surfaces and InterfacesОценок пока нет
- Electronically Tunable Chaotic Oscillators Using OTA-C Derived From Jerk ModelДокумент23 страницыElectronically Tunable Chaotic Oscillators Using OTA-C Derived From Jerk ModelKhunanon KarawanichОценок пока нет
- Heatcraft Condensing UnitsДокумент12 страницHeatcraft Condensing UnitsValentin LupascuОценок пока нет
- mc2 enДокумент15 страницmc2 enTkd-sar Song Mu KwanОценок пока нет
- Reyrolle 7SR1003Документ2 страницыReyrolle 7SR1003Vuqar JafarovОценок пока нет
- Split-Core CTs for Energy MonitoringДокумент7 страницSplit-Core CTs for Energy MonitoringJyoti ShresthaОценок пока нет
- Standards Specifications For Instrument CablesДокумент10 страницStandards Specifications For Instrument CablesAmmar AltamimyОценок пока нет
- Model Pc100 Temperature Controller User Manual: Rev AДокумент87 страницModel Pc100 Temperature Controller User Manual: Rev AAnonymous mDLYFQuОценок пока нет
- Littelfuse ProtectionRelays SE 601 DatasheetДокумент1 страницаLittelfuse ProtectionRelays SE 601 DatasheettrueavatharОценок пока нет
- Newton-Raphson Method For Power Flow Equations in Matlab EnvironmentДокумент5 страницNewton-Raphson Method For Power Flow Equations in Matlab Environmentashikhmd4467Оценок пока нет
- 7 1 2 Valerio - LippariniДокумент35 страниц7 1 2 Valerio - LippariniDILLIBABU EОценок пока нет
- Electronic Timer CircuitДокумент3 страницыElectronic Timer CircuitSrinivasMunubarthiОценок пока нет
- v100 Ku-to-Ka Convertible: Installation and Operation ManualДокумент159 страницv100 Ku-to-Ka Convertible: Installation and Operation ManualSergeyОценок пока нет
- Catalog Hoap 2Документ0 страницCatalog Hoap 2jiji1183Оценок пока нет
- MODUS FLY8000 pendant luminaire tech sheetДокумент2 страницыMODUS FLY8000 pendant luminaire tech sheetvikiОценок пока нет
- Data Sheet For Three-Phase Squirrel-Cage-Motors SIMOTICS: Motor Type: SD100 FS: 286T - 4p - 30 HPДокумент5 страницData Sheet For Three-Phase Squirrel-Cage-Motors SIMOTICS: Motor Type: SD100 FS: 286T - 4p - 30 HPandersson benito herreraОценок пока нет
- C500-0055 QSL9 C300D6 OPENSET-Rev00Документ2 страницыC500-0055 QSL9 C300D6 OPENSET-Rev00Jonatas de AndradeОценок пока нет
- Dongguan Liesheng Electronics Co., LTD.: Haylou-GT5 True Wireless Earbuds User ManualДокумент1 страницаDongguan Liesheng Electronics Co., LTD.: Haylou-GT5 True Wireless Earbuds User ManualBennettОценок пока нет
- Siemens Electric Motor 15hp 1500rpmДокумент17 страницSiemens Electric Motor 15hp 1500rpmShamsul HaqueОценок пока нет
- MiCOM P44XДокумент8 страницMiCOM P44XMahesh YadaОценок пока нет
- Bill of Materials: Item # Quantity Part Ref ValueДокумент3 страницыBill of Materials: Item # Quantity Part Ref Valuemushahid980Оценок пока нет
- Exper-10 Digital Comparator CircuitДокумент5 страницExper-10 Digital Comparator CircuitMohammed Dyhia AliОценок пока нет
- Green Recloser: Chardon KoreaДокумент6 страницGreen Recloser: Chardon KoreatusarОценок пока нет
- Growatt ManualДокумент28 страницGrowatt ManualDenis Carneiro SantosОценок пока нет
- Introduction To ArpaДокумент8 страницIntroduction To ArpaHEIDI ROSE MENDOZAОценок пока нет
- Von Neumann Machine Architecture (CSO)Документ33 страницыVon Neumann Machine Architecture (CSO)TBОценок пока нет