Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
1
Загружено:
Bhashkar Bhawani NandanИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
1
Загружено:
Bhashkar Bhawani NandanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
1. How Cavitation can be eliminated in a Pump? Cavitation means bubbles are forming in the liquid.
To avoid Cavitation, we have to increase the Pump size to One or Two Inch; To increase the pressure of the Suction Head, or Decrease the Pump Speed.
2. Which pump is more efficient Centrifugal pump or Reciprocating pump? Centrifugal pump. Because flow rate is higher compared to reciprocating pump. Flow is smooth and it requires less space to install. Lower initial cost and lower maintenance cost.
3. Why Centrifugal Pump is not called as a Positive Displacement Type of Pump? The centrifugal has varying flow depending on pressure or head, whereas the Positive Displacement pump has more or less constant flow regardless of pressure. Likewise viscosity is constant for positive displacement pump where centrifugal pump have up and down value because the higher viscosity liquids fill the clearances of the pump causing a higher volumetric efficiency. When there is a viscosity change in supply there is also greater loss in the system. This means change in pump flow affected by the pressure change. One more example is, positive displacement pump has more or less constant efficiency, where centrifugal pump has varying efficiency rate.
4. Why the centrifugal pump is called high discharge pump? Centrifugal pump is a kinetic device. The centrifugal pump uses the centrifugal force to push out the fluid. So the liquid entering the pump receives kinetic energy from the rotating impeller. The centrifugal action of the impeller accelerates the liquid to a high velocity, transferring mechanical (rotational) energy to the liquid. So it discharges the liquid in high rate. It is given in the following formulae: Centrifugal force F= (M*V2)/R. Where, M-Mass V-Velocity R-Radius
5. Why cavitation will occur in Centrifugal Pumps and not in Displacement pumps? The formation of cavities (or bubbles) is induced by flow separation, or non-uniform flow velocities, inside a pump casing. In centrifugal pumps the eye of the pump impeller is smaller than the flow area of pipe. This decrease in flow area of pump results in increase in flow rate. So pressure drop happened between pump suction and the vanes of the impeller. Here air bubbles or cavities are formed because of liquid vapour due to increase in temperature in impeller. This air bubbles are transmitted to pump which forms cavitation. THE DEMINGS PHILOSOPHY
Dr. W. Edward-Deming was a protege of Dr. Walter Shewhart, who pioneered statistical process control (SPC) at Bell Laboratories. He Spent one year studying under Sir Ronald Fisher, who pioneered design of experiments. Dr. Deming is credited with providing the foundations of the Japanese quality miracle and resurgence as an economic power. He developed the following 14 points as a theory for management for improvement of quality, productivity and competitive position.
1. Create and publish the Aims and Purposes of the Organization Management must demonstrate constantly their commitments to this statement. It must include investors, customers, suppliers, employees, the community and a quality philosophy. Organization must develop a long-term view of at least 10 years and plan to stay in business by setting long-range goals. Resources must be allocated for research, training and continuing education to achieve the goals. A family organizational philosophy is developed to send the message that every one is part of the organization. 2. Learn the New Philosophy Top management and every one must learn the new philosophy. Organizations must seek never ending improvement and refuse to accept non conformance customer satisfaction is the number one priority, because dissatisfied customers will not continue to purchase non confirming products and service. Every one in the organization, including the union, must be involved in the quality journey and change his or her attitude about quality. 3. Understand the Purpose of Inspection Management must understand that the purpose of inspection is to improve the process and reduce its cost. Statistical evidence is required of self and supplier every effort should be made to reduce and then eliminate acceptance sampling. 4. Stop Awarding Business based on Price Alone The organization must stop awarding business based on the low bid, because price has no-meaning without quality. The goal is to have single suppliers for each item to develop a long-term relationship of loyalty and trust thereby providing improved products and service. 5. Improve Constantly and forever the System Management must take more responsibility for problems by actively finding and correcting. Problems so that quality and productivity are continually and permanently improved and costs are reduced. The focus is on preventing problems before they happen variation is expected but these must be a continual striving for its reduction using control charts. 6. Institute Training Each employee must be oriented to the organization philosophy of commitment to never-ending improvements management must allocate resources to train employees to perform their jobs in the best manner possible. 7. Teach and Institute Leadership Improving supervision is managements responsibility. They must provide supervision with training in statistical methods and these 14 points so the new philosophy can be implemented. Instead of focusing on a negative. Fault-finding atmosphere, supervisors should create a positive, supportive one where pride in workmanship can flourish. 8. Drive out fear, Create Trust, and Create a Climate for Innovation Management must encourage open, effective communication and teamwork. Fear is caused by a general feeling of being powerless to control important aspects of ones life. It is caused by a lack of Job security, possible physical harm, performance appraisals, ignorance of organization goals, poor supervision and not knowing the job. Driving fear out of the work place involves managing for success. When people are treated with density, fear can be eliminated and people will work for the general good of the organization. In this climate, they will provide ideas for improvement. 9. Optimize the Efforts of Teams, Groups and Staff Areas Management must optimize the efforts of teams, work groups and staff areas to achieve the aims and purposes of the organization. Barriers exist internally among levels of management, among departments, within departments and among shifts. To break down the barriers, management will need a long-term perspective. All the different areas must work together. Attitudes need to be changed ; communication channels opened project teams organized and training in team work implemented. 10. Eliminate Exhortations for the Work Forces Exhortations that ask for increased productivity without providing specific improvement methods can handicap an organizations. They do nothing but express managements desires. They do not produce a better product or service, because the workers are limited by the system. 11. (a) Eliminate Numerical Quotas for the Work Force
Instead of quotas, management must learn and Institute methods for improvement. Quotas and work standards focus on quantity rather than quality. They encourage poor workman ship in order to meet their Quotas. Quotas should be replaced with statistical methods of process control. 11. (b) Eliminate Management by Objective Instead of management by objective, management must learn the capabilities of the process and how to improve them. Internal goals set by management, without a method are a burlesque. 12. Remove Barriers that Rob People of Pride of Workmanship Loss of pride in workmanship exists throughout organizations because (1) Workers do not know how to relate to the organizations mission. (2) They are being blamed for system problems. (3) Poor designing leads to the production of Junk. (4) Inadequate training is provided. (5) Punitive supervision exists. (6) Inadequate or ineffective equipment is provided for performing the required work. Restoring pride will require a long term commitment by management. When workers are proud of their work, they will grow to the fullest of their job. By restoring pride, everyone in the organization will be working for the common good. A barrier for people on salary is the annual rating of performance. 13. Encourage Education and Self-improvement for Everyone What an organization needs is people who are improving with education. A long term commitment to continuously train and educate people must be made by management Demings 14 points and the organizations mission should be the foundation of the education program. 14. Take Action to Accomplish the Transformation Management has to accept the primary responsibility for the never-ending improvement of the process, it has to create a corporate structure to implement the philosophy. A cultural change is required from the previous business as usual attitude. Management must be committed, involved and accessible if the organization is to succeed in implementing the new philosophy. The PDA is used to assess your organizations product development process against over 260 best practices for product development. This assessment serves as a benchmark and identifies the highest impact opportunities for further improvement. Twenty-eight (28) product development dimensions are addressed.
Business and Product Strategy Product and Pipeline Management Technology Management Management and Leadership Early Involvement Product Development Teams Organizational Environment Process Management Process Improvement Understanding the Customer Requirements and Specifications Management Development Process Integration Supplier/Subcontractor Integration Product Launch Configuration Management Design Assurance Project & Resource Management Design for Manufacturability Product Cost Management Robust Design Integrated Test Design and Program Design for Operation and Support Product Data Design Automation Simulation and Analysis Computer-Aided Manufacturing Support Technology Knowledge Management They are organized into a framework with five major dimensions: Strategy, Organization,
Process, Design optimization and Technology.
The PDA was developed by a consortium led by DRM Associates which was chartered to identify product development and time-to-market best practices. These practices were derived from: corporate visits, consulting assignments, conferences, workshops and meetings, literature review, telephone discussions, technology vendors, the Navy Best Manufacturing Program, the Software Engineering Institutes (SEI) Capability Maturity Model (CMM), the AT&T Handbook series, and other corporate handbooks 1. What is the importance of the Thermodynamics in the field of Mechanical Engineering? All the mechanical engineering systems are studied with the help of thermodynamics. Hence it is very important for the mechanical engineers. 2. How many Laws of Thermodynamics are there? There are three laws of the thermodynamics. First Law: Energy can be neither created nor destroyed. It can only change forms.In any process in an isolated system, the total energy remains the same. Second Law: When two isolated systems in separate but nearby regions of space, each in thermodynamic equilibrium in itself, but not in equilibrium with each other at first, are at some time allowed to interact, breaking the isolation that separates the two systems, and they exchange matter or energy, they will eventually reach a mutual thermodynamic equilibrium. The sum of the entropies of the initial, isolated systems is less than or equal to the entropy of the final exchanging systems. In the process of reaching a new thermodynamic equilibrium, entropy has increased, or at least has not decreased. Third Law: As temperature approaches absolute zero, the entropy of a system approaches a minimum. 3. State Laws of conservation of energy? According to the laws of conservation of energy, energy can neither be created nor be destroyed. It can only be transformed from one form to another. 4. Is the boiler a closed system? Yes definitely the boiler is a closed system. 5. What is Carnot engine? It was being designed by Carnot and let me tell you that Carnot engine is an imaginary engine which follows the Carnot cycle and provides 100% efficiency. 6. Which formula forms a link between the Thermodynamics and Electro chemistry? Gibbs Helmholtz formula is the formula which forms the link between the thermodynamics and electromagnetism. Hs/R = [ lnp / (1/T)]x where: x mole fraction of CO2 in the liquid phase p CO2 partial pressure (kPa) T temperature (K) R universal gas constant mole ratio in the liquid phase (mole CO2 per mole of amine) 7. Which is the hardest compound known? Diamond. 8. What is Hess Law? According to the Hess law the energy transfer is simply independent of the path being followed. If the reactant and the product of the whole process are the same then same amount of energy will be dissipated or absorbed. 9. Which has more efficiency: Diesel engine or Petrol engines? Off course Diesel engine has the better efficiency out of two. CATIA V5 is the leading product development solution for all manufacturing organizations, from OEMs through their supply chains to small independent producers. The range of its capabilities allows CATIA V5 to be applied in a wide variety of industries, such as aerospace, automotive, industrial machinery, electrical, electronics, shipbuilding, plant design, and consumer goods, including design for such diverse products as jewelry and clothing. CATIA V5 is the only solution capable of addressing the complete product development process, from product concept specifications through product-in-service, in a fully integrated and associative manner. It facilitates true collaborative engineering across the multi-disciplinary extended enterprise, including style and form design, mechanical design and equipment and systems engineering, managing digital mock-up, machining, analysis, and simulation. CATIA products are based on the open, scalable V5 architecture. By enabling enterprises to reuse product design knowledge and accelerate development cycles, CATIA V5 helps companies speed their responses to market needs and helps free users to focus on creativity and innovation. Catia Exercises 1:
Catia Exercises 2:
Catia Exercises 3:
Catia Exercises 4:
Catia Exercises 5:
Material & Description ABS Good general purpose material, very tough yet very hard and rigid, good impact and electrical. Available in gauges from .040 to .475 with several extruded textures. Comes opaque and can be matched in custom colors.
ABS/PC A blend or alloy of ABS and polycarbonate that thermoforms well, weathers well, good color retention, very hard, excellent impact.
ABS/PVC Flame retardant, tough.
Acrylic
Outstanding weather resistance, excellent optics and electrical properties, poor impact, high gloss and deep luster. Available in standard gauges from .080 to over 1". Available in clear, transparent and opaque colors.
Acrylic, cell cast Excellent optics and hot strength, more expensive. Acrylic, continuous and extrusion cast. Large volume use and best price, good optics.
Acrylic film 3 or 6 mil film for laminating, decorating, and weathering of extruded ABS.
DR Acrylic Modified acrylic with higher impact properties.
Acrylic/PVC A blend of acrylic and PVC that is a tough, chemical-resistant material that weathers well and is flame resistant. Available in custom colors.
HDPE (high-density polyethylene) Crystalline, very tough materials, good weather resistance with UV inhibitors, resistant to many chemicals. Available in standard gauges from .040 to .500. Available in opaque custom colors. Tough and stiff. Good low temperature. Economical.
HMWPE (high molecular weight) Excellent environmental stress crack properties, thermoforms well, good low temperature.
HIPS (high impact polystyrene) Good general-purpose material, rigid. Available in clear but usually opaque custom colors from .030 to .350, low cost.
PVC (vinyl) Good general-purpose material, good abrasion and chemical resistance. Available in clear but usually opaque custom colors from .030 to .125.
Expanded PVC Stiff, light, flat, thermoformable. Available in stock colors and gauges, generally 3 and 6 mm but others also available.
PETG Clear, higher impact than acrylic, easy to form. Available in gauges from .030 to .500.
You might also like
Twin Sheet Forming | Twin Sheet Thermoforming | Twin Sheet Vacuum Forming
Twin sheet thermoforming has advantages over other methods of thermoforming and other plastics manufacturing...
Pressure Forming | Pressure Thermoforming | Blow Forming
Pressure Forming: Pressure Forming is the method used to produce injection mold quality, high definition...
Poissons Ratio | Basics Of Mechanical Material Handling Of Materials | Material Engineering Handling System | Material Handling Equipment When an element is stretched in one direction, it tends to get
In any production system, (either industrial/ Agricultural), the producer is always confronted with... thinner in the other two directions....
Thumblated Related Post
.Tagged with: materials for vacuum forming mechanical forming metals pressure forming materials Thermoforming Materials thermoforming mold materials thermoforming plastic materials vacuum forming material uses Vacuum Forming Materials
May
17
Pressure Forming | Pressure Thermoforming | Blow Forming
Manufacturing Engineering, Manufacturing process, Manufacturing technologyNo Comments
Pressure Forming: Pressure Forming is the method used to produce injection mold quality, high definition plastic component parts, housings and containers without the huge expense of tooling. It involves positive pressure to force the heated plastic into the mold cavity. This is called pressure thermoforming or blow forming
Pressure Forming Working Operation:
The highly versatile pressure forming process utilizes air pressure, from 20 to 150 psi, to force the heated sheet into a temperature controlled mold cavity. Vent holes are provided in the mold to exhaust the trapped air. The final part features sharp definition of intricate contours and tight radii. Textures and accurate details are built right into the tooling. Low-cost, highly aesthetic plastic parts of varying sizes are possible due to the application of air pressure, as well as more sophisticated process controls that better monitor tool and sheet temperatures while controlling material shrinkage during forming.
Types Of Molding operation:
Positive Mold Negative Mold
Negative molds have concave cavities. A positive mold has a convex shape.
Pressure Forming over Thermo Forming: The basic advantage of Pressure Forming over Thermo forming is the cost advantage for small production items. The mould cost for thermo forming is considerably higher in comparison to pressure forming thus for a lower quantity precision job the best suitable method used is pressure forming.
Application:
Pressure forming is used to create in a wide array of plastic products used for packaging of food trays, blisters, covers, internal parts, housings equipment, bezels, bases, and spare parts for use in business machines, electronics, computers and peripherals, bio-medical applications, and instruments.
Features:
Pressure forming achieves features beyond the capabilities of vacuum forming including louvers, ribs, recessed areas, crisp details and logos.
Pressure forming is ideal for small to medium sized production runs that do not justify the high cost of injection molding dies. Additionally, because the aluminum tooling used in pressure forming has an unlimited lifecycle, due to the non-abrasive process versus injection, it saves a great deal of money over many years of continued use. Pressure form tooling usually costs less than 10% the cost of an injection tool. There is also a significant time savings (sometimes 25%) in tooling lead time. Sheet gauges .020" .500" are capable of being pressure formed.
Twin sheet thermoforming has advantages over other methods of thermoforming and other plastics manufacturing processes depending on the part and its use.
Has a lower tooling cost about 20-30% less than blow molding Yields parts with high structural integrity and rigidity compared to single walled thermoforming Allows for an enclosed cavity Can include various internal reinforcements, including structural elements and rigid foam components Can have molded-in attachments and other features Typical Application: To Produce Hollow Molding Parts, Structural Products.
Working Of Twin Sheet Thermoforming Process:
Twin sheet forming is a process of vacuum and compression forming two sheets of plastic simultaneously with a separate mold on the top platen and a separate mold on the bottom platen. Once the plastic sheets have been vacuum formed, they remain in their respective molds. While both sheets still remain at their forming temperature, the two molds are brought together under high platen pressures and the two sheets are bonded together wherever the mold-designed knit areas dictate. This will result in one single product with hollow areas and no secondary bonding required.The twin sheet process creates 3-dimensional parts with formed features on both sides.
The production of twin sheet pallets up to 4 pallets per cycle are being made giving an individual cycle per part in seconds, not minutes. Production capacity therefore can be as large as required by sizing the equipment as required.
Methods:
Vacuum Forming Pressure Forming Mechanical Forming Properties:
The parts are typically very strong, rigid and lightweight. Increased Structural Integrity Enclosed Cross-Section Capability Low Tooling Cost Internal Reinforcement Options: Structural Member, Rigid Foam, Etc. Materials:
HIPS, Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), TPO, High Density Polyethylene (HDPE), Polypropylene (PP), TPU, & PETG
Important Points: After forming of the bottom sheet and the entry of the top sheet into the forming area, there is an opportunity to insert other items such as wood, metal, foam etc. These can be inserted to add strength, give the ability to attach the final product to other items after forming, such as door hinges or even give the final product the ability to float as in the manufacture of floating docks. Also engineering plastics can be thermoformed by this method into detailed technical twin sheet parts.
Application:
Pallets, Industrial drainage, Portable toilets, Medical housings, Surfboards, Fuel tanks, Air/ventilation ducts, Electrical enclosures, Recreational boats, Cases, Toys, Marine products, Doors, Tables, Spine boards and Numerous transportation-related products.
You might also like
Pressure Forming | Pressure Thermoforming | Blow Forming
Pressure Forming: Pressure Forming is the method used to produce injection mold quality, high definition...
Interview Questions On Strength of Materials
Can anybody please provide any link to calculate force required to bend a metal sheet into pipe? or...
SolidWorks COSMOS Use | SolidWorks COSMOS Analysis | Plastics Application | Elastomer Application | Metal-Forming Applications
Plastics Application: Household appliances, medical devices, electrical fittings among others incorporate...
Thermoforming Materials | Vacuum Forming Materials | Pressure Forming Materials
Material & Description ABS Good general purpose material, very tough yet very hard and rigid,...
Thumblated Related Post
.Tagged with: Thermoforming Molds Thermoforming Process Twin Forming Twin Sheet Forming Twin Sheet Forming Process Twin Sheet Thermoforming Twin Sheet Thermoforming process Twin Sheet Vacuum Forming Twin Sheets vacuum forming methods vacuum forming process
Apr
10
RT Prototyping | Rapid Tooling
Manufacturing Engineering, Manufacturing process, Manufacturing technology, Rapid PrototypingNo Comments
An Application of Rapid prototyping is Rapid tooling, this an automatic fabrication of machine tools. Tooling is one of the most costly steps in the manufacturing process.
Tools are often complex and need to be wear resistant for production. To meet these requirements, molds and dies are traditionally made by CNC machining, EDM or other methods. All traditional methods are expensive and time consuming; making rapid tooling prototyping the desired alternative. Many believe tooling and design cost may be cut by 50% to 70% by using rapid prototyping.
Rapid tooling is divided in two categories; indirect tooling and direct tooling.
Indirect Tooling
Most rapid tooling today is indirect tooling. Rapid prototyping parts are used as patterns for making molds and dies. These models can be in the following manufacturing processes.
Investment Casting
Some rapid prototyping can be used as investment casting patterns. Patterns must retain size when heated and not crack during the finishing process.
Injection Modeling
A Stereo lithography machine is used to make a match-plate pattern of the desired molding. To form this mold it is plated with metal material such as nickel; then reinforced with ceramic. The two halves are separated to remove the pattern, leaving a perfect model capable to producing thousands of injection models.
Sand Casting
A rapid prototyping model is used as a pattern which sand mold or casting is built. (make the following link) Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM) machines can be used for this process. A LOM model can produce nearly 100 sand molds.
Vacuum Casting
The oldest and simplest rapid tooling prototyping technique; a pattern is suspended in a vat of liquid silicon. When the material cures, the pattern may be removed. The silicon molds can produce 15 or more patterns.
Direct Tooling
To make metal tooling direct from CAD file through rapid prototyping process; is the answer to every production engineers dream.
Rapid tool A process which uses SLS to sinter poly- coated steel pellets together to produce metal mold.
Laser Engineering Net Shaping (LENS)
A process that can create metal tools directly from a CAD file. This process is capable of using multiple materials, stainless steel, HSS, tungsten carbide as well as others. A laser beam melts the top layer of the part in areas where material is to be added until the part is complete. Unlike sintering, LENS does produce a solid metal part since the metal was melted.
Direct AIM
Another technique provided by 3D Systems of Valencia, Ca. Stereo lithography produced cores are used with traditional metal molds for injection moldings from HDPE, Polystyrene, polypropylene and ABS.
LOM Composite
A method of using ceramic composite material for Laminated Object Manufacturing.
Sand Molding
A rapid prototyping technique that constructs sand molds directly from a CAD file.
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- PV TechnologyДокумент14 страницPV TechnologyhatebookОценок пока нет
- Business Taxation 3Документ47 страницBusiness Taxation 3Prince Isaiah JacobОценок пока нет
- Catalogue Rotary Cam SwitchesДокумент92 страницыCatalogue Rotary Cam Switchesrajpre1213Оценок пока нет
- 315 ManualДокумент119 страниц315 ManualLizardo Astudillo CruzОценок пока нет
- IEEE STD 979-2012, IEEE Guide For Substation Fire ProtectionДокумент99 страницIEEE STD 979-2012, IEEE Guide For Substation Fire ProtectionM Alim Ur Rahman100% (2)
- ARC India Company ProfileДокумент10 страницARC India Company ProfilesingenaadamОценок пока нет
- 2019.3.5 Clarification For New SPM ProjectДокумент1 страница2019.3.5 Clarification For New SPM ProjectAvijit DasguptaОценок пока нет
- Fmea HXДокумент2 страницыFmea HXNora NaranjoОценок пока нет
- A Guide To Calculating Your Boiler Emissions: A Step-By-Step Manual For Your ConvenienceДокумент22 страницыA Guide To Calculating Your Boiler Emissions: A Step-By-Step Manual For Your ConvenienceRamon CardonaОценок пока нет
- ReymillWindmill Sta Rosa NEДокумент8 страницReymillWindmill Sta Rosa NEIssey Mari TiongcoОценок пока нет
- PODEM ANUPAM Brochure CraneComponentДокумент28 страницPODEM ANUPAM Brochure CraneComponentJnanamОценок пока нет
- New Products and Services: Analysis of Regulation Shaping New MarketsДокумент268 страницNew Products and Services: Analysis of Regulation Shaping New MarketsdmaproiectОценок пока нет
- Phe ProfilДокумент19 страницPhe ProfilandriaerospaceОценок пока нет
- Earthing in Mines and Quarries Slide Presentation Phillip WallДокумент45 страницEarthing in Mines and Quarries Slide Presentation Phillip WallMaksut H. KaptanОценок пока нет
- 21200Документ2 страницы21200Talha TariqОценок пока нет
- Naval Reactor Handbook Vol 1Документ1 562 страницыNaval Reactor Handbook Vol 1Peter AngeloОценок пока нет
- Thesis BBS 4th Year Profitability Analysis of NEA Rashi FINALEДокумент47 страницThesis BBS 4th Year Profitability Analysis of NEA Rashi FINALERashi Goyal100% (1)
- Offshore Wind Farm AnalysisДокумент22 страницыOffshore Wind Farm AnalysisShahab SadeghpourОценок пока нет
- Full Report, Feasibility of Renewable Energy in The ArcticДокумент77 страницFull Report, Feasibility of Renewable Energy in The ArcticNunatsiaqNewsОценок пока нет
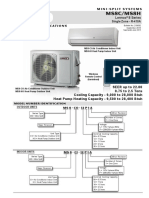
- Lennox MS8H Mini Split Heat Pump SpecsДокумент16 страницLennox MS8H Mini Split Heat Pump SpecsMeselao Meselao MeselaoОценок пока нет
- Data KapasitorДокумент7 страницData KapasitorMuhammad Ardi AnggaraОценок пока нет
- Summer Internship Report: Indian Oil Corporation LimitedДокумент34 страницыSummer Internship Report: Indian Oil Corporation Limitedshakti shanker0% (1)
- Energy Meter Using at Domestic PurposeДокумент30 страницEnergy Meter Using at Domestic PurposeirahkaОценок пока нет
- CEPL - Company ProfileДокумент11 страницCEPL - Company ProfileKamalОценок пока нет
- JD and JSДокумент3 страницыJD and JSMd. Faisal BariОценок пока нет
- Biomass Based Power Plant in South SudanДокумент23 страницыBiomass Based Power Plant in South SudanYogendra PalОценок пока нет
- Renewable Energy KoreaДокумент7 страницRenewable Energy Koreashantanu91Оценок пока нет
- Sahara Prime City LimitedДокумент23 страницыSahara Prime City LimitedincognitorohitОценок пока нет
- Solar Car Parks: A Guide For Owners and DevelopersДокумент28 страницSolar Car Parks: A Guide For Owners and DevelopersAMIR100% (1)
- Qatar Companies ListДокумент10 страницQatar Companies ListSyed Abbu Hurerah50% (2)