Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Improve Activity Tolerance Through Rest and Relaxation
Загружено:
KrisJane Ratilla AbivaИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Improve Activity Tolerance Through Rest and Relaxation
Загружено:
KrisJane Ratilla AbivaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
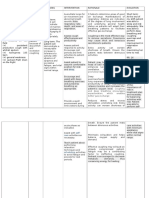
1 Ineffective Breathing Pattern
Ineffective breathing pattern occurs when inspiration and expiration does not provide adequate ventilation. Pleural inflammation causes sharp localized pain that increases deep of breathing, coughing and movement. This can result to shallow and rapid breathing pattern. Distal airways and alveoli may not expand optimally with each breath, increasing the possibility of atelectasis and impaired gas exchange.
Assessment Subjective: Dyspnea Objectives: The patient manifested the following:
Tachypnea Presence of crackles on both lung fields upon auscultation use of accessory muscles RR of 28
The patient may manifest the following:
Cyanosis Orthopnea Diaphoresis
Nursing Nursing InterExpected Planning Rationale Diagnosis ventions Outcome Ineffective Short Term: - Establish - To gain pt/ Short Term: Breathing rapport SOs trust and After 3 hours The patient Pattern RT cooperation of nursing - Monitor and shall have Decreased interventions record vital - To obtain demonstrated Lung the patient signs baseline data appropriate Volume will coping Capacity demonstrate - Assess breath - To note for behaviors and as appropriate sounds, methods to respiratory evidenced coping improve respiratory rate, abnormalities by behaviors and depth and that may indicate breathing tachypnea, methods to rhythm early respiratory pattern. presence of improve compromise and crackles on breathing Long term: - Elevate head hypoxia both lung pattern. of the pt. fields and - To promote The patient dyspnea Long term: - Provide lung expansion shall have applied relaxing After 1 to 2 environment techniques - To promote days of that improved adequate rest nursing periods to limit breathing - Administer interventions, supplemental fatigue pattern and be the patient free from oxygen as would be able ordered - To maximize signs and to apply oxygen available symptoms of techniques respiratory -Assisst client in for cellular that would distress AEB uptake the use of improve respiratory relaxation breathing rate within technique -To provide pattern and be normal range, relief of free from causative factors absence of - Administer signs and cyanosis, prescribed symptoms of medications as - For the effective respiratory ordered pharmacological breathing and distress. management of minimal use of accessory the patients -Maximize muscles
respiratory condition during effort with good breathing. posture and -To promote effective use if wellness accessory muscles. - to limit fatigue -Encourage adequate rest periods between activities
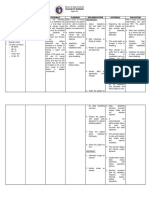
2 Impaired Gas Exchange
Impaired gas exchange is a state in which there is excess or deficit oxygenation and carbon dioxide elimination. The compensatory mechanism of lungs is to lose effectiveness of its defense mechanisms and allow organisms to penetrate the sterile lower respiratory tract where inflammation develops. Disruption of mechanical defenses and ciliary motility leads to colonization of lungs and subsequent infection. Inflamed and fluid-filled alveolar sacs cannot exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide effectively. The release of endotoxins by the microbes can lodge in the brain, affecting the respiratory center in medulla resulting to altered oxygen supply.
Nursing Nursing InterExpected Planning Rationale Diagnosis ventions Outcome Subjective: Impaired Short term: - Establish rapport - To gain Short term: (none) Gas pt./SOs trust After 1 hour - Monitor and record The patient Exchange and cooperation of nursing vital signs shall have Objective: R/T interventions, verbalized - To obtain Alveolar understanding The patient Capillary the pt will - Monitor respiratory baseline data verbalize of the manifested Membrane rate, depth and rhythm understanding - To assess for interventions Changes of the Several - Assess pts general rapid or shallow given to and respiration that improve episodes of respiratory interventions condition given to occur because patients pallor fatigue improve of hypoxemia condition. - Auscultate breath Secondary patients Tachypnea to Pleural sounds, note areas of and stress condition. Long term: decreased/adventitious Effusion breath sounds as well - To note for Restlessness Long term: as fremitus etiology The patient precipitating shall manifest nasal flaring After 1-2 factors that can no signs of - Elevate head of the days of lead to impaired respiratory depth of Assessment
breathing Use of accessory muscles for breathing The pt. may manifest the ff: Confusion Cyanosis Diaphoresis
nursing pt. gas exchange distress. interventions, the pt. will - Note for presence of -To evaluate demonstrate cyanosis degree of improved compromise ventilation -Encourage frequent and adequate position changes and - To enhance oxygenation deep-breathing lung expansion of tissues exercises AEB absence - To assess of symptoms -Provide supplemental inadequate of respiratory oxygen at lowest systemic distress. concentration oxygenation or indicated by hypoxemia laboratory results and client symptoms/ -To promote situation optimum chest expansion - Review laboratory results To correct/ improve - Provide health existing teaching on how to deficiencies alleviate pts condition - To determine pts Administer prescribed oxygenation medications as status ordered - To empower SO and pt For the pharmacological management of the patients condition
4 Acute Pain
Pain may be considered as Pleuritic chest pain. Pleuritic chest pain derives from inflammation of the parietal pleura, the site of pleural pain fibers. Occasionally, this symptom is accompanied by an audible or palpable pleural rub, reflecting the movement of abnormal pleural tissues.
Nursing Nursing InterExpected Planning Rationale Dx ventions Outcome Subjective: Acute Short Term: Assess patient To identify Short Term: pain pain for intensity, (none) After 3-4 Patient shall intensity using precipitating factors hours of have a pain rating and location to nursing verbalized a Objective: scale, for assist in accurate interventions, decrease in location and diagnosis. the patients pain from a Patient for pain will Assessing response scale of 7 to manifested: precipitating decrease determines 3. factors. from 7 to 3 effectiveness of (+) DOB as verbalized Assess the medication and Long Term: by the response to whether further Complains to patient. medications interventions are The patient chest pain on every 5 required. shall have the minutes Long Term: demonstrated thoracostomy To provide activities and site Provide nonpharmacological behaviors After 2-3 comfort pain management. that will days of Facial measures. nursing prevent the grimaces interventions, A quiet recurrence of upon the patient Establish a environment pain. movement will quiet reduces the energy demonstrate environment. demands on the Reports of activities and patient. pain on the behaviors Elevate head of thoracostomy that will bed. Elevation improves area, prevent the chest expansion and described as recurrence of Monitor vital oxygenation. sharp pain. signs, provoked by especially Tachycardia and breathing pulse and elevated blood nonblood pressure, pressure usually radiating, every 5 occur with angina with a pain minutes until and reflect scale of 7 out pain subsides. compensatory of 10 mechanisms Teach patient secondary to Patient may sympathetic relaxation manifest: techniques and nervous system stimulation. how to use Restlessness them to reduce stress. Anginal pain is Confusion often precipitated by emotional stress Assessment
Irritability
that can be relieved nonpharmacological measures such as relaxation.
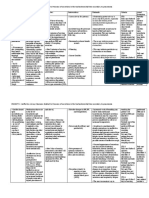
3 Activity Intolerance
Presence of a space-occupying liquid in the pleural space, the lung recoils, inward, the chest wall recoils outward, and the diaphragm is depressed inferiorly. This may lead to decrease lung volume and may result to significant hypoxemia and can only be relieved by thoracentesis. Due to inadequate ventilation there would be limitations in activity as tolerance to activity may occur.
Assessment Subjective: (none) Objective: Patient manifested: generalized weakness limited range of motion as observed use of accessory muscles during breathing (+) DOB
Nursing Diagnosis Activity intolerance related to insufficient oxygen for activities of daily living
Expected Outcome Short Term: To gain clients Short Term: participation After 3-4 hours The patient and of nursing Monitor and shall have cooperation in interventions, record Vital used the nurse the patient will Signs identified patient use identified techniques to interaction techniques to Assess patients improve improve To obtain activity general condition activity baseline data intolerance intolerance Adjust clients daily activities To note for any Long Term: Long Term: abnormalities and reduce intensity of level. and The patient deformities After 2-3 days Discontinue shall have present within reported of nursing activities that interventions, cause undesired the body measurable the patient will psychological increase in report changes To prevent activity measurable strain and intolerance. increase in overexertion Instruct client in activity unfamiliar intolerance. activities and in To conserve alternate ways of energy and conserve energy promote safety Planning Rationale Encourage to relax the
Nursing Interventions Establish Rapport
patient to have body adequate bed rest and sleep to provide relaxation Provide the patient with a to prevent risk calm and quiet for falls that environment could lead to injury Assist the client in ambulation fatigue affects both the Note presence of clients actual factors that could and perceived contribute to ability to fatigue participate in activities Ascertain clients ability to stand to determine and move about current status and degree of and needs assistance needed associated with or use of participation in equipment needed or desired activities Give client information that provides to sustain evidence of daily motivation of or weekly client progress to enhance Encourage the sense of well client to maintain being a positive attitude to promote Assist the client easy breathing in a semi-fowlers position to maintain an open airway Elevate the head of the bed to prevent injuries Assist the client in learning and to avoid risk demonstrating
appropriate safety for falls measures to help Instruct the SO minimize not to leave the frustration and client unattended rechannel energy Provide client with a positive to indicate atmosphere need to alter activity level Instruct the SO to monitor response of patient to an activity and recognize the signs and symptoms
Вам также может понравиться
- Ineffective Breathing PatternДокумент8 страницIneffective Breathing PatternJansen Arquilita Rivera100% (2)
- Ineffective Breathing PatternДокумент5 страницIneffective Breathing PatternruguОценок пока нет
- Causes and Nursing Care of Pleural EffusionДокумент4 страницыCauses and Nursing Care of Pleural EffusionHania Polangi100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceДокумент1 страницаNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceImation DataОценок пока нет
- NCP For PneumoniaДокумент3 страницыNCP For PneumoniaKahMallari100% (10)
- Copd NCPДокумент16 страницCopd NCPSuperMaye100% (1)
- NCPДокумент9 страницNCPEjie Boy Isaga67% (3)
- 6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansДокумент7 страниц6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansShaina Fe RabaneraОценок пока нет
- Ineffective Breathing PatternДокумент3 страницыIneffective Breathing PatternReichelle Perlas62% (13)
- NCP Ineffective Breathing Pattern TalaДокумент1 страницаNCP Ineffective Breathing Pattern TalaJhen Bitco Fidel70% (10)
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceДокумент5 страницNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceEmm Estipona HaoОценок пока нет
- NCP TBДокумент6 страницNCP TBGrhace Aquino100% (3)
- Assessing and Managing Respiratory DistressДокумент3 страницыAssessing and Managing Respiratory DistressGen RodriguezОценок пока нет
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceДокумент5 страницNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceArt Christian Ramos100% (1)
- Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 10/07/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. Zoleta: Nursing Care Plan: PneumoniaДокумент9 страницLopez, Maria Sofia B. 10/07/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. Zoleta: Nursing Care Plan: PneumoniaSofia Lopez100% (2)
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern - NCPДокумент2 страницыIneffective Breathing Pattern - NCPHsintan HsuОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan: Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related ToДокумент4 страницыNursing Care Plan: Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related ToFrudz OrjalezaОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan: Name of Patient: Attending Physician: Age: Impression/DiagnosisДокумент3 страницыNursing Care Plan: Name of Patient: Attending Physician: Age: Impression/DiagnosisMelody B. Miguel0% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Breathing ActualДокумент3 страницыNCP Ineffective Breathing ActualArian May Marcos100% (1)
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPДокумент4 страницыImpaired Gas Exchange NCPkimglaidyl bontuyanОценок пока нет
- Ineffective Breathing PatternДокумент3 страницыIneffective Breathing PatternTrixie Anne Gamotin100% (3)
- NCP - Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент4 страницыNCP - Impaired Gas ExchangeRene John Francisco100% (1)
- Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент5 страницImpaired Gas ExchangeKM67% (3)
- Pneumonia-Ineffective Airway ClearanceДокумент2 страницыPneumonia-Ineffective Airway ClearanceNursesLabs.com86% (7)
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmДокумент2 страницыIneffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmReylan Garcia100% (4)
- NCP PneumoniaДокумент2 страницыNCP PneumoniaSteffanie Serrano100% (1)
- NCP 1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceДокумент2 страницыNCP 1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceDivine Jane PurciaОценок пока нет
- NCP For AsthmaДокумент1 страницаNCP For AsthmaMelvin Martinez100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Breathing PatternДокумент3 страницыNCP Ineffective Breathing PatternEds Sy50% (4)
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Exudates in The Alveoli TBДокумент3 страницыNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Exudates in The Alveoli TBMa. Elaine Carla Tating0% (1)
- Effective airway clearance for pneumonia patientДокумент5 страницEffective airway clearance for pneumonia patientCamille Serrano100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент1 страницаNursing Care Plan Impaired Gas Exchangecuicuita100% (3)
- NCP # 1 Acute PainДокумент3 страницыNCP # 1 Acute Painernst_bondoc50% (2)
- NCP For Pleural EffusionДокумент4 страницыNCP For Pleural EffusionLilian Linogao71% (7)
- NCP For Aspiration PnuemoniaДокумент11 страницNCP For Aspiration PnuemoniaChristy Rose AgrisОценок пока нет
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance For PneumoniaДокумент5 страницNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance For PneumoniaKullin Rain100% (1)
- NCP PediaДокумент2 страницыNCP PediaJacinth Rizalino40% (5)
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Presence of Secretion in Trachea-Bronchial Tree Secondary To History of CAPДокумент2 страницыNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Presence of Secretion in Trachea-Bronchial Tree Secondary To History of CAPpa3kmedina100% (1)
- Nursing Diagnosis and Interventions for Impaired Gas Exchange and Ineffective Airway ClearanceДокумент4 страницыNursing Diagnosis and Interventions for Impaired Gas Exchange and Ineffective Airway ClearanceKen Simon100% (1)
- NANDA Page 658Документ5 страницNANDA Page 658Ashley Gaton Alindogan100% (1)
- Impaired Gas Exchange R/T Ventilation-Perfusion Imbalance Care PlanДокумент2 страницыImpaired Gas Exchange R/T Ventilation-Perfusion Imbalance Care PlanCristina Centurion100% (10)
- NCP Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент2 страницыNCP Impaired Gas ExchangeCharissa Magistrado De LeonОценок пока нет
- NCP For Ineffective Airway ClearanceДокумент3 страницыNCP For Ineffective Airway ClearanceJennelyn BayleОценок пока нет
- Ineffective Breathing PatternДокумент1 страницаIneffective Breathing Patternimneverwrong249280% (5)
- POC Ineffective Breathing PatternДокумент1 страницаPOC Ineffective Breathing PatterncuicuitaОценок пока нет
- ANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationДокумент2 страницыANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationEdrianne Tui100% (2)
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPДокумент1 страницаImpaired Gas Exchange NCPCj AlconabaОценок пока нет
- NCPДокумент2 страницыNCPDidith AbanОценок пока нет
- Assessing and Managing Ineffective Airway ClearanceДокумент3 страницыAssessing and Managing Ineffective Airway ClearanceNelle Agni100% (1)
- Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент2 страницыImpaired Gas ExchangeHanya Bint PotawanОценок пока нет
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceДокумент2 страницыNCP - Ineffective Airway Clearancelarapatricia1215Оценок пока нет
- NCP Impaired Gas Exchange STROKEДокумент2 страницыNCP Impaired Gas Exchange STROKEMa. Elaine Carla TatingОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Sleep NCPДокумент4 страницыNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Sleep NCPderic100% (2)
- Pleural Effusion NCPsДокумент7 страницPleural Effusion NCPsJaja Nagallo100% (2)
- 4 NCP's FinalДокумент9 страниц4 NCP's FinalZenel Yap100% (1)
- Nursing Interventions and Expected Outcomes for a Patient with Generalized Weakness and Activity IntoleranceДокумент4 страницыNursing Interventions and Expected Outcomes for a Patient with Generalized Weakness and Activity IntoleranceValerie BaracaoОценок пока нет
- PTB NCPДокумент12 страницPTB NCPNiel LeeОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan for Respiratory ConditionsДокумент7 страницNursing Care Plan for Respiratory ConditionsJonathan Delos ReyesОценок пока нет
- Asthma Nanda Diagnoses Goals InterventionsДокумент4 страницыAsthma Nanda Diagnoses Goals InterventionsZinya RobinsonОценок пока нет
- AssessmentДокумент2 страницыAssessmentEjoy Rayos AdawagОценок пока нет
- Vital SignsДокумент131 страницаVital SignskasingaОценок пока нет
- 05 Polycythemia in The NewbornДокумент11 страниц05 Polycythemia in The NewbornMorales Eli PediatraОценок пока нет
- Trauma in Pregnancy Criddle, Laura M. PHD, RN, Cen, CCRN, FaenДокумент6 страницTrauma in Pregnancy Criddle, Laura M. PHD, RN, Cen, CCRN, FaenMeder Vivero Go IIIОценок пока нет
- Transcutaneous Oximetry in Clin Practice - ConsensusДокумент11 страницTranscutaneous Oximetry in Clin Practice - ConsensusTony LeeОценок пока нет
- Physiology Question BankДокумент9 страницPhysiology Question BankShriyaОценок пока нет
- Aldenderfer 1998 - Montane Foragers - Asana and The South-Central Andean ArchaicДокумент344 страницыAldenderfer 1998 - Montane Foragers - Asana and The South-Central Andean ArchaicAndré Valencia Garcia100% (2)
- The Infant of An Addicted MotherДокумент15 страницThe Infant of An Addicted Mothernursereview100% (8)
- Postoperative HypoxiaДокумент33 страницыPostoperative HypoxiasrinidhiОценок пока нет
- Chronic Obstructive Bronchitis Is An Inflammation of The BronchiДокумент9 страницChronic Obstructive Bronchitis Is An Inflammation of The Bronchiinamaliit100% (1)
- Respiration CoppДокумент50 страницRespiration CoppsyamaladevinОценок пока нет
- COPD Group Assignment InsightsДокумент5 страницCOPD Group Assignment InsightsDan Floyd FernandezОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care of The Client With High-Risk Labor Delivery Her FamilyДокумент135 страницNursing Care of The Client With High-Risk Labor Delivery Her Familycoosa liquorsОценок пока нет
- NCP GunshotДокумент13 страницNCP GunshotMichael John F. Natividad0% (1)
- Hyperoxia: Jed Wolpaw, MD, M.EdДокумент71 страницаHyperoxia: Jed Wolpaw, MD, M.EdJustin WangОценок пока нет
- RespirationДокумент10 страницRespirationADWAIT LALUОценок пока нет
- The Miskatonic University Expedition: The National Geographic MagazineДокумент24 страницыThe Miskatonic University Expedition: The National Geographic Magazinejack100% (1)
- Respiration: Physiology / 2009-10 Dr. Ahmad .S. AlarabiДокумент23 страницыRespiration: Physiology / 2009-10 Dr. Ahmad .S. AlarabiJerome EkohОценок пока нет
- Our Lady of Lourdes HospitalДокумент19 страницOur Lady of Lourdes HospitalJerald Oliver MacabayaОценок пока нет
- Cellular Adaptation: Pathophysiology: The Cell Is The Fundamental Unit of DiseaseДокумент51 страницаCellular Adaptation: Pathophysiology: The Cell Is The Fundamental Unit of DiseaseJerneth Nyka FloresОценок пока нет
- Human Performance and Limitations QuestionsДокумент326 страницHuman Performance and Limitations QuestionsFarah100% (19)
- ABG Interpretation 3.0Документ73 страницыABG Interpretation 3.0Jesus Mario Lopez100% (1)
- Respiratory Case StudiesДокумент6 страницRespiratory Case Studiesadom09Оценок пока нет
- HemoDynamics and CardiologyДокумент452 страницыHemoDynamics and CardiologyYuliawati Haruna100% (1)
- RT Student CRT Entry Exam Review QuestionsДокумент71 страницаRT Student CRT Entry Exam Review QuestionsRenita Washington100% (4)
- MEDICAL SURGICAL NURSING DISCUSSION ON SHOCKДокумент22 страницыMEDICAL SURGICAL NURSING DISCUSSION ON SHOCKNavpreet Kaur100% (1)
- Fundamentals of NursingДокумент5 страницFundamentals of NursingLance Sta AnaОценок пока нет
- Anoxic Brain InjuryДокумент9 страницAnoxic Brain InjuryGymnastK27Оценок пока нет
- Nursing Care of CHF PatientsДокумент25 страницNursing Care of CHF PatientsIrwan100% (2)
- Disturbances in The Pulmonary CirculationДокумент13 страницDisturbances in The Pulmonary CirculationironОценок пока нет
- Periplus Universum 3 MedicineДокумент28 страницPeriplus Universum 3 MedicineAdam YatesОценок пока нет