Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Bahagian Mikroskope
Загружено:
Muhammad Husni Bin RamliИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Bahagian Mikroskope
Загружено:
Muhammad Husni Bin RamliАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Eyepieces There are various types of eyepieces used in microscopes but there are those specially built for
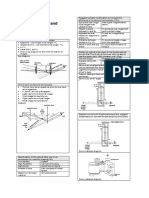
r metallurgical microscopes. Eyepieces are one half of what makes the total magnification of a microscope. They are also what determines the field of view or how much of the image of the sample you can see. The best eyepieces cannot improve low levels or quality of the objective lenses youre using but a poorly designed eyepiece can reduce the quality of image resolution provided by the microscopes objectives. Objective As it is with all types of microscopes, its important for you to invest in a good to excellent quality of objective lenses. Its in fact better if you work with a pair of excellent objectives rather than have various lenses of mediocre quality. There are also various types of objectives sold in the market today and you can use two different types of objectives at the same time in certain occasions. Objectives make the other half of your microscopes magnification. Multiplying the eyepiece magnification with that of the objectives will give you your microscopes total magnification. Condenser In an upright metallurgical microscope, youll find it beneath the stage and thats why its often referred to as the substage condenser. In inverted metallurgical microscopes, however, the condenser is located above the stage. A condenser is one of the most important parts of a microscopes illumination system. When the light source beams off light, it will be collected, concentrated, and controlled by the condenser. It is also partly because of the condenser that a metallurgical microscope is able to use various types of illumination such as polarized light and epi bright field optics. People mistakenly adjust the condensers focus knobs to adjust light intensity. If this is the problem, you shouldnt be adjusting the condenser but rather the aperture iris diaphragm. If field brightness thats the problem then adjust or change the filter youre using and not the condenser. The condenser focus knob is simply there to adjust its vertical height and nothing else. Aperture Iris Diaphragm This is part of your metallurgical microscopes condenser. Adjusting it enables you to reduce or increase light angle coming from the condenser. Filter and Filter Holder or Carrier Filters are also the other reason why you can use several illumination systems for your metallurgical microscope. The filter carrier is attached or found right next to the substage condenser. Purchase of additional filters can expand the applications of your microscope and the types of objects it is able to study. Nosepiece This is also known as the objective changer and it is where the objective lenses of a metallurgical microscope are located. A nosepiece holding five lenses is more than enough but four is good as well. Three is adequate but two or one might be troublesome because youd then have to manually change lenses when the two currently attached are unsuitable for the object youre examining. Stage This is where you place your object. Also known as your microscopes platform, a stage may be built-in or integrated with the rest of the microscope or mechanical. It may come with a simple plane design or in a XY style for better precision in positioning your object. Interchangeability of stages depends primarily on the model you wish to purchase. Coarse Adjustment Knobs These are the bigger knobs found on your metallurgical microscope and are there to lift or lower the stage or body tube. Fine Focus Knob These are the smaller knobs on your metallurgical microscope and are there to adjust focus on the object. Foot This represents the base of your metallurgical microscope. If possible, look for one with a magnetic base to allow you to study objects at any angle.
Eyepiece Tube This is where the eyepiece is inserted and its what connects the eyepiece to the rest of the metallurgical microscope. This is where video and camera accessories may also be attached.
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in BiologyДокумент4 страницыA Detailed Lesson Plan in Biologyapi-26797930495% (19)
- Fgfa Color Agnar Manual PDFДокумент1 страницаFgfa Color Agnar Manual PDFCarlosОценок пока нет
- MCQ BJMC 205Документ3 страницыMCQ BJMC 205Isa KakakhailОценок пока нет
- PDFДокумент9 страницPDFDocОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 & 2 SPДокумент31 страницаUnit 1 & 2 SParpit anandОценок пока нет
- Long Quiz Science 7 Microscope Parts Functions Plant CellДокумент1 страницаLong Quiz Science 7 Microscope Parts Functions Plant Celljulie tuazonОценок пока нет
- Lab Worksheet - Exercise 2 PDFДокумент5 страницLab Worksheet - Exercise 2 PDFmariammanutdОценок пока нет
- Filter List VI DEPT: AHU Filters/ Hepa Filters Type Washable / Non Washable Varient Diemension Quantity RemarkДокумент1 страницаFilter List VI DEPT: AHU Filters/ Hepa Filters Type Washable / Non Washable Varient Diemension Quantity Remarknakul ahirraoОценок пока нет
- Hasselblad Lens GuideДокумент34 страницыHasselblad Lens Guideseifadiaz100% (3)
- Spesifikasi Nikon Mikroskop Eclipse E100 PDFДокумент1 страницаSpesifikasi Nikon Mikroskop Eclipse E100 PDFHarto waldiОценок пока нет
- MB522 Series Professional Biological MicroscopesДокумент1 страницаMB522 Series Professional Biological MicroscopesLucia BurdujaОценок пока нет
- Basic Laboratory Glassware and EquipmentДокумент11 страницBasic Laboratory Glassware and EquipmentSheila Mae BaranganОценок пока нет
- Microscopy and Its Application in Microbiology andДокумент5 страницMicroscopy and Its Application in Microbiology andDoanh NguyenОценок пока нет
- CX43 MikroskopДокумент4 страницыCX43 MikroskopGElangCatur Arifianto PurbalinggaОценок пока нет
- Service Kit Contents 380.480.680.780.750. 1150.350.550 & 650 All New MachinesДокумент13 страницService Kit Contents 380.480.680.780.750. 1150.350.550 & 650 All New Machinestazjuan1Оценок пока нет
- Gilson SpecsДокумент3 страницыGilson Specsbianca_mafalda4779Оценок пока нет
- New MRP LISTДокумент67 страницNew MRP LISTishan jainОценок пока нет
- Parts and Function of A MicroscopeДокумент4 страницыParts and Function of A MicroscopeFria mae AbellanoОценок пока нет
- Ebarra Pumps PDFДокумент99 страницEbarra Pumps PDFJudy Ann CastorОценок пока нет
- Bunsen BurnerДокумент17 страницBunsen BurnerMaiza TiborОценок пока нет
- ISo Pump Performance Data 60 HZДокумент33 страницыISo Pump Performance Data 60 HZRon Don jr0% (1)
- Macro Photography Cheat SheetДокумент1 страницаMacro Photography Cheat SheetRhiannon MorseОценок пока нет
- National University student explores visual techniquesДокумент4 страницыNational University student explores visual techniquesBeryl JacobaОценок пока нет
- Micro-Para Laboratory Equipment: Microbiology & Parasitology Activities For The BSN StudentsДокумент5 страницMicro-Para Laboratory Equipment: Microbiology & Parasitology Activities For The BSN StudentsJill Cabasag BustaliñoОценок пока нет
- V1 Nexus Template SpreadsheetДокумент299 страницV1 Nexus Template SpreadsheetJabir JabirОценок пока нет
- Zeiss Microscopy From The Very BeginningДокумент66 страницZeiss Microscopy From The Very BeginningCarmen KetОценок пока нет
- EDFAДокумент2 страницыEDFATuấn Tươi TỉnhОценок пока нет
- The Invention of The MicroscopeДокумент1 страницаThe Invention of The MicroscopeMaureen Gabrielle ColinaresОценок пока нет
- Problem Solving Chapter 5 1Документ2 страницыProblem Solving Chapter 5 1Ruuban0% (1)
- The Emancipation of Juan in The World of The Fourth EstateДокумент42 страницыThe Emancipation of Juan in The World of The Fourth EstateMiyaka Galvez EscalanteОценок пока нет