Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Electrical Power Distribution and Utilization Assignment No: 2 Submitted To: Engr. Masood Arayn
Загружено:
Haroon SajidИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Electrical Power Distribution and Utilization Assignment No: 2 Submitted To: Engr. Masood Arayn
Загружено:
Haroon SajidАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Electrical power distribution and Utilization Assignment no: 2 Submitted to: Engr.
Masood Arayn
Submitted by: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Awais ur Rehman (EE-27) Muhammad Ibrahem (EE-101) Muhammad Uzair Zahid (EE-121) Muhammad Abrar Muhammad Irfan
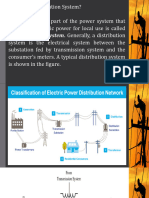
Radial distribution system:
A representative schematic of a radial distribution system is shown in figure 4-1. You should note that the independent feeders branch out to several distribution centers without intermediate connections between feeders. The most frequently used system is the radial distribution system because it is the simplest and least expensive system to build. Operation and expansion are simple. It is not as reliable as most systems unless quality components are used. The fault or loss of a cable, primary supply, or transformer will result in an outage on all loads served by the feeder. Furthermore, electrical service is interrupted when any piece of service equipment must be de-energized to perform routine maintenance and service. Service on this type of feeder can be improved by installing automatic circuit breakers that will reclose the service at predetermined intervals. If the fault continues after a predetermined number of closures, the breaker will lock out until the fault is cleared and service is restored by hand reset.
In radial system, we have basically two types of radial systems 1 . Conventional simple radial system 2. Expanded Radial Distribution System
Conventional Simple-Radial Distribution System: In the simple-radial system, distribution is at the
utilization voltage. A single primary service and distribution transformer supply all the feeders. There is no duplication of equipment. System investment is the lowest of all circuit arrangements. Operation and expansion are simple. Reliability is high if quality components are used, however, loss of a cable, primary supply, or transformer will cut off service. Further, electrical service is interrupted when any piece of service equipment must be deenergized to perform routine maintenance and servicing.
Expanded Radial Distribution System:The advantages of the radial system may be applied to larger
loads by using a radial primary distribution system to supply a number of unit substations located near the load centers with radial secondary systems . The advantages and disadvantages are similar to those described for the simple radial system.
Ring loop system:
The loop, or ring, system of distribution starts at the substation and is connected to or encircles an area serving one or more distribution transformers or load centers. The conductor of the system returns to the same substation. The loop system (fig. 4-2) is more expensive to build than the radial type, but it is more reliable. It may be justified in an area where continuity of service is of considerable importance, for example, a medical center. In the loop system, circuit breakers sectionalize the loop on both sides of each distribution transformer connected to the loop. The two primary feeder breakers and the sectionalizing breakers associated with the loop feeder are ordinarily controlled by pilot wire relaying or directional overcurrent relays. Pilot wire relaying is used when there are too many secondary substations to obtain selective timing with directional over current relays. A fault in the primary loop is cleared by the breakers in the loop nearest the fault, and power is supplied the other way around the loop without interruption to most of the connected loads. Because the load points can be supplied from two or more directions, it is possible to remove any section of the loop from service for maintenance without causing an outage at other load points. If a fault occurs in a section adjacent to the distribution substation, the entire load may have to be fed from one side of the loop until repairs are
made. Sufficient conductor capacity must be provided in the loop to permit operation without excessive voltage drop or overheating of the feeder when either side of the loop is out of service. If a fault occurs in the distribution transformer, it is cleared by the breaker in the primary leads; and the loop remains intact.
Which system should you prefer for the distribution for an area of approx 15km? The more suitable system would b ring loop system. Because the load points can be supplied from two or more directions, it is possible to remove any section of the loop from service for maintenance without causing an outage at other load points.
Вам также может понравиться
- Project ReportДокумент34 страницыProject ReportSumit Sharma75% (4)
- Power System Loss Analysis-EngДокумент5 страницPower System Loss Analysis-EngRatana KemОценок пока нет
- Siemens Interview QuestionsДокумент4 страницыSiemens Interview QuestionsBala SubramaniyanОценок пока нет
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionОт EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Electrical DistributionДокумент3 страницыElectrical DistributionBskster BskОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 Distribution SystemДокумент103 страницыChapter 4 Distribution SystemDanieal HakimОценок пока нет
- EE17 Lecture NotesДокумент10 страницEE17 Lecture NotesRoselyn MatienzoОценок пока нет
- Power Distribution Systems and Its Characteristics IIДокумент35 страницPower Distribution Systems and Its Characteristics IIquangspktОценок пока нет
- Aamir: M. Sohail Khan & Sufyan Saleem Dept, of Electrical Engineering Bahaudian Zakariya University Multan, PakistanДокумент32 страницыAamir: M. Sohail Khan & Sufyan Saleem Dept, of Electrical Engineering Bahaudian Zakariya University Multan, PakistanSanthosh KumarОценок пока нет
- Power Distribution Systems and Its CharacteristicsДокумент50 страницPower Distribution Systems and Its CharacteristicsquangspktОценок пока нет
- 1 - Electrical Distribution System ComponentsДокумент22 страницы1 - Electrical Distribution System Components7sn omerОценок пока нет
- Eee2 SLM1Документ20 страницEee2 SLM1Perez Trisha Mae D.Оценок пока нет
- Chapter6 PDFДокумент38 страницChapter6 PDFJaved LakanwalОценок пока нет
- REACTIVE POWER COMPENSATION IN RADIAL DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS USING DIST FLOW METHOD ProjectДокумент66 страницREACTIVE POWER COMPENSATION IN RADIAL DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS USING DIST FLOW METHOD ProjectNitish Nageshwara RaoОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2 - Basic Power Distribution Arrangements in MinesДокумент17 страницLecture 2 - Basic Power Distribution Arrangements in MinesAmar RathodОценок пока нет
- Radial, Loop Double and Grid Form SystemsДокумент29 страницRadial, Loop Double and Grid Form SystemsHamid RazaОценок пока нет
- Electrical Distribution System Arrangements ExplainedДокумент12 страницElectrical Distribution System Arrangements ExplainedWendi HaryadiОценок пока нет
- Distribution System 2Документ12 страницDistribution System 2ismiОценок пока нет
- Electrical Distribution: Second Class Installation Distribution SystemsДокумент4 страницыElectrical Distribution: Second Class Installation Distribution SystemsJerry CañeroОценок пока нет
- Overview of Distribution Systems 2Документ29 страницOverview of Distribution Systems 2Lander MinaОценок пока нет
- SubstationsДокумент2 страницыSubstationsVIJORN ANDRE DIZONОценок пока нет
- Power System Basics: Tawsif Hossain Chowdhury Thchowdhury@seu - Edu.bdДокумент21 страницаPower System Basics: Tawsif Hossain Chowdhury Thchowdhury@seu - Edu.bdMahmud HasanОценок пока нет
- Distribution System: Topic 3Документ54 страницыDistribution System: Topic 3hashim_mokhtar9286Оценок пока нет
- Report On Radial Feeder ProtectionДокумент15 страницReport On Radial Feeder ProtectionHarshit SharmaОценок пока нет
- Electrical Distribution System in Office BuildingДокумент35 страницElectrical Distribution System in Office BuildingApurva Anand100% (1)
- Substation Switching SchemeДокумент13 страницSubstation Switching Schememehrbloor@gmail.comОценок пока нет
- DSSDДокумент4 страницыDSSDkonoham851Оценок пока нет
- CHAPTER5Документ10 страницCHAPTER5Mukesh ParewaОценок пока нет
- Exp.6 Double BusbarДокумент11 страницExp.6 Double BusbarMohammed Abu Al HaijaОценок пока нет
- Busbar SchemeДокумент26 страницBusbar Schemeanirooddha_patelОценок пока нет
- Lineas de Transmision de VequieraДокумент100 страницLineas de Transmision de Vequieraa_papuicoОценок пока нет
- Particle Swarm Optimization Based Capacitor Placement On Radial Distribution SystemsДокумент37 страницParticle Swarm Optimization Based Capacitor Placement On Radial Distribution SystemsMudavath ChandramОценок пока нет
- Classification of Distribution - LanjutДокумент8 страницClassification of Distribution - Lanjut1A TEN - Devi KurniaОценок пока нет
- B. Tech Minor Project Report Chapter FormatДокумент10 страницB. Tech Minor Project Report Chapter FormatTanishq SinghОценок пока нет
- Basic SubstationДокумент13 страницBasic SubstationevilcomputerОценок пока нет
- Basics of Distribution Substations For Electrical Engineers (Beginners)Документ14 страницBasics of Distribution Substations For Electrical Engineers (Beginners)Prashant RajputОценок пока нет
- Experiment No 09 Fault Scenario Simulation in A FeederДокумент6 страницExperiment No 09 Fault Scenario Simulation in A FeederKaustubh PatilОценок пока нет
- Batch - 14 - Protection Scheme of Busbars and Transmission LinesДокумент26 страницBatch - 14 - Protection Scheme of Busbars and Transmission LinesYugendran KumaravelОценок пока нет
- LayoutДокумент2 страницыLayoutPawan_Pawar_4955Оценок пока нет
- Substation Switching SchemesДокумент7 страницSubstation Switching Schemeskukos setosariОценок пока нет
- INTRODUCTION-WPS OfficeДокумент6 страницINTRODUCTION-WPS OfficeAbdulrahaman AbdulraheemОценок пока нет
- Report On Radial Feeder ProtectionДокумент20 страницReport On Radial Feeder ProtectionSubhamGangdeb78% (9)
- EE007 Lecture1Документ32 страницыEE007 Lecture1Merryll CapucaoОценок пока нет
- Electrical Power System of A Nuclear Power PlantДокумент26 страницElectrical Power System of A Nuclear Power PlantJohn JeromeОценок пока нет
- Busbar ArrangementsДокумент6 страницBusbar ArrangementsUmair KhanОценок пока нет
- Protection System of Grid Substation Transformer: Assignment - 1Документ9 страницProtection System of Grid Substation Transformer: Assignment - 1nahidОценок пока нет
- 33 KV SubstationДокумент18 страниц33 KV SubstationRohit PatilОценок пока нет
- Overview of Distribution SystemДокумент20 страницOverview of Distribution SystemKelvin OoОценок пока нет
- Technical Subjective QuestionsДокумент52 страницыTechnical Subjective QuestionsEngr AHmed Ali DallОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 - NotesДокумент27 страницUnit 1 - NotesMarshmellow FFОценок пока нет
- LEC-Primary DistributionДокумент11 страницLEC-Primary DistributionAyeshaОценок пока нет
- Electrical EHV SubstationsДокумент111 страницElectrical EHV Substationsjiguparmar20094903Оценок пока нет
- ProjectДокумент70 страницProjectRizwan AshrafОценок пока нет
- Power Distribution SystemДокумент8 страницPower Distribution SystemRyuuichi KishimaОценок пока нет
- 400kv SubstationДокумент5 страниц400kv SubstationJothi PriyaОценок пока нет
- Wahab PTDU Lab 12Документ3 страницыWahab PTDU Lab 12Ali ArshadОценок пока нет
- Chapter Iii: Project DesignДокумент7 страницChapter Iii: Project DesignCelina RoxasОценок пока нет
- It Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingОт EverandIt Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingОценок пока нет
- Empowering Networks: A Comprehensive Guide to Medium Voltage SwitchgearОт EverandEmpowering Networks: A Comprehensive Guide to Medium Voltage SwitchgearОценок пока нет
- 3103 EM35MR Gas Valve - Product ManualДокумент50 страниц3103 EM35MR Gas Valve - Product ManualJoão Pedro MoreiraОценок пока нет
- 2014-02 TestingCathodicProtectionSystems Slides 508Документ49 страниц2014-02 TestingCathodicProtectionSystems Slides 508shejin R.SОценок пока нет
- COA MODULE - Memory OrganizationДокумент43 страницыCOA MODULE - Memory OrganizationDesyilalОценок пока нет
- DbatuДокумент30 страницDbatuLaxmikant BagaleОценок пока нет
- 1 Delta Ia-Hmi Dop-110cs TДокумент8 страниц1 Delta Ia-Hmi Dop-110cs TTuấn Anh LươngОценок пока нет
- TP03AL220S03LSW 2W 85-265VAC Input 3.3VDC OutputДокумент3 страницыTP03AL220S03LSW 2W 85-265VAC Input 3.3VDC OutputtoppowerОценок пока нет
- Cadence Tut 1, Cadence TutorialДокумент91 страницаCadence Tut 1, Cadence Tutorialrajivsharma1610Оценок пока нет
- Alarms ListДокумент2 страницыAlarms ListSreejith SlОценок пока нет
- List of EquipmentДокумент32 страницыList of EquipmentsutanuprojectsОценок пока нет
- C6140-0060 - Control Cabinet Industrial PC: VariantsДокумент2 страницыC6140-0060 - Control Cabinet Industrial PC: Variantsdarinel88Оценок пока нет
- DatasheetДокумент4 страницыDatasheetGrupo EpufmОценок пока нет
- Equinox Lipo Cell Balancer-ManualДокумент6 страницEquinox Lipo Cell Balancer-ManualKin TiriyasОценок пока нет
- 121 Handout 1Документ8 страниц121 Handout 1abby wamikeОценок пока нет
- Eis Relays Pl2010Документ14 страницEis Relays Pl2010Nour Al-HattabОценок пока нет
- TCC Number 165-6Документ1 страницаTCC Number 165-6Alvaro Solis VegaОценок пока нет
- Comparison of Various PWM Techniques For Field Oriented Control Vsi Fed PMSM DriveДокумент9 страницComparison of Various PWM Techniques For Field Oriented Control Vsi Fed PMSM DrivechaitanyaОценок пока нет
- Transas AIS T-201 Operational ManualДокумент70 страницTransas AIS T-201 Operational ManualBhavin DoshiОценок пока нет
- Anritsu - MS2830A Based PMR SolutionsДокумент6 страницAnritsu - MS2830A Based PMR SolutionsScribdFgОценок пока нет
- Fpga SlidesДокумент20 страницFpga Slidesankit407Оценок пока нет
- Bizhub C652 C552 Theory of OperationДокумент400 страницBizhub C652 C552 Theory of Operationtesla500Оценок пока нет
- 1720D/L Low Range Process Turbidimeter ManualДокумент102 страницы1720D/L Low Range Process Turbidimeter ManualHamed YadegariОценок пока нет
- OFV-5000 Vibrometer Controller: Measuring VibrationsДокумент4 страницыOFV-5000 Vibrometer Controller: Measuring VibrationsvnetawzОценок пока нет
- Evga X79 Motherboard: User GuideДокумент35 страницEvga X79 Motherboard: User GuideronuildoОценок пока нет
- M7A39v1.4 B350M GAMING PRO Placa Baza PC IonutДокумент21 страницаM7A39v1.4 B350M GAMING PRO Placa Baza PC IonutdjbobyОценок пока нет
- Data Sheet: TDA1310AДокумент17 страницData Sheet: TDA1310ARogerio E. SantoОценок пока нет
- Digital Signal Processing (EE-394) : Practical Work BookДокумент13 страницDigital Signal Processing (EE-394) : Practical Work BookHermain Fayyaz KarimОценок пока нет
- Siemens MRI MAGNETOM-World MR-Basics MRI-brochure English 1800000001924325Документ46 страницSiemens MRI MAGNETOM-World MR-Basics MRI-brochure English 1800000001924325Paulo HenriqueОценок пока нет
- DM7416 Hex Inverting Buffers With High Voltage Open-Collector OutputsДокумент3 страницыDM7416 Hex Inverting Buffers With High Voltage Open-Collector OutputsnooorОценок пока нет
- MS-7003 ManualДокумент5 страницMS-7003 ManualDaniel Pulido RojasОценок пока нет
- Electrical SystemsДокумент2 страницыElectrical SystemsMārcis RancānsОценок пока нет