Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Oct 2010a P3: 2. LN (1) 1 2 LN LN (1) 1 LN LN (1) LN 1 (1) (1) 1 1 LN 1 (1) 1 1 (LN
Загружено:
NobodyetИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Oct 2010a P3: 2. LN (1) 1 2 LN LN (1) 1 LN LN (1) LN 1 (1) (1) 1 1 LN 1 (1) 1 1 (LN
Загружено:
NobodyetАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Oct 2010a P3
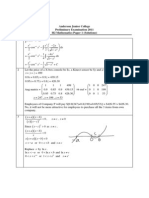
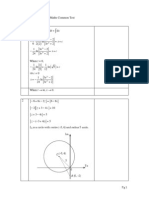
1. 2|x 3| > |3x + 1| |2x 6| >|3x + 1|
2 2 2 2 2
2 2
2 2 2
2 2
2. ln(1 ) 1 2ln ln(1 ) 1 ln ln(1 ) ln 1
(1 ) (1 ) 1 1
ln 1 (1 )
1 1
( ln
Q x x x x x x
x x
e x ex x x
x x e e
negative root inadmissable as of such a number impossible
+ = + + = + + =
+ +
= = + = = =
0 0
3. ( 60) 2sin cos cos 60 sin sin60 2sin
1 3
cos sin 2sin 0.5cos 1.1339sin tan 0.174
2 2
9.9 ;189.9
Q Cos u u u u u
u u u u u u
u
+ = =
= = =
=
3
3
2
-1/3
y=2x-6
y=-2x+6
y=-3x-1
x = 1
x = -7
Inequality holds when the bold line is above black line.
i.e. when -7 < x < 1
y=3x+1
Q4.
2
2
1 0
1
2
3
4
5
0.6, cot 4 1 1.02 0
1, cot 4 1 2.36 0
' 0.6 1
1
sin 1 cot 0.7
2
0.739466
0.739401
0.729921
0.727598
0.728498
0.73 2
n n
when x x x
when x x x
So there s a root between and
U g iteration x x with x
x
x
x
x
x
root to dp
+
= + = >
= + = <
= + =
=
=
=
=
=
=
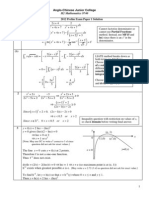
y = 4x
2
-1
y = cotx
One root for cotx = 4x
2
-1
| |
2
1
0
2 2
2
6 6 6
2 0 0 0
6
6
0
0
5. ; 2sin 2cos 2cos
4
1
0 sin 0 0; 1 sin
2 6
4sin 4sin
2cos 2cos 4sin
2cos
4 4sin
2(1 cos 2 ) 2 sin 2 [ sin
3 3
x dx
Q I dx substituting x dx d
d x
When x When x
So I d d d
I d
t t t
t
t
u u u u
u
t
u u u u
u u
u u u u u u
u
u
t t
u u u u
= = = =
= = = = = =
= = =
= = =
}
} } }
}
3
] 0
3 2
t
=
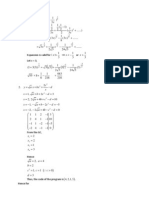
Q6. z = 3 + i = 2( 3 + i) = 2(cos30 + isin30). So |z| = 2 and arg(z) = 30
0
z
*
= 3 i 2z + z
*
= 2(3 + i) + 3 i = 33 i
iz
*
= i3 i
2
= 1 + 3i = 2( + 3i) = 2(cos60 + isin60) = 2e
i60
While z = 2(cos30 + isin30) = 2e
i30
Hence iz
*
= 2e
i60
= e
i30
= cos30 + isin30
= 3 + i
z 2e
i30
A: z; B: iz
*
Q7. OA = a = i + 2j + 2k and OB = b = 3i + 4j.
(i) A vector equation for the line AB is r = a + d = i + 2j + 2k + (2i + 2j - 2k)
(ii) The point P lies on the line AB OP = (2+1)i + (2+2)j +(-2+2)k
As OP is perpendicular to AB; OP.d = 0 [(2+1)i + (2+2)j +(-2+2)k]. (2i + 2j - 2k) = 0
2(2+1) + 2(2+2) -2(-2+2) = 0 12 + 2 = 0 = -1/6
So the position vector of P = OP = 2/3i + 5/3j + 7/3k
(iii) The normal to the plane which contains AB and which is perpendicular to the plane OAB
will be parallel to OP: this is because OP lies in the plane OAB and is perpendicular to AB.
So the equation of this plane is r.n = n.a where n = 2/3i + 5/3j + 7/3k or 2i + 5j + 7k
and n.a = (2i + 5j + 7k).( i + 2j + 2k) = 2 + 10 + 14 = 26
So the equation of the plane is (xi + yj + zk).(2i + 5j + 7k) = 26 or 2x + 5y + 7z =26
30
0
O
A: arg 30
0
x
i
B: arg 60
0
30
0
Clearly Angle
AOB =30
0
2
2 2
1 2 1
2 2
2 3
3
8. 3 (1 2 ) ( )(1 )
(1 )(1 2 ) 1 1 2
1 3 3 1
0 0 1
1 3 3 2 2 3 3 2 2 2
3 1 2 1
(1 ) (2 1)(1 2 )
(1 )(1 2 ) 1 1 2
(1 1. 2 1. 2. 3 ) (2
2! 3!
x a bx c
Q x a x bx c x
x x x x
x a a
x a c c
x a b c b b
x x
x x x
x x x x
x x
x x
+
+ + + + +
+ + + +
= =
= + =
= + + + + =
+
+ = + + + +
+ + + +
= +
2 4
2 3 2
2 3 3 2
2 3
1)(1 1.2 )
(1 ) (2 1)(1 2 .......)
1 ) (2 4 .......1 2 .......)
3 3 3 .....
x terms involving x or higher
x x x x x
x x x x x x
x x x
+ +
= + + + +
= + + + + +
= +
3 2 3 2 2
2
3
1 1
3
3
1
9. ln 3 .ln . 3 .ln
1
0 (3ln 1) 0 0 ln
3
3 3
dy
Q y x x x x x x x x
dx x
dy
x x x or x
dx
e e
Visually x coordinate of M is x e and y coordinate y
= = + = +
= + = = =
= = =
16
15
2 ln 4 ]
16
1
4
1
. 1 [ln ]
16
16
4
16
. 2 [ln ]
16 4
. [ln
]
4 4
. [ln ]
4
.
1
4
. [ln ln
1 0 ln 0 ln int
2
1
4 4
2
1
3 4
2
1
4
2
1
4
3
3
= = =
= = =
= = =
} } }
x x
x
dx
x x
x dx
x
x
x
x xdx x area required the So
x x x x where is again axis x the meets curve the which at po The
20 ) 0 1 ( 20 ) 2 (
9 . 7 ) 1 ( 20 ) 2 ( 10
) 2 ......( ) 1 ( 20 20 20
20
20
05 . 0
20
20
ln 05 . 0 ) 20 ln( 20 ln
) 20 ln( 0 0
) 1 .....( 05 . 0 ) 20 ln( 05 . 0
20
1
) 20 ( 05 . 0 05 . 0 20 1 1 , 0
) 20 ( ) 20 ( . 10
5 . 0
05 . 0 05 . 0
05 . 0
=
~ = =
= =
=
=
= = =
+ = =
= = = = =
=
} }
x implies equation t When
gms e x implies equation t When
e x e x
e
x
t
x
t x
c t when x
c t x dt dx
x
x
dt
dx
k k
dt
dx
x When
x k
dt
dx
x to al proportion x of change of Rate Q
t t
t
Вам также может понравиться
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesОт EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesОценок пока нет
- NYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1Документ10 страницNYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongОценок пока нет
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageОт EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageОценок пока нет
- BT2 Revision Package Solutions (2008 Prelims)Документ111 страницBT2 Revision Package Solutions (2008 Prelims)gerwynngОценок пока нет
- Ajc h2 Math p1 SolutionsДокумент15 страницAjc h2 Math p1 SolutionsjimmytanlimlongОценок пока нет
- 2012 ACJC Prelim H2 Math SolnДокумент15 страниц2012 ACJC Prelim H2 Math Solnckhowh_23284524667% (3)
- Yjc h2 Math p1 SolutionsДокумент12 страницYjc h2 Math p1 SolutionsjimmytanlimlongОценок пока нет
- JC2 Prelim H2 Math Solution Paper 1Документ10 страницJC2 Prelim H2 Math Solution Paper 1Huixin LimОценок пока нет
- Nyjc h2 Math p1 SolutionДокумент10 страницNyjc h2 Math p1 SolutionjimmytanlimlongОценок пока нет
- HCI H2 Maths 2012 Prelim P1 SolutionsДокумент12 страницHCI H2 Maths 2012 Prelim P1 Solutionsnej200695Оценок пока нет
- 2008 Ext1 PDFДокумент3 страницы2008 Ext1 PDFBrandi RoseОценок пока нет
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm AДокумент8 страницAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremОценок пока нет
- ACJC 2014 H2 Maths Supp Exam (Solution For Students)Документ9 страницACJC 2014 H2 Maths Supp Exam (Solution For Students)RaymondZhangОценок пока нет
- Rvhs h2 Math p1 SolutionsДокумент13 страницRvhs h2 Math p1 SolutionsjimmytanlimlongОценок пока нет
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm AДокумент12 страницAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremОценок пока нет
- AJC H2 Math 2013 Prelim P1 SolutionsДокумент15 страницAJC H2 Math 2013 Prelim P1 Solutionsnej200695Оценок пока нет
- QN Solution 1: H2 Math Paper 1Документ11 страницQN Solution 1: H2 Math Paper 1Alex SoonОценок пока нет
- IIT JEE Maths SolutionsДокумент7 страницIIT JEE Maths SolutionsVishal GaudОценок пока нет
- Exercise 1 (C) : DX DyДокумент7 страницExercise 1 (C) : DX DyGokul NathОценок пока нет
- Mi h2 Math Solutions p1Документ10 страницMi h2 Math Solutions p1jimmytanlimlongОценок пока нет
- (3x) (1+ 1 3x) 1 2 3x + 1 2 (1 2 1) 2 (1 3x) + ...... ) (3x) + 1 2 (3x) 1 8 (3x) + ......Документ10 страниц(3x) (1+ 1 3x) 1 2 3x + 1 2 (1 2 1) 2 (1 3x) + ...... ) (3x) + 1 2 (3x) 1 8 (3x) + ......Matthew ShiaОценок пока нет
- SPM Addmath 2007 AnswerДокумент3 страницыSPM Addmath 2007 Answermaieqa8738% (8)
- MJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1Документ22 страницыMJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongОценок пока нет
- ACJC JC2 H2 Maths 2012 Year End Exam Solutions Paper 1Документ10 страницACJC JC2 H2 Maths 2012 Year End Exam Solutions Paper 1ofji4oОценок пока нет
- 2014 2 SARAWAK SMKStJoseph Kuching MATHS QAДокумент11 страниц2014 2 SARAWAK SMKStJoseph Kuching MATHS QASK100% (3)
- 2010 AJC Paper 2solДокумент5 страниц2010 AJC Paper 2solFang Wen LimОценок пока нет
- Acjc h2 Math p2 SolutionsДокумент8 страницAcjc h2 Math p2 SolutionsjimmytanlimlongОценок пока нет
- HW 1 - SolutionsДокумент2 страницыHW 1 - SolutionsMahir MahmoodОценок пока нет
- 2007 Ajc h2 Prelims Paper 1 SolutionsДокумент9 страниц2007 Ajc h2 Prelims Paper 1 Solutionsvincesee85Оценок пока нет
- Paper B SolutionДокумент11 страницPaper B SolutiontimchanymОценок пока нет
- Functions Ex.2 (B)Документ20 страницFunctions Ex.2 (B)Gokul NathОценок пока нет
- 2007 YJC Paper 1solДокумент12 страниц2007 YJC Paper 1solYudi KhoОценок пока нет
- Recitation 5: Sections 12.1-12.3Документ40 страницRecitation 5: Sections 12.1-12.3Oğuzhan ÖzdemirОценок пока нет
- Mathematics Sample Paper Solutions Section-AДокумент19 страницMathematics Sample Paper Solutions Section-APoonamBhardwajОценок пока нет
- Iit - Jee Model Grand Test - Ii Paper - 1 SolutionsДокумент6 страницIit - Jee Model Grand Test - Ii Paper - 1 SolutionsSayan Kumar KhanОценок пока нет
- Concept Recapitulation Test I/Advanced/PAPER-1/Answer/AnswerДокумент8 страницConcept Recapitulation Test I/Advanced/PAPER-1/Answer/Answerullasagw100% (1)
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm AДокумент5 страницAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremОценок пока нет
- Part - Ii: Mathematics: SECTION - I (Single Correct Choice Type)Документ13 страницPart - Ii: Mathematics: SECTION - I (Single Correct Choice Type)Mohammed IqbalОценок пока нет
- 04 03 2012 XIII VXY Paper I Final Test Code A SolДокумент19 страниц04 03 2012 XIII VXY Paper I Final Test Code A Solvishal110085Оценок пока нет
- ClassXII Topper Sample Paper 50Документ26 страницClassXII Topper Sample Paper 50Mohit SharmaОценок пока нет
- AJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1Документ12 страницAJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongОценок пока нет
- 2010 AJC Paper 1solДокумент6 страниц2010 AJC Paper 1solnothingtodo1992Оценок пока нет
- Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia: This Examination Paper Consists of 5 PagesДокумент13 страницUniversiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia: This Examination Paper Consists of 5 PagesCM Zain CrcoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 02Документ13 страницChapter 02Sudipta GhoshОценок пока нет
- Edexcel C3 June 2005 To June 2011 All Questions Mark SchemeДокумент44 страницыEdexcel C3 June 2005 To June 2011 All Questions Mark SchemeOrhan AtestemurОценок пока нет
- Mat Sup 03062011 A B TM SolДокумент5 страницMat Sup 03062011 A B TM SolVictor MartinezОценок пока нет
- Answers Are You Ready For CalculusДокумент6 страницAnswers Are You Ready For CalculusKevin HsiehОценок пока нет
- RVHS JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsДокумент14 страницRVHS JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongОценок пока нет
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm AДокумент10 страницAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADeepak KumarОценок пока нет
- NYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 2Документ7 страницNYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 2jimmytanlimlongОценок пока нет
- JJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsДокумент14 страницJJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongОценок пока нет
- Eamcet 2014 Engineering Key SolutionsДокумент42 страницыEamcet 2014 Engineering Key Solutionsandhracolleges100% (1)
- Info Booklet, Revised 2011Документ27 страницInfo Booklet, Revised 2011ordinanceОценок пока нет
- 2010 DHS Paper 1solДокумент10 страниц2010 DHS Paper 1solnothingtodo1992Оценок пока нет
- 2013 - 2014 H2 Maths JJC Promo SolnsДокумент11 страниц2013 - 2014 H2 Maths JJC Promo SolnsLionel Torres LeeОценок пока нет
- 2015 AJC Prelim Paper 1 QnsДокумент7 страниц2015 AJC Prelim Paper 1 QnsYing Ru ChuaОценок пока нет
- 2014 H2 Maths Prelim Papers - NJC P1 SolutionДокумент13 страниц2014 H2 Maths Prelim Papers - NJC P1 Solutioncherylhzy0% (4)
- Narayana Grand Test - 8Документ12 страницNarayana Grand Test - 8Meet ShahОценок пока нет
- m7 REVIEW PDFДокумент6 страницm7 REVIEW PDFSkyezine Via Kit FoxОценок пока нет
- Johor Smktinggikluang Mathst p1 2015 QaДокумент5 страницJohor Smktinggikluang Mathst p1 2015 QalingbooОценок пока нет
- Tutorial - Catia V5 SketcherДокумент29 страницTutorial - Catia V5 SketchersalehmeiabadiОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic TheoryДокумент10 страницElectromagnetic Theory2025eie34palashОценок пока нет
- Setting Out of Circular CurvesДокумент9 страницSetting Out of Circular CurvesEvarist EdwardОценок пока нет
- Tetrad Formulation of The Einstein Field Equations: The Newman-Penrose EquationsДокумент16 страницTetrad Formulation of The Einstein Field Equations: The Newman-Penrose EquationsRockBrentwoodОценок пока нет
- L4 CH Lat, DLat, MlatДокумент12 страницL4 CH Lat, DLat, MlatMoamen AbdienОценок пока нет
- Catenary WikipediaДокумент17 страницCatenary Wikipediaatmane1984Оценок пока нет
- Bachelor'S Degree Programme Term-End Examination June, 2010 Mathematics Mte-5: Analytical GeometryДокумент6 страницBachelor'S Degree Programme Term-End Examination June, 2010 Mathematics Mte-5: Analytical GeometryVasudha SinghОценок пока нет
- Application of Mohr's CircleДокумент22 страницыApplication of Mohr's CircleMohit ShivaneОценок пока нет
- An Album of Map Porjections (USGS) PDFДокумент262 страницыAn Album of Map Porjections (USGS) PDFLuther BlissettОценок пока нет
- Successclap: Question Bank SeriesДокумент44 страницыSuccessclap: Question Bank SeriesAjay PalriОценок пока нет
- CAD QuestionsДокумент1 страницаCAD QuestionsblackbirdОценок пока нет
- Analytic GeometryДокумент3 страницыAnalytic GeometryRon PascualОценок пока нет
- Pre Calculus Week 1 4Документ16 страницPre Calculus Week 1 4Hannah NacarОценок пока нет
- 1 Z 1 X Z 4 X y Z 1 12Документ5 страниц1 Z 1 X Z 4 X y Z 1 12Rohan ZendeОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2 BДокумент35 страницLecture 2 BWolf DragonneОценок пока нет
- Physics CPP FIITJEE PDFДокумент24 страницыPhysics CPP FIITJEE PDFAshish RanjanОценок пока нет
- Nptel 1Документ57 страницNptel 1Lanku J GowdaОценок пока нет
- Maths Class 10 Chapter 13 Exercise 13.1 Surface Areas and Volumes Ncert QaДокумент2 страницыMaths Class 10 Chapter 13 Exercise 13.1 Surface Areas and Volumes Ncert QaJyoti tyagiОценок пока нет
- 2nd PU Maths 2014 PDFДокумент3 страницы2nd PU Maths 2014 PDFPrasad C MОценок пока нет
- Diff CalДокумент40 страницDiff CalRobertBellarmineОценок пока нет
- 11-Tangents To CirclesДокумент4 страницы11-Tangents To Circlesapi-458166115100% (1)
- The Associated FamilyДокумент9 страницThe Associated FamilyJose Luis GiriОценок пока нет
- Feynman Path Integrals in Curved Spaces: Bruce DriverДокумент33 страницыFeynman Path Integrals in Curved Spaces: Bruce DriverAhmed BougheraraОценок пока нет
- Vygodsky - Mathematical Handbook - Higher Mathematics - MirДокумент935 страницVygodsky - Mathematical Handbook - Higher Mathematics - MirMarion100% (2)
- Chapter 6 Trigonometric FunctionsДокумент5 страницChapter 6 Trigonometric FunctionsZayan KhanОценок пока нет
- Gauge Theory: José Figueroa-O'FarrillДокумент37 страницGauge Theory: José Figueroa-O'Farrillcifarha venantОценок пока нет
- Torsion of A CurveДокумент3 страницыTorsion of A CurveewbОценок пока нет
- Ace Ahead Mathematic T Exam Practise Chapter 5Документ10 страницAce Ahead Mathematic T Exam Practise Chapter 5James OoiОценок пока нет
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseОт EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (69)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)От EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (157)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingОт EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldОт EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (64)
- Infinite Powers: How Calculus Reveals the Secrets of the UniverseОт EverandInfinite Powers: How Calculus Reveals the Secrets of the UniverseРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (126)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesОт EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (2193)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceОт EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (51)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeОт EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeОценок пока нет
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterОт EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (410)
- Mastering Logical Fallacies: The Definitive Guide to Flawless Rhetoric and Bulletproof LogicОт EverandMastering Logical Fallacies: The Definitive Guide to Flawless Rhetoric and Bulletproof LogicРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (91)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowОт EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (49)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayОт EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (125)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidОт EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1396)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceОт EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldОт EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (60)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessОт EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (6)
- A Natural History of Color: The Science Behind What We See and How We See itОт EverandA Natural History of Color: The Science Behind What We See and How We See itРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (13)
- AP Physics 1 Premium, 2024: 4 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeОт EverandAP Physics 1 Premium, 2024: 4 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeОценок пока нет
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismОт EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (500)
- What If?: Serious Scientific Answers to Absurd Hypothetical QuestionsОт EverandWhat If?: Serious Scientific Answers to Absurd Hypothetical QuestionsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldОт EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (54)