Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Lovenox (Enoxaparin)
Загружено:
E100%(5)100% нашли этот документ полезным (5 голосов)
21K просмотров1 страницаLovenox anticoagulants, antithrombotics 40 mg SQ qid Peak Onset Duration Normal dosage range unknown unknown 12 hrs 40mg SQ daily Common side effects Dizziness, headache, insomnia, constipation, urinary retention, bleeding, anemia, thrombocytopenia interactions with other patient drugs, OTC or herbal Lab value alterations caused by medicine medicines (ask patient specifically)
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Lovenox (enoxaparin)
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документLovenox anticoagulants, antithrombotics 40 mg SQ qid Peak Onset Duration Normal dosage range unknown unknown 12 hrs 40mg SQ daily Common side effects Dizziness, headache, insomnia, constipation, urinary retention, bleeding, anemia, thrombocytopenia interactions with other patient drugs, OTC or herbal Lab value alterations caused by medicine medicines (ask patient specifically)
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
100%(5)100% нашли этот документ полезным (5 голосов)
21K просмотров1 страницаLovenox (Enoxaparin)
Загружено:
ELovenox anticoagulants, antithrombotics 40 mg SQ qid Peak Onset Duration Normal dosage range unknown unknown 12 hrs 40mg SQ daily Common side effects Dizziness, headache, insomnia, constipation, urinary retention, bleeding, anemia, thrombocytopenia interactions with other patient drugs, OTC or herbal Lab value alterations caused by medicine medicines (ask patient specifically)
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 1
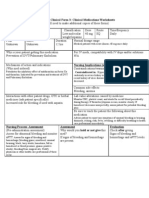
Clinical Medications Worksheets
Generic Name Trade Name Classification Dose Route Time/frequency
enoxaparin Lovenox Anticoagulants, antithrombotics 40 mg SQ qid
Peak Onset Duration Normal dosage range
Unknown unknown 12 hrs 40mg SQ daily
Why is your patient getting this medication For IV meds, compatibility with IV drips and/or solutions
Prevention of thrombus formation. Systemic anticoagulation N/A
for prevention of ischemic or thrombotic events (e.g., MI,
stroke)
Mechanism of action and indications Nursing Implications (what to focus on)
(Why med ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactions
Systemic anticoagulation Hypersensitivity, uncontrolled bleeding, GI
Potentiates the inhibitory effect of antithrombin on factor Xa bleeding/ulceration/pathology. Geriatric patients (enoxaparin
and thrombin elimination prolonged). Retinopathy (hypertensive or diabetic).
Untreated hypertension. History of congenital or acquired bleeding
disorder. Recent history of ulcer disease. Hemorrhagic stroke.
Common side effects
Dizziness, headache, insomnia, constipation, N/V, urinary retention,
bleeding, anemia, thrombocytopenia
Interactions with other patient drugs, OTC or herbal Lab value alterations caused by medicine
medicines (ask patient specifically) Reversible increase in liver enzymes, monitor CBC, platelet count and
Plavix: Drugs that can affect hemostasis such as dextran, , monitor closely if thrombocytopenia occurs, if decrease in hematocrit
platelet inhibitors, thrombin inhibitors, thrombolytic agents, or occurs, assess for hemorrhage
other anticoagulants may potentiate the risk of bleeding Be sure to teach the patient the following about this medication
complications associated with the use of a low molecular Advise patient to report any symptoms of unusual bleeding or bruising,
weight heparin (LMWH), heparinoid, or fondaparinux. In dizziness, itching, rash, fever, swelling, or difficulty breathing to health
patients receiving neuraxial anesthesia or spinal puncture, the care professional immediately. Instruct patient not to take aspirin,
risk of developing an epidural or spinal hematoma during naproxen, or ibuprofen without consulting health care professional
LMWH, heparinoid, or fondaparinux therapy may also be while on enoxaparin therapy.
increased by the concomitant use of other drugs that affect
coagulation. The development of epidural and spinal
hematoma can lead to long-term or permanent paralysis.
ASA: In patients receiving neuraxial anesthesia or spinal
puncture, the risk of developing an epidural or spinal
hematoma during low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) or
heparinoid therapy may be increased by the concomitant use of
other drugs that affect coagulation, including nonsteroidal anti-
inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). The development of epidural
and spinal hematoma can lead to long-term or permanent
paralysis.
Nursing Process- Assessment Assessment Evaluation
(Pre-administration assessment) Why would you hold or not give this med? Check after giving
Assess for signs and symptoms of bleeding and Hypersensitivity (chills, fever, urticaria). Unusual bleeding or hemorrhage.
hemorrhage (bleeding gums; nosebleed; unusual Assess for signs of bleeding and hemorrhage Prevent DVT/clot formation.
bruising; black, tarry stools; hematuria; fall in (bleeding gums; nosebleed; unusual bruising; Observe injection sites for
hematocrit or blood pressure; guaiac-positive black, tarry stools; hematuria; fall in hematomas, ecchymosis, or
stools), assess for signs and symptoms of hematocrit or blood pressure; guaiac-positive inflammation.
thrombosis, observe injection sites for hematomas. stools); bleeding from surgical site. Notify
physician or other health care professional if
these occur.
Вам также может понравиться
- Generic Name: Brand Name: Route: Frequency: Before:: AE: HemorrhageДокумент2 страницыGeneric Name: Brand Name: Route: Frequency: Before:: AE: HemorrhageKim SunooОценок пока нет
- Enoxaparin (Lovenox)Документ1 страницаEnoxaparin (Lovenox)EОценок пока нет
- XareltoДокумент2 страницыXareltoMichael Kuzbyt100% (1)
- Lisinopril Prinivil Zestril)Документ1 страницаLisinopril Prinivil Zestril)EОценок пока нет
- EsmololДокумент2 страницыEsmololtherock316_995149Оценок пока нет
- Enoxaparin FDAДокумент40 страницEnoxaparin FDAImam Nur Alif Khusnudin100% (2)
- Nebivolol for BP Lowering (BystolicДокумент1 страницаNebivolol for BP Lowering (BystolicshaeОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент6 страницDrug StudyGeraldine Gallaron - CasipongОценок пока нет
- Eliquis (apixaban) drug cardДокумент1 страницаEliquis (apixaban) drug cardTee Wood100% (1)
- Difflam Drug StudyДокумент1 страницаDifflam Drug StudyDanlee EstandaОценок пока нет
- Novolog (Insulin Aspart)Документ3 страницыNovolog (Insulin Aspart)EОценок пока нет
- Drug Study (Aspirin)Документ3 страницыDrug Study (Aspirin)Mae Therese B. MAGNOОценок пока нет
- Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine) : 1mg/mLДокумент5 страницNoradrenaline (Norepinephrine) : 1mg/mLBrian RelsonОценок пока нет
- Managing Memantine Therapy for Alzheimer's PatientsДокумент2 страницыManaging Memantine Therapy for Alzheimer's PatientsSОценок пока нет
- Allopurinol Drug Study for Gout TreatmentДокумент1 страницаAllopurinol Drug Study for Gout TreatmentAbigail CastroОценок пока нет
- Mannitol Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыMannitol Drug StudyNo Vem BerОценок пока нет
- Nalbuphine (Nubain)Документ2 страницыNalbuphine (Nubain)Adrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Generic Name: Brand Name:: ClassificationsДокумент2 страницыGeneric Name: Brand Name:: ClassificationsbillyktoubattsОценок пока нет
- Cefepime MaxipimeДокумент2 страницыCefepime MaxipimeKristi Wray100% (1)
- Drug Card PropofolДокумент1 страницаDrug Card PropofolBenОценок пока нет
- Brand Name Generic Name Indication and Contraindication Nursing Consideration Action of The Drug Dose and Administration Side EffectsДокумент2 страницыBrand Name Generic Name Indication and Contraindication Nursing Consideration Action of The Drug Dose and Administration Side EffectsCarla Dana GozumОценок пока нет
- Atrovent (Ipratropium)Документ1 страницаAtrovent (Ipratropium)E100% (2)
- Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseДокумент1 страницаMedication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseMarina Wasem NetzlaffОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыDrug StudyLee JennyОценок пока нет
- VancomycinДокумент1 страницаVancomycinE100% (2)
- Manage hypertension with LisinoprilДокумент2 страницыManage hypertension with LisinoprilKristinelou Marie Reyna100% (1)
- Cholestyramine (Drug Study)Документ2 страницыCholestyramine (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888Оценок пока нет
- AmiodaroneДокумент4 страницыAmiodaroneTri Purma SariОценок пока нет
- Oxycodone Acetaminophen PercocetДокумент1 страницаOxycodone Acetaminophen PercocetEОценок пока нет
- Docusate Sodium (Colace)Документ2 страницыDocusate Sodium (Colace)E100% (1)
- Ramipril Drug StudyДокумент3 страницыRamipril Drug StudyCheezy Bread0% (1)
- Drug Study: Acetadote, Mucomyst MucolyticsДокумент2 страницыDrug Study: Acetadote, Mucomyst MucolyticsMae Ann Bueno CastillonОценок пока нет
- Brand Name: Dilzem Generic Name: Diltiazem Indications: Angina Pectoris IncludingДокумент3 страницыBrand Name: Dilzem Generic Name: Diltiazem Indications: Angina Pectoris Includingianecunar0% (1)
- Subcutaneous Injection: Humalog U-100 or U-200: More CommonДокумент2 страницыSubcutaneous Injection: Humalog U-100 or U-200: More Commonahmad ryanОценок пока нет
- Alprazolam Dosage, Uses, Side EffectsДокумент2 страницыAlprazolam Dosage, Uses, Side EffectsKristi WrayОценок пока нет
- DRUG STUDY-LidocaineДокумент3 страницыDRUG STUDY-LidocaineCarissa Mae Tapec Estrada100% (1)
- TramadolДокумент2 страницыTramadolAllen Vincent Cauton TulaganОценок пока нет
- Drug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToДокумент2 страницыDrug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToSHEILA MAE SACLOTОценок пока нет
- MorphineДокумент2 страницыMorphineNinoska Garcia-Ortiz80% (5)
- Ditropan Drug CardДокумент2 страницыDitropan Drug CardBenОценок пока нет
- Name of Drug Classification Action Indication Side Effects Intervention and EvaluationДокумент3 страницыName of Drug Classification Action Indication Side Effects Intervention and EvaluationMikz JocomОценок пока нет
- THEOPHYLLINE - Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыTHEOPHYLLINE - Drug Studyeric macabiogОценок пока нет
- NPH Insulin NPHДокумент1 страницаNPH Insulin NPHE100% (1)
- Levetiracetam PDFДокумент3 страницыLevetiracetam PDFShaira TanОценок пока нет
- HydrochlorothiazideДокумент3 страницыHydrochlorothiazideapi-3797941Оценок пока нет
- Na HCO3Документ2 страницыNa HCO3Niño Karol Zamora100% (1)
- Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыDrug StudyJan Lianne BernalesОценок пока нет
- Dopamine HydrochlorideДокумент1 страницаDopamine HydrochlorideJoannes SanchezОценок пока нет
- Morphine SulfateДокумент5 страницMorphine Sulfateapi-3797941100% (4)
- Lovenox (Enoxaparin)Документ1 страницаLovenox (Enoxaparin)E100% (1)
- LovenoxДокумент1 страницаLovenoxKatie McPeek100% (2)
- Lovenox (Enoxaparin) 80mgДокумент1 страницаLovenox (Enoxaparin) 80mgAdrianne BazoОценок пока нет
- LovenoxДокумент1 страницаLovenoxAdrianne BazoОценок пока нет
- LovenoxДокумент1 страницаLovenoxSrkocherОценок пока нет
- Rathna Drug Card in (Lovenox)Документ1 страницаRathna Drug Card in (Lovenox)erdos13Оценок пока нет
- Drug LovenoxДокумент2 страницыDrug LovenoxSrkocherОценок пока нет
- Medication Card HeparinДокумент2 страницыMedication Card HeparinEllieОценок пока нет
- Plavix ClopidogrelДокумент2 страницыPlavix ClopidogrelAdrianne Bazo50% (2)
- Haematology DrugsДокумент17 страницHaematology DrugsParyОценок пока нет
- Lovenox 40 MLДокумент1 страницаLovenox 40 MLfaithsamp6Оценок пока нет
- Pyelonephritis 1 Running Head: PYELONEPHRITISДокумент4 страницыPyelonephritis 1 Running Head: PYELONEPHRITISEОценок пока нет
- Left-Side CHF PathoДокумент5 страницLeft-Side CHF PathoEОценок пока нет
- Congestive Heart FailureДокумент4 страницыCongestive Heart FailureEОценок пока нет
- Chemical Burns PathoДокумент2 страницыChemical Burns PathoEОценок пока нет
- Hyponatremic Dehydration PathoДокумент4 страницыHyponatremic Dehydration PathoEОценок пока нет
- Autonomic DysreflexiaДокумент2 страницыAutonomic DysreflexiaEОценок пока нет
- Hyperparathyroidism PathoДокумент2 страницыHyperparathyroidism PathoEОценок пока нет
- Iron Deficiency Anemia PathoДокумент6 страницIron Deficiency Anemia PathoEОценок пока нет
- Influenza B PathoДокумент4 страницыInfluenza B PathoEОценок пока нет
- Congestive Heart Failure-ABДокумент3 страницыCongestive Heart Failure-ABEОценок пока нет
- Acute Pancreatitis PathoДокумент5 страницAcute Pancreatitis PathoEОценок пока нет
- Bowel Resection PathoДокумент7 страницBowel Resection PathoEОценок пока нет
- Subluxation c6c7 Short PathoДокумент1 страницаSubluxation c6c7 Short PathoEОценок пока нет
- Pneumonia Short PathoДокумент2 страницыPneumonia Short PathoEОценок пока нет
- Campral (Acamprosate Calcium)Документ1 страницаCampral (Acamprosate Calcium)E100% (1)
- Clinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsДокумент1 страницаClinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsEОценок пока нет
- Buspar (Buspirone)Документ1 страницаBuspar (Buspirone)EОценок пока нет
- Pancreatitis Short PathoДокумент2 страницыPancreatitis Short PathoEОценок пока нет
- Geodon (Ziprasidone)Документ2 страницыGeodon (Ziprasidone)EОценок пока нет
- Prozac (Fluoxetine) 40mgДокумент1 страницаProzac (Fluoxetine) 40mgEОценок пока нет
- Lexapro (Escitalopram Oxalate)Документ2 страницыLexapro (Escitalopram Oxalate)EОценок пока нет
- Zosyn (Piperacillin/tazobactram)Документ2 страницыZosyn (Piperacillin/tazobactram)E67% (3)
- ZofranДокумент1 страницаZofranKatie McPeek0% (1)
- Silvadene (Silver Sulfadiazine)Документ1 страницаSilvadene (Silver Sulfadiazine)EОценок пока нет
- FiberCon (Polycarbophil)Документ1 страницаFiberCon (Polycarbophil)EОценок пока нет
- Reglan (Metoclopramide)Документ3 страницыReglan (Metoclopramide)E100% (1)
- Darvocet (Propoxyphene Napsylate/Acetaminophen)Документ1 страницаDarvocet (Propoxyphene Napsylate/Acetaminophen)EОценок пока нет
- Theragran (Multiple Vitamins)Документ3 страницыTheragran (Multiple Vitamins)EОценок пока нет
- Florinef (Fludrocortisone)Документ3 страницыFlorinef (Fludrocortisone)E100% (1)
- Keppra (Levetiracetam)Документ2 страницыKeppra (Levetiracetam)E100% (1)
- Anaemia in Dogs and Cats (Part 2) : Continuing EducationДокумент6 страницAnaemia in Dogs and Cats (Part 2) : Continuing EducationAchmad NugrohoОценок пока нет
- Leunase and TrombolismДокумент12 страницLeunase and TrombolismSanta UlinaОценок пока нет
- Anticoagulant PresentationДокумент29 страницAnticoagulant Presentationrozha100% (2)
- Anticoagulation in OrthopedicsДокумент32 страницыAnticoagulation in Orthopedicsehabede6445Оценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 56 - Unstable Angina and Non-ST ElevationДокумент34 страницыCHAPTER 56 - Unstable Angina and Non-ST ElevationSatria WardanaОценок пока нет
- 2017 06 16 Stroke in PregnancyДокумент49 страниц2017 06 16 Stroke in PregnancyayubahriОценок пока нет
- VTE Risk Assessment and Prophylaxis GuidelinesДокумент2 страницыVTE Risk Assessment and Prophylaxis Guidelinessakanon100% (1)
- Pro TaminaДокумент2 страницыPro TaminaArcenciel26Оценок пока нет
- Management of Patients With AnticoagsДокумент12 страницManagement of Patients With AnticoagsAlexander NatroshviliОценок пока нет
- Coumadin Dosing GuideДокумент3 страницыCoumadin Dosing Guidemorale28Оценок пока нет
- Disseminated Intravascular CoagulationДокумент5 страницDisseminated Intravascular CoagulationElenaОценок пока нет
- Controversies in Venous Thromboembolism - To Treat or Not To Treat Superficial Vein ThrombosisДокумент8 страницControversies in Venous Thromboembolism - To Treat or Not To Treat Superficial Vein ThrombosisNestor DuránОценок пока нет
- Clexane and Clexane Forte : Name of The MedicineДокумент20 страницClexane and Clexane Forte : Name of The MedicineMarin MarianОценок пока нет
- AspirinДокумент7 страницAspirinCornel UrsuОценок пока нет
- Switching To-From AnticoagulantsДокумент8 страницSwitching To-From AnticoagulantsAlex AlxОценок пока нет
- Thromboprophylaxis in The ICUДокумент31 страницаThromboprophylaxis in The ICUdocansh100% (1)
- Management of Acute Limb Ischemia in The Pediatric PopulationДокумент5 страницManagement of Acute Limb Ischemia in The Pediatric PopulationPendidikan Dokter Unsyiah 2015Оценок пока нет
- Anticoagulation in Hemodialysis: Arlene S. Munoz MD, FPCP, FPSNДокумент51 страницаAnticoagulation in Hemodialysis: Arlene S. Munoz MD, FPCP, FPSNBryant MunozОценок пока нет
- NHMRC VTE Prevention Guideline Summary For CliniciansДокумент2 страницыNHMRC VTE Prevention Guideline Summary For CliniciansRatnaSuryati100% (1)
- Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and Treatment of Neonatal Sepsis: Review ArticleДокумент7 страницPathophysiology, Diagnosis and Treatment of Neonatal Sepsis: Review ArticleZakia DrajatОценок пока нет
- Ischemic Limb Gangrene With PulsesДокумент14 страницIschemic Limb Gangrene With PulsesJustin Ryan TanОценок пока нет
- Sanofi Annual Report 2014Документ85 страницSanofi Annual Report 2014MirzaОценок пока нет
- Hemostasis, Clotting Disorder and AnticoagulantsДокумент87 страницHemostasis, Clotting Disorder and AnticoagulantsSomit Jain100% (1)
- Notes: Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (Hit)Документ6 страницNotes: Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (Hit)MOHIT SHARMAОценок пока нет
- Venous DiseaseДокумент45 страницVenous DiseaseNinch Nagac100% (1)
- En Ox A Par inДокумент3 страницыEn Ox A Par inapi-3797941Оценок пока нет
- Hippokratia 11 013 PDFДокумент9 страницHippokratia 11 013 PDFGraham Allen ShowОценок пока нет
- Sontra Medical TechДокумент3 страницыSontra Medical TechThong MinyewОценок пока нет
- ReviewerДокумент20 страницReviewerKC PalattaoОценок пока нет
- Anticoagulant & Thrombolytic DrugsДокумент68 страницAnticoagulant & Thrombolytic Drugsezrider7Оценок пока нет