Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Nursing Care Plan Mobility Sample
Загружено:
n2biologyАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Nursing Care Plan Mobility Sample
Загружено:
n2biologyАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
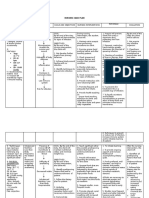
Cypress College Department of Nursing
Nursing Care Plan Subjective Data:
09/15/11 at 0850: Pain level at 7 after walking to bathroom 09/15/11 at 1255: My pain is at a 3 after being medicated
Objective Data:
Dx: Osteoarthritis Surgery: Left Total Knee (Total Joint Anthroplasty) PT: Patient has limited bending Knee bends at 65 CPM machine set at 80 09/15/11 at 0850: Independently ambulate to bathroom and back. 09/15/11 at 1135: Independently ambulate 150ft. with front-wheeled walker Facial grimacing when left leg is moved Cannot lift left leg up while on bed
Nursing Diagnosis: (NANDA)
Impaired mobility r/t loss of integrity of bone structures secondary to surgical procedure as evidenced by inability to ambulate independently
Goal / Expected Outcome(s)
The patient will: 1. Improve mobility As evidenced by: a. Get out of bed independently without assist.
Target Date/Time 09/15/11
b. Ability to ambulate independently with walker 100 feet by 1500
Goal / Expected Outcome(s)
The patient will: 2. Be able to have 90 degrees of flexion in the operative knee upon discharge. As evidenced by: a. b.
Target Date/Time Discharge
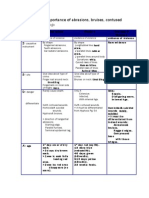
Plan of Care:
Nursing Interventions The nurse will: Monitor VS and pain Q4H, before and after activity Rationale for Nursing Interventions Vital signs and level of pain needs to be assessed before, during and after activity. This evaluates patients activity tolerance and need for medication. (Taylor et al., 2011, p.1050) Effectiveness of Interventions Patients vital signs were taken every 4 hours and before patients appointment with physical therapist and occupational therapist. Pain displayed through facial grimacing and labored breathing when walking without pain medication. Pain is controlled when walking with pain medication. The dorsal-pedal pulse on the left leg was slightly stronger than the right leg. Patient did not verbalize any abnormal sensation in her leg. Mobility on the left leg was limited. Patient has a hard time flexing and
Check circulation, sensation, and mobility (CSM) Q2H
When there is musculoskeletal trauma, especially in the lower leg, there is an increased pressure that compromises the circulation to the area of trauma. The internal pressure results from blood or fluid accumulation. Pressure on the nerve may cause a tingling or numb sensation on the lower leg. Checking the CSM helps identify post-surgical complicationswhich may affect
Nursing Interventions The nurse will: M Medicate patient Q4H/PRN before activity
Effectiveness of Interventions patients mobility. (Ignatavicus & Workman, 2006, p. 1191) extending her leg. Managing of pain level help achieve comfort level goal as well as encouraging patients agreement to take on recommended activity. (Ignatavicus & Workman, 2006, p. 349) Patient c/o pain of 7 when ambulating at 0850 to bathroom without medication. She refused to continue walking. When medications were given an hour before her physical and occupational therapy session, patient showed more compliance as evidenced by walking 150ft. Before the patient stands up, she sits on the edge of the bed to acclimate herself.
Rationale for Nursing Interventions
Once the patient is standing, evaluate patient for orthostatic hypotension.
Place ted hose on patient. Take them off after 8 hours and wait for one hour before putting it back on.
Turn on sequential compression device(SCD) per MD order.
Orthostatic hypotension usually occurs when a person experience dizziness and lightheadedness when she moves from a supine, flat position to a sitting or standing position. When a patient exhibit orthostatic hypotension, they are very susceptible to falling. Falling is very dangerous as it is the leading cause of injury fatality. (Ignatavicus & Workman, 2006, p. 691) (Taylor, Lillis, LeMone, and Lynn, 2011, p.619) Immobility makes patients susceptible to thrombi formation due to venous stasis. This occurs because calcium leaves the bones and enters the blood stream. This increase blood coagulation and leads to an increase risk of thrombus formation. To prevent thrombus formation, ted hose are placed. TED hoses are compression socks that help maintain pressure on the patients lower extremity.( Ignatavicus & Workman, 2006, p. 812) (Taylor, Lillis, LeMone, and Lynn, 2011, p.843) SCD enhances blood flow and venous return on the legs by applying pressure on the legs in increments. Pressure is is caused by the air pump that is connected to the extremity sleeves. It is used to decrease the risk of thromboplebitis after surgery because patients are not as active. (Taylor, Lillis, LeMone, and Lynn, 2011, p.844)
Ted hose were place on the patient and were taken off every eight hours.
Patient was placed on SCD when she is laying in bed. Only take it off when she is ambulating.
Nursing Interventions The nurse will: Encourage patient to ambulate Q4H as tolerate
Rationale for Nursing Interventions
Physical activity reduces risk of cardiovascular and respiratory complications after an operation. It is imperative that patient engage in physical activity to achieve optimal recovery. (Taylor, Lillis, LeMone, and Lynn, 2011, p.883) Reposition patient Q2H/PRN. Although dislocation is not a big concern for total knee Make sure patient is in proper replacement and special repositioning is not important, body alignment. Use pillows repositioning prevents pressure sores and maintains PRN to alleviate pressure alignment. The knee should be in neutral position and not sores. rotated internally or externally. Correct alignment promotes proper healing.(Ignatavicus & Workman, 2006, p. 390) Encourage patient to discuss Discussion helps relieves anxiety towards mobility. This any concerns related to also helps establish a helping relationship between nurse ambulation and patient. (Taylor, Lillis, LeMone, and Lynn, 2011, p. 1051) Place ice pack on site of Swelling and bruising is common at the surgical site. incision per MD order. Placing ice packs over the surgical site will decrease swelling. (Ignatavicus & Workman, 2006, p. 390) Teach patient how to use The incentive spirometer is used to induce deep breathing incentive spirometer 10 times because the lungs completely expand. This will prevent over an hour while awake. pulmonary problems such pneumonia. To use the incentive spirometer, the patient must seal lips around the mouthpiece and inhale. She must hold her breath 3 to 5 seconds. Repeat cycle at least three times. (Ignatavicus & Workman, 2006, p. 309) Assess dressing for bleeding Dressing should remain dry and intact. Drainage amount or other drainage Q4H. Ensure and color should be monitored. Large amount of dressing does not constrict sanguineous drainage indicates a possible internal circulation or sensation. bleeding. (Ignatavicus & Workman, 2006, p. 346)
Effectiveness of Interventions Patient got up out of bed at least twice every 4 hour. Patient engages in physical activity with OT and PT. She ambulates to the bathroom with oversight. The patient kept her legs in neutral position unless when her left leg is on the CPM machine. Patient c/o pain when leg is not in correctly placed on the CPM machine. Patient verbalized her worries about ambulation when she is out of the hospital. The ice machine on the floor was broken. Ice pack was placed on surgical site at 1420. Patient already knew how to use the incentive spirometer already. However, the importance of using it was reinforced. Patient used the spirometer throughout the shift when laying in bed. Dressing and surrounding area was dry and intact. There was blood on patients shorts but no sign of bleeding at the actual surgical site. Drainage was not visible. Patient followed surgeons protocol. Left knee was on CPM
Place continuous passive motion (CPM) machine per
The CPM machine keeps the prosthetic knee in motion and prevents the formation of scar tissue. Scar tissue can
Nursing Interventions The nurse will: MD order.
Rationale for Nursing Interventions obstruct mobility and aggravate postoperative pain. The degree of knee flexion gradually increases. (Ignatavicus & Workman, 2006, p. 390)
E D
Instruct family member, significant other or caregiver to help patient for 4-6 weeks after discharge.
Patient is not fully recovered once they are discharged. It is imperative that someone is home to with the patient at all times because it is the time where they need the most help. Patient is susceptible to falling and hurting herself if there is no one assisting her. (Ignatavicus & Workman, 2006, p. 393)
Effectiveness of Interventions machine for 2 hours and was off for 2 hours before repeating the cycle. At 1420 on 09/15/11, OT set machine at 80 of flexion and full extension (0). Patient stated that her husband(retired) will be at home at all times to help her with activities.
Evaluation of Expected Outcome(s):
As of Date:09/15/11 Time: 1645
Discuss if the goal/expected outcome(s) was met, not met or partially met. Describe actual patient changes assessed that indicate progress towards expected outcomes. Discuss your recommendations for further nursing care planning.
1. a. The expected outcome was met. Patient was able to get out of bed without assistance. She utilizes her right leg to assist her left leg when she swivels her body to the edge of the bed. She used her upper body strengths and right leg to help her get up on the walker. b. The expected outcome was met. Patient was able to independently ambulate down the hallway and back with a front-wheeled walker. Patient exhibit a steady gait. The OT stated that patient has the opportunity to either go home the following day (09/16/11) or stay at the hospital longer. Her physical status lies between the two options. Patient stated that she can only ambulate with pain medication. Patient shows progress in ambulation when she has pain medication an hour prior to activity.
Reinforce the need of activity to the patient. Encourage patient to walk 200ft. with the assistance of a front wheeled walker after dinner time. 2. The goal was partially met. Patient was able to flex her operative knee to 65. She displays progress in flexing her operative knee. Patient will continue to engage in physical exercises. Instruct her to use the CPM machine to increase her ability to flex her operative knee. Patient will be able to have 90 of flexion on operative knee upon discharge.
References: (APA)
Ignativicus, D.D. & Workman, M.L (2006) Medical-surgical nursing: Critical thinking for collaborative care (4th ed.) Philadelphia:W.B Saunders Company Taylor, C, Lillis, C, LeMone, P, & Lynn, P(2011). Fundamentals of nursing:the art and science of nursing care. (7 ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Wiliams & Wilkins.
Вам также может понравиться
- 22 Ways To Kill A Man With Your BareДокумент3 страницы22 Ways To Kill A Man With Your Barecourtney80% (5)
- 150 Tips and Tricks for New Nurses: Balance a hectic schedule and get the sleep you need…Avoid illness and stay positive…Continue your education and keep up with medical advancesОт Everand150 Tips and Tricks for New Nurses: Balance a hectic schedule and get the sleep you need…Avoid illness and stay positive…Continue your education and keep up with medical advancesРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For "End of Life - Hospice Care"Документ9 страницNursing Care Plan For "End of Life - Hospice Care"jhonroks89% (19)
- Knee Replace Care PlanДокумент11 страницKnee Replace Care PlanLaura Romness100% (2)
- Hammer Pulse TempДокумент12 страницHammer Pulse Temppeter911cm100% (1)
- First-Year Nurse: Advice on Working with Doctors, Prioritizing Care, and Time ManagementОт EverandFirst-Year Nurse: Advice on Working with Doctors, Prioritizing Care, and Time ManagementРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- Construction Risk Assessment Form Example PDFДокумент3 страницыConstruction Risk Assessment Form Example PDFZaka Ur RehmanОценок пока нет
- Concept Map PEДокумент3 страницыConcept Map PERobert MariasiОценок пока нет
- Nursing Assessment Cheat SheetДокумент7 страницNursing Assessment Cheat Sheetanne009100% (2)
- Post Operative Nursing CareДокумент5 страницPost Operative Nursing CareJenjen Cortey100% (4)
- Nursing care plan for perioperative knee replacement patientДокумент31 страницаNursing care plan for perioperative knee replacement patientStephen Paul100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For UTIДокумент3 страницыNursing Care Plan For UTIbeatriceОценок пока нет
- Nursing Diagnosis With Related FactorsДокумент15 страницNursing Diagnosis With Related FactorsArnulfo Armamento87% (23)
- Gerontological Nursing: Scope and Standards of Practice, 2nd EditionОт EverandGerontological Nursing: Scope and Standards of Practice, 2nd EditionОценок пока нет
- Developing A Coaching StrategyДокумент6 страницDeveloping A Coaching StrategyChady JasonОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plans WideДокумент232 страницыNursing Care Plans WideTomohiro Horie100% (5)
- SbarДокумент2 страницыSbarbojums100% (2)
- Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Part I: Emergency Department (ED)Документ8 страницNovel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Part I: Emergency Department (ED)Uzumaki K100% (1)
- Head To Toe Narrative ChartingДокумент1 страницаHead To Toe Narrative ChartingDianne Macaraig100% (3)
- Ergonomics in ConstructionДокумент5 страницErgonomics in ConstructionZeeshan BajwaОценок пока нет
- BF GuidelinesДокумент89 страницBF Guidelinesnzi_eX6943Оценок пока нет
- 3705 0901 84 CS14 CrawlerДокумент34 страницы3705 0901 84 CS14 Crawleredwin100% (2)
- Nursing Care PlanДокумент12 страницNursing Care Planzsazsageorge86% (21)
- Small Bowel Obstruction Care PlanДокумент11 страницSmall Bowel Obstruction Care PlanKatie YarnellОценок пока нет
- Attorney General Response To Anthony Fox ConvictionДокумент25 страницAttorney General Response To Anthony Fox ConvictionThereseApelОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plans for Deficient Fluid VolumeДокумент6 страницNursing Care Plans for Deficient Fluid VolumeLalaine RomeroОценок пока нет
- Narrative ChartДокумент5 страницNarrative Charthady920100% (1)
- Community Focused Nursing: Passbooks Study GuideОт EverandCommunity Focused Nursing: Passbooks Study GuideОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan GuideДокумент4 страницыNursing Care Plan Guidemarie99% (134)
- Key Issues Desired Outcomes Interventions Actual OutcomesДокумент4 страницыKey Issues Desired Outcomes Interventions Actual OutcomesAngel FiloteoОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan WordДокумент115 страницNursing Care Plan WordKi C PungitОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care PlanДокумент10 страницNursing Care PlanGinel Laquiores100% (1)
- Concept Map StrokeДокумент1 страницаConcept Map StrokeMary GiuntiniОценок пока нет
- Edith Jacobson Care PlanДокумент10 страницEdith Jacobson Care PlanKarina Rodriguez100% (3)
- Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of My Nctvet CertificationДокумент25 страницSubmitted in Partial Fulfillment of My Nctvet CertificationJaii100% (1)
- Essential Stroke Nursing GuideДокумент5 страницEssential Stroke Nursing GuideAshleigh Johnstone100% (1)
- A Handbook for Student Nurses, 201617 edition: Introducing key issues relevant for practiceОт EverandA Handbook for Student Nurses, 201617 edition: Introducing key issues relevant for practiceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Nursing Care PlanДокумент53 страницыNursing Care Planztvill88% (26)
- Self-Care for Nurses: 100+ Ways to Rest, Reset, and Feel Your BestОт EverandSelf-Care for Nurses: 100+ Ways to Rest, Reset, and Feel Your BestОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan For "DYSRHYTHMIAS"Документ12 страницNursing Care Plan For "DYSRHYTHMIAS"jhonroks79% (14)
- Therapeutic Communication Techniques 2Документ3 страницыTherapeutic Communication Techniques 2Marc King MagsambolОценок пока нет
- Care Plan For Bowel ResectionДокумент4 страницыCare Plan For Bowel Resectionviki840488% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan 6 Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент9 страницNursing Care Plan 6 Impaired Gas Exchangedbryant0101100% (12)
- Gordon'sДокумент2 страницыGordon'sCham Rafaela ConeseОценок пока нет
- Peripheral Vascular Disease NursingДокумент13 страницPeripheral Vascular Disease NursingCatlyn Chatpman100% (1)
- ElectrosurgeryДокумент5 страницElectrosurgeryMustafaОценок пока нет
- Teaching Plan For DiabetesДокумент4 страницыTeaching Plan For DiabetesanrefОценок пока нет
- Heart Nursing: Learn, Grow & Succeed in the First Year of PracticeОт EverandHeart Nursing: Learn, Grow & Succeed in the First Year of PracticeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Managing Impaired Gas Exchange in an Elderly COPD PatientДокумент23 страницыManaging Impaired Gas Exchange in an Elderly COPD PatientKaren Joyce Costales Magtanong100% (3)
- Hip Fracture Nursing Care PlanДокумент6 страницHip Fracture Nursing Care PlanRnspeakcom100% (1)
- Urinary Incontinence Nursing ManagementДокумент3 страницыUrinary Incontinence Nursing ManagementRnspeakcomОценок пока нет
- Nursing Case Study Ch46 Med SurgДокумент1 страницаNursing Case Study Ch46 Med SurgPriyal ParikhОценок пока нет
- Neuro Nursing-Seizure DisorderДокумент8 страницNeuro Nursing-Seizure DisorderBell Jose50% (4)
- Disharge Plan Patient'S Outcome Criteria Nursing OrderДокумент2 страницыDisharge Plan Patient'S Outcome Criteria Nursing OrderDianne Loregas SanchezОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care PlanДокумент22 страницыNursing Care PlanjamОценок пока нет
- Altered Bowel EliminationДокумент1 страницаAltered Bowel EliminationneoclintОценок пока нет
- NCPДокумент5 страницNCPSheana TmplОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plans For UTIДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plans For UTIHannah Pin67% (3)
- Nursing Care PlanДокумент10 страницNursing Care PlanSittie Rohaina SabanОценок пока нет
- Risk For Aspiration: Risk For Aspiration: at Risk For Entry of Gastrointestinal Secretions, Oropharyngeal SecretionДокумент6 страницRisk For Aspiration: Risk For Aspiration: at Risk For Entry of Gastrointestinal Secretions, Oropharyngeal SecretionAngie MandeoyaОценок пока нет
- Care Plan Hip Replacement 11-13-14Документ13 страницCare Plan Hip Replacement 11-13-14api-25636238050% (2)
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideОт EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideОценок пока нет
- Comp NEWBN AssessmentДокумент3 страницыComp NEWBN Assessmentn2biologyОценок пока нет
- Domestic Violence Health Fair ProjectДокумент6 страницDomestic Violence Health Fair Projectn2biologyОценок пока нет
- Full Size Cypress RefДокумент15 страницFull Size Cypress Refn2biologyОценок пока нет
- Pharmacology Unit 5Документ19 страницPharmacology Unit 5n2biologyОценок пока нет
- Environmental Safety & Surg Aesepsis Student OutlineДокумент12 страницEnvironmental Safety & Surg Aesepsis Student Outlinen2biologyОценок пока нет
- Communication PrinciplesДокумент2 страницыCommunication Principlesn2biologyОценок пока нет
- Preview of "Unit 5 CVD"Документ29 страницPreview of "Unit 5 CVD"n2biologyОценок пока нет
- CNS Outline Unit 6Документ2 страницыCNS Outline Unit 6n2biologyОценок пока нет
- Medication Math For The Nursing StudentДокумент47 страницMedication Math For The Nursing StudentBryan Paul Mesana UrdasОценок пока нет
- CNS Stimulants Overview Amanda MeyersДокумент10 страницCNS Stimulants Overview Amanda Meyersn2biologyОценок пока нет
- Micro 33 Lab SlidesДокумент1 страницаMicro 33 Lab Slidesn2biologyОценок пока нет
- Mana LawsonДокумент8 страницMana Lawsonchapojnr7Оценок пока нет
- Lecture 1 Chest TraumaДокумент19 страницLecture 1 Chest Traumaj.doe.hex_870% (1)
- Blunt Force Trauma: Slide 1Документ19 страницBlunt Force Trauma: Slide 1Achmad MuflihОценок пока нет
- Foot DropДокумент2 страницыFoot DropSaravanan SridharanОценок пока нет
- General NosologyДокумент13 страницGeneral Nosologyyasingada100% (1)
- Hornsby and Laverick, Goldsborough Signal StationДокумент28 страницHornsby and Laverick, Goldsborough Signal StationIonutz IonutzОценок пока нет
- SC-2103681-ME1a - Manual 660.YTC. (1x6.5kW) .6 M1546-51G K460-4522-12FO-FC-R M9PG-OT-WP-LCBT + DG90-DB120 + 2xDG45 4xM1Документ61 страницаSC-2103681-ME1a - Manual 660.YTC. (1x6.5kW) .6 M1546-51G K460-4522-12FO-FC-R M9PG-OT-WP-LCBT + DG90-DB120 + 2xDG45 4xM1kiên phạm trungОценок пока нет
- Stanley MBX138-MBX608 English User Manual 2-2016Документ62 страницыStanley MBX138-MBX608 English User Manual 2-2016luismdmj100% (1)
- Edx Braquial PlexusДокумент30 страницEdx Braquial PlexusMariana GОценок пока нет
- Trauma Medulla SpinalisДокумент79 страницTrauma Medulla SpinalisiqiqiqiqiqОценок пока нет
- An 1.1 - Introduction Anatomical Terminology DR - GosaiДокумент46 страницAn 1.1 - Introduction Anatomical Terminology DR - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiОценок пока нет
- Ac ManualДокумент18 страницAc Manualim4uim4uim4uОценок пока нет
- Dutchess County: Traffic Safety DataДокумент30 страницDutchess County: Traffic Safety DataDaily FreemanОценок пока нет
- Effect of Mcconnell Taping On Pain, Rom & Grip Strength in Patients With Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex InjuryДокумент9 страницEffect of Mcconnell Taping On Pain, Rom & Grip Strength in Patients With Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex InjuryDr. Krishna N. SharmaОценок пока нет
- Göran Kropp - Death in The Couleé, by Erden Eruc 10 May 2002Документ4 страницыGöran Kropp - Death in The Couleé, by Erden Eruc 10 May 2002Mayayo: Carrerasdemontana.comОценок пока нет
- Rnbe-16-0312-Nae High Output Sell SheetДокумент2 страницыRnbe-16-0312-Nae High Output Sell SheetYacine Tarik AizelОценок пока нет
- 113034153s 45971675 254009105 Causeeffect Essay Final DraftДокумент6 страниц113034153s 45971675 254009105 Causeeffect Essay Final Draftapi-320097699Оценок пока нет
- Medico-Legal Importance of WoundsДокумент3 страницыMedico-Legal Importance of Woundsapi-383014680% (5)
- Basic anatomical terminology guideДокумент30 страницBasic anatomical terminology guideNur ShamrinzОценок пока нет
- Oms - New WhoДокумент77 страницOms - New WhoLuis Ferdinand Dacera-Gabronino Gamponia-NonanОценок пока нет