Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
NCP Proper 1
Загружено:
Noreen PinedaИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
NCP Proper 1
Загружено:
Noreen PinedaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
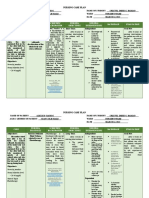
NURSING CARE PLAN PROPER 1 Problem 1: Nursing Diagnosis: Impaired Gas Exchange related to immaturity of the lungs secondary
to premature t/c hyaline membrane disease Goal: After all nursing interventions, the patient will be able to breathe normally without any devices such as oxygen therapy, incubator and being stimulated, and injecting surfactants Objective: After a week of nursing interventions, the patient will be able to manifest signs and symptoms of improvement of normal breathing continuously by a. Reduce suffering of RDS, with reduces work of breathing b. Maintain periodic breathing pattern and normal vital signs c. Maintain PaO2 and PaCO2 levels within normal d. Leading to normal laboratory or diagnostic studies CUES Subjective: Objectives: On incubator On oxygen therapy @ 1 lpm With D5 IMD x 7-8mgtts Afebrile Apgar score of 6-7 @1.5 min With a current weight of 1.2 kg Current VS: RR-32; CR-128; T-36.8C Temperature fluctuates easily With slight clammy pale extremities Abnormal breathing pattern with episodes of apnea Lies in an extended position Low muscle tone and activity Thin and less body fat EXPLANATION A premature baby, or preemie, is born before the 37th week of pregnancy. Premature birth occurs in between 8 percent to 10 percent of all pregnancies in the United States. Because they are born too early, preemies weigh much less than full-term babies. They may have health problems because their organs did not have enough time to develop. Preemies need special medical care in a neonatal intensive care unit, or NICU. They stay there until their organ systems can work on their own. Respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) is a breathing disorder that affects newborns. RDS is more common in premature infants because their lungs aren't able to make enough surfactant. Surfactant is a liquid that coats the inside of the lungs. It helps keep them open so that infants can breathe in air once they're born. Without surfactant, the lungs collapse and the infant has to work hard to breathe. He or she might not be able to breathe in enough oxygen to support the body's organs.
INTERVENTIONS Dx: Assess respiratory status, noting signs of respiratory distress such as tachypnea , bradypnea or periods of apnea, grunting, retractions or use of accessory muscles such as abdominal muscle or nasal flaring
RATIONALE Tachynea, bradypnea or apnea indicate respiratory distress, especially when respirations are >75cpm or <30cpm. Expiratory grunting represents an attempt to maintain alveolar expansion; use of accessory muscles is a compensatory mechanism to increase diameter of nares and increase oxygen intake.
CRITERIA FOR EVALUATION Goal:
EVALUATION
Goal is fully met if patient
breathe normally without any devices such as oxygen therapy, incubator and being stimulated, and injecting surfactants Goal is partially met if patient normally breath with one or two of any devices such as oxygen therapy, incubator and being stimulated, and injecting surfactants
Monitor body temperature of not
<36.6 C and >38 C together with the cardiac rate of
Cold stress increases infants oxygen
consumption, may promote acidosis, and further impair surfactant production and a slight increase or decrease in environmental temperature san lead to apnea
Goal is no met if patient breath
with the help more or more devices such as oxygen therapy, incubator and being stimulated, and injecting surfactants Objectives: Objectives are fully met if patient manifest all signs and symptoms of improvement of normal breathing continuously by a. Reduce suffering of RDS, with reduces work of breathing b. Maintain periodic breathing pattern and normal vital signs c. Maintain PaO2 and PaCO2 levels within normal d. Leading to normal laboratory or diagnostic studies
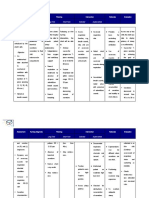
Dehydration impairs ability to clear Monitor fluid intake and output;
Weight infant as indicated by protocol airways because mucus becomes thickened. Overhydration may contribute to alveolar ifiltration or pulmonary edema. Weight loss and increase urine output may indicate diuretic phase of RDS/HMD. Monitor for signs of necrotizing enterocolitis Hypoxia may cause shunting of blood to brain, thereby reducing circulation to the intestines, with resultant intestinal cell damage and invasion by gas-forming bacteria
Amount of oxygen administered is
Monitor oxygen therapy closely and record hourly; adjust level and/or limit duration of administration as needed determined individually, based on capillary blood samples. Prolonged high levels of serum oxygen combined with prolonged high pressure may predispose infant to bronchopulmonary dysplasia and retinal damage.
Objectives are partially met if patient
manifest all but not one or two signs and symptoms of improvement of normal breathing continuously by a. Reduce suffering of RDS, with reduces work of breathing b. Maintain periodic breathing pattern and normal vital signs
Cyanosis is a late sign of low Po2 and
Observe for evidence and location of does not appear until there is slightly more than 3g/dl of reduced Hgt in
cyanosis
central arterial blood, or 4-6g/dl in capillary blood or until oxygen saturation is only 75%-85%, with Po2 levels of 32-41 mmHg.
Hypoxemia, hypercapnia and acidosis Evaluate laboratory or diagnostic
studies such as ABGs, Hgt/Hct, serum glucose level reduce surfactant production. Pa02 levels should be 50-70 mmHg or higher, PaC02 levels should be 3545mmHg and Oxygen saturation should be 95-100%. Decreased iron stores at birth, repeated blood sampling and hemorrhagic episodes increase the likelihood that preterm infant will be anemic, thereby reducing the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood. Hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia suggests infection
Maintain PaO2 and PaCO2 levels within normal d. Leading to normal laboratory or diagnostic studies Objectives are not met if patient did not manifest all signs and symptoms of improvement of normal breathing continuously by a. Reduce suffering of RDS, with reduces work of breathing b. Maintain periodic breathing pattern and normal vital signs c. Maintain PaO2 and PaCO2 levels within normal d. Leading to normal laboratory or diagnostic studies
c.
Prolonged labor increases risk of
hypoxia, and respiratory depression may follow maternal drug administration or usage. In addition, infants who required resuscitative measures at birth, or those with apgar scores, may require more intense interventions to stabilize blood gases and may have suffered CNS injury with the damage to the hypothalamus, which controls respiratory functioning. Administration of corticosteroids to mother within 1wk of delivery fosters the infants lung maturity and surfactant production Sudden or unexplained deterioration of respiratory function may indicate onset of pneumothorax
Review information related to infants condition, such as length of labor, type of deliver, apgar score, need for resuscitation measures at delivery, and maternal medications taken during pregnancy or delivery
Investigate sudden deterioration in condition associated with cyanosis, diminished or absent sounds, shift of point maximal impact, bulging of chest wall or cardiac dysrhythmias
To do prompt interventions necessary
Tx:
Report to physicians all conditions that needs physicians presence Administrations of surfactant (artificial or exogenous) Place or apply pulse oximeter in appropriate place such as in lower extremities and record and change probe levels hourly Position infant in supine position with rolled small towel beneath shoulders to produce slight hyperextention Provide prompt tactile stimulations such as rubbing infants back or tapping or flicking infants foot if apnea occurs Provide mouth care using saline or glycerin swabs It decreases severity of condition and associated complications. Provides constant noninvasive monitoring oxygen level
Such positioning may facilitate respiration and reduce episodes of apnea especially in the presence of hypoxia, metabolic acidosis or hypercapnia Stimulates CNS to promote body movement and spontaneous return of respirations. Helps prevent drying and cracking of lips associated with absence of oral intake or the drying effects of oxygen therapy Reduces metabolic rate and oxygen consumption.
Edx:
Promote rest by minimizing stimulation if necessary and energy expenditure Inform parents about infants behavioral cues and responses to stressors Encouraged parental contact
So that they can effectively intervene
to minimize stress and facilitate the infants positive adaptation to entrauterine life Sometimes, infants experience fewer or no episodes of apnea or bradycardia if parents touch and talk to them. Avoids further abdominal trauma and infection to the infant
Encourage parents to do hand hygiene before and after and minimize handling infant Encourage parents to provide stroking
Enhances emotional and stroking
of head, hands and feet and talk to infant
needs through quiet conversation
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Causes: UTI during pregnancy
Temperature fluctuates easily
Ineffective Thermoregulati on Imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements Low weight Immature CNS development Small stomach capacity
Experienced preterm labor
Risk for Infection Easily traumatized tissue
Ineffectiv e protection
Results to preterm infant Immature development of lungs Lack of pulmonary surfactant in the airspaces
Immature immune system
Fragile skin Appear as an eosinophilic, amorphoAs material, lining or filling the air spaces and blocking gas exchange Blood passing through the lungs is unable to pick up oxygen and unload carbon dioxide Blood oxygen levels fall and carbon dioxide rises, resulting in rising blood acid levels and hypoxia Use of accessory muscles such as abdominal muscle and nasal flaring Breathing deficiency Impaired gas exchange
Low lung volume in expiration Blood oxygen levels fall and carbon dioxide rises Impaired gas exchange
High surface tension within fluid-lined airspaces
Dysfunction of surfactant
Lungs will likely collapse Increase RR Poor pulmonary compliance
Hyaline Distress syndrome
DEATH
Sudden or unexplained deterioration in condition associated with cyanosis, diminished or absent sounds, shift of point maximal impact, bulging of chest wall or cardiac dysrhythmias
Вам также может понравиться
- Premature Infant Breathing DifficultiesДокумент5 страницPremature Infant Breathing DifficultiesRustan FrozenОценок пока нет
- Post-maturity Nursing Assessment and InterventionДокумент6 страницPost-maturity Nursing Assessment and InterventionJeanne Mari CostalesОценок пока нет
- Manage Preterm Labor with Bed Rest and TocolysisДокумент4 страницыManage Preterm Labor with Bed Rest and TocolysisYeni PuspitaОценок пока нет
- Medication ThalassemiaДокумент3 страницыMedication ThalassemiaDivya ToppoОценок пока нет
- St. Anthony's College Nursing Department Patient Care Plan for S.LДокумент2 страницыSt. Anthony's College Nursing Department Patient Care Plan for S.LAirme Raz AlejandroОценок пока нет
- NCP - Preeclampsia (A)Документ6 страницNCP - Preeclampsia (A)Ronel ResurricionОценок пока нет
- New Born NCPДокумент8 страницNew Born NCPCarl Vincent Marrion Rejuso100% (1)
- Managing diabetes during pregnancyДокумент8 страницManaging diabetes during pregnancyAbdelmar SusulanОценок пока нет
- Tetralogy of Fallot Nursing Diagnosis and ManagementДокумент2 страницыTetralogy of Fallot Nursing Diagnosis and ManagementKarl KiwisОценок пока нет
- Nursing Plan for Preterm Infant with Respiratory IssuesДокумент2 страницыNursing Plan for Preterm Infant with Respiratory IssuesJay VillasotoОценок пока нет
- Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals/ Objectives Nursing Intervention S Rational E EvaluationДокумент21 страницаNursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals/ Objectives Nursing Intervention S Rational E EvaluationJoanne Bernadette Aguilar100% (1)
- Post-Term Pregnancy Emergency C-Section Due to Non-Reassuring Fetal Heart RateДокумент7 страницPost-Term Pregnancy Emergency C-Section Due to Non-Reassuring Fetal Heart RateCameron De GuzmanОценок пока нет
- Woman's Risk of Eclampsia at 38 Weeks PregnantДокумент6 страницWoman's Risk of Eclampsia at 38 Weeks PregnantChristian Joseph OpianaОценок пока нет
- NCP On Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент6 страницNCP On Impaired Gas Exchangeallkhusairy6tuansiОценок пока нет
- NCP Meningitis Sure NaniДокумент2 страницыNCP Meningitis Sure NaniARISОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan for Fluid Volume DeficitДокумент9 страницNursing Care Plan for Fluid Volume DeficitYesha Mae MartinОценок пока нет
- Case Presentation HydrocephalusДокумент48 страницCase Presentation HydrocephalusSu Osman50% (2)
- NCP PPHДокумент2 страницыNCP PPHMark Joseph Christian100% (1)
- A Case Study In:: Hirschsprung DiseaseДокумент18 страницA Case Study In:: Hirschsprung DiseaseJaimie La PenaОценок пока нет
- Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals/ Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationДокумент20 страницNursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals/ Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationElaine Grace Timbol-Babasa100% (1)
- NCP - BronchopneumoniaДокумент11 страницNCP - BronchopneumoniaMaria Ivy Mendoza100% (1)
- Anatomy &physiology JaundiceДокумент2 страницыAnatomy &physiology JaundiceHCX dghhqОценок пока нет
- Neonatal Jaundice Nursing Care PlanДокумент3 страницыNeonatal Jaundice Nursing Care PlanCristyl Shine BariaoОценок пока нет
- 5 Nursing Diagnoses and Interventions for HypertensionДокумент7 страниц5 Nursing Diagnoses and Interventions for Hypertensionmelerine16Оценок пока нет
- Nursing Care PlanДокумент6 страницNursing Care PlanAnthea ValinoОценок пока нет
- Tetralogy of FallotДокумент5 страницTetralogy of FallotCharity OaniaОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceДокумент6 страницNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceCaroline ChaОценок пока нет
- Reflection 1Документ5 страницReflection 1api-400554289Оценок пока нет
- Neonatal Jaundice Treatment GuidelinesДокумент12 страницNeonatal Jaundice Treatment GuidelinesJustine NyangaresiОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective Data: Short Term IndependentДокумент5 страницNursing Care Plan: Subjective Data: Short Term IndependentIrish May SignioОценок пока нет
- Assessing and Treating Pneumonia Through Respiratory Monitoring and InterventionsДокумент3 страницыAssessing and Treating Pneumonia Through Respiratory Monitoring and InterventionsDyanne BautistaОценок пока нет
- Neonatal Sepsis Case StudyДокумент6 страницNeonatal Sepsis Case StudyCatherine PradoОценок пока нет
- Neonatal Respiratory Distress SyndromenhschoicesДокумент6 страницNeonatal Respiratory Distress SyndromenhschoicessehatkanОценок пока нет
- Respiratory DistressДокумент10 страницRespiratory DistressnilmbbsОценок пока нет
- CS Case PresentationДокумент16 страницCS Case PresentationjisooОценок пока нет
- Pediatric Pneumonia Case StudyДокумент44 страницыPediatric Pneumonia Case StudyPreiane PayladoОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermДокумент4 страницыNursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermErika Danalle ArceoОценок пока нет
- NCP - PCGHДокумент9 страницNCP - PCGHLucelle ArellanoОценок пока нет
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationДокумент1 страницаNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationCharina AubreyОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Analysis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationДокумент4 страницыNursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Analysis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationElla EvangelistaОценок пока нет
- Altered Tissue Perfusion UteroplacentalДокумент4 страницыAltered Tissue Perfusion UteroplacentalAlyОценок пока нет
- Fluorosis Diagnosis, Patient Management, Monitoring and RecoveryДокумент24 страницыFluorosis Diagnosis, Patient Management, Monitoring and RecoverydrjriОценок пока нет
- Assessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationДокумент6 страницAssessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationimnasОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan for a Patient with Multiple Bruises and Difficulty BreathingДокумент3 страницыNursing Care Plan for a Patient with Multiple Bruises and Difficulty BreathingLeogalvez BedanoОценок пока нет
- Anemia Unspecified FinalДокумент47 страницAnemia Unspecified FinalMaria Paula BungayОценок пока нет
- Gender: FemaleДокумент9 страницGender: FemaleNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3AОценок пока нет
- Neonatal JaundiceДокумент24 страницыNeonatal JaundiceJOSLINОценок пока нет
- PP Insect Bite 2007 (Print)Документ16 страницPP Insect Bite 2007 (Print)Ali RumiОценок пока нет
- A Mini Case Presentation On Influenza VirusДокумент22 страницыA Mini Case Presentation On Influenza Virusangelo100% (1)
- Pre EclampsiaДокумент13 страницPre EclampsiaEniamrahs DnalonОценок пока нет
- NCP SepsisДокумент6 страницNCP SepsisgopscharanОценок пока нет
- Case CHFДокумент10 страницCase CHFAgnes Erlita Distriani Patade50% (2)
- Power Point For The Case Study About PneumoniaДокумент16 страницPower Point For The Case Study About PneumoniaJai - Ho86% (7)
- NCPДокумент15 страницNCPCamille PinedaОценок пока нет
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsДокумент3 страницыNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsSarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanОценок пока нет
- Respiratory Distress Syndrome (Iniego Carlo Jay)Документ9 страницRespiratory Distress Syndrome (Iniego Carlo Jay)Carlojay IniegoОценок пока нет
- Idiopathic Respiratory Disease SyndromeДокумент30 страницIdiopathic Respiratory Disease SyndromeAllan-VonОценок пока нет
- NCP NicuДокумент3 страницыNCP NicuNoel Telosa100% (1)
- 1) Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS) Hyaline Membrane Disease (HMD)Документ9 страниц1) Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS) Hyaline Membrane Disease (HMD)ُEssraa AdeelОценок пока нет
- Neonatal Respiratory Distress SyndromeДокумент4 страницыNeonatal Respiratory Distress SyndromePahw BaluisОценок пока нет
- Human RightsДокумент2 страницыHuman RightsNoreen PinedaОценок пока нет
- NCP Proper 1Документ6 страницNCP Proper 1Noreen PinedaОценок пока нет
- PenaltyДокумент6 страницPenaltyNoreen PinedaОценок пока нет
- GustatoryДокумент2 страницыGustatoryNoreen PinedaОценок пока нет
- Combination of Lisinopril and Nifedipine GITS.10Документ7 страницCombination of Lisinopril and Nifedipine GITS.10Andi PermanaОценок пока нет
- Organ Systems ComparisonДокумент12 страницOrgan Systems ComparisonJeffrey YumangОценок пока нет
- Placenta FunctionsДокумент46 страницPlacenta Functionsvenkata sryanamala50% (2)
- Genetic material in adenovirus virionsДокумент51 страницаGenetic material in adenovirus virionsBatool SherbiniОценок пока нет
- Hip FractureДокумент1 страницаHip FractureHAILIE23100% (3)
- Fournier's Gangrene: Yang Lu MS3 AUC School of MedicineДокумент15 страницFournier's Gangrene: Yang Lu MS3 AUC School of MedicineYang JunОценок пока нет
- PASSIVE MOVEMENT TECHNIQUESДокумент58 страницPASSIVE MOVEMENT TECHNIQUESabdulahОценок пока нет
- Manage High-Risk PregnanciesДокумент33 страницыManage High-Risk PregnanciesDakshayini MbОценок пока нет
- Perbedaan Kepadatan Lalat Yang Hinggap Pada Fly Grill Yang Berbeda Warna Di Pasar SrimangunanДокумент80 страницPerbedaan Kepadatan Lalat Yang Hinggap Pada Fly Grill Yang Berbeda Warna Di Pasar SrimangunanIrina MayasisianaОценок пока нет
- Criptorquidia en PerrosДокумент4 страницыCriptorquidia en PerrosDanielaОценок пока нет
- DiagramДокумент12 страницDiagramJessica CindyОценок пока нет
- Cyanotic Congenital Heart DiseaseДокумент6 страницCyanotic Congenital Heart DiseaseSimran JosanОценок пока нет
- Clinical Practice Guideline for Pharmacologic Treatment of Chronic InsomniaДокумент43 страницыClinical Practice Guideline for Pharmacologic Treatment of Chronic InsomniaAna Cristina BrazОценок пока нет
- Aminophylline (Theophylline Ethylenediamine) : TruphyllineДокумент4 страницыAminophylline (Theophylline Ethylenediamine) : TruphyllineRosalie SepayaОценок пока нет
- Electo Homeopathy MedicinesДокумент3 страницыElecto Homeopathy MedicinesKoushik MaitraОценок пока нет
- Amended Modern Pharmacology Syllabus 051218Документ26 страницAmended Modern Pharmacology Syllabus 051218harshad patelОценок пока нет
- Greyson 2019Документ10 страницGreyson 2019Ziha Zia Leonita FauziОценок пока нет
- Amacon2022 - Total Paper Poster List: SR No Presentor Name Contact Number Institute Type of Present Ation Title SubjectДокумент35 страницAmacon2022 - Total Paper Poster List: SR No Presentor Name Contact Number Institute Type of Present Ation Title SubjectViraj ShahОценок пока нет
- Formula of Vital Health IndicatorsДокумент3 страницыFormula of Vital Health IndicatorsZyntrx Villas100% (1)
- Nitsbin(ንጽቢን) I. Medicine 1st Edition - (Revised)-1Документ1 380 страницNitsbin(ንጽቢን) I. Medicine 1st Edition - (Revised)-1bedanetibeso0Оценок пока нет
- Merged Document 14 PDFДокумент9 страницMerged Document 14 PDFMurali SmatОценок пока нет
- Science: Quarter 2 - Module 1Документ20 страницScience: Quarter 2 - Module 1Kate BatacОценок пока нет
- Sonopuls 490 User ManualДокумент57 страницSonopuls 490 User ManualMaryam BushraОценок пока нет
- Hensleys Practical Approach To Cardiothoracic Anesthesia Sixth EditionДокумент62 страницыHensleys Practical Approach To Cardiothoracic Anesthesia Sixth Editiontimothy.daniels842100% (39)
- Prevalence of Gestational Diabetes and Contributing Factors Among Pregnant Jordanian Women Attending Jordan University HospitalДокумент8 страницPrevalence of Gestational Diabetes and Contributing Factors Among Pregnant Jordanian Women Attending Jordan University HospitalManar ShamielhОценок пока нет
- Lagier2022 Atelectasia en AnestesiologiaДокумент31 страницаLagier2022 Atelectasia en AnestesiologiaNicolas SuarezОценок пока нет
- Live Donor Liver Transplantation: Caq CornerДокумент12 страницLive Donor Liver Transplantation: Caq CornerBarbara ZabraОценок пока нет
- Enterobacter QuizДокумент8 страницEnterobacter QuizDan Paolo Sanchez100% (2)
- Comparative Study of Hepatoprotective Activity of Proprietary Polyherbal Preparations Against paraДокумент5 страницComparative Study of Hepatoprotective Activity of Proprietary Polyherbal Preparations Against paraassemОценок пока нет
- 10 Must Know Factors of OcclusionДокумент2 страницы10 Must Know Factors of OcclusionGreg Sitek0% (1)