Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
MiraLax (Polyethylene Glycol)
Загружено:
E100%(2)100% нашли этот документ полезным (2 голоса)
24K просмотров1 страницаMiraLax glycol is an osmotic agent, drawing water into the lumen of the GI tract. Common side effects include abdominal bloating, cramping, flatulence, nausea. Fludrocortisone, Hydrocortisone: The overuse or abuse of laxatives can cause significant loss of medication electrolytes and potentiate the risk of hypokalemia.
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
MiraLax (polyethylene glycol)
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документMiraLax glycol is an osmotic agent, drawing water into the lumen of the GI tract. Common side effects include abdominal bloating, cramping, flatulence, nausea. Fludrocortisone, Hydrocortisone: The overuse or abuse of laxatives can cause significant loss of medication electrolytes and potentiate the risk of hypokalemia.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
100%(2)100% нашли этот документ полезным (2 голоса)
24K просмотров1 страницаMiraLax (Polyethylene Glycol)
Загружено:
EMiraLax glycol is an osmotic agent, drawing water into the lumen of the GI tract. Common side effects include abdominal bloating, cramping, flatulence, nausea. Fludrocortisone, Hydrocortisone: The overuse or abuse of laxatives can cause significant loss of medication electrolytes and potentiate the risk of hypokalemia.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 1
Clinical Medications Worksheets
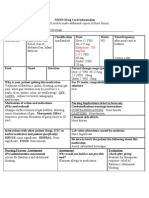
Generic Name TradeName Classification Dose Route Time/frequenc
polyethylene MiraLax Laxatives, osmotics 1 packet PO y
glycol qd
Peak Onset Duration Normal dosage range
2-4 days Unknown Unknown 17g. (One heaping teaspoon) in 8 oz. of water may be
used for up to two weeks
Why is your patient getting this medication For IV meds, compatibility with IV drips and/or
Constipation solutions
N/A
Mechanism of action and indications Nursing Implications (what to focus on)
Acts as an osmotic agent, drawing water into the Contraindications/warnings/interactions
lumen of the GI tract. Indicated for evacuation of the GI obstruction, gastric retention, toxic colitis,
GI tract without water or electrolyte imbalance. Megacolon. Use cautiously in abdominal pain of
uncertain cause, particularly if accompanied by fever.
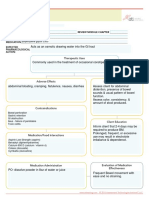
Common side effects
Abdominal bloating, cramping, flatulence, nausea
Interactions with other patient drugs, OTC or Lab value alterations caused by medicine
herbal medicines (ask patient specifically) None known for this drug
Fludrocortisone, Hydrocortisone: The overuse or
Be sure to teach the patient the following about this
abuse of laxatives can cause significant loss of
medication
electrolytes and potentiate the risk of hypokalemia
Inform patient that 2-4 days may be required to produce a
associated with corticosteroid therapy.
bowel movement. Should not be used for more than 2
Corticosteroids promote the retention of sodium and
wk. Prolonged, frequent, or excessive use may result in
water and the excretion of potassium. Although these
electrolyte imbalance and laxative dependence. Advise
effects are primarily associated with
patient to notify health care professional if unusual
mineralocorticoids like fludrocortisone, they may
cramps, bloating, or diarrhea occurs
also occur with higher dosages of glucocorticoids or
adrenocorticotropic agents, particularly if given
systemically for longer than brief periods.
Demadex: The chronic use or abuse of laxatives may
potentiate the pharmacologic effects of diuretics.
Laxatives can cause significant losses of fluid and
electrolytes, including sodium, potassium,
magnesium and zinc, and these effects may be
additive to those of diuretics.
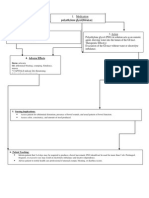
Nursing Process- Assessment Assessment Evaluation
(Pre-administration assessment) Why would you hold or not give this med? Check after giving
Assess patient for abdominal distention, Diarrhea, obstruction. A soft, formed bowel
presence of bowel sounds, and usual movement.
pattern of bowel function.
Вам также может понравиться
- Drug MiralaxДокумент1 страницаDrug MiralaxSrkocher100% (1)
- Drug Cards Milk of MagnesiaДокумент1 страницаDrug Cards Milk of MagnesiaAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Colace (Docusate Sodium)Документ1 страницаColace (Docusate Sodium)E100% (1)
- Docusate Sodium (Colace)Документ2 страницыDocusate Sodium (Colace)E100% (1)
- Drug Card BenadrylДокумент1 страницаDrug Card BenadrylAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- NIOIN Drug Card OB-SimethiconeДокумент1 страницаNIOIN Drug Card OB-SimethiconeDavid McHughОценок пока нет
- Protonix (Pantoprazole)Документ1 страницаProtonix (Pantoprazole)CassieОценок пока нет
- DilaudidДокумент2 страницыDilaudidAdrianne Bazo100% (2)
- Drug Card ToradolДокумент2 страницыDrug Card ToradolAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Promethazine (Phenergan)Документ1 страницаPromethazine (Phenergan)Adrianne BazoОценок пока нет
- Coumadin WarfarinДокумент1 страницаCoumadin WarfarinSheri490100% (1)
- Drug Senna Drug CardДокумент1 страницаDrug Senna Drug CardSrkocher100% (2)
- Ondansetron (Zofran)Документ1 страницаOndansetron (Zofran)Cassie100% (1)
- Zosyn Drug CardДокумент1 страницаZosyn Drug CardSheri490Оценок пока нет
- Ditropan Drug CardДокумент2 страницыDitropan Drug CardBenОценок пока нет
- Drug Card Motrin 800mgДокумент2 страницыDrug Card Motrin 800mgAdrianne BazoОценок пока нет
- RocephinДокумент1 страницаRocephinCassieОценок пока нет
- Methylprednisolone (Solu Medrol)Документ3 страницыMethylprednisolone (Solu Medrol)Adrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Drug Card LasixДокумент2 страницыDrug Card LasixAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- NPH Insulin NPHДокумент1 страницаNPH Insulin NPHE100% (1)
- Atrovent (Ipratropium)Документ1 страницаAtrovent (Ipratropium)E100% (2)
- Drug NeurontinДокумент1 страницаDrug NeurontinSrkocher100% (2)
- Levaquin Drug CardДокумент1 страницаLevaquin Drug CardSheri490100% (1)
- LantusДокумент1 страницаLantusCassie100% (4)
- Sennosides (Senokot)Документ1 страницаSennosides (Senokot)E100% (1)
- Plavix Clopidogrel Drug CardДокумент1 страницаPlavix Clopidogrel Drug CardSheri490100% (1)
- Protonix (Pantoprazole)Документ1 страницаProtonix (Pantoprazole)EОценок пока нет
- Cephalexin (Keflex)Документ1 страницаCephalexin (Keflex)EОценок пока нет
- Manage Insulin Therapy SafelyДокумент3 страницыManage Insulin Therapy SafelyTri Purma SariОценок пока нет
- AtroventДокумент2 страницыAtroventKatie McPeekОценок пока нет
- AtroventДокумент1 страницаAtroventSheri490100% (1)
- Drug Card AcetaminophenДокумент1 страницаDrug Card AcetaminophenAdrianne Bazo100% (3)
- DigoxinДокумент1 страницаDigoxinSheri490100% (2)
- Enoxaparin (Lovenox)Документ1 страницаEnoxaparin (Lovenox)EОценок пока нет
- Keppra (Levetiracetam)Документ2 страницыKeppra (Levetiracetam)E100% (1)
- ErythromycinДокумент6 страницErythromycinapi-3797941100% (1)
- LorazepamДокумент1 страницаLorazepamMichael KuzbytОценок пока нет
- Drug MetoprololДокумент1 страницаDrug MetoprololSrkocher0% (1)
- Lopressor (Metoprolol) 100mgДокумент2 страницыLopressor (Metoprolol) 100mgAdrianne Bazo100% (2)
- Mira LaxДокумент1 страницаMira LaxCassieОценок пока нет
- Drug Study - LactuloseДокумент2 страницыDrug Study - LactuloseCath Bril100% (1)
- FurosemideДокумент1 страницаFurosemideCassie100% (1)
- Micro K (Potassium Chloride)Документ2 страницыMicro K (Potassium Chloride)EОценок пока нет
- Drug Card SennaДокумент1 страницаDrug Card SennaAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Drug Potassium ChlorideДокумент1 страницаDrug Potassium ChlorideSrkocherОценок пока нет
- Zaroxolyn MetolazoneДокумент1 страницаZaroxolyn MetolazoneCassieОценок пока нет
- Aldactone SpironlactoneДокумент1 страницаAldactone SpironlactoneCassie100% (1)
- Dulcolax SuppositoryДокумент1 страницаDulcolax SuppositoryAdrianne BazoОценок пока нет
- Senokot-S (Senna Concentrate 8.6mg + Docusate Sodium 50mg)Документ2 страницыSenokot-S (Senna Concentrate 8.6mg + Docusate Sodium 50mg)E100% (1)
- Drug Map Polyethylene Glycol (MiraLax)Документ1 страницаDrug Map Polyethylene Glycol (MiraLax)EricaОценок пока нет
- Prescribing Information: 1. Name of The Medicinal ProductДокумент5 страницPrescribing Information: 1. Name of The Medicinal Productddandan_20% (1)
- Dulcolax Stool Softener Supp (Docusate Sodium)Документ2 страницыDulcolax Stool Softener Supp (Docusate Sodium)EОценок пока нет
- Florinef (Fludrocortisone)Документ3 страницыFlorinef (Fludrocortisone)E100% (1)
- Potassium ChlorideДокумент2 страницыPotassium ChlorideAdrianne BazoОценок пока нет
- Dyrenium Triamterene Drug CardДокумент1 страницаDyrenium Triamterene Drug CardSheri490Оценок пока нет
- Dilantin PhenytoinДокумент2 страницыDilantin PhenytoinCassieОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент4 страницыDrug StudyCheriz LukbanОценок пока нет
- Solu-Cortef (Hydrocortisone)Документ3 страницыSolu-Cortef (Hydrocortisone)E100% (2)
- Drug Potassium Chloride KCLДокумент1 страницаDrug Potassium Chloride KCLSrkocher100% (3)
- AcetazolamideДокумент1 страницаAcetazolamideKyuSheenОценок пока нет
- Pyelonephritis 1 Running Head: PYELONEPHRITISДокумент4 страницыPyelonephritis 1 Running Head: PYELONEPHRITISEОценок пока нет
- Left-Side CHF PathoДокумент5 страницLeft-Side CHF PathoEОценок пока нет
- Congestive Heart FailureДокумент4 страницыCongestive Heart FailureEОценок пока нет
- Chemical Burns PathoДокумент2 страницыChemical Burns PathoEОценок пока нет
- Hyponatremic Dehydration PathoДокумент4 страницыHyponatremic Dehydration PathoEОценок пока нет
- Autonomic DysreflexiaДокумент2 страницыAutonomic DysreflexiaEОценок пока нет
- Hyperparathyroidism PathoДокумент2 страницыHyperparathyroidism PathoEОценок пока нет
- Iron Deficiency Anemia PathoДокумент6 страницIron Deficiency Anemia PathoEОценок пока нет
- Influenza B PathoДокумент4 страницыInfluenza B PathoEОценок пока нет
- Congestive Heart Failure-ABДокумент3 страницыCongestive Heart Failure-ABEОценок пока нет
- Acute Pancreatitis PathoДокумент5 страницAcute Pancreatitis PathoEОценок пока нет
- Bowel Resection PathoДокумент7 страницBowel Resection PathoEОценок пока нет
- Subluxation c6c7 Short PathoДокумент1 страницаSubluxation c6c7 Short PathoEОценок пока нет
- Pneumonia Short PathoДокумент2 страницыPneumonia Short PathoEОценок пока нет
- Campral (Acamprosate Calcium)Документ1 страницаCampral (Acamprosate Calcium)E100% (1)
- Clinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsДокумент1 страницаClinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsEОценок пока нет
- Buspar (Buspirone)Документ1 страницаBuspar (Buspirone)EОценок пока нет
- Pancreatitis Short PathoДокумент2 страницыPancreatitis Short PathoEОценок пока нет
- Geodon (Ziprasidone)Документ2 страницыGeodon (Ziprasidone)EОценок пока нет
- Prozac (Fluoxetine) 40mgДокумент1 страницаProzac (Fluoxetine) 40mgEОценок пока нет
- Lexapro (Escitalopram Oxalate)Документ2 страницыLexapro (Escitalopram Oxalate)EОценок пока нет
- Zosyn (Piperacillin/tazobactram)Документ2 страницыZosyn (Piperacillin/tazobactram)E67% (3)
- ZofranДокумент1 страницаZofranKatie McPeek0% (1)
- Silvadene (Silver Sulfadiazine)Документ1 страницаSilvadene (Silver Sulfadiazine)EОценок пока нет
- FiberCon (Polycarbophil)Документ1 страницаFiberCon (Polycarbophil)EОценок пока нет
- Reglan (Metoclopramide)Документ3 страницыReglan (Metoclopramide)E100% (1)
- Darvocet (Propoxyphene Napsylate/Acetaminophen)Документ1 страницаDarvocet (Propoxyphene Napsylate/Acetaminophen)EОценок пока нет
- Theragran (Multiple Vitamins)Документ3 страницыTheragran (Multiple Vitamins)EОценок пока нет
- Florinef (Fludrocortisone)Документ3 страницыFlorinef (Fludrocortisone)E100% (1)
- Keppra (Levetiracetam)Документ2 страницыKeppra (Levetiracetam)E100% (1)
- AbdomenДокумент7 страницAbdomenAbhishek DussaОценок пока нет
- Medication - ALT-Template Polythene GlycolДокумент1 страницаMedication - ALT-Template Polythene GlycolNancyAmissahОценок пока нет
- L. plantarum 299v Reduces Inflammation and Normalizes Motility in IBS Mouse ModelДокумент6 страницL. plantarum 299v Reduces Inflammation and Normalizes Motility in IBS Mouse ModelMarin GregurinčićОценок пока нет
- MIMS 1a - 1eДокумент6 страницMIMS 1a - 1eJuvy Anne LozanoОценок пока нет
- Mira LaxДокумент1 страницаMira LaxCassieОценок пока нет
- Reflexes in The GutДокумент2 страницыReflexes in The GutJeffrey TseОценок пока нет
- HH-I-70 VP Shunt - Care at HomeДокумент2 страницыHH-I-70 VP Shunt - Care at HomeIbraheim AlwaraqiОценок пока нет
- The History of Hiatal Hernia SurgeryДокумент9 страницThe History of Hiatal Hernia SurgeryDaniel PredaОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan HemorroidsДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan Hemorroidsderic77% (22)
- Digestive System Lab PDFДокумент2 страницыDigestive System Lab PDFFirman Agus GeaОценок пока нет
- No Jenis Keterangan 1. Air Under The Diaphragm: Nama: Adilah Zatil Kurnia Rahma AfifahДокумент6 страницNo Jenis Keterangan 1. Air Under The Diaphragm: Nama: Adilah Zatil Kurnia Rahma AfifahMona Indah PutrianiОценок пока нет
- Eucarbon CompositionДокумент1 страницаEucarbon Compositionit8777Оценок пока нет
- Helicobacter PyloriДокумент12 страницHelicobacter PylorigjaenОценок пока нет
- Bulk Forming PurgativesДокумент12 страницBulk Forming PurgativesabcdОценок пока нет
- Defecography: Technique, Interpretation, and Current Use: Arden M. Morris and Susan C. ParkerДокумент14 страницDefecography: Technique, Interpretation, and Current Use: Arden M. Morris and Susan C. ParkerSuraj KurmiОценок пока нет
- JatamansiДокумент2 страницыJatamansiDinesh Joshi100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for DiarrheaДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan for DiarrheaBert GasalОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan for Patient with ConstipationДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan for Patient with ConstipationAbby GonzalesОценок пока нет
- AbdomenДокумент31 страницаAbdomenEuscelle Grace LimenОценок пока нет
- NEJM Testosterone For Low Libido - 2009Документ2 страницыNEJM Testosterone For Low Libido - 2009Guillermo CorreaОценок пока нет
- Assessment of Digestive and Gi FunctionДокумент3 страницыAssessment of Digestive and Gi FunctionEmi EspinoОценок пока нет
- Keerai and Its Uses - Tamilnadu Home Remedies & Beauty TipsДокумент4 страницыKeerai and Its Uses - Tamilnadu Home Remedies & Beauty TipsNirvanajunctureОценок пока нет
- Pyloric StenosisДокумент46 страницPyloric Stenosishayssam rashwan81% (16)
- A Homeopathic Approach To Inflammatory Bowel Disease (Crohn's and Colitis)Документ7 страницA Homeopathic Approach To Inflammatory Bowel Disease (Crohn's and Colitis)Saad MasoodОценок пока нет
- MiraLax (Polyethylene Glycol)Документ1 страницаMiraLax (Polyethylene Glycol)E100% (2)
- 02 DyspepsiaДокумент42 страницы02 Dyspepsiaacatrinei_daniela_2Оценок пока нет
- Duodenal UlcerДокумент1 страницаDuodenal UlcerNeferterieManguinaoVillanueva100% (1)
- Gastrointestinal System Drug GuideДокумент33 страницыGastrointestinal System Drug GuideleonОценок пока нет
- Colostomy and Nursing CareДокумент63 страницыColostomy and Nursing CareSangeeta BSRОценок пока нет
- 1 OMD, Indikasi, Dan Mekanisme Rujukan PanoramicДокумент57 страниц1 OMD, Indikasi, Dan Mekanisme Rujukan PanoramicDian KafahasindayaОценок пока нет