Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Introduction To Biology
Загружено:
Nurulfalah Abdul GhaniИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Introduction To Biology
Загружено:
Nurulfalah Abdul GhaniАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
INTRODUCTION TO Biology
1) Biology is the study of life or living organisms. - bios - life - logy - (original: logos) which means study. 2) Importance of Biology better understanding on the functions of human body. better understanding on the causes of diseases and its cure. better understanding on ecology and hence improve the management of problems related to the environment. saving animal and plant species which are facing extinction. 3) Fields of Biology Research - Anatomy (study about structure of living things) - Physiology (study of how living systems function e.g. how cells, molecules carry out their chemical or physical function) - Cell biology - Molecular biology - Genetics (study about human genetics and traits e.g. DNA) - Microbiology (study of life and organisms that are too small to be seen with the naked eye) - Bacteriology 4) Career Related to Biology Medicine Doctor, nurse, dentist, pharmacist, veterinarian, physiotherapist Biotechnologist, nutritionist, food technologist Estate manager, botanist, agricultural officer Research officer, scientist - Entomology (scientific study on insects - Developmental biology (study of the process by which organisms grow and develop) - Ecology - Zoology - Botany - Taxonomy (science of classification, e.g. human {mammal class}) - Histology (study of the microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues of plants)
Biotechnology Agriculture Industry
5) Characteristic of Living Organism Metabolism: Respiration: Nutrition: Locomotion: Reproduction: Growth: Excretion: Obtain energy for life and activities Breakdown food to obtain energy for growth, movement.... -Sources of energy and growth -Repair damaged tissue Moving from place to place (only for animal) Reproduce offspring Increasing in size Expelled waste from body
Theory of Cell
All organisms are made up of one or more cells unicellular (e.g. bacteria, yeast, amoeba) or multicellular (e.g. human, plants, animals) organisms Cells are the fundamental and structural unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing cells.
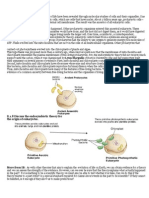
1) Non-organelle Structures of Cell Plasma membrane (contains jelly-like matrix, contains all components of cell) Cytoplasm (thin layer, partially permeable, flexible) Cell wall (plant cell only) 2) Organelle Structures of a Cell Nucleus
Endoplasmic Recticulum Mitochondrion Ribosom Golgi apparatus Vacuole Chloroplast (plant cell only)
3) Plasma Membrane Separates the content of the cell from its external environment. Regulates the movement of substances entering and leaving the cell. Allows the exchange of nutrients, respiratory gases and wastes products between the cell and its environment 4) Cytoplasm Maintain the shape of the cell. Acts as a medium for the biochemical reactions occur within the cell Storing chemical substances such as glicogen granules (in animal cells), starch granules (implant cells) and enzymes. Stores a variety of organelle. 5) Cell Wall Support the cell and the plant. Maintain the shape of the cell. Prevents the cell from bursting when too much water enters the cell through osmosis. Allows substances to move through it. 6) Nucleus Contains the genetic material of a cell. Controls the activities of the cell. Produces ribosomes and ribonucleic acids (RNA). 7) Endoplasmic Recticulum (ER) Rough Endoplasmic Recticulum: Transporting the newly synthesised protein. Involve in the systhesis of protein. Provides surface for chemical reaction Smooth Endoplasmic Recticulum: Transporting lipids and glycerols. Synthesising lipids and other non-protein substances.
8) Mitochondrion Produces ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) Site of energy production through cellular respiration. Contains a matrix of ribosomes , a cellular DNA molecule and phosphate granules
9) Ribosomes Site for synthesising protein. 10) Golgi Apparatus Site for the production of enzyme and lysosome. Produces polysacharides, glycoproteins and secretory enzyme. Storing and modifying carbohydrate and glycoprotein. Transport and store lipid. 11) Vacuole Stores food (Carbohydrate, amino acid) and water. Support herbaceous plants when it is turgid. Stores organic waste (in leaf cells). 12) Chloroplast Contain chlorophyll and hence a site for photosynthesis to take place.
Вам также может понравиться
- Moby Dick Form 3 (Q&A)Документ7 страницMoby Dick Form 3 (Q&A)Nurulfalah Abdul Ghani100% (4)
- Reorganized Moby Dick MindmapДокумент7 страницReorganized Moby Dick MindmapNurulfalah Abdul Ghani50% (2)
- Reorganized Moby Dick MindmapДокумент7 страницReorganized Moby Dick MindmapNurulfalah Abdul Ghani50% (2)
- pt2 Akhir TahunДокумент13 страницpt2 Akhir TahunNurulfalah Abdul GhaniОценок пока нет
- English Language Carnival 2015 Officiating SpeechДокумент2 страницыEnglish Language Carnival 2015 Officiating SpeechNurulfalah Abdul Ghani88% (8)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- DNA Vs RNAДокумент17 страницDNA Vs RNABeenish MuazzamОценок пока нет
- Letter: Hemimastigophora Is A Novel Supra-Kingdom-Level Lineage of EukaryotesДокумент19 страницLetter: Hemimastigophora Is A Novel Supra-Kingdom-Level Lineage of EukaryotesLeon RodriguesОценок пока нет
- Cytophysiology Revised 2014Документ19 страницCytophysiology Revised 2014Julienne Sanchez-SalazarОценок пока нет
- Dna Extraction From Blood: Preparation of BuffersДокумент2 страницыDna Extraction From Blood: Preparation of Buffershely shahОценок пока нет
- March 2018 (v2) QP - Paper 2 CIE Biology A-LevelДокумент16 страницMarch 2018 (v2) QP - Paper 2 CIE Biology A-LevelSalman Farsi TaharatОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Living WorldДокумент69 страницIntroduction To Living WorldBhoomikaОценок пока нет
- General Science Ability 2021Документ3 страницыGeneral Science Ability 2021Naeem RehmanОценок пока нет
- Bernard-Soulier SyndromeДокумент23 страницыBernard-Soulier SyndromeDavidОценок пока нет
- Section 3 Reading Comprehension: Time: 55 MinutesДокумент11 страницSection 3 Reading Comprehension: Time: 55 Minutesdanang iqbhal al anwari50% (2)
- Top 8 Anti-Aging Supplements That WorkДокумент4 страницыTop 8 Anti-Aging Supplements That WorkDure KashafОценок пока нет
- 9700 s09 QP 1Документ16 страниц9700 s09 QP 1IlincaVasilescuОценок пока нет
- CSEC Integrated Science Study GuideДокумент193 страницыCSEC Integrated Science Study GuideKeke SmithОценок пока нет
- Synthetic Biology: Advancing The Design of Diverse Genetic SystemsДокумент34 страницыSynthetic Biology: Advancing The Design of Diverse Genetic SystemsShampa SenОценок пока нет
- BiologyДокумент6 страницBiologySuraj KumarОценок пока нет
- Cellular Injury, Adaptation and Death: Mechanisms and MorphologyДокумент40 страницCellular Injury, Adaptation and Death: Mechanisms and MorphologySuleiman KikulweОценок пока нет
- Shankar CSP23T05SДокумент141 страницаShankar CSP23T05SSamar PratapОценок пока нет
- Biopsych Trans Chap 2Документ13 страницBiopsych Trans Chap 2Chantelle SiyОценок пока нет
- Endosymbiotic Theory HandoutДокумент1 страницаEndosymbiotic Theory Handoutkathryn_bruyère0% (1)
- A Textbook of Botany. StrasburgerДокумент820 страницA Textbook of Botany. StrasburgerKevin I. SanchezОценок пока нет
- How Do Organisms Reproduce Important Questions PDFДокумент12 страницHow Do Organisms Reproduce Important Questions PDFSomik JainОценок пока нет
- NIOS Biology CH 1 Origin and Evolution of Life Part 6Документ4 страницыNIOS Biology CH 1 Origin and Evolution of Life Part 6Samuel OsuОценок пока нет
- ImmunityДокумент37 страницImmunityRand Hussein100% (1)
- Morphology of Livng ThingsДокумент9 страницMorphology of Livng ThingsBalarabe EL-Hussain100% (1)
- 1.3. Classification of Living ThingsДокумент134 страницы1.3. Classification of Living ThingsLehn Cruz MiguelОценок пока нет
- 50 Important Facts You Probably Forgot Between 5th Grade and CollegeДокумент8 страниц50 Important Facts You Probably Forgot Between 5th Grade and CollegeElgieraydolph BuisonОценок пока нет
- Assignment 7 Sydney BiggsДокумент6 страницAssignment 7 Sydney Biggsapi-570536484Оценок пока нет
- The Three Domains and Six Kingdoms of LifeДокумент14 страницThe Three Domains and Six Kingdoms of LifeRowena NimОценок пока нет
- CBSE Class 9 Science The Fundamental Unit of Life MCQsДокумент3 страницыCBSE Class 9 Science The Fundamental Unit of Life MCQsDinesh KumarОценок пока нет
- IGCSE Biology Section 1 Lesson 2Документ59 страницIGCSE Biology Section 1 Lesson 2ෆОценок пока нет
- Microscopy of Living Microbes: Experiment 1Документ6 страницMicroscopy of Living Microbes: Experiment 1Lakber MandОценок пока нет