Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Osam ER Drugs
Загружено:
Dhan LopezИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Osam ER Drugs
Загружено:
Dhan LopezАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
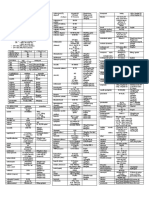
DRUG CLASSIFICATION INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION SIDE EFFECTS NSG.
RESPONSIBILITY
Citicoline CNS Stimulant CVD in acute & recovery phase,
symptoms & signs oI cerebral
insuIIiciency
Parasympathetic hypertonia Gastrointestinal disorders Somazine must not be
administered along with
medicaments containing
meclophenoxate
Dopamine Inotropic, vasopressor
To treat shock and correct
hemodnamic imbalances, improve
perIusion oI vital organs, to increase
cardiac output, and to correct
hypotension.
Contraindicated in patient
with uncorrected
tachyarrhythmias,
pheocromocytoma, or
ventricular Iibrillation.
- Use cautiously in patients
with occlusive vascular
disease, cold injuries,
diabetic endarteritis, and
arterial embolism; in
pregnant woman; with a
history oI sulIite sensitivity;
and in those taking MAO
inhibitor.
Side EIIects:
CNS: headache
GI: nausea
During inIusion, Irequently
monitor ECG, BP, cardiac
output, CVP, pulmonary
artery wedge pressure, pulse
rate, urine output, and color
and temperature oI the limbs.
II diastolic pressure rises
disproportionately, decrease
perIusion rate and watch out
careIully Ior Iurther signs oI
vasoconstriction unless such
action is desired.
Observe Ior adverse reaction.
Check Ior urine output.
Hydralazine
Hydrochloride
antihypertension For hypertensive patient tachycardia, palpitation, angina pectoris,
severe headache, dizziness, weight gain, GI
disturbances, pruritus, rashes, nausea and
vomiting
O Give oral drug with Iood to
increase
bioavailability(drug should
be given in a consistent
relationship ti ingestion oI
Iood Ior consistent
response to therapy).
O Drug may cause a
syndrome resembling
systemic lupus
erythematosus (SLE).
Arrange Ior CBC, LE cell
preparations, and ANA
titers beIore and
periodically during
prolonged therapy, even in
the asymptomatic patient.
Discontinue iI blood
dyscrasias occur.
Reevaluate therapy iI ANA
or LE tests are positive.
O Arrange Ior pyridoxine iI
patient develops symptoms
oI peripheral neuritis.
O Monitor patient Ior
orthostatic hypotension
which is most marked in
the morning and in hot
weather, and with alcohol
or exercise.
Isosorbide dinatrate
cardiovascular
agent; nitrate vasodilator
It is prescribed as a coronary
vasodilator in the treatment oI
angina pectoris and congestive heart
Iailure and esophageal spasm caused
by GI reIlux.
Closed-angle glaucoma,
known hypersensitivity to
this drug, concurrent use oI
drugs Ior erectile
dysIunction, narrow-angle
glaucoma, head trauma, or
severe anemia prohibits its
use.
O Iast, slow, pounding, or uneven heart
rate;
O worsening angina pain;
O blurred vision or dry mouth;
O nausea, vomiting, sweating, pale skin,
Ieeling like you might pass out; or
O blue-colored skin, tiredness, and
Ieeling...
Make position changes
slowly, particularly Irom
recumbent to upright
posture, and dangle Ieet
and ankles beIore
walking.
Lie down at the Iirst
indication oI light-
headedness or Iaintness.
eep a record oI anginal
attacks and the number oI
sublingual tablets
required to provide relieI.
Do not drink alcohol
because it may increase
possibility oI light-
headedness and Iaintness.
Do not breast Ieed while
taking this drug without
consulting physician.
Atropine SulIate Anticholinergic - Antidote to overdosage with
cholinergic substances (nerve gases,
poisonous mushroom)
- Pre-op medication to reduce salivary
and resp. tract secretions.
Contraindicated in
patients with glaucoma,
pyloric stenosis or
prostatic hypertrophy,
except in doses ordinarily
used Ior preanesthetic
medication.
Can cause blurred vision, dilated pupils,
dry mouth, palpitations urinary retention,
tachycardia drowsiness, and conIusion
monitor level oI
consciousness
O do not sit up or stand up
quickly
O advise patient to stay out oI
bright light
O chew sugarless gums and
suck hard candies to avoid
mouth dryness
O use lubricating drops is
wearing contact lenses
avoid extreme heat
Sodium Chloride Electrolyte supplement Hydrating solution; hyperosmolar
diabetes
Normal or elevated
electrolyte levels (with 3
and 5 solutions)
Fluid retention
CV: edema (when given too rapidly or in
excess), thrombophlebitis, heart failure
exacerbation
Metabolic: Iluid and electrolyte
disturbances (such as hypernatremia and
hyperphosphatemia), aggravation of
existing metabolic acidosis (with
excessive inIusion)
Respiratory: pulmonary edema
Other: pain, swelling, local tenderness,
abscess, or tissue necrosis at I.V. site
Teach patient to recognize
and immediately report
serious adverse reactions,
such as breathing problems or
swelling.
Instruct patient to report
pain, tenderness, or swelling
at injection site.
As appropriate, review all
other signiIicant and liIe-
threatening adverse reactions
and interactions, especially
those related to the tests
mentioned above.
Cordarone Adrenergic blocker Life-threatening ventricular
arrhythmias
Hypersensitivity to
drug
Cardiogenic shock
Second- or third-
degree AV block
Marked sinus
bradycardia
Breastfeeding
Neonates
CNS: dizziness, fatigue, headache,
insomnia, paresthesia, peripheral
neuropathy, poor coordination,
involuntary movements, tremor,
sleep disturbances
CV: hypotension, heart faiIure,
worsening arrhythmia, AV bIock,
sinoatriaI node dysfunction,
bradycardia, asystoIe, cardiac
arrest, cardiogenic shock,
eIectromechanicaI dissociation,
ventricuIar tachycardia
EENT: corneal microdeposits,
corneal or macular degeneration,
visual disturbances, dry eyes, eye
discomfort, optic neuritis or
neuropathy, scotoma, lens
opacities, photophobia, visual
Monitor patient closely.
Drug may cause serious
or life-threatening
adverse reactions.
Watch for slow onset of
life-threatening
arrhythmias, especially
after giving loading
dose.
Monitor ECG
continuously during
loading dose and when
dosage is changed.
halos, 5a5iIIedema
GI: nausea, vomiting, constipation,
abdominal pain, abnormal
salivation, anorexia
GU: decreased libido
HematoIogic: coaguIation
abnormaIities,
thrombocyto5enia
He5atic: nonspecific hepatic
disorders, he5atic dysfunction
MetaboIic: hypothyroidism,
hyperthyroidism
Res5iratory: cough, aduIt
res5iratory distress syndrome,
5uImonary infIammation or
fibrosis, 5uImonary edema
Skin: flushing, photosensitivity,
toxic epidermal necrolysis
Other: abnormal taste and smell,
edema, fever, Stevens-Johnson
syndrome
Nicardipine Antianginals
Chronic stable angina
Patient who are
hypersensitive to
nicardipine
O Dizziness
O Headache
O Paresthesis
O Drowsiness
O Peripheral edema
O Palpitations
O Tachycardia
O Nausea
O Dry mouth
O Abdominal discomIort
Patients with hepatic
impairment should receive
lower dose
Monitor blood pressure.
Allow atleast 3 days between
dosage adjustment to achieve
steady plasma levels.
Advise patient to report
immediately iI experiencing
O Rash
O Flushing
chest pain
Diazepam Antiepileptic Management oI anxiety disorders
Acute alcohol withdrawal
Muscle relaxant
Treatment oI tetanus
Antiepileptic: severe recurrent
convulsive seizures.
Unlabeled use: Treatment oI panic
attacks
Contraindicated with
hypersensitivity to
benzodiazepines; psychoses,
acute narrow-angle
glaucoma, shock, coma,
acute alcoholic intoxication;
pregnancy, lactation.
- CNS:
1) dizziness
2) drowsiness
3) lethargy
4) hangover
5) headache
6) depression
- EENT:
1) blurred vision
- RESP:
1) respiratory depression
- CV:
1) hypotension
- GI:
1) constipation
2) diarrhea
3) nausea
4) vomiting
- DERM:
1) rashes
- LOCAL:
1) pain (IM)
2) phlebitis (IV)
3) venous thrombosis
- MISC:
1) physical & psychological depen-dence
2)tolerance
Take this drug exactly as
prescribed. Do not stop
taking this drug without
consulting your health care
provider.
Caregiver should learn to
assess seizures, administer
rectal Iorm, and monitor
patient.
You may experience these
side eIIects: Drowsiness,
dizziness , GI upset (take
drug with Iood); dreams,
diIIiculty concentrating,
Iatigue, nervousness, crying
(reversible).
Report severe dizziness,
weakness, drowsiness that
persists, rash or skin lesions,
palpitations, swelling oI the
ankles, visual or hearing
disturbances, diIIiculty
voiding.
Calcium Gluconate Electrolytes and
replacement solutions
Hypocalcemia, hypocalcemic tetany,
magnesium toxicity,
hypoparathyroidism
Hypercalcemia, ventricular
Iibrillation, renal canaliculi
GI irritation
hemorrhage
constipation
vomiting
thirst
renal canaliculi
hypercalcemia
polyuria
O Use cautiously in patients
with sarcoidosis and renal
or cardiac disease and in
digitalized patients.
monitor blood calcium level
Irequently.
Nalbuphine
Hydrochloride
pioid agonist-
antagonist
Moderate to severe pain Hypersensitivity to
drug
CNS: dizziness, sedation,
headache, vertigo
CV: hypertension, hypotension,
nstruct patient to
change position slowly
and carefully to avoid
dizziness from sudden
blood pressure
tachycardia, bradycardia
EENT: miosis
GI: nausea, vomiting, dry mouth
Res5iratory: dyspnea, res5iratory
de5ression
Skin: sweating, clammy skin
Other: hypersensitivity reactions
including ana5hyIaxis
decrease.
Tell patient to avoid
CNS depressants
(including alcohol,
sedative-hypnotics, and
some herbs) for at least
24 hours after taking
nalbuphine.
Advise patient to
consult prescriber
before taking herbs.
anticonvulsant drug
Furosemide Loop Diuretic acute pulmonary edema
edema
hypertension
O Anuria
O hepatic coma & precoma
O severe hypokalemia &/or
hyponatremia
O hypovolemia w/ or w/o
hypotension
Hypersensitivity to
Iurosemide or sulIonamides
vertigo,
dizziness,
headache,
paresthesia,
orthostatic
hypotension,
thrombophlebitis,
abdominal pain,
hypokalemia,
anemia
muscle spasm
O To prevent nocturia, give
preparation in the morning
and early in the aIternoon
O atch Ior signs oI
hpokalemia
O do not conIuse with
Torsemide or Lasix with
Lonox
O advise patient to take drug
with Iood to prevent GI
upset
inIorm patient oI possible
need Ior potassium or
magnesium supplements
Digoxin
Cardiac Glycosides
V-Iib, V-Ilutter, CHF, pulmonary
edema, atrial Iibrillation and or
Ilutter, and paroxysmal atrial
contractions
Contraindicated in patients
hypersensitive to the drug or
any oI its components and
in those with digitalis-
induced toxicity, ventricular
Iibrillation, or ventricular
tachycardia unless caused
by heart Iailure.
Side Effects.
CNS: agitation, dizziness, Iatigue,
generalized weakness, headache, malaise.
GI: Nausea
Monitor , Mg, ECG,
liver/renal Iunction tests,
drug level (therapeutic level
0.5-2.0 mg/ml, toxicity is
~2.0 mg/ml).
BeIore each dose assess
apical pulse Ior Iull minute,
record and report changes in
rate or rhythm.
ithhold drug and contact
provider iI pulse is 60/min.
or ~100 (adults) or
110/minute (children)
eigh daily
Monitor I&O and signs oI
CHF
Phenobarbital CNS DRUGS-
HYPNOTICS/
SEDATIVES
Short-term treatment oI insomnia,
long- term treatment oI generalized
toni-clonic seizures
Hypersensitivity to
barbiturates, pregnancy,
severe renal, hepatic, resp.
impairment
PRECAUTION:
Impaired renal, hepatic cardiac or resp.
Iunctions
ADVERSE RXN
Dizziness, headache, hangover, conIusion
in elderly, GI disturbances, allergic
reactions, sedation and depression may
occur
~instruct pt. to avoid alcohol
and other CNS depressant to
prevent inc. depression
~ withdrawal insomnia may
occur aIter short-term use,
insomnia improves in 1-3
nights
~on empty stomach, 30-60
mins beIore bedtime Ior
expected sleeplessness
~advice pt to change
positions slowly to prevent
orthostatic hypotension
Morphine SulIate Analgesics (Opioid) RelieI oI moderate to severe pain
not responsive to non-narcotic
analgesics. Premed. Analgesic
adjunct in general anesth esp in
pain associated w/ cancer, MI &
surgery. Alleviates anxiety
associated w/ severe pain.
Hypnotic Ior pain-related
sleeplessness.
Lightheadedness, dizziness, sedation,
nausea, vomiting, constipation & sweating.
O Caution patient not to
chew or crush controlled-
release preparations.
O Dilute and administer
slowly IV to minimize
likelihood oI adverse
eIIects.
O Tell patient to lie down
during IV administration.
O eep opioid antagonist and
Iacilities Ior assisted or
controlled respiration
readily available during IV
administration.
O Use caution when injecting
SC or IM into chilled areas
or in patients with
hypotension or in shock;
impaired perIusion may
delay absorption; with
repeated doses, an
excessive amount may be
absorbed when circulation
is restored.
O Reassure patients that they
are unlikely to become
addicted; most patients
who receive opioids Ior
medical reasons do not
develop dependence
syndromes.
Epinephrine Alpha-adrenergic agonist,
Beta
1
and beta
2
-adrenergic
agonist, Cardiac stimulant,
Vasopressor,
Bronchodilator
Acute asthmatic attacks, Advanced
cardiac liIe support
Hypersensitivity drowsiness, headache, nervousness,
tremors, cerebral hemorrhage, dizziness,
weakness, vertigo, pain
O Monitor heart rate.
O Use extreme caution when
calculating and preparing
doses; epinephrine is a
very potent drug;
O Use minimal doses Ior
minimal periods oI time
O Protect drug solutions Irom
light, extreme heat, and
Ireezing; do not use pink or
brown solutions.
O Shake the suspension Ior
injection well beIore
withdrawing the dose.
Phenytoin anticonvulsant drug t is prescribed as an
anticonvulsant for the
treatment and prevention of
tonic-clonic seizures, complex
partial seizures, and seizures
resulting from head trauma or
surgery.
hypersensitivity to this
drug
ataxia, nystagmus, hypersensitivity
reactions, and gingival hyperplasia
Assess blood
pressure, ECG, and
heart rate, especially
during .V. loading dose.
Watch for adverse
reactions.
Monitor phenytoin
blood level; therapeutic
range is 10 to 20
mcg/ml.
Evaluate CBC and
kidney and liver function
tests.
Closely monitor
prothrombin time and
nternationalized
Normal Ratio in patients
receiving warfarin
concurrently.
Monitor drug efficacy.
Sodium Bicarbonate Alkalizing Agent, BuIIer,
Antacid, electrolyte
4 Hyperacidity
4 Peptic ulcer
4 Hyperkalemia
4 Tricyclic antidepressant
OD
4 Shock associated with
severe diarrhea,
dehydration, uncontrolled
DM
ReIlux esophagitis
Contraindicated in patients
with metabolic or
respiratory alkalosis;
patients who are losing
chlorides Irom vomiting or
continuous GI suction;
patients taking diuretics
known to produce
hypochloremia alkalosis;
and patients with
hypocalcemia in which
alkalosis may produce
tetany, hypertension,
seizures, or heart Iailure.
Oral sodium bicarbonate is
contraindicated in patients
with acute ingestion oI
strong mineral acids.
GI: Gastric distention, belching, Ilatulence.
Metabolic: metabolic alkalosis,
hypernatremia, hypokalemia,
hyperosmolarity (with overdose).
Other: Pain and irritation at injection site.
Monitor urinary pH, calcium,
electrolytes and phosphate
levels.
Record amount and
consistency oI stools.
Clients on low-sodium diets
should evaluate sodium
contents oI antacids.
Aminophylline
Dobutamine Andrenergics Increased cardiac output in short-
term treat ment oI cardiac
decompensation caused by depressed
contractility, such as during
reIractory heart Iailure; adjunctive
therapy in cardiac surgery
Contra indicated in patients
hypersensitive to drug and
in those with idiopathic
hypertrophic subaortic
stenosis
Use cautiously in patients
with history oI hypertension
because drug may increase
pressor response
Use cautiously in patients
with history oI sulIite
sensitivity
Increased heart rate, hypertension,
Angina, phlebitis, nonspeciIic chest pain,
palpitations, hypotension, nausea,
vomiting, shortness oI breath,
hypersensitivity reactions
O BeIore starting dobutamine
therapy: (1) give a plasma
volume expander to correct
hypovolemia (2) give
cardiac glycoside
O Continuously monitor
ECG, blood pressure,
pulmonary artery wedge
pressure, cardiac output
and urine output
O Monitor Electrolyte levels.
Drug may lower potassium
level
O Do not conIuse with
Dopamine
O Tell patient to report
adverse reactions promptly,
especially labored
breathing and drug-induced
headache
Instruct patient to report
discomIort at IV insertion site
Oxacillin
CeItriaxone 3
rd
generation
Cephalosporin
Lower Respiratory Tract InIection Patients who are
hypersensitive to
cephalosporins or penicillins
Iever, dizziness, headache, chills,
thrombocytosis, nausea and vomiting
- Administer the drug slowly
via IVTT
- Assess Ior presence oI
phlebitis and pain upon
administration oI drug, as
well as other side and adverse
eIIects
- Assess Ior consistency oI
stools
CeIuroxime cephalosporin
CeIazolin First generation
cephalosphorins
W%7eatment of.
Skin & skin structure inIections;
pneumonia; urinary tract inIections;
bone & joint inIections
Hypersensitivity to
cephalosphorins. Serious
hypersensitivity to
penicillin.
CNS:
Seizures (high doses)
GI:
Pseudomembranous colitis, diarrhea,
nausea, vomiting, cramps
GU:
Interstitial nephritis
DERM:
Rashes, urticaria
HEMAT:
Blood dyscrasias, hemolytic anemia
LOCAL:
Pain at IM site, phlebitis at IV site
MISC:
Allergic reactions including Anaphylaxis
and Serum sickness, superinIection
Assess patient Ior inIection
at beginning and during
therapy.
BeIore initiating therapy,
obtain a history to determine
previous use oI and reactions
to penicillins or
cephalosphorins.
Obtain specimens Ior
culture and sensitivity beIore
initiating therapy.
Observe patient Ior signs
and symptoms oI
anaphylaxis.
Monitor site Ior
thrombophlebitis.
Instruct patient to report
signs oI superinIection and
allergy.
Omeprazole Antisecretory drug Short-term treatment oI active
duodenal cancer
Contraindicated with
hypersensitivity to
omeprazole or its
CNS; headache, dizziness, asthenia,
vertigo, insomnia, apathy, anxiety,
paresthesias, dream abnormalities
Assessment:
1. History :hypersensitivity to
omeprazole or any oI its
Short-term treatment oI active
benign gastric ulcer
Eradication oI Helicobacter Pylori
First-line therapy Ior treatment oI
heartburn or symptoms oI GERD.
components.
Use cautiously with
pregnancy, lactation.
Dermatologic: rash, inIlammation,
urticaria, pruritus, alopecia, dry skin
GI: diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea,
vomiting, constipation, dry mouth, tongue
atrophy
Respiratory: URI symptoms, cough,
epistaxis
components; pregnancy,
lactation
2. Physical: skin lesions;
reIlexes; urinary output;
abdominal examination;
respiratory auscultation
Interventions:
1. Administer beIore meals.
2. Administer antacids with,
iI needed.
3. Have regular medical
Iollow-up visits.
4. Report severe headache,
worsening oI symptoms,
Iever, chills.
CeItazidine
Sodium SulIate
Isordil
Cloridine tab
Paracetamol tab Analgesics (Non-Opioid)
& Antipyretics
Pyrexia oI unknown origin. Fever &
pain
Hematological, skin & other allergic
reactions
O Use liquid Iorm Ior
children and patients who
have diIIiculty swallowing.
O In children, don`t exceed
Iive doses in 24 hours.
O Advise patient that drug is
only Ior short term use and
to consult the physician iI
giving to children Ior
longer than 5 days or
adults Ior longer than 10
days.
O Advise patient or caregiver
that many over the counter
products contain
acetaminophen; be aware
oI this when calculating
total dailydose.
O arn patient that high
doses or unsupervised long
term use can cause liver
damage.
Hydrocortisone
Hyoscine-
Nobutylbromide
Sodium Chloride
Isosorbide Dinitrite
Gentamicin SulIate
DidoIenal
Dilantil
CiproIloxacin
Chloramphenicol
Chlorphenamine
Ampicillin
Atropine SulIate
Vit.
Phytomenadione
Aqua-Mephyton, Vitamin
O Anticoagulant-induced
prothrombin deIiciency
caused by coumarin or
indanedione derivatives;
O Prophylaxis and therapy oI
hemorrhagic disease oI the
newborn;
O hypoprothrombinemia due
to anti-bacterial therapy;
O hypoprothrombinemia
secondary to Iactors
limiting absorption or
synthesis oI vitamin ,
e.g., obstructive jaundice,
biliary Iistula, sprue,
ulcerative coilitis, celiac
disease, intestinal
resection, cystic Iibrosis oI
the pancreas, and regional
enteritis;
other drug-induced
hypoprothrombinemia.
Hypersensitivity to any
component oI this
medication
Transient"Ilushing sensations" and
"peculiar" sensations oI taste have been
observed, as well as rare instances oI
dizziness, rapid and weak pulse, proIuse
sweating, brieI hypotension, dyspnea, and
cyanosis.
Pain, swelling, and tenderness at the
injection site may occur.
Tramadol Analgesic Decreased pain.
Assess type, location, and
intensity oI pain beIore and
2-3 hr (peak) aIter
administration.
Assess BP & RR beIore and
periodically during
administration.
Assess bowel Iunction
routinely.
Assess previous analgesic
history.
Encourage patient to cough
and breathe deeply every 2 hr
to prevent atelactasis and
pneumonia.
Terbutaline SO4
Sodium Chloride
Ranitidine Histamine
2
Antagonists Treatment and prevention oI
heartburn, acid indigestion, and sour
stomach.
Hypersensitivity, Cross-
sensitivity may occur; some
oral liquids contain alcohol
and should be avoided in
patients with known
intolerance.
CNS:
ConIusion, dizziness, drowsiness,
hallucinations, headache
CV:
Arrhythmias
GI:
Altered taste, black tongue, constipation,
dark stools, diarrhea, drug-induced
hepatitis, nausea
GU:
Assess patient Ior
epigastric or abdominal pain
and Irank or occult blood in
the stool, emesis, or gastric
aspirate.
Nurse should know that it
may cause Ialse-positive
results Ior urine protein; test
with sulIosalicylic acid.
InIorm patient that it may
cause drowsiness or
dizziness.
InIorm patient that
increased Iluid and Iiber
intake may minimize
constipation.
InIorm patient that
Decreased sperm count, impotence
ENDO:
Gynecomastia
HEMAT:
Agranulocytosis, Aplastic Anemia,
neutropenia, thrombocytopenia
LOCAL:
Pain at IM site
MISC:
Hypersensitivity reactions, vasculitis
medication may temporarily
cause stools and tongue to
appear gray black.
Potassium Chloride
Penicillin G ANTI-INFECTIVES-
Penicillins
Metochlopromide GASTROINTESTINAL
DRUGS- ANTI-
FLATULENTS
Gastrointestinal motility, nausea,
vomiting oI central and peripheral
origin assoc. with surgery
GI hemorrhage, epileptics,
hypersensitivity, lactation,
pts. ith breast cancer
PRECAUTION:
Activities requiring mental alertness,
elderly, lactation
ADVERSE RXN
Restlessness, drowsiness, Iatigue,
insomnia, headache, dizziness, nausea
~give 30 mins beIore meals
and at bed time
~ assess mental status during
treatment
~tell pt. To avoid driving &
other hazardous activities Ior
at least 2 hrs
~advice pt. to avoid alcohol
and other CNS depressant
that enhance sedating
properties oI this drug
Nitroglycerine Patch Anti-Anginal Drugs oI angina pectoris due to coronary
artery disease
Headache. Transient episodes oI
lightheadedness. InIrequently, hypotension.
Syncope, crescendo angina, rebound HTN,
allergic & anaphylactoid reactions. Rarely
severe, application site irritation
O Administer transdermal
systems to skin site Iree oI
hair and not subject to
much movement. Shave
areas that have a lot oI
hair. Do not apply to distal
extremities. Change sites
slightly to decrease the
chance oI local irritation
and sensitization. Remove
transdermal system beIore
attempting deIibrillation or
cardioversion.
O To use transdermal
systems, you may need to
shave an area Ior
application. Apply to a
slightly diIIerent area each
day. Use care iI changing
brands; each system has a
diIIerent concentration.
Nicardepine Calcium Antagonists Hypertensive emergencies or
urgencies, peri-op & post-op
HTN, hypertensive states oI NPO
patients.
Peripheral edema, headache,
tachycardia, palpitations, localized
thrombophlebitis & hypotension.
O Patients with hepatic
impairment should receive
lower dose.
O Monitor blood
pressure.Allow atleast 3
days between dosage
adjustment to achieve
steady plasma levels.
O Advise patient to report
immediately iI
experiencing chest pain
etorolac Nonopioid Analagesics Short term management oI pain - Hypersensitivity
- Cross-sensitivity with
other NSAIDs may
existPre- or perioperative
use
- nown alcohol
intoleranceUse cautiously
in:
1) History oI GI bleeding
2) Renal impair-ment
(dosage reduction may be
required)
3) Cardiovascular disease
- CNS:
1) drowsiness
2) abnormal thinking
3) dizziness
4) euphoria
5) headache-
- RESP:
1) asthma
2) dyspnea
- CV:
1) edema
2) pallor
3) vasodilation
- GI:
1) GI Bleeding
2) abnormal taste
3) diarrhea
4) dry mouth
5) dyspepsia
6) GI pain
7) nausea
- GU:
- Patients who have asthma,
aspirin-induced allergy, and
nasal polyps are at increased
risk Ior developing
hypersensitivity reactions.
Assess Ior rhinitis, asthma,
and urticaria.
- Assess pain (note type,
location, and intensity) prior
to and 1-2 hr Iollowing
administration.
- etorolac therapy should
always be given initially by
the IM or IV route. Oral
therapy should be used only
as a continuation oI
parenteral therapy.
- Caution patient to avoid
concurrent use oI alcohol,
aspirin, NSAIDs,
acetaminophen, or other OTC
medications without
1) oliguria
2) renal toxicity
3) urinary Irequency
- DERM:
1) pruritis
2) purpura
3) sweating
4) urticaria
- HEMAT:
1) prolonged bleeding time
- LOCAL:
1) injection site pain
- NEURO:
1) paresthesia
- MISC:
1) allergic reaction, anaphylaxis
consulting health care
proIessional.
- Advise patient to consult iI
rash, itching, visual
disturbances, tinnitus, weight
gain, edema, black stools,
persistent headche, or
inIluenza-like syndromes
(chills,Iever,muscles aches,
pain) occur.
- EIIectiveness oI therapy can
be demonstrated by decrease
in severity oI pain. Patients
who do not respond to one
NSAIDs may respond to
another.
Dexamethasone Corticosteroids InIlammation oI corticosteroid-
responsive dermatoses
Patient had an allergic
reaction previously.
Have an active peptic ulcer
Have an active herpes
simplex Iungal or
mycobacterial inIection ot
the eye, ear inIection
Active tuberculosis
Have psychoneurosis or
psychosis
Increased appetite
eight gain
ater retention
Increased BC
Hypokalemia
Skin rash
Dizziness
Insomia
Headache
Stop drug and notiIy doctor iI
patient develops signs oI
systemic absorption.
BeIore applying, gently wash
skin to prevent damage to
skin rub medication gently.
Treatment should be
continued Ior a Iew days aIter
clearing oI lesions to prevent
recurrence
Вам также может понравиться
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Nursing Care Plan Pott's DiseaseДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan Pott's Diseasederic95% (21)
- Michael H. Antoni, Roselyn Smith-Stress Management Intervention For Women With Breast Cancer-Amer Psychological Assn (2003)Документ222 страницыMichael H. Antoni, Roselyn Smith-Stress Management Intervention For Women With Breast Cancer-Amer Psychological Assn (2003)KmoespinoОценок пока нет
- Growth and DevelopmentДокумент64 страницыGrowth and DevelopmentRahul Dhaker100% (1)
- See - The.messages - Within.You.2013 - DR - Harvey.Bigelsen PDFДокумент38 страницSee - The.messages - Within.You.2013 - DR - Harvey.Bigelsen PDFSam100% (2)
- Pharmacovigilance - An Overview: Dr. Sukanta Sen MD, DNB, DM (Clin Pharmacology)Документ31 страницаPharmacovigilance - An Overview: Dr. Sukanta Sen MD, DNB, DM (Clin Pharmacology)FranchescaAmoréBrodithe100% (1)
- Physical AssessmentДокумент4 страницыPhysical AssessmentDhan Lopez100% (1)
- Sleep and Rest NCPДокумент2 страницыSleep and Rest NCPDhan LopezОценок пока нет
- Diazepam Drug StudyДокумент1 страницаDiazepam Drug StudyAndee Salegon100% (3)
- Health Problem Family Nursing Problem Goal of Care Objectives of Care Intervention PlanДокумент5 страницHealth Problem Family Nursing Problem Goal of Care Objectives of Care Intervention PlanCel Limbre Rabia100% (10)
- Drug CefuroximeДокумент2 страницыDrug CefuroximeDhan LopezОценок пока нет
- Drug CarbocisteineДокумент1 страницаDrug CarbocisteineDhan LopezОценок пока нет
- Lesson 10: Sexual Aspect of Self: Name: Ramil D Malapo Course: BEEDДокумент15 страницLesson 10: Sexual Aspect of Self: Name: Ramil D Malapo Course: BEEDJOANA MANAOGОценок пока нет
- Dorothea Orem: Self-Care TheoryДокумент16 страницDorothea Orem: Self-Care TheoryHazel LezahОценок пока нет
- Meiosis GizmosДокумент9 страницMeiosis GizmosShaylee TorresОценок пока нет
- Mediclaim Policy - Buy Group Health Insurance Online - Future GeneraliДокумент39 страницMediclaim Policy - Buy Group Health Insurance Online - Future GeneraliRizwan KhanОценок пока нет
- 109 513 1 PB PDFДокумент11 страниц109 513 1 PB PDFKolu koyОценок пока нет
- Analytical Case Study of Bmiof Mildly Symptomatic Covid-19 Patients With Reference To MizajДокумент7 страницAnalytical Case Study of Bmiof Mildly Symptomatic Covid-19 Patients With Reference To MizajyusufОценок пока нет
- Annotated Bibliography - Research ProjectДокумент3 страницыAnnotated Bibliography - Research Projectapi-237847760Оценок пока нет
- English Composition II 1Документ11 страницEnglish Composition II 1api-548473407Оценок пока нет
- MMC 8Документ27 страницMMC 8Neil Patrick AngelesОценок пока нет
- Normal Periodontium 1Документ49 страницNormal Periodontium 1mdio midoОценок пока нет
- A Potential Siddha Mineral Drug Pavala ParpamДокумент8 страницA Potential Siddha Mineral Drug Pavala Parpamjmanuel108yahoo.co.ukОценок пока нет
- J Potratz ResumeДокумент3 страницыJ Potratz Resumeapi-216040679Оценок пока нет
- Zybio Company Profile 20211109CДокумент46 страницZybio Company Profile 20211109CĐức Hòa100% (1)
- Intra-Arterial Catheterization For Invasive Monitoring: Indications, Insertion Techniques, and Interpretation - UpToDateДокумент40 страницIntra-Arterial Catheterization For Invasive Monitoring: Indications, Insertion Techniques, and Interpretation - UpToDatejuanpbagurОценок пока нет
- Brain Cancer ScriptДокумент2 страницыBrain Cancer Scriptapi-251981413Оценок пока нет
- You Get To Know "Why" in Everything You Do, You'll Know More Than You Knew. 2Документ16 страницYou Get To Know "Why" in Everything You Do, You'll Know More Than You Knew. 2ChaoticMikiОценок пока нет
- Evaluating Diagnostics: A Guide For Diagnostic EvaluationsДокумент5 страницEvaluating Diagnostics: A Guide For Diagnostic EvaluationsYanneLewerissaОценок пока нет
- At Merienda - Individual ActivityДокумент6 страницAt Merienda - Individual ActivityMoreno, John Gil F.Оценок пока нет
- (Tergecef) DR - Estoque: FluidsДокумент2 страницы(Tergecef) DR - Estoque: FluidsSean SialanaОценок пока нет
- Design Theory: Boo Virk Simon Andrews Boo - Virk@babraham - Ac.uk Simon - Andrews@babraham - Ac.ukДокумент33 страницыDesign Theory: Boo Virk Simon Andrews Boo - Virk@babraham - Ac.uk Simon - Andrews@babraham - Ac.ukuzma munirОценок пока нет
- Aliphatic and Aromatic HydrocarbonsДокумент13 страницAliphatic and Aromatic HydrocarbonsdhaineyОценок пока нет
- Presc Audit ReportДокумент85 страницPresc Audit ReportAnuj KaushalОценок пока нет
- Cystic Hygroma - Symptoms - Diagnosis - Treatment of Cystic Hygroma - NY Times Health InformationДокумент3 страницыCystic Hygroma - Symptoms - Diagnosis - Treatment of Cystic Hygroma - NY Times Health InformationRenno AdiОценок пока нет
- Caffein Intox PDFДокумент3 страницыCaffein Intox PDFSejahtera SurbaktiОценок пока нет