Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Cardiovascular PBLs
Загружено:
Aya Sobhi0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
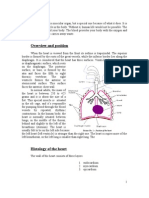
100 просмотров8 страницThe pericardium is a double walled fibroserous sac which encloses the heart and roots of the great vessels. There are 2 venae cavae - Superior drains the upper trunk, head and limbs - Both empty into the right atrium. There are 4 PULMONARY VEINS which empty into the left ventricle. The Pulmonary trunk leaves the right ventricle to supply The Pulmonary circulation with deoxygenated blood. The aorta leaves
Исходное описание:
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThe pericardium is a double walled fibroserous sac which encloses the heart and roots of the great vessels. There are 2 venae cavae - Superior drains the upper trunk, head and limbs - Both empty into the right atrium. There are 4 PULMONARY VEINS which empty into the left ventricle. The Pulmonary trunk leaves the right ventricle to supply The Pulmonary circulation with deoxygenated blood. The aorta leaves
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
100 просмотров8 страницCardiovascular PBLs
Загружено:
Aya SobhiThe pericardium is a double walled fibroserous sac which encloses the heart and roots of the great vessels. There are 2 venae cavae - Superior drains the upper trunk, head and limbs - Both empty into the right atrium. There are 4 PULMONARY VEINS which empty into the left ventricle. The Pulmonary trunk leaves the right ventricle to supply The Pulmonary circulation with deoxygenated blood. The aorta leaves
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 8
DESCRIBE THE FORM AND NAME THE CHAMBERS
AND VALVES OF THE HEART. DEFINE THE
PERICARDIUM. NAME AND DESCRIBE BRIEFLY THE
VENAE CAVAE, PULMONARY VEINS, PULMONARY
TRUNK AND AORTA.
SVC and VC Right Atrium Tricuspid (AV) Valve Right Ventricle Pulmonary valve
(semilunar) Pulmonary trunk LUNGS Pulmonary Veins Left atrium Mitral valve
(bicuspid) Left Ventricle Aortic Valve (semilunar) Aorta
The pericardium is a double walled fibroserous sac which encloses the heart and roots of the
great vessels.
The fibrous pericardium (outer layer) protects the heart from sudden overfilling as it is
unyielding.
Pericardial cavity is the potential space between the parietal pericardium which lines the
fibrous pericardium and the serous pericardium which forms the epicardium of the heart.
- Contains a thin layer of serous fluid which allows the hart to beat in a
frictionless environment.
There are 2 venae cavae
- Superior drains the upper trunk, head and limbs
- Both empty into the right atrium
There are 4 pulmonary veins which empty into the left ventricle
The pulmonary trunk leaves the right atrium to supply the pulmonary circulation with
deoxygenated blood
The aorta leaves the left ventricle to supply the body and heart.
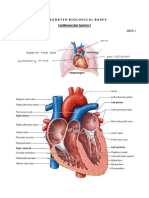
DESCRIBE THE RIGHT VENTRICLE,
INTERVENTRICULAR SEPTUM AND THE TRICUSPID
AND PULMONARY VALVES.
The right ventricle forms the largest part of the anterior surface of the heart
- nterior has irregular muscular projections called trabeculae carnae
O Roughen out the smooth surface of the hear to prevent suction
which would hinder blood flow.
Right AV orifice is surrounded by a fibrocollagenous ring (part of the fibrous skeleton of the
heart) Resists dilatation.
The wall of the right ventricle is thinner than that of the left.
The tricuspid (atrioventicular) valve guards the right AV orifice
O Posterior to the sternum at the level of the 4
th
and 5
th
intercostals spaces.
O Bases of the cusps attach to the fibrous ring
O Chordae tendinae (tendinous cords) attach to the free edges and ventricular surfaces
of the cusps.
4 Like cords to a parachute.
O Papillary muscles attach to chordate tendinae and the ventricular wall
4 Begin contraction before the ventricular wall
4 Bring cusps together
4 Prevents prolapsed of cusps into atrium with systolic pressure of ventricular
contraction.
The Pulmonary (semilunar) valve is at the level of the 3
rd
costal cartilage
- 3 Cusps
The interventricular septum is a stong, obliquely placed partition with membranous and
muscular parts between the right and left ventricles forming part of the walls of each.
O Contains the moderator band
O Carries part of the right bundle branch
4 Shortcut to the papillary muscles
CuLllne Lhe hlsLologlcal feaLures of
cardlac muscle and Lhe funcLlonlng
of Lhe conducLlng sysLem of Lhe
hearL
very baslc whaL you would see lf you looked down a mlcroscope
O ardlac cells are branched cyllnders 83100 mlcromeLres long and 13
mlcromeLres wlde wlLh a slngle cenLrally locaLed nucleus
O orm of sLrlaLed muscle
O lffers from skeleLal musclehave an arrangemenL of acLln and myosln
O They are mononuclear and much shorter than skeletal muscles
O ong cardiac muscle Iibres are produced by linking numerous cardiac
muscle cells end to end via anchoring type cell junctions
O They do not have stem cell properties and so regeneration and renewal
cannot occur.
O
Cardiac muscle:
Conducting system, what we talked about in the slides, i.e. SA node, AV node
involvement oI Purkinje Iibres, Bundle oI His etc
Вам также может понравиться
- Embryology Made Ridiculously Simple HandoutДокумент15 страницEmbryology Made Ridiculously Simple HandoutAya Sobhi96% (28)
- Anatomy and Physiology of HeartДокумент69 страницAnatomy and Physiology of HeartRitu Arun Kaushik100% (1)
- Chapter 19 The Circulatory System - The HeartДокумент14 страницChapter 19 The Circulatory System - The HeartGary Bowen100% (1)
- The Heart: Overview and PositionДокумент11 страницThe Heart: Overview and PositionLil_QuinceОценок пока нет
- Anatomy NstemiДокумент3 страницыAnatomy NstemiSheana Tmpl100% (1)
- Pericardium & HeartДокумент52 страницыPericardium & HeartShimmering MoonОценок пока нет
- CardiovascularДокумент92 страницыCardiovascularRolinette DaneОценок пока нет
- Circulatory System: A Tutorial Study GuideОт EverandCirculatory System: A Tutorial Study GuideРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- Embryology Made Ridiculously Simple Presentation (1) Updated (1) AgainДокумент100 страницEmbryology Made Ridiculously Simple Presentation (1) Updated (1) AgainAya Sobhi100% (4)
- Embryology Made Ridiculously Simple Presentation (1) Updated (1) AgainДокумент100 страницEmbryology Made Ridiculously Simple Presentation (1) Updated (1) AgainAya Sobhi100% (4)
- Anatomy of Heart: Mr. Binu Babu MBA, M.Sc. (N) Asst. Professor Mrs. Jincy Ealias M.Sc. (N) LecturerДокумент71 страницаAnatomy of Heart: Mr. Binu Babu MBA, M.Sc. (N) Asst. Professor Mrs. Jincy Ealias M.Sc. (N) Lecturerjyoti kunduОценок пока нет
- The Respiratory SystemДокумент147 страницThe Respiratory SystemAya SobhiОценок пока нет
- Evolution of Heart in VertebratesДокумент4 страницыEvolution of Heart in Vertebratesनितिन कुमारОценок пока нет
- Chapter 19 Heart Marie BДокумент29 страницChapter 19 Heart Marie BomarОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Histology of The Cardiovascular SystemДокумент16 страницAnatomy and Histology of The Cardiovascular SystemTasmiah HossainОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of The ThoraxДокумент7 страницAnatomy of The Thoraxsnowy__owlОценок пока нет
- Heart by Aritra SahaДокумент15 страницHeart by Aritra SahaAritra SahaОценок пока нет
- Special CirculationДокумент19 страницSpecial Circulationapi-19824701Оценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Heart Made Easy Part 1Документ22 страницыAnatomy and Physiology of The Heart Made Easy Part 1adedayodavid860Оценок пока нет
- Project BioДокумент18 страницProject Bioyanshu falduОценок пока нет
- CVSДокумент184 страницыCVStee su lingОценок пока нет
- Heart .Which Divides Right and Left, Structures of TheДокумент5 страницHeart .Which Divides Right and Left, Structures of Thecabas114Оценок пока нет
- V. Trachea: Zoology-IIДокумент22 страницыV. Trachea: Zoology-IIVenkatesh JoguОценок пока нет
- Angiology NoteДокумент13 страницAngiology NoteSantosh Bhandari100% (2)
- The Heart: Dr. Silvia BoyajianДокумент44 страницыThe Heart: Dr. Silvia BoyajianAsem YousefОценок пока нет
- Internal Striucture of HeartДокумент2 страницыInternal Striucture of HeartDhilahHarfaDhilahОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular System DR Aarti Abhishek Shah NmimsДокумент33 страницыCardiovascular System DR Aarti Abhishek Shah NmimsnoshОценок пока нет
- ССС 2019Документ83 страницыССС 2019bekafop813Оценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Cardiovascular System Functions of The HeartДокумент3 страницыAnatomy and Physiology of The Cardiovascular System Functions of The HeartPeej ReyesОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiolog1Документ5 страницAnatomy and Physiolog1Isabel Barredo Del MundoОценок пока нет
- The Cardiovascular System The HeartДокумент9 страницThe Cardiovascular System The HeartMarjorie AbelgasОценок пока нет
- Heart Structure - 1Документ28 страницHeart Structure - 1Daniel McfarlaneОценок пока нет
- Week Objectives 1-5Документ295 страницWeek Objectives 1-5qvqck4zmnnОценок пока нет
- 7.8.heart and VesselsДокумент11 страниц7.8.heart and Vesselssomebody_maОценок пока нет
- Case 1 ObsДокумент31 страницаCase 1 ObsMatheesha HerathОценок пока нет
- HeartДокумент7 страницHeartKaryll AguilaОценок пока нет
- DFF FFF AaaaaДокумент5 страницDFF FFF AaaaaffffffffОценок пока нет
- System CardiovascularДокумент22 страницыSystem Cardiovascularvk seruniОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of HeartДокумент65 страницAnatomy of HeartSadab AlamОценок пока нет
- Chapter 13 - HeartДокумент5 страницChapter 13 - Heartbussniesm05Оценок пока нет
- HeartДокумент27 страницHeartJeevitha VanithaОценок пока нет
- BIO - Week 1 CVДокумент36 страницBIO - Week 1 CVjul.watson97Оценок пока нет
- Circulatory System FKM'12Документ55 страницCirculatory System FKM'12muhammadsudrajadОценок пока нет
- Heart AnatomyДокумент19 страницHeart Anatomydeepika kushwahОценок пока нет
- Checklist 3Документ9 страницChecklist 3FranklinSappОценок пока нет
- Human Anatomy and Physiology - The Cardiovascular SystemДокумент10 страницHuman Anatomy and Physiology - The Cardiovascular SystemKraig Andre RellegueОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of CVS: 2. The HeartДокумент68 страницAnatomy of CVS: 2. The Heartsultan khabeebОценок пока нет
- The Human Heart: Dr. Nwosu C.I.A., MSC, MBBS, MDДокумент38 страницThe Human Heart: Dr. Nwosu C.I.A., MSC, MBBS, MDcoolblue89Оценок пока нет
- Anatomy of The HeartДокумент5 страницAnatomy of The HeartxXjhmXxОценок пока нет
- Septum Formation in The VentriclesДокумент43 страницыSeptum Formation in The VentriclesAhsan IslamОценок пока нет
- Lec 1 - AnatomyДокумент7 страницLec 1 - Anatomyأ. علي محمدОценок пока нет
- Struktur Dan Fungsi Jantung Dasar: Ken Young Lin Elazer R. Edelman Gary Strichartz Leonard S. LillyДокумент8 страницStruktur Dan Fungsi Jantung Dasar: Ken Young Lin Elazer R. Edelman Gary Strichartz Leonard S. LillyThieFeezaeОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular Sys Part 1Документ10 страницCardiovascular Sys Part 1LawrenceОценок пока нет
- Aorta 2Документ3 страницыAorta 2naviОценок пока нет
- Acfrogb 7ik4ojriyfu8nvvwmohozvp1pcb2hjyh47jdwvhnpmnhiyornnhy - Xeyhodxnx4wlzdu5sc59 1gvhetgkpoh5ws31c2bftcevdfose32075g4qf78x9c08Документ60 страницAcfrogb 7ik4ojriyfu8nvvwmohozvp1pcb2hjyh47jdwvhnpmnhiyornnhy - Xeyhodxnx4wlzdu5sc59 1gvhetgkpoh5ws31c2bftcevdfose32075g4qf78x9c08Bala GanapathyОценок пока нет
- The Heart TransДокумент15 страницThe Heart TransAmelie Sta RomanaОценок пока нет
- LearningPacket COMPACirculatorySystemДокумент7 страницLearningPacket COMPACirculatorySystemLei Jenevive UmbayОценок пока нет
- Cardiology: Patent LumenДокумент5 страницCardiology: Patent LumenDeepthi VallabhaneniОценок пока нет
- Anatomia Del CorazonДокумент21 страницаAnatomia Del CorazonAndrea OrtizОценок пока нет
- Pig Heart Dissection Manual STEMДокумент8 страницPig Heart Dissection Manual STEMSir JoshОценок пока нет
- Lesson 1 Cardiovascular System and The BloodДокумент12 страницLesson 1 Cardiovascular System and The BloodPathy LinОценок пока нет
- Whitaker 2010Документ3 страницыWhitaker 2010Gabriel Jose CarvajalОценок пока нет
- Anatomy Lec.6Документ5 страницAnatomy Lec.6aminqasm111Оценок пока нет
- Circulatory SДокумент110 страницCirculatory SMohammed HabibОценок пока нет
- Clinical Pharmacology For Second YearsДокумент55 страницClinical Pharmacology For Second YearsAya SobhiОценок пока нет
- Kidneys: Sherif Elsobky MB5Документ72 страницыKidneys: Sherif Elsobky MB5Aya SobhiОценок пока нет
- Bones OnlineДокумент74 страницыBones OnlineAya SobhiОценок пока нет
- Tooth StructureДокумент8 страницTooth StructureAya SobhiОценок пока нет
- In The Name of Allah, Most Beneficent, Most MercifulДокумент5 страницIn The Name of Allah, Most Beneficent, Most MercifulAya SobhiОценок пока нет
- Immunology Handouts FridayДокумент9 страницImmunology Handouts FridayAya SobhiОценок пока нет
- The Basics of Immunology Presentation (Updated)Документ51 страницаThe Basics of Immunology Presentation (Updated)Aya SobhiОценок пока нет
- The Basics of Immunology Presentation (Updated)Документ51 страницаThe Basics of Immunology Presentation (Updated)Aya SobhiОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular Anatomy Gumsa (1) - 1Документ27 страницCardiovascular Anatomy Gumsa (1) - 1Aya SobhiОценок пока нет
- GUMSA Mentoring Scheme PresentationДокумент13 страницGUMSA Mentoring Scheme PresentationAya SobhiОценок пока нет
- Americans' Attitudes Toward Mental Health Treatment Seeking: 1990-2003Документ10 страницAmericans' Attitudes Toward Mental Health Treatment Seeking: 1990-2003Aya SobhiОценок пока нет
- GICДокумент7 страницGICmusbahiayaОценок пока нет