Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Comparative Bone Anatomy
Загружено:
Kaylee RodriguezИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Comparative Bone Anatomy
Загружено:
Kaylee RodriguezАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Physiology Laboratory Activity
Comparative Bone Anatomy
Part A: The Upper Limb The wing of the chicken contains several bones. The wing enables the chicken to fly. Besides bone, there are several other tissue types on the wing. As you proceed with this lab, be sure to keep all dissected materials (tissue) together. Do not throw any tissues away until you are ready to clean up.
A.
Place the chicken wing in the dissecting tray.
B. Remove the skin carefully. C. Identify the fatty skin. Fat is the yellowish tissue found in small clumps. D. Separate the muscles from each other. Dissect out a blood vessel and a nerve. Nerves are usually found between muscles and bones and they are white and about the diameter of a pencil lead.
E.
Look for the ligaments and the tendons. A ligament is a tough white tissue that holds the bones together. A tendon is a tough white tissue that attaches muscle to bone.
F.
G. Remove the muscle tissue from the bone. Look at the joints.
H.
Complete and drawing form by doing the following tasks: Draw the complete bone structure of the wing. Please label the radius, ulna, humerus, metacarpals, & phalanges.
1.
2.
Complete the comments section: i.
ii.
Describe all the major tissue types found in the wing, Describe all sub varieties you can identify.
iii.
Decide which human appendage to which the chicken wing is analogous, and compare and contrast the two structures.
Physiology Laboratory Activity
Comparative Bone Anatomy
Part B: The Lower Limb The human skeleton is not remarkably different from the skeletons of the other vertebrates. Humans are mammals, and mammalian skeletal structures are very much alike; at least, they all follow a basic plan with modifications. The fact that humans walk erect calls for some structural changes to enable them to maintain balance and carry weight on the inferior appendages. The curvatures of the vertebral column become modified and the pelvis shortens. The forelimbs or arms, freed from their weight-carrying function, become much more flexible, and the hand is adapted for many uses. The legs continue their function of locomotion and weight-bearing and the foot is specialized also for these functions. In this portion of the lab you will be examining a cow femur and comparing it to that of a human. A. Observe the exterior of the femur. Note the cartilage at the ends. Draw a scale diagram of the femur on a new drawing form. Label the following: a. Epiphysis (proximal and distal) b. Diaphysis c. Periosteum
B.
Draw a scale diagram of a longitudinal cross section of the femur. You may use the same drawing form as for B if you have room. Label the following: a. Epiphysis (proximal and distal) b. Diaphysis c. Periosteum d. Spongy bone region e. Medullary cavity f. Compact bone region g. Marrow
C.
D. Observe and diagram a cross section femur disk. Draw it as actual size. Label the following: a. Periosteum b. Endosteum c. Medullary cavity d. Marrow e. Spongy or compact bone region (depending on what you have) E. Complete the comments section.
Lab Questions. Please answer the following questions on a separate sheet of paper. Although you dont have to rewrite the question, your ANSWERS need to be in complete sentences. Part A 1. What type of muscle did you find in the chicken wing? 2. Is the muscle in long sheets, or in wrapped bundles? 3. Describe any covering you may have noticed on the muscle. 4. Describe any blood vessels you found. 5. What is the purpose of the blood vessel in the wing? 6. What type of joint is formed by the bones of the wing? (Refer to color pages for types) Part B 7. Describe the outside surface of the beef femur. 8. Why is it necessary for the ends of bones to be smooth? 9. What is the function of the cartilage at the ends of the bone? 10. Which type of cell is made in the red marrow of bones? 11. What is the function of the small holes in the bone surface? (Hint: what needs to go in and out?) 12. Explain the difference in locations and structure of spongy and compact bone and relate this to the function.
Compare and contrast this bone to the analogous human femur. Include length, width, and mass in your comparison. Use your own words!!! b. Describe the function of all labeled parts
a.
Lab Questions. Please answer the following questions on a separate sheet of paper. Although you dont have to rewrite the question, your ANSWERS need to be in complete sentences. Part A 1. What type of muscle did you find in the chicken wing? 2. Is the muscle in long sheets, or in wrapped bundles? 3. Describe any covering you may have noticed on the muscle. 4. Describe any blood vessels you found. 5. What is the purpose of the blood vessel in the wing? 6. What type of joint is formed by the bones of the wing? (Refer to color pages for types) Part B 7. 8. Describe the outside surface of the beef femur. Why is it necessary for the ends of bones to be smooth?
9. What is the function of the cartilage at the ends of the bone? 10. Which type of cell is made in the red marrow of bones? 11. What is the function of the small holes in the bone surface? (Hint: what needs to go in and out?) 12. Explain the difference in locations and structure of spongy and compact bone and relate this to the function.
Вам также может понравиться
- Spinal Coding HandoutДокумент66 страницSpinal Coding HandoutagnaveenanОценок пока нет
- McRae - Practical Fracture Treatment 4th EdДокумент432 страницыMcRae - Practical Fracture Treatment 4th EdJ7 Prime100% (2)
- 2016 ANAT2241 Course Manual FinalДокумент66 страниц2016 ANAT2241 Course Manual FinalDijattx100% (1)
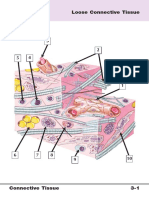
- Connective TissueДокумент20 страницConnective TissueWadabiОценок пока нет
- Histology of Nervous Tissue and Medulla SpinalisДокумент32 страницыHistology of Nervous Tissue and Medulla SpinalisSuhas Kapse100% (1)
- Cerebrum +pons LectureДокумент53 страницыCerebrum +pons LectureIsrael Olusegun100% (1)
- Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) : Biology 105 - Human BiologyДокумент26 страницEssentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) : Biology 105 - Human BiologyAntoinette Battiato WilliamsОценок пока нет
- Gross Veterinary Anatomy: Binarao, Maria Beatriz L. DVM Ii-A 1Документ3 страницыGross Veterinary Anatomy: Binarao, Maria Beatriz L. DVM Ii-A 1BeatrizОценок пока нет
- 2 - Comparative Vertebrate AnatomyДокумент35 страниц2 - Comparative Vertebrate AnatomyGlen MangaliОценок пока нет
- ZOO301 Parade of VertebratesДокумент14 страницZOO301 Parade of VertebratesPatricia Hariramani100% (1)
- Chapter1-AN INTRODUCTION TO THE HUMAN BODYДокумент9 страницChapter1-AN INTRODUCTION TO THE HUMAN BODYKie MusstisqueОценок пока нет
- Histology Lecture: Minerva Diana A. Dichoso, RMTДокумент108 страницHistology Lecture: Minerva Diana A. Dichoso, RMTVernadel ApolloОценок пока нет
- Cestodes and Trematodes - ReviewerДокумент2 страницыCestodes and Trematodes - ReviewerAnna LouisaОценок пока нет
- Neuroanatomy Labs#1 PhotosДокумент35 страницNeuroanatomy Labs#1 PhotosParam DaveОценок пока нет
- Biology 453 - Comparative Vert. Anatomy WEEK 1, LAB 1: Anatomical Terms & Introduction To Chordates AssignmentsДокумент10 страницBiology 453 - Comparative Vert. Anatomy WEEK 1, LAB 1: Anatomical Terms & Introduction To Chordates AssignmentsKerbie Jayd0% (1)
- Skeletal System - Study MaterialДокумент4 страницыSkeletal System - Study MaterialNabeel UndreОценок пока нет
- World Health Organization - WHO Standard Accupuncture Point LocationsДокумент249 страницWorld Health Organization - WHO Standard Accupuncture Point LocationsMirjana Adzic100% (2)
- Kaufman’s Atlas of Mouse Development Supplement: With Coronal SectionsОт EverandKaufman’s Atlas of Mouse Development Supplement: With Coronal SectionsRichard BaldockОценок пока нет
- AIIMS & NEET Memory Questions on AnatomyДокумент28 страницAIIMS & NEET Memory Questions on AnatomyShweta SaraswatОценок пока нет
- A Field Guide To Joint Disease in Archaelogy - J. Rogers and T. Waldron OCR ReduitДокумент66 страницA Field Guide To Joint Disease in Archaelogy - J. Rogers and T. Waldron OCR ReduitCeilidh Lerwick83% (6)
- Effectiveness of The Teacher-Made SciencДокумент4 страницыEffectiveness of The Teacher-Made SciencElaDonatoAriolaОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of Digestive System!!Документ31 страницаAnatomy of Digestive System!!Bio SciencesОценок пока нет
- Evolution of Anatomy Through Comparative StudiesДокумент2 страницыEvolution of Anatomy Through Comparative StudiesCezaraTeodorescuОценок пока нет
- Comparative Anatomy of The BoneДокумент53 страницыComparative Anatomy of The BoneCherry SantosОценок пока нет
- Comparative Anatomy of Integumentary Glands in VertebratesДокумент3 страницыComparative Anatomy of Integumentary Glands in VertebratesViswadeep Das100% (1)
- Idoc - Pub Anatomy-Viva PDFДокумент6 страницIdoc - Pub Anatomy-Viva PDFhieulee84Оценок пока нет
- Comparative Anatomy LecДокумент2 страницыComparative Anatomy LecKerbie JaydОценок пока нет
- Anatomy 090819Документ30 страницAnatomy 090819Vaishnavi GourabathiniОценок пока нет
- Frog S Muscular System PDFДокумент9 страницFrog S Muscular System PDFVia CabardaОценок пока нет
- AAB Human Skull Anatomy ActivityДокумент2 страницыAAB Human Skull Anatomy ActivityCamila VorkapicОценок пока нет
- Dental Anatomy Final ReviewДокумент11 страницDental Anatomy Final Reviewvitro4Оценок пока нет
- Comparative Anatomy of Aortic ArchesДокумент2 страницыComparative Anatomy of Aortic ArchesTibian_Mallick94% (16)
- CT Anatomy of OrbitДокумент31 страницаCT Anatomy of OrbitMaajid Mohi Ud Din MalikОценок пока нет
- POLY Anatomy PDFДокумент2 страницыPOLY Anatomy PDFGady SzeОценок пока нет
- Borders: Teachmeseries LTDДокумент3 страницыBorders: Teachmeseries LTDlecturioОценок пока нет
- 15 PharynxДокумент9 страниц15 Pharynxapi-3757921Оценок пока нет
- Urinary System (Anatomy and Physiology)Документ4 страницыUrinary System (Anatomy and Physiology)ALESSANDRA BALBONTIN PEGARIDOОценок пока нет
- Exercise 3 Phylum CoelenterataДокумент34 страницыExercise 3 Phylum CoelenterataClemence Marie FuentesОценок пока нет
- Histology Notes 2Документ13 страницHistology Notes 2Lukas BüchlerОценок пока нет
- DR - Khin Myo Thu Faculty Perubatan UitmДокумент19 страницDR - Khin Myo Thu Faculty Perubatan UitmAshbirZammeriОценок пока нет
- 15 - Anatomy Mcqs HistologyДокумент14 страниц15 - Anatomy Mcqs HistologyNasan ShehadaОценок пока нет
- Lower Limb InjuriesДокумент47 страницLower Limb InjuriesDaisyyhyОценок пока нет
- A4 QB-MC Ch02 The Cell As The Basic Unit of LifeДокумент29 страницA4 QB-MC Ch02 The Cell As The Basic Unit of LifeReg ChooОценок пока нет
- PhysiologyДокумент31 страницаPhysiologyraza20Оценок пока нет
- Internal Anatomy of FishДокумент18 страницInternal Anatomy of FishPokemongo Shu TingОценок пока нет
- Exercise on Upper Limb Bones and JointsДокумент2 страницыExercise on Upper Limb Bones and JointsLem A SharОценок пока нет
- Bones of Upper and Lower Limbs - RevisionДокумент15 страницBones of Upper and Lower Limbs - RevisionChess Nuts100% (1)
- Flatworms: Phylum Platyhelminthes OverviewДокумент19 страницFlatworms: Phylum Platyhelminthes OverviewBudi AfriyansyahОценок пока нет
- Upper Limb: Pectoral RegionДокумент13 страницUpper Limb: Pectoral RegionMariam Alavidze0% (1)
- Brachial Plexus Self QuizДокумент2 страницыBrachial Plexus Self Quizsan100% (1)
- Austin Journal of AnatomyДокумент12 страницAustin Journal of AnatomyAustin Publishing GroupОценок пока нет
- DДокумент5 страницDDaeng Arya01Оценок пока нет
- Frog DissectionДокумент7 страницFrog DissectionKhairin KhairudinОценок пока нет
- Lecture 3 AnatomyДокумент14 страницLecture 3 AnatomyZA IDОценок пока нет
- 1-Bones of The Upper Limb Final-2Документ18 страниц1-Bones of The Upper Limb Final-2DrVasu Mudiraj100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology: Allen Octaviano Cudiamat, RNДокумент29 страницAnatomy and Physiology: Allen Octaviano Cudiamat, RNᜀᜎ᜔ᜎᜒᜈ᜔ ᜃᜓᜇᜒᜀᜋᜆ᜔Оценок пока нет
- 2015 Final ExamДокумент17 страниц2015 Final ExamlОценок пока нет
- Comparative Vertebrate AnatomyДокумент9 страницComparative Vertebrate AnatomyJayson Tafalla LopezОценок пока нет
- Examples of Superior Examples of Inferior: PlanesДокумент2 страницыExamples of Superior Examples of Inferior: PlanesDorothy MaglenteОценок пока нет
- Skeletal System ExamДокумент9 страницSkeletal System ExamBijay Kumar Mahato100% (1)
- 2 - Bones of The Lower LimbДокумент23 страницы2 - Bones of The Lower LimbHamzaОценок пока нет
- 09 Skull and Visceral SkeletonДокумент6 страниц09 Skull and Visceral SkeletonKaye Coleen Cantara NueraОценок пока нет
- Anatomy Embryology II SemДокумент5 страницAnatomy Embryology II SemCpopОценок пока нет
- Axillary Artery: Branches First (1 Branch) Second Part (2 Branches) Third (3 Branches) 1 2 4Документ14 страницAxillary Artery: Branches First (1 Branch) Second Part (2 Branches) Third (3 Branches) 1 2 4foster18Оценок пока нет
- Cell Structures and FunctionsДокумент3 страницыCell Structures and FunctionsLea IoaОценок пока нет
- Histology Self Quiz Intro and EpitheliumДокумент3 страницыHistology Self Quiz Intro and EpitheliumJoonHong An100% (1)
- Procedures of The Cervical and Thoracic SpineДокумент28 страницProcedures of The Cervical and Thoracic SpinemiracleОценок пока нет
- Ebook MriДокумент26 страницEbook MrikadekОценок пока нет
- Dsem TRM 0115 0290 3 - LRДокумент64 страницыDsem TRM 0115 0290 3 - LRNadya IrawanОценок пока нет
- Norm CatalogueДокумент60 страницNorm Cataloguetanthimcsa0% (1)
- SkullДокумент15 страницSkullGynewОценок пока нет
- Osteoid Osteoma: Multimodality Imaging With Focus On Hybrid ImagingДокумент18 страницOsteoid Osteoma: Multimodality Imaging With Focus On Hybrid ImagingCătălin Paul CernișencuОценок пока нет
- Anatomi Blok 5Документ5 страницAnatomi Blok 5dfghjk lkjhgОценок пока нет
- Degenerative Retrolisthesi 2013Документ6 страницDegenerative Retrolisthesi 2013Dan CarcamoОценок пока нет
- 5joints (Unit-V)Документ22 страницы5joints (Unit-V)Urdu KahaniОценок пока нет
- VISCEROCRANIUMДокумент157 страницVISCEROCRANIUMTrần NamОценок пока нет
- Ficha para Inventario de HuesosДокумент24 страницыFicha para Inventario de HuesosAntony CevallosОценок пока нет
- TMJ & Its MovementsДокумент26 страницTMJ & Its Movementsdeepinder27100% (1)
- Anatomy of Pelvis and Fetal SkullДокумент41 страницаAnatomy of Pelvis and Fetal SkullHakimah K. Suhaimi100% (1)
- 4 - The Periodontium (Mahmoud Bakr)Документ128 страниц4 - The Periodontium (Mahmoud Bakr)MobarobberОценок пока нет
- Coluna VertebralДокумент39 страницColuna Vertebral070971we0% (1)
- Osteoporosis: Brittle Bone DiseaseДокумент28 страницOsteoporosis: Brittle Bone DiseaseandhitaОценок пока нет
- Osteology of Maxillofacial Skeleton IДокумент36 страницOsteology of Maxillofacial Skeleton Isailajanekkanti03Оценок пока нет
- 4.prenatal and Post Natal Growth of MandibleДокумент62 страницы4.prenatal and Post Natal Growth of MandiblePranaliОценок пока нет
- Core Radiology - Head & Neck ImagingДокумент106 страницCore Radiology - Head & Neck ImagingefqsdfqsОценок пока нет
- AO Principles of Fracture Management - 3rd Ed. - Thieme - 2017Документ7 страницAO Principles of Fracture Management - 3rd Ed. - Thieme - 2017Roberto GuanipaОценок пока нет
- PDF Cervical Spine AnatomyДокумент71 страницаPDF Cervical Spine AnatomyAqilla Fadia HayaОценок пока нет
- Appendicular Body - Muscles (Upper Limb) PDFДокумент13 страницAppendicular Body - Muscles (Upper Limb) PDFSarath KumarОценок пока нет
- The Skeletal System The Skeletal System: © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. 1Документ16 страницThe Skeletal System The Skeletal System: © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. 1lourd nabОценок пока нет
- Anatomy in Practice: The Sacrotuberous LigamentДокумент4 страницыAnatomy in Practice: The Sacrotuberous LigamentAjay Pal NattОценок пока нет