Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
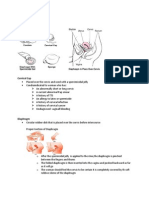
The Human Male Reproductive System
Загружено:
Ta BuenzИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
The Human Male Reproductive System
Загружено:
Ta BuenzАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
The human male reproductive system (or male genital system) consists of a number of sex organs that are
a part of the human reproductive process. In this type of reproductive system, these sex organs are located outside the body, around the pelvic region. The main anatomically male sex organs are the penis and the testes which produce semen and sperm, which as part of sexual intercourse fertilize an ovum in an anatomically female person's body and the fertilized ovum (zygote) gradually develops into a fetus, which is later born as a child [citation needed].
The female reproductive system (or female genital system) contains two main parts: the uterus, which hosts the developing fetus, produces vaginal and uterine secretions, and passes the anatomically male person's sperm through to the fallopian tubes; and the ovaries, which produce the anatomically female person's egg cells. These parts are internal; the vagina meets the external organs at the vulva, which includes the labia, clitoris and urethra. The vagina is attached to the uterus through the cervix, while the uterus is attached to the ovaries via the Fallopian tubes. At certain intervals, the ovaries release an ovum, which passes through the Fallopian tube into the uterus.
If, in this transit, it meets with sperm, the sperm penetrate and merge with the egg, fertilizing it. The fertilization usually occurs in the oviducts, but can happen in the uterus itself. The zygote then implants itself in the wall of the uterus, where it begins the processes of embryogenesis and morphogenesis. When developed enough to survive outside the womb, the cervix dilates and contractions of the uterus propel the fetus through the birth canal, which is the vagina.
The ova are larger than sperm and have formed by the time an anatomically female person is born. Approximately every month, a process of oogenesis matures one ovum to be sent down the Fallopian tube attached to its ovary in anticipation of fertilization. If not fertilized, this egg is flushed out of the system through menstruation.
Process of conceiving a child conception
Conception is the process of becoming pregnant. Most women ovulate each month, this is when an egg is released by the ovaries. For women with a 28-day menstrual cycle, ovulation typically occurs on day 14. During intercourse the man will ejaculate and sperm will be passed from the testicles via the penis into the woman's vagina. If a sperm meets the egg, fertilisation may occur. During a male ejaculation, there are anywhere between 60 million and 500 million sperm that have a go at the 'big race'. They cross the collar of the uterus pretty much within ten minutes. Only about 100 to 200 of the 'chosen ones' will arrive at the most strategic place. The egg can be impregnated for approximately 24 hours from when it leaves the follicle. Once one sperm is successful and penetrates the egg it will lose it's tail and it's head will increase in size. This entrance creates an 'activation' in the egg and it too begins to
enlarge. If the egg has been fertilised (the process of the sperm fusing with the egg) it will move to the uterus and attach itself to the uterine lining, a process called implantation. The cells are called a zygote. The cells will begin to divide which will lead to the development of an embryo and hopefully produce a baby in nine months time! A simple game of genetics will determine the sex of your baby. Every man and woman constitutes 22 pairs of chromosomes plus one pair that is the difference between them; these are the sexual chromosomes X and Y. Men have the chromosomes pairing of XY and women have the pairing of XX. *Both the egg and the sperm have 23 chromosomes *The egg is always the carrier of the X chromosome *The sperm can carry either an X or a Y chromosome
This means that it is the male side that determines the sex of the baby.
Вам также может понравиться
- 12 Population PDFДокумент12 страниц12 Population PDFMahroof YounasОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- In-Vitro FertilizationДокумент48 страницIn-Vitro FertilizationRenz L. Salumbre100% (2)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Animal Reprodcation and Developmental BiologyДокумент88 страницAnimal Reprodcation and Developmental Biologyvivek kumarОценок пока нет
- The Responsible Parenthood and Reproductive Health Act of 2012Документ1 страницаThe Responsible Parenthood and Reproductive Health Act of 2012Divina Gracia Fabicon AranaОценок пока нет
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Safe SexДокумент11 страницSafe SexnathanОценок пока нет
- SpermДокумент1 страницаSpermEve Karen PobleteОценок пока нет
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Brgy Bolo Sep 2007Документ42 страницыBrgy Bolo Sep 2007Rodney Angustia CantoriaОценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Responsible Parenthood and Reproductive Health:: Family PlanningДокумент37 страницResponsible Parenthood and Reproductive Health:: Family PlanningalyssaОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Legal Update Is It in Conflict With PCPNDT?: Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) ActДокумент32 страницыLegal Update Is It in Conflict With PCPNDT?: Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) ActRakersh PatidarОценок пока нет
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Level of Awareness On The Methods of Contraception of The (Repaired)Документ49 страницLevel of Awareness On The Methods of Contraception of The (Repaired)YhanaAdarne100% (3)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- INTRO ObsgynДокумент33 страницыINTRO ObsgynmariarossyyОценок пока нет
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Preconception ClientДокумент2 страницыThe Preconception ClientNurseRiemОценок пока нет
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- CB Advanced Digital Ovulation TestДокумент12 страницCB Advanced Digital Ovulation TestSharon AndrewsОценок пока нет
- Barrier MethodДокумент3 страницыBarrier MethodJaninaPatriciaBОценок пока нет
- Contraceptiv WilliamДокумент85 страницContraceptiv WilliamPridina SyadirahОценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Gynaecology Clerking NoteДокумент10 страницGynaecology Clerking NoteHarithx97Оценок пока нет
- Acrosome ReactionДокумент4 страницыAcrosome ReactionKuldip DwivediОценок пока нет
- ReproductiveHealthCare ppt-1Документ16 страницReproductiveHealthCare ppt-1Maebelyn JinonОценок пока нет
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- Causes of Semen Abnormalities Abnormal CountДокумент3 страницыCauses of Semen Abnormalities Abnormal Countspajda69Оценок пока нет
- Food and Fertility: What Should Women Consume When Trying To Conceive?Документ2 страницыFood and Fertility: What Should Women Consume When Trying To Conceive?Gerry FonziОценок пока нет
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Basic Issues in Development EgyankoshДокумент78 страницBasic Issues in Development EgyankoshIrfanullah FarooqiОценок пока нет
- Your Body Your ChoiceДокумент10 страницYour Body Your Choiceapi-519452875Оценок пока нет
- Abortion EssayДокумент6 страницAbortion EssayAmelia PurcellОценок пока нет
- Karakteristik Dan Perilaku Berisiko Pasangan InferДокумент9 страницKarakteristik Dan Perilaku Berisiko Pasangan InferRizki NurbaitiОценок пока нет
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- An Ethical Comparison - Vitro Fertilization: Rev. Juan R. VélezДокумент11 страницAn Ethical Comparison - Vitro Fertilization: Rev. Juan R. VélezMica BongalaОценок пока нет
- Alterations in The Morphology and Motility of Spermatozoa: Relation With Total Sperm CountДокумент4 страницыAlterations in The Morphology and Motility of Spermatozoa: Relation With Total Sperm CountRolly IswantoОценок пока нет
- Methods of Contraception: John Marl NoelДокумент10 страницMethods of Contraception: John Marl NoelJenna OlileОценок пока нет
- Excuse Me, Madam SpeakerДокумент3 страницыExcuse Me, Madam Speakerbetsyk1Оценок пока нет
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Skkri 2007Документ225 страницSkkri 2007sutopo patriajati100% (3)
- Human Reproductive SystemДокумент3 страницыHuman Reproductive SystemHarvey SaludesОценок пока нет