Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Assessment Nsg. Diagnosis Sci. Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Загружено:
RoMarie AbainzaИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Assessment Nsg. Diagnosis Sci. Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Загружено:
RoMarie AbainzaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
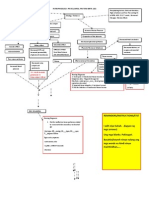
ASSESSMENT
NSG. DIAGNOSIS
SCI. EXPLANATION Risk factors
PLANNING
INTERVENTION
RATIONALE
EVALUATION
ABRUPTIO PLACENTA Subjective data:
Acute pain related to collection of blood between uterine wall and placentas evidenced by sharp, stabbing pain at epigastric area.
Short term: After 2 hrs. of nursing intervention, the client will be able to:
Independent: Monitor amount of To measure the bleeding by weighing amount of blood loss. all pads.
Discharge outcome: After 2 days, the client: -reported controlled pain. -vital signs in normal range.
Premature separation of the placenta
Objective data: sharp, stabbing pain at epigastric area. Presence of uterine rigidity and tenderness Painful, tender, tense (board-like) abdomen Crying Attention is distracted BP: 80/50 PR: 58 RR: 16
Pooling of blood under the placenta
Blood infiltrates the uterine musculature
Hard,boardlike uterus
Uterus become tense and feels rigid to touch
-report reduction of Investigate pain Changes in location pain into tolerable level reports, noting or intensity are not location, duration, uncommon but may -perform 3/5 nonintensity (0-10 scale), reflect developing pharmacologic pain and characteristics complications. management (dull, sharp, constant). Discharge outcome: Monitor maternal Early recognition of After 2 days, the client vital signs and fetal possible adverse will be able to: heart rate through effects allows for continuous prompt intervention. -report absence of pain. monitoring. -maintain vital signs in normal range. Measure and record Fundal height may fundal height. increase with concealed bleeding. Position mother in the left lateral position, with the head of the bed elevated. Provide comfort measure like back rubs, deep breathing. To enhance placental perfusion.
Short term: After 2 hrs, the client: -reported pain reduction. -verbalized 3 non pharmacologic pain management. GOAL ACHIEVED
Pain on epigastric area
Promotes relaxation and may enhance patients coping abilities by refocusing attention.
Collaborative: Administer oxygen as To supply adequate indicated oxygen to the fetus and mother and prevents further complication.
ABAINZA, Rochelle Marie T. ASSESSMENT NSG. DIAGNOSIS SCI. EXPLANATION Increased cardiac out put PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
PIH Subjective Data:
Objective Data: Generalized edema Decrease Hct and platelet level Epigastric pain Feet edema +2 Proteinuria of 300 mg/ L Urine output of 500 mL/ 24 hr.
Deficient fluid volume related to plasma protein loss secondary to PIH as evidenced by proteinuria of 300 mg/L and generalized edema.
Short Term Goal: After 8 hrs of nursing intervention, the client will be able to:
Independent: Weigh client routinely. Encourage client to monitor weight at home between visits. Sudden, significant weight gain (e.g., more than 3.3 lb (1.5 kg)/month in the second trimester or more than 1 lb (0.5 kg)/wk in the third trimester) reflects fluid retention. Fluid moves from the vascular to interstitial space, resulting in edema.
Discharge outcome: After 4 days, the client: Was free from generalized edema Has Hct and platelet level within normal range Have absence of proteinuria and 30 cc of urine output per hr.
Injury to endothelial cells of arteries
Show decrease facial and feet edema from +2 to +1. Verbalize understanding of need for close monitoring of weight, BP, urine protein, and edema. Discharge Outcome: After 4 days, the client will be able to:
Decreased responsiveness of the blood vessels to blood pressure
Vasospasm Interstitial effects
Distinguish between physiological and pathological degree of pitting.
Diffusion of fluid from Be free of signs of generalized edema: blood stream into (epigastric pain, interstitial tissue cerebral symptoms, dyspnea, nausea/vomiting) Edema Display Hct and platelet level within normal range.
The presence of Short Term Goal: pitting edema (mild, 1+ to 2+; severe, 3+ to Has decreased edema 4+) of face, hands, up to grade of +1. legs, sacral area, abdominal wall, or Verbalized edema that does not understanding of disappear after 12 hr need for close of bed rest is monitoring of weight, significant. Note: BP, urine protein, and Significant edema edema. may actually be present in non-pre eclamptic clients and absent in clients with mild or moderated
PIH. Showed absence of proteinuria and has a urine output of at least 30 cc/ hr. Note changes in Hct/Hb levels. Identifies degree of hemoconcentration caused by fluid shift. If Hct is less than 3 times Hb level, hemoconcentration exists.
Reassess dietary Adequate nutrition intake of proteins and reduces incidence of calories. Provide prenatal hypovolemia information as and hypoperfusion; needed. inadequate protein/calories increases the risk of edema formation and PIH. Intake of 80100 g of protein may be required daily to replace losses. Monitor intake and output. Note urine color, measure specific gravity as indicated. Urine output is a sensitive indicator of blood volume. Oliguria and specific gravity of 1.040 indicate severe hypovolemia and kidney involvement. Note: Administration of magnesium sulfate (MgSO4) may cause transient increase in output. Lateral recumbent
Place client on strict
regimen of bedrest; encourage lateral position.
position decreases pressure on the vena cava, increasing venous return and circulatory volume. This enhances placental and renal perfusion, reduces adrenal activity, and may lower BP as well as account for weight loss through diuresis of up to 4 lb in 24-hr period.
Collaborative: Replace fluids either Fluid replacement orally or parenterally corrects hypovolemia, via infusion pump, as yet must be indicated. administered cautiously to prevent overload, especially if interstitial fluid is drawn back into circulation when activity is reduced. With renal involvement, fluid intake is restricted; i.e., if output is reduced (less than 700 ml/24 hr), total fluid intake is restricted to approximate output plus insensible loss. Use of infusion pump allows more accurate
control delivery of IV fluids.
Вам также может понравиться
- Case Study, Chapter 70, Management of Patients WithOncologic or Degenerative Neurologic DisordersДокумент1 страницаCase Study, Chapter 70, Management of Patients WithOncologic or Degenerative Neurologic Disordersclyde i am100% (1)
- Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeДокумент40 страницAcute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDavid Seroney100% (1)
- 1 Ineffective Peripheral Tissue PerfusionДокумент1 страница1 Ineffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusionjean_fabulaОценок пока нет
- Product PlanДокумент19 страницProduct Planlily30109150% (2)
- What Is RCM and RBIДокумент2 страницыWhat Is RCM and RBIChihiya Fitria Nurhayati0% (1)
- PATHOPHYSIO (Megaloblastic Anemia)Документ3 страницыPATHOPHYSIO (Megaloblastic Anemia)Giselle EstoquiaОценок пока нет
- Spina Bifida, Meningocele MyelomeningoceleДокумент1 страницаSpina Bifida, Meningocele MyelomeningocelesmilingstarsОценок пока нет
- ABRUPTIO PLACENTAE PathophysiologyДокумент3 страницыABRUPTIO PLACENTAE PathophysiologyBarda GulanОценок пока нет
- Leukemias: Care SettingДокумент11 страницLeukemias: Care SettingTinОценок пока нет
- Schistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Документ10 страницSchistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Tiger Knee100% (1)
- Addison's DiseaseДокумент14 страницAddison's Diseasedivya4nirmalaОценок пока нет
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Core CompetenciesДокумент13 страницAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Core CompetenciesMina RacadioОценок пока нет
- Communicating Pathophysiology: Impaired Absorption of The CSF in The Arachnoid SpaceДокумент2 страницыCommunicating Pathophysiology: Impaired Absorption of The CSF in The Arachnoid SpaceAyaBasilioОценок пока нет
- PathophysiologyДокумент1 страницаPathophysiologyHazel PalomaresОценок пока нет
- Abruptio Placenta. Final OutputДокумент15 страницAbruptio Placenta. Final OutputCharles Loriaga Cruz IIОценок пока нет
- Atun Maricris Jorre Ca2 Au Legarda Leadership Managemet Research DownloadableДокумент2 страницыAtun Maricris Jorre Ca2 Au Legarda Leadership Managemet Research DownloadableCharissa Magistrado De LeonОценок пока нет
- St. Paul University Philippines: School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences College of NursingДокумент5 страницSt. Paul University Philippines: School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences College of NursingChristian UmosoОценок пока нет
- Lapkas HegДокумент1 страницаLapkas HegkurniaОценок пока нет
- Complications in PregnancyДокумент36 страницComplications in PregnancyJADE PATEGAОценок пока нет
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Hemophilia: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurДокумент1 страницаNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Hemophilia: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurCharina AubreyОценок пока нет
- Handout # 10Документ22 страницыHandout # 10Ram August100% (1)
- Ectopic Pregnancy NCP (Vizconde, Ehreiz Raiden C. BSN2-A)Документ10 страницEctopic Pregnancy NCP (Vizconde, Ehreiz Raiden C. BSN2-A)Raiden VizcondeОценок пока нет
- Sudden Infant Death SyndromeДокумент5 страницSudden Infant Death SyndromeJanelle Gift SenarloОценок пока нет
- Sheehan's Syndrome PathophysiologyДокумент2 страницыSheehan's Syndrome PathophysiologyirismgallОценок пока нет
- Volume ImpairmentДокумент32 страницыVolume ImpairmentAcohCChaoОценок пока нет
- Nursing DiagnosisДокумент16 страницNursing DiagnosisShemie TutorОценок пока нет
- Ariane NCP 1Документ2 страницыAriane NCP 1Kristian Ray EraulaОценок пока нет
- H MoleДокумент2 страницыH MoleJoanna Marie Datahan EstomoОценок пока нет
- TAHBSO ReportДокумент4 страницыTAHBSO ReportsachiiMeОценок пока нет
- Pyloric StenosisДокумент5 страницPyloric Stenosisensoooooooooo100% (1)
- Pathophysiology: Cholecystitis Non Modifiable Factors Modifiable FactorsДокумент4 страницыPathophysiology: Cholecystitis Non Modifiable Factors Modifiable FactorsLovely DaroleОценок пока нет
- Rheumatic Heart DiseaseДокумент13 страницRheumatic Heart Diseasedy15Оценок пока нет
- Intussusception: PathophysiologyДокумент8 страницIntussusception: PathophysiologyNaufal AndaluОценок пока нет
- Personal-Soc Interpretation: Tower of 4 CubesДокумент15 страницPersonal-Soc Interpretation: Tower of 4 CubesteuuuuОценок пока нет
- EndometriosisДокумент6 страницEndometriosissalamredОценок пока нет
- NCP - Activity Intolerance & Excess Fluid VolumeДокумент2 страницыNCP - Activity Intolerance & Excess Fluid VolumeCindy MariscotesОценок пока нет
- Post-Partum Hemorrhage Pathophysiology PaperДокумент5 страницPost-Partum Hemorrhage Pathophysiology Paperapi-399619969Оценок пока нет
- Acute Cholecystitis SeminarДокумент42 страницыAcute Cholecystitis SeminarNatnaelОценок пока нет
- NCP PlanningDecreased in Cardiac Output Related To Low Hemoglobin and Hematocrit CountДокумент6 страницNCP PlanningDecreased in Cardiac Output Related To Low Hemoglobin and Hematocrit CountMabelle SorianoОценок пока нет
- NCP IcuДокумент2 страницыNCP IcuDiana MuañaОценок пока нет
- NCPДокумент10 страницNCPRobin HaliliОценок пока нет
- Pregnancy HypertensionДокумент30 страницPregnancy HypertensionJon Gab PaquitОценок пока нет
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionДокумент2 страницыIneffective Tissue PerfusionMary Hope BacutaОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of AppendicitisДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology of AppendicitisSherry Mae Rizza GonzalesОценок пока нет
- Health Assessment FHP - Nutrition and MetabolismДокумент25 страницHealth Assessment FHP - Nutrition and MetabolismKim DajaoОценок пока нет
- Addison'sДокумент4 страницыAddison'sKoRnflakesОценок пока нет
- Management For Acute Lymphocytic LeukemiaДокумент3 страницыManagement For Acute Lymphocytic LeukemiamarivohОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of PihДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology of PihMargueretti Delos ReyesОценок пока нет
- Thyroid Lobectomy and IsthmusectomyДокумент12 страницThyroid Lobectomy and IsthmusectomyAgustina100% (1)
- Reflective Journal 1Документ4 страницыReflective Journal 1api-365605511Оценок пока нет
- Tetralogy of FallotДокумент38 страницTetralogy of FallotJohn Paul MedalloОценок пока нет
- Case (Acute Gastroenteritis) Group 4Документ36 страницCase (Acute Gastroenteritis) Group 4EljhayrosОценок пока нет
- Common ER EquipmentsДокумент3 страницыCommon ER EquipmentsApple LlanesОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care in MR.X With Urinary Retention: Disusun OlehДокумент4 страницыNursing Care in MR.X With Urinary Retention: Disusun OlehHafin WardanaОценок пока нет
- Kawasaki DiseaseДокумент7 страницKawasaki DiseaseRitamariaОценок пока нет
- Kardex: Diet: Interventions IVF (Indicate Date and Time Started) Room Number: 313Документ2 страницыKardex: Diet: Interventions IVF (Indicate Date and Time Started) Room Number: 313kuro hanabusaОценок пока нет
- DS - CatapresДокумент2 страницыDS - CatapresDOni CorleoneОценок пока нет
- Date and Time Focus Data Action Response 12/10/21Документ2 страницыDate and Time Focus Data Action Response 12/10/21ANGEL AKIRA TORRESОценок пока нет
- Hirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОт EverandHirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentДокумент23 страницыCues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentWendy EscalanteОценок пока нет
- NCP and DStudyДокумент8 страницNCP and DStudyJessica Rosan Hewald ManapatОценок пока нет
- BAYBAY AwardsДокумент63 страницыBAYBAY AwardsClennil Palmes SustraidoОценок пока нет
- Cookery 1 Module 4 g11Документ12 страницCookery 1 Module 4 g11Rochel SistonaОценок пока нет
- Barangay Peace and Order and Public Safety PlanДокумент3 страницыBarangay Peace and Order and Public Safety PlanPeter Fritz Boholst100% (1)
- Rewirement With Notes The Science of Well-BeingДокумент33 страницыRewirement With Notes The Science of Well-Beingswikar AcharyaОценок пока нет
- Share FORM 10 - Workplace Application Evaluation ToolДокумент3 страницыShare FORM 10 - Workplace Application Evaluation ToolRocel Ann CarantoОценок пока нет
- Scientific Point of ViewДокумент2 страницыScientific Point of Viewpavans EnglishОценок пока нет
- Contractor Safety Management ProcessДокумент14 страницContractor Safety Management Processsrkam100% (2)
- ENA - TS - 41-37 - Part - 3 CBДокумент40 страницENA - TS - 41-37 - Part - 3 CBRodolfo DelgadoОценок пока нет
- CPRДокумент45 страницCPRJames Elwood DoyolaОценок пока нет
- BW Health-5Документ2 страницыBW Health-5Michael JaballasОценок пока нет
- Pengaruh Aplikasi Pyraclostrobin Terhadap Serangan Penyebab Penyakit Bulai Pada Lima Varietas Jagung (Zea Mays)Документ8 страницPengaruh Aplikasi Pyraclostrobin Terhadap Serangan Penyebab Penyakit Bulai Pada Lima Varietas Jagung (Zea Mays)Rajif S. YahyaОценок пока нет
- UConn Prosthodontics Clinic Manual 12-13Документ69 страницUConn Prosthodontics Clinic Manual 12-13lippincott2011Оценок пока нет
- Genflex Roofing Systems, LLC Material Safety Data SheetДокумент4 страницыGenflex Roofing Systems, LLC Material Safety Data SheetgjroddyОценок пока нет
- SMK Sinar Bintang, Segambut Kuala Lumpur Yearly Plan Science Form 3Документ16 страницSMK Sinar Bintang, Segambut Kuala Lumpur Yearly Plan Science Form 3Azie HarunОценок пока нет
- 00 - 7565 SigmaTherm 350Документ3 страницы00 - 7565 SigmaTherm 350Elcio VilanculoОценок пока нет
- Office Memo - Drug Free WorkplaceДокумент2 страницыOffice Memo - Drug Free WorkplaceAnthony ElmaОценок пока нет
- TRICARE Program Integrity 2010 ReportДокумент25 страницTRICARE Program Integrity 2010 ReportGovtfraudlawyerОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan 2 Knowledge DeficitДокумент7 страницNursing Care Plan 2 Knowledge Deficitdbryant0101100% (3)
- Trastorno de AdaptacionДокумент11 страницTrastorno de AdaptacionEduardo AguilarОценок пока нет
- Rigging TechniquesДокумент27 страницRigging TechniquesDeepak ShettyОценок пока нет
- MSDS-Muriate of Potash 2017Документ11 страницMSDS-Muriate of Potash 2017Inoe69Оценок пока нет
- The Gittinger Assessment SystemДокумент19 страницThe Gittinger Assessment SystemeheymanОценок пока нет
- Coonrad Morrey ElbowДокумент2 страницыCoonrad Morrey Elbowgcif88Оценок пока нет
- Survey QuestionnaireДокумент3 страницыSurvey Questionnairebintot882Оценок пока нет
- Routes of Drug AdministrationДокумент24 страницыRoutes of Drug Administrationmftaganas100% (1)
- Applying A Feminist Lens To Indias Foreign Policy A Compendium of EssaysДокумент124 страницыApplying A Feminist Lens To Indias Foreign Policy A Compendium of EssaysRasced AliОценок пока нет
- Travel Nurse Pdf1Документ2 страницыTravel Nurse Pdf1Med NetОценок пока нет