Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Topic1 1101H Sociology
Загружено:
Jona MacaslingИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Topic1 1101H Sociology
Загружено:
Jona MacaslingАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
TOPIC 1: WHAT IS SOCIOLOGY?
I. DEFINITION OF SOCIOLOGY
II. PURPOSES OF SOCIOLOGICAL RESEARCH
III. EXAMPLE: DURKHEIMS STUDY OF SUICIDE
IV. MORE EXAMPLES OF THE SOCIOLOGICAL APPROACH
I. DEFINITION OF SOCIOLOGY
Sociology is a scientific discipline which focuses on how groups influence how individuals think, feel, act, and live
(1) Sociology is empirical: data-based research to test arguments/hypotheses/theories
(2) Sociology examines how groups affect individuals Value: general statement of what is right, beautiful, proper, etc.
Norm: specific prescription of how an individual ought to behave to be consistent with value. Vary according to degree of: conditionality intensity consensus
Sanctions: penalties or pressures designed to enforce compliance informal (social) formal (legal)
Values & Norms
Group Memberships
Individual Behavior
Sanctions
2 points to note: a. individuals belong to multiple groups with different values and norms norms, sanctions, and behavior are dynamic not static: they change (they are socially constructed)
b.
II. PURPOSES OF SOCIOLOGICAL RESEARCH
(1) Fact-finding: e.g., crime rate, poverty rate, income distribution, birth rate, family composition, church attendance
(2) Causal Analysis: relationships among variables
Examples?
Note: sociology produces generalizations not laws
(3) Theory Building and Testing: developing general explanations of phenomena or testing two (or more) explanations to see which is supported by the data
Example: deviance Deterrence Theory: greater social control and stronger enforcement of social norms reduce deviant behavior Labeling Theory: when people are treated as deviants, they grow to accept this definition of themselves and become increasingly deviant
III. EXAMPLE: DURKHEIMS STUDY OF SUICIDE
Emile Durkheims (1858-1917) most famous finding about suicide in Europe: (1) suicide rate higher for Protestants than for Catholics (and Jews) How does Durkheim explain this? How does he go about deciding which variables are important and unimportant as a cause of suicide?
Other findings:
(2) suicide rate higher for unmarried people than for married people
(3) suicide rate higher in peacetime than in wartime
Explanation?
Egoistic suicide
(4) suicide rate higher for soldiers than for civilians
(5) suicide rate higher for volunteers than for draftees
Explanation?
Altruistic suicide
(6) suicide rate higher in countries that experienced economic growth and recession than in economically stable countries (7) suicide rate higher for divorced people than married people
Explanation?
Anomic suicide
Whats Durkheims general theory?
IV.
MORE EXAMPLES OF THE SOCIOLOGICAL APPROACH
(1)
The Pattern of Christmas Gift-Giving in Middletown (Theodore Caplow):
Questions he poses - who gives gifts? - who receives gifts? - what kinds of gifts are given? - what explains the patterns?
Data; how does he collect data on this topic?
Gift Giving and Gender (Table 4) % of All Gifts - Receivers Givers Male Female Male & Female Totals Male 4.2% 17.0% Female 11.1% 17.4% Male & Female 0.9% 2.2% Total 16.2% 36.6%
18.0% 39.2%
23.1% 51.6%
6.1% 9.2%
47.2% 100%
What are the main findings in this table?
Gift Giving by Relationship and Residential Distance (Table 6) % of relationships marked by gifts Relationship to Respondent Fathers Mothers Children Childrens spouses Grandparents Grandchildren Siblings Siblings spouses Siblings children Parents siblings Within 50 miles Over 50 miles
100% 98% 96% 92% 96% 90% 32% 24% 19% 15%
85% 90% 95% 94% 50% 77% 35% 24% 15% 10%
What are the findings in this table?
What do these patterns indicate?
(2) Whats in a name? Lieberson and Bell, Childrens First Names and Social Taste, American Journal of Sociology, Nov. 1992 Question: what patterns are there in girls and boys names? Top 6 Girls and Boys Names of Children Born in New York State, 19731985 GIRLS % of all girls names 4.2 3.1 2.3 2.0 1.9 1.8 15% BOYS % of all boys names 5.7 3.4 2.7 2.6 2.6 2.6 20%
Name Jennifer Christine Jessica Melissa Michelle Nicole TOTAL
Name Michael Christopher John David Matthew Joseph TOTAL
Finding: less variation in boys names than girls names
What do you think the reason for this is?
Do we see the same results in a different sample? SOCI 1101 - SPRING 2002 Top 6 Girls and Boys Names of Students in SOC 1101 FEMALES (201) Name Lauren Sara(h) Katherine/ (C)Kathryn Jennifer Jessica Lindsay/ Lindsey/ Lyndsey % of all girls names 5.5 4.5 4.0 Name Matthew Michael Benjamin MALES (99) % of all boys names 9.0 4.0 4.0
3.5 3.0 3.0
Andrew Jonathan Brian
4.0 3.0 3.0
TOTAL
23.5%
TOTAL
27.0%
If Lieberson and Bell are correct, then there should be less variation over time in boys names compared to girls names Top 5 Girls and Boys Names of Maternal Grandparents of Students in SOCI 1101 (parentheses are # of students in class with same name)
Name Mary Dorothy Martha Ruth Betty
Number 14 (3) 7 (1) 7 (0) 5 (1) 5 (0)
Name Robert William John Thomas Jack
Number 18 (2) 16 (2) 11 (2) 9 (2) 8 (0)
Вам также может понравиться
- Ko Et Al. (In Press), PerspectivesДокумент81 страницаKo Et Al. (In Press), PerspectivesOmar AdilОценок пока нет
- Diener 2012Документ8 страницDiener 2012Gildardo Bautista HernándezОценок пока нет
- Harris & Sim - Who Is MultiracialДокумент15 страницHarris & Sim - Who Is MultiracialAndi TothОценок пока нет
- Review of SIT and StereotypingДокумент26 страницReview of SIT and StereotypingBarqueros libros y papeleríaОценок пока нет
- Swimsuit Sweater Study PDFДокумент16 страницSwimsuit Sweater Study PDFfotinimavr94Оценок пока нет
- UCSC Psychology 1Документ638 страницUCSC Psychology 1YasuoОценок пока нет
- Character Strengths in Fifty-Four Nations and The FiftyДокумент13 страницCharacter Strengths in Fifty-Four Nations and The FiftyPaulo LuísОценок пока нет
- Social NetworkingДокумент23 страницыSocial Networkingapi-358155650Оценок пока нет
- SocioculturalДокумент79 страницSocioculturalkaymmmmmmmОценок пока нет
- Rayburn 2009Документ3 страницыRayburn 2009Ryan HaryoОценок пока нет
- The Biological Foundations of Organizational BehaviorОт EverandThe Biological Foundations of Organizational BehaviorStephen M. ColarelliОценок пока нет
- 2008 SheldonKasser MOEMДокумент10 страниц2008 SheldonKasser MOEMNeno Aisyah HadiyantiОценок пока нет
- Inequality by Design: Cracking the Bell Curve MythОт EverandInequality by Design: Cracking the Bell Curve MythРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (6)
- Manuscript Gomila Paluck Preprint Forthcoming JSPP Deviance From Social Norms Who Are The DeviantsДокумент48 страницManuscript Gomila Paluck Preprint Forthcoming JSPP Deviance From Social Norms Who Are The DeviantstpОценок пока нет
- Democracy at Risk: How Terrorist Threats Affect the PublicОт EverandDemocracy at Risk: How Terrorist Threats Affect the PublicОценок пока нет
- Social Anxiety, Self-Regulation, and Fear of Negative EvaluationДокумент12 страницSocial Anxiety, Self-Regulation, and Fear of Negative Evaluationselamet apriyantoОценок пока нет
- 9.3+Evolutionary+Theory+and+Political+Leadership+ Smith+et.+al PDFДокумент16 страниц9.3+Evolutionary+Theory+and+Political+Leadership+ Smith+et.+al PDFxFloydxОценок пока нет
- Moral Politics: How Liberals and Conservatives ThinkОт EverandMoral Politics: How Liberals and Conservatives ThinkРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (93)
- Lilienfeld Giving Debiasing AwayДокумент9 страницLilienfeld Giving Debiasing AwayDecu IoanaОценок пока нет
- The Welfare Experiments: Politics and Policy EvaluationОт EverandThe Welfare Experiments: Politics and Policy EvaluationОценок пока нет
- Dark Core Personality TestДокумент1 страницаDark Core Personality TestNofriza EndahОценок пока нет
- Dark Core Personality TestДокумент1 страницаDark Core Personality TestNofriza EndahОценок пока нет
- StereotypesДокумент3 страницыStereotypesAlice Mendeleyeva100% (1)
- Dangerous Frames: How Ideas about Race and Gender Shape Public OpinionОт EverandDangerous Frames: How Ideas about Race and Gender Shape Public OpinionРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (2)
- JPSP 2009 Moral FoundationsДокумент18 страницJPSP 2009 Moral FoundationsPapuna ChivadzeОценок пока нет
- Influencia Del Atractivo Fisico en Las Relaciones InterpersonalesДокумент11 страницInfluencia Del Atractivo Fisico en Las Relaciones InterpersonalesIvan Eduardo Hernandez GomezОценок пока нет
- Victoria's Dirty SecretДокумент15 страницVictoria's Dirty SecretDesiree Grace Tan-LinОценок пока нет
- A Theory of System Justification: Science BriefДокумент10 страницA Theory of System Justification: Science BriefVíctor Jiménez-BenítezОценок пока нет
- Sexual Orientation and Psychodynamic Psychotherapy: Sexual Science and Clinical PracticeОт EverandSexual Orientation and Psychodynamic Psychotherapy: Sexual Science and Clinical PracticeРейтинг: 2 из 5 звезд2/5 (2)
- A perspective on how our Society was Built, Topics on Power in AmericaОт EverandA perspective on how our Society was Built, Topics on Power in AmericaОценок пока нет
- American Cool: Constructing a Twentieth-Century Emotional StyleОт EverandAmerican Cool: Constructing a Twentieth-Century Emotional StyleРейтинг: 1.5 из 5 звезд1.5/5 (3)
- Why Welfare States Persist: The Importance of Public Opinion in DemocraciesОт EverandWhy Welfare States Persist: The Importance of Public Opinion in DemocraciesОценок пока нет
- Prism of GenderДокумент51 страницаPrism of Genderwalyuk50% (2)
- Exploring Social Psychology 8th Edition Myers Solutions ManualДокумент25 страницExploring Social Psychology 8th Edition Myers Solutions ManualRobertCookdktg100% (66)
- Comprehensive Handbook of Personality and Psychopathology, Personality and Everyday FunctioningОт EverandComprehensive Handbook of Personality and Psychopathology, Personality and Everyday FunctioningОценок пока нет
- Culture, Personality, and Subjective Well-BeingДокумент34 страницыCulture, Personality, and Subjective Well-BeingEka CitraОценок пока нет
- Dwnload Full Exploring Social Psychology 8th Edition Myers Solutions Manual PDFДокумент35 страницDwnload Full Exploring Social Psychology 8th Edition Myers Solutions Manual PDFsiphilisdysluite7xrxc100% (12)
- The Bedan Journal of Psychology 2008Документ262 страницыThe Bedan Journal of Psychology 2008San Beda Alabang100% (5)
- Social Stigma and Self-Esteem The Self-ProtectiveДокумент70 страницSocial Stigma and Self-Esteem The Self-ProtectiveRatu Nurul AfiniОценок пока нет
- DescriminationДокумент6 страницDescriminationG BОценок пока нет
- The Extended EssayДокумент13 страницThe Extended EssayMaria KochańskaОценок пока нет
- Obedience To Authority: Order and ChaosДокумент8 страницObedience To Authority: Order and ChaosAlex LeonardОценок пока нет
- National Security Through a Cockeyed Lens: How Cognitive Bias Impacts U.S. Foreign PolicyОт EverandNational Security Through a Cockeyed Lens: How Cognitive Bias Impacts U.S. Foreign PolicyОценок пока нет
- The Concepts of Conformity and ObedienceДокумент8 страницThe Concepts of Conformity and Obedienceapi-545354167Оценок пока нет
- The Social and Psychological Characteristics of NoДокумент26 страницThe Social and Psychological Characteristics of NoLarisa - Maria BărnuțОценок пока нет
- Subject and Verb Agreement - Grade 5 - Video ScriptДокумент6 страницSubject and Verb Agreement - Grade 5 - Video ScriptJona Macasling100% (1)
- 4 Periodical Test Computer 1Документ2 страницы4 Periodical Test Computer 1Jona MacaslingОценок пока нет
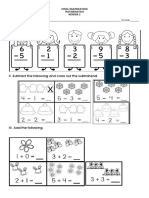
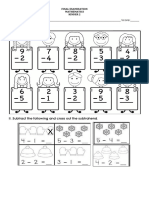
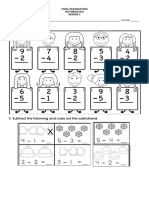
- II. Subtract The Following and Cross Out The SubtrahendДокумент1 страницаII. Subtract The Following and Cross Out The SubtrahendJona MacaslingОценок пока нет
- 4 TH MATHk 2Документ1 страница4 TH MATHk 2Jona MacaslingОценок пока нет
- I. Subtract The Following.: Name: - ScoreДокумент1 страницаI. Subtract The Following.: Name: - ScoreJona MacaslingОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan: I. ObjectivesДокумент3 страницыLesson Plan: I. ObjectivesJona MacaslingОценок пока нет
- Water Cycle I - Objectives: WWW - Primaryresources.co - Uk/english/docs/explanation - Watercycle.d OcДокумент3 страницыWater Cycle I - Objectives: WWW - Primaryresources.co - Uk/english/docs/explanation - Watercycle.d OcJona MacaslingОценок пока нет
- American Sociological AssociationДокумент9 страницAmerican Sociological AssociationShaziaОценок пока нет
- Deviance, Crime and Social Control - Course Content PlanДокумент2 страницыDeviance, Crime and Social Control - Course Content Plannimra khaliqОценок пока нет
- Essays On Cultural Formation of KeralaДокумент15 страницEssays On Cultural Formation of Keralasuhair1951100% (3)
- Durkheim & Weber: Comparison & Relevance TodayДокумент2 страницыDurkheim & Weber: Comparison & Relevance TodayThe CSS Point100% (2)
- Buddhist Values and The Religious Tradition of Jagannath Temple at PuriДокумент11 страницBuddhist Values and The Religious Tradition of Jagannath Temple at PuriRamanuj GangulyОценок пока нет
- BA Semester I and IIДокумент366 страницBA Semester I and IIrakeshtrikha8668100% (1)
- Revised Soc. Sci Notes LONGДокумент14 страницRevised Soc. Sci Notes LONGEchuserang FrogletОценок пока нет
- JCR10 2 PDFДокумент6 страницJCR10 2 PDFmanugeorgeОценок пока нет
- Modern Socio-Technology: Set by de SitterДокумент12 страницModern Socio-Technology: Set by de SitterSAMSUL ARIF RAMADANIОценок пока нет
- Public Policy An IntroductionДокумент22 страницыPublic Policy An IntroductionPrincess100% (3)
- Fidp Diass IbabaoДокумент10 страницFidp Diass IbabaoNikki Anne BerlanasОценок пока нет
- Ucspol 2Документ18 страницUcspol 2ciaaa.maeeeОценок пока нет
- 1000 MCQs (Human Development and Family Studies)Документ112 страниц1000 MCQs (Human Development and Family Studies)Jude OnitiОценок пока нет
- Tutor-Marked AssignmentДокумент3 страницыTutor-Marked AssignmentZed DyОценок пока нет
- MED SyllabusДокумент67 страницMED SyllabusDigbi's CreationОценок пока нет
- Caldwell, J. C. 1996 Demography PDFДокумент30 страницCaldwell, J. C. 1996 Demography PDFMaríaОценок пока нет
- Cultural History and Its Neighbours: C & H D J 1 (1) June 2012, E006 eISSN 2253-797XДокумент9 страницCultural History and Its Neighbours: C & H D J 1 (1) June 2012, E006 eISSN 2253-797XerluiОценок пока нет
- Hans MorgenthauДокумент182 страницыHans MorgenthauPan RemyОценок пока нет
- Theories and Causes of Crimes: Chapter OneДокумент29 страницTheories and Causes of Crimes: Chapter OneJudessa Mae Pronce Cadacio100% (1)
- Nature and Scope of JurisprudenceДокумент7 страницNature and Scope of JurisprudenceShivam Kumar67% (3)
- Asa12 ProgrammeДокумент184 страницыAsa12 ProgrammeChand M BashaОценок пока нет
- Hedström y Wittrock (Eds.) (2009) - Frontiers of SociologyДокумент457 страницHedström y Wittrock (Eds.) (2009) - Frontiers of SociologyMarcelo Miño100% (1)
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Soc4v97.012.11f Taught by Bobby Alexander (Bcalex)Документ6 страницUT Dallas Syllabus For Soc4v97.012.11f Taught by Bobby Alexander (Bcalex)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupОценок пока нет
- Diass ExaminationДокумент4 страницыDiass ExaminationRonald AlmagroОценок пока нет
- Factors AFFECTING READING PERFORMANCEДокумент6 страницFactors AFFECTING READING PERFORMANCEJerreza Casagnap Jacob100% (2)
- Socio 203 NotesДокумент64 страницыSocio 203 NotesloulourafdalОценок пока нет
- Sociological Perspective & Theorists: A Breakdown of Functionalism, Conflict Theory and Symbolic InteractionismДокумент85 страницSociological Perspective & Theorists: A Breakdown of Functionalism, Conflict Theory and Symbolic InteractionismRodnie Flores BaguioОценок пока нет
- 1 - Azevedo-2019-African Studies and The State of The ArtДокумент37 страниц1 - Azevedo-2019-African Studies and The State of The ArtSebastian GarciaОценок пока нет
- "Cultural Citizenship" - Jan PakulskiДокумент31 страница"Cultural Citizenship" - Jan PakulskiPaper TigerlilyОценок пока нет
- Feminist EpistemologyДокумент13 страницFeminist EpistemologyJoyal Samuel JoseОценок пока нет