Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Healthy Thinking Includes All Except
Загружено:
Sreeram SankarИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Healthy Thinking Includes All Except
Загружено:
Sreeram SankarАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Healthy thinking includes all except a)continuity b)constancy c)organisation d)clarity Ans is d i.e.
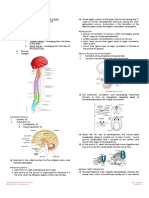
Clarity Ref: Fish's Clinical Psychopathology: Signs and Symptoms in Psychiatry By Patricia R. Casey, Brendan Kelly 3/e p47 Schneider suggested there were three features of healthy thinking: . Constancy: this is characteristic of a completed thought that does not change in content unless and until it is superseded by another consciously-derived thought . Organisation: the contents of thought are related to each other in consciousness and do not blend with each other, but are separated in an organised way. . Continuity: there is a continuity of the sense continuum, so that even the most heterogenous subsidiary thoughts, sudden ideas or observations that emerge are arranged in order in the whole content of consciousness. Correction in Nov 09 Q no. 10; answer remains the same, explanation is changed. 10. Vaginal sphincter is formed by all except: a) Internal urethral sphincter b) External urethral sphincter c) Pubovaginalis d) Bulbospongiosus 10. Ans is a i.e. Internal urethral sphincter [Ref: Moores Anatomy 5/e p402; Anatomy at a glance By Omar Faiz, David Burns Moffa p61; Grays Anatomy 40/e p1094-1096; BDC 4/e vol. 2 p393; Practical guide to female pelvic medicine By Gamal M. Ghoniem, G. Willy Davila] There is no internal urethral sphincter in females. It is present in males at the bladder neck and proximal urethral. Its function is to prevent retrograde ejaculation of semen into the bladder during the time of ejaculation. In males the detrusor muscle fibers of the bladder at the region of bladder neck and proximal urethra are organized into internal urethral sphincter which is under involuntary control. In females the musculature surrounding the internal urethral orifice of the bladder is not organized into an internal sphincter. External urethral sphincter is present in both males and females.
Vaginal sphincter is formed by the fibres of pubococcygeus known as pubovaginalis. There are other muscles also which contribute in compressing the vaginal orifice. The Bulbospongiosus muscle fibres run anteriorly on either side of the vagina to attach to the corpora cavernosa of the clitoris and posteriorly to perineal body. Bulbospongiosus in females acts to constrict the vaginal orifice and express the secretions of greater vestibular glands. The external urethral sphincter is composed of 3 muscles - sphincter urethrae, compressor urethrae, and urethrovaginalis sphincter (or muscle); last 2 muscles found in females only. When external urethral sphincter contracts to compress the urethra, it compresses the vaginal orifice also.
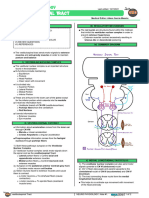
We have made changes in the question and answer of q no 177 of Nov 08. Ans remains the same. This question has also been repeated in Nov 10. A 20year female patient with 6th cranial nerve palsy and proptosis on T2 weighted MRI shows a hyperintense lesion in cavernous sinus which shows homogenous contrast enhancement. Most probable diagnosis is? a) schwannoma b) meningioma c) cavernous sinus hemangioma d) astrocytoma Ans is a i.e. Schwannoma Ref: Osborn Neuroradiology 1/e p501; CT and MRI of the Whole Body 4/e p162, 166; http://www.ajnr.org/cgi/content/full/25/2/280; http://www.ajnr.org/cgi/content/full/24/6/1148 Common tumors within cavernous sinus are: Schwannoma, Meningioma and Metastasis. (Ref: Osborn Neuroradiology) Cavernous sinus hemangioma is a very rare tumor of this region. (http://www.ajnr.org/cgi/content/full/24/6/1148) All the cavernous sinus tumors can cause sixth nerve palsy (and proptosis). So the diagnosis is to be made on the basis of incidence and MR chaaracterstics. MR characteristics: Menigioma Usually hypointense to isointense on T1-weighted and isointense to hyperintense with T2-weighted images. Somebooks write that it is mostly isointense on T2 wt sequences. Enhances homogenously on post contrast scans. Schwannoma Mostly hypointense on T1 and hyperintense on T2. Smaller tumors show homogenous density and strong homogenous enhancement. Larger tumors demonstrate heterogeneity of both density and contrast enhancement because of the presence of intratumoral cystic degeneration & xanthomatous changes. Cavernous hemangioma Mostly hypointense on T1 and hyperintense on T2. Shows good homogenous contrast enhancement. Thus meningioma can be ruled out as it usually isointense on T2. We are left with Schwannoma and Cavernous hemangioma. We would personally like to go with Schwannoma as it is one of the commonest tumors of the cavernous sinus and smaller tumors have homogenous enhancement. Cavernous hemangioma though matches more with the contrast enhancement characteristics, is a very rare tumor of this region.
Вам также может понравиться
- The Orrery - A Handbook To The Spheres of PowerДокумент113 страницThe Orrery - A Handbook To The Spheres of PowerAnonymous PtMxUHm9RoОценок пока нет
- Anatomy PDFДокумент114 страницAnatomy PDFkhualabear101100% (1)
- X ANATOMY HEAD AND NECKДокумент16 страницX ANATOMY HEAD AND NECKArijeet77Оценок пока нет
- Total Reflexology: The Reflex Points for Physical, Emotional, and Psychological HealingОт EverandTotal Reflexology: The Reflex Points for Physical, Emotional, and Psychological HealingРейтинг: 2.5 из 5 звезд2.5/5 (2)
- Sound Devices Used in PoetryДокумент10 страницSound Devices Used in PoetryPrince Ronson SabadoОценок пока нет
- Spinal CordДокумент65 страницSpinal CordDr. Vinod Gupta100% (1)
- Anaesthesiology NAGY TESZTKÖNYVДокумент1 064 страницыAnaesthesiology NAGY TESZTKÖNYVoroszgabor100% (10)
- The Amazing Human Body The Nervous SystemДокумент81 страницаThe Amazing Human Body The Nervous SystemAll_Stars100% (2)
- Lo 1 Week 5 NeuroДокумент36 страницLo 1 Week 5 NeuroInna DamaОценок пока нет
- Chick Embryo 72 HoursДокумент48 страницChick Embryo 72 HoursogheeluvОценок пока нет
- PPK ILMU PENYAKIT PerinatologiДокумент31 страницаPPK ILMU PENYAKIT PerinatologiRico AndreawanОценок пока нет
- The Dental Distress Syndrome QuantifiedДокумент37 страницThe Dental Distress Syndrome QuantifiedDentalbay GrОценок пока нет
- Class II MalocclusionДокумент67 страницClass II Malocclusionsonal agarwal100% (1)
- TG Im Not Scared 10 PagesДокумент10 страницTG Im Not Scared 10 Pagesapi-116304916100% (1)
- Development of The Nervous SystemДокумент5 страницDevelopment of The Nervous SystemChaGonzalesОценок пока нет
- MRCS Book 2Документ24 страницыMRCS Book 2Adaad Ahmad67% (3)
- Dog Anatomy, A Pictorial Approach To Canine Structure (VetBooks - Ir)Документ79 страницDog Anatomy, A Pictorial Approach To Canine Structure (VetBooks - Ir)Risha Catra PradhanyОценок пока нет
- Muscular System Tour Activity FormДокумент19 страницMuscular System Tour Activity Formmr_afmОценок пока нет
- AnatomyДокумент30 страницAnatomyMariam A. KarimОценок пока нет
- How Do You Feel?: An Interoceptive Moment with Your Neurobiological SelfОт EverandHow Do You Feel?: An Interoceptive Moment with Your Neurobiological SelfРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- Cerebrospinal FluidДокумент13 страницCerebrospinal Fluidsakshi panwarОценок пока нет
- Anatomy - Dr. Rajesh KaushalДокумент33 страницыAnatomy - Dr. Rajesh KaushalScribbleCoolioОценок пока нет
- New Text DocumentДокумент63 страницыNew Text DocumentKiran TemkarОценок пока нет
- F PDFДокумент31 страницаF PDFAvinash kumar NirmalОценок пока нет
- Aiims May 2009Документ50 страницAiims May 2009Gowri ShankarОценок пока нет
- Voie Descendante VestibulospinaleДокумент2 страницыVoie Descendante VestibulospinaleJJОценок пока нет
- Biopsychology NotesДокумент13 страницBiopsychology NotesSandhiya KОценок пока нет
- Jurnal Internasional - Kelenjar CowperДокумент10 страницJurnal Internasional - Kelenjar CowperAnggita MelaniОценок пока нет
- Spinal Cord AnatomyДокумент6 страницSpinal Cord AnatomyBharath Raj YadavОценок пока нет
- Woodburne 1960Документ7 страницWoodburne 1960nimaelhajjiОценок пока нет
- Ectodermal Derivatives of Pig EmbryoДокумент7 страницEctodermal Derivatives of Pig EmbryoChristalie Bea FernandezОценок пока нет
- 5 Pelvic Floor AJ 2022 v2Документ79 страниц5 Pelvic Floor AJ 2022 v2Husam OsmanОценок пока нет
- 4 - Muscular SystemДокумент39 страниц4 - Muscular SystemMaryam ElammaryОценок пока нет
- Some Macroscopic and Microscopic Observation On The Pituitary Gland of Guinea-Pig PDFДокумент7 страницSome Macroscopic and Microscopic Observation On The Pituitary Gland of Guinea-Pig PDFLuay O HamzaОценок пока нет
- Modul Task Anatomy StudentДокумент18 страницModul Task Anatomy StudentNindy TjionganataОценок пока нет
- The History of Nerve RepairДокумент32 страницыThe History of Nerve RepairWim ZhuОценок пока нет
- Nervous System 2Документ12 страницNervous System 2Darwin MangabatОценок пока нет
- Neuro 2009Документ181 страницаNeuro 2009mcie22dwestОценок пока нет
- Maranatha University Nervous System Questions and AnswersДокумент22 страницыMaranatha University Nervous System Questions and AnswersKojo Yeboah EnchillОценок пока нет
- Neurociencias: Dr. Arturo Cervantes SorianoДокумент28 страницNeurociencias: Dr. Arturo Cervantes Sorianomariisa_saysОценок пока нет
- Lab Exercise 2Документ4 страницыLab Exercise 2Angela Robles0% (1)
- Manual of Nervous DiseasesДокумент342 страницыManual of Nervous DiseasesAnonymous HDOLl9Оценок пока нет
- Spinal Cord Tumors: Mahmoud Wahdan Benha UniversityДокумент61 страницаSpinal Cord Tumors: Mahmoud Wahdan Benha Universitybasmarizk deabsОценок пока нет
- Lo Wo 3Документ24 страницыLo Wo 3KesyaОценок пока нет
- The Spinal Cord: Lec-11-Dr - Maysoon AlkazzazДокумент12 страницThe Spinal Cord: Lec-11-Dr - Maysoon AlkazzazRose ParisОценок пока нет
- Physiological Psychology: Physiological Psychology Studies TheДокумент18 страницPhysiological Psychology: Physiological Psychology Studies The31316969Оценок пока нет
- Lumbar Puncture in PediatricsДокумент5 страницLumbar Puncture in PediatricsMarsianus UslОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 UNIT 1Документ19 страницChapter 2 UNIT 1Ayen LatosaОценок пока нет
- Central and Peripheral Nervous System, Spinal Cord and Spinal NervesДокумент4 страницыCentral and Peripheral Nervous System, Spinal Cord and Spinal NervesDaniel DanielОценок пока нет
- Neuroanatomy, Brainstem - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfДокумент13 страницNeuroanatomy, Brainstem - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfKritika MalhotraОценок пока нет
- Anat 6.5 Basal Ganglia - QuijanoДокумент6 страницAnat 6.5 Basal Ganglia - Quijanolovelots1234Оценок пока нет
- MDS 1005 Dissections 1-3 - 2015Документ6 страницMDS 1005 Dissections 1-3 - 2015Brooke Lynn FalzonОценок пока нет
- Key PointsДокумент12 страницKey PointsspotxОценок пока нет
- Assesment NeuroДокумент15 страницAssesment Neuroerfan ghadirianОценок пока нет
- Anatomy AssessmentДокумент12 страницAnatomy Assessmentdirshayedilaba24Оценок пока нет
- Essentials of Regional Anesthesia Anatomy NYSORA - The New York School of Regional AnesthesiaДокумент31 страницаEssentials of Regional Anesthesia Anatomy NYSORA - The New York School of Regional Anesthesiajorge ceballos troncosoОценок пока нет
- Remember Question MDSДокумент26 страницRemember Question MDSBinayak UpadhyayaОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 LecNotesДокумент49 страницUnit 1 LecNotesAnn NguyenОценок пока нет
- Seidels Guide To Physical Examination 8th Edition Ball Test BankДокумент15 страницSeidels Guide To Physical Examination 8th Edition Ball Test Banksheddingslank8cgu100% (27)
- Seidels Guide To Physical Examination 8Th Edition Ball Test Bank Full Chapter PDFДокумент36 страницSeidels Guide To Physical Examination 8Th Edition Ball Test Bank Full Chapter PDFchieverespectsew100% (8)
- Anatomy & Physiological Alteration of Central Neuraxial BlocksДокумент4 страницыAnatomy & Physiological Alteration of Central Neuraxial Blocksakif48266Оценок пока нет
- Anatomia - Diagnostica (PPTshare)Документ70 страницAnatomia - Diagnostica (PPTshare)DANIEL ALEJANDRO100% (1)
- Lumbar Puncture in PediatricsДокумент9 страницLumbar Puncture in PediatricsAulia Rahardjo100% (1)
- Lect. 50 Histology Review 2Документ93 страницыLect. 50 Histology Review 2Mira ThakkarОценок пока нет
- Autonomic Nervous System A. Structure/function of ANSДокумент5 страницAutonomic Nervous System A. Structure/function of ANSXiao Kui LirioОценок пока нет
- 1.4 LecturesДокумент115 страниц1.4 LecturesLuana SavagetОценок пока нет
- Assignment No 2: Name: Adeel Afzal SAP ID: 70126263 Section: C Subject: Anatomy Submitted To: Mam Mahreem JabarДокумент11 страницAssignment No 2: Name: Adeel Afzal SAP ID: 70126263 Section: C Subject: Anatomy Submitted To: Mam Mahreem JabarAdeel AfzalОценок пока нет
- Animal Protect Themselves Folio Thanis 1Документ25 страницAnimal Protect Themselves Folio Thanis 1Kisor SorОценок пока нет
- Makhraj Student HandoutsДокумент50 страницMakhraj Student HandoutsZakia Rehman100% (1)
- Introductory Guide To Zooplankton Identification: Australian Plankton SurveyДокумент35 страницIntroductory Guide To Zooplankton Identification: Australian Plankton SurveyHarry VenturaОценок пока нет
- Dolphins On Duty: Dolphins On Duty The U.S. Navy Trains These Supersmart Animals To Work On Lifesaving MissionsДокумент3 страницыDolphins On Duty: Dolphins On Duty The U.S. Navy Trains These Supersmart Animals To Work On Lifesaving MissionsAira Ysabel PutunganОценок пока нет
- 1 - Arlington Park RETROSPECTOSДокумент8 страниц1 - Arlington Park RETROSPECTOSFelix Velasquez CastilloОценок пока нет
- Stem CellДокумент14 страницStem CellsattwikaОценок пока нет
- Ankoneus CLUBДокумент4 страницыAnkoneus CLUBAndi Dytha Pramitha SamОценок пока нет
- Robert Church HistoryДокумент108 страницRobert Church HistoryNathan DavisОценок пока нет
- Marine Science Second Semester ReviewДокумент11 страницMarine Science Second Semester ReviewMario HerreraОценок пока нет
- The Dragon Village ScriptДокумент2 страницыThe Dragon Village ScriptZachary Rafael DellaОценок пока нет
- Poultry LivingДокумент24 страницыPoultry LivingIrene LebrillaОценок пока нет
- mFljvnkhGvPApK1G3Krj PDFДокумент110 страницmFljvnkhGvPApK1G3Krj PDFAhxhsОценок пока нет
- PuntilascanДокумент67 страницPuntilascanMaria Silvia BettiОценок пока нет
- What Is A Tissue? Ans:: Class: 9 (Science) Tissues Chapter - 2Документ21 страницаWhat Is A Tissue? Ans:: Class: 9 (Science) Tissues Chapter - 2The Silent RepentantОценок пока нет
- ProiecttДокумент4 страницыProiecttAdriana Elena DoneОценок пока нет
- Fish and Shellfish Identification and FabricationДокумент21 страницаFish and Shellfish Identification and FabricationSenthil KumarОценок пока нет
- Is and ThrombosisДокумент5 страницIs and ThrombosisQurat KhanОценок пока нет
- A NEW CLASSIFICATION OF MAMMALS, SimpsonДокумент36 страницA NEW CLASSIFICATION OF MAMMALS, SimpsoneligeokОценок пока нет
- Discussion Essay Tips and StrategiesДокумент22 страницыDiscussion Essay Tips and StrategiesLoreen MtangaraОценок пока нет
- Plysu People No.3 Autumn 1971Документ8 страницPlysu People No.3 Autumn 1971Richard LarbeyОценок пока нет
- 40 Amazing Facts About The Human BodyДокумент2 страницы40 Amazing Facts About The Human BodyDr.Eswara Reddy Siddareddy100% (2)
- Shree Vidya MantrasДокумент4 страницыShree Vidya MantrasVishal Sharma100% (2)