Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
9I Sats Questions Booklet
Загружено:
Nilusha93Исходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
9I Sats Questions Booklet
Загружено:
Nilusha93Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Unit 9I (Energy and Electricity)
Question No.
Level
Mark
1(05) 6
2(05) 6
3(97) 6
4(01)
5(95) 6
6(03) 6
7(03) 6
8(01) 7
9(99)
10(05) 7
11(97) 7
12(01) 8
Rainford High Technology College 1
Unit 9I (Energy and Electricity)
1.
Alex makes an electromagnet.
She winds insulated wire around an iron nail.
She connects the wire to a power supply.
She uses the electromagnet to pick up some steel paper-clips.
This is her prediction.
The more turns of wire around the iron nail the stronger
the electromagnet becomes.
(a)
(i)
Give the one factor she should change as she investigates her prediction.
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
1 mark
(ii)
Give one factor she should keep the same.
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
1 mark
(iii)
Describe how she could use the paper-clips to measure the
strength of the electromagnet.
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
1 mark
Rainford High Technology College 2
Unit 9I (Energy and Electricity)
(b)
Alex wrote a report of her investigation.
What would an odd result suggest?
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
1 mark
(c)
(i)
Which size paper-clips would Alex use to make her results more
accurate?
Tick the correct box.
1 mark
(ii)
Give a reason for your choice.
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
1 mark
maximum 6 marks
Rainford High Technology College 3
Unit 9I (Energy and Electricity)
2.
The drawing below shows a garden water feature. It is solar-powered.
The solar cell absorbs energy from the Sun.
The solar cell is connected to a motor in the bowl.
The motor drives a pump.
Water is pumped up to the jug and it flows back down to the bowl.
(a)
Use the information above to help you to complete the following sentences.
Choose words from the list.
c h e m
g r a v i t a t i o n a l
i c a l e l e c t r i c a l p o t e n t i a l k i n e t i c
l i g h t
(i)
s o u n d
t h e r m
a l
The useful energy change in the solar cell is from
light to .................................... energy.
1 mark
(ii)
The useful energy change in the motor is from
electrical energy to .................................... energy.
1 mark
(iii)
As the water flows from the jug to the bowl ....................................... energy
is changed into .................................... energy.
2 marks
(b)
Give one advantage and one disadvantage of using a solar cell to power the
water feature.
advantage ....................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
1 mark
disadvantage ................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
1 mark
Rainford High Technology College 4
Unit 9I (Energy and Electricity)
maximum 6 marks
3.
(a)
A torch battery is an energy resource. How is the energy stored in a torch
battery?
Tick the correct box.
as chemical energy
as kinetic energy
as potential energy
as thermal energy
1 mark
(b)
When a torch is switched on, energy is transferred from the battery to the bulb.
How is energy transferred from the battery to the bulb?
Tick the correct box.
by electricity
by light
by sound
by thermal energy
1 mark
(c)
Energy is transferred from the torch bulb to the surroundings.
Choose from the following terms to complete the sentences.
electricity
(i)
light
sound
thermal transfer
Energy is transferred from the torch bulb to the surroundings in a
useful way by ...............................................
1 mark
(ii)
Some energy is wasted. The wasted energy is transferred from the
bulb to the surroundings by ...............................................
Rainford High Technology College 5
Unit 9I (Energy and Electricity)
1 mark
Rainford High Technology College 6
Unit 9I (Energy and Electricity)
(d)
The torch is lifted up and put on a high shelf.
Energy is transferred to the torch as it is lifted up. The energy is stored in
the torch while it stays on the shelf.
What energy has the torch gained?
....................................................................................................................
1 mark
Maximum 5 marks
Rainford High Technology College 7
Unit 9I (Energy and Electricity)
4.
The drawings show a weightlifter. The stages in weightlifting are labelled A, B, C, D and
E.
lift e d
f a llin g
p r e p a r in g
lift in g
(a)
(i)
h itt in g
flo o r
Complete the sentences below.
As the weights were lifted up, energy was transferred from
the man to the weights. This energy had been stored as
energy in the of the mans
arms.
2 marks
(ii)
How was energy stored in the weights at stage C?
Tick the correct box.
as chemical energy
as elastic energy
as kinetic energy
as gravitational potential
energy
1 mark
(b)
Complete the sentences below.
(i)
In stage D, as the weights were falling, the energy was transferred
from energy to energy.
1 mark
(ii)
In stage E, as the weights hit the floor, the energy was transferred
from energy to energy.
1 mark
Maximum 5 marks
Rainford High Technology College 8
Unit 9I (Energy and Electricity)
5.
A bookshelf is 1 metre above the floor. As a book falls from the shelf to the floor it
loses 7.5 J of potential energy.
(a)
(i)
Tick the box by the correct statement about the kinetic energy of the book.
W h ile t h e b o o k w a s r e s t in g o n th e s h e lf
it h a d 7 . 5 J o f k in e tic e n e r g y .
W h ile t h e b o o k w a s fa llin g , it s p o t e n t ia l
e n e r g y w a s b e in g tr a n s f o r m e d in to
k in e tic e n e r g y .
W h ile t h e b o o k w a s fa llin g , it s k in e tic
e n e r g y r e m a in e d c o n s t a n t.
W h ile t h e b o o k w a s fa llin g , it lo s t
k in e tic e n e r g y .
1 mark
(ii)
How much kinetic energy does the book have just before it hits the
floor?
.......................................................................................................... J
1 mark
(b)
When the book hits the floor it stops and loses all its kinetic energy.
What happens to this energy?
.....................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................
1 mark
Maximum 3 marks
Rainford High Technology College 9
Unit 9I (Energy and Electricity)
6.
(a)
Jacquie has a mobile phone. Energy is stored in the battery of the phone.
The drawing shows the battery being charged.
(i)
Which energy transfer takes place in the battery as it is being charged? Tick
the correct box.
chemical to sound
sound to thermal
electrical to chemical
thermal to electrical
1 mark
(ii)
When the battery is fully charged, Jacquie unplugs the phone.
Which energy transfers take place when the mobile phone rings?
Tick the correct box.
chemical to electrical to sound
electrical to chemical to sound
kinetic to electrical to sound
thermal to electrical to sound
1 mark
Rainford High Technology College 10
Unit 9I (Energy and Electricity)
(b)
Jacquie can change the ring-tone of her phone.
The diagrams below show the patterns made by four sound waves on an
oscilloscope screen.
They are all drawn to the same scale.
Write the letter of the sound wave that matches each of the descriptions below.
(i)
a loud sound with a low pitch
.................
(ii)
a quiet sound with a high pitch .................
(iii)
a loud sound with a high pitch
.................
3 marks
Maximum 5 marks
Rainford High Technology College 11
Unit 9I (Energy and Electricity)
7.
Peter measured the current through each of three similar bulbs in a parallel circuit.
A1
A2
A3
He had only one ammeter and he placed it first at A1, then A2, then A3, in order to
measure the currents.
The table shows his results.
(a)
position of ammeter
current, in amps
A1
0.14
A2
0.16
A3
0.15
He expected the current readings to be the same for each bulb but found they
were different.
Suggest two reasons why the readings were different.
1. ................................................................................................................
2. ................................................................................................................
2 marks
Rainford High Technology College 12
Unit 9I (Energy and Electricity)
(b)
Peter then measured the current at A4 and recorded it as 0.45 A. He concluded
that the current at A4 could be calculated by adding together the currents through
each of the bulbs at positions A1, A2 and A3.
A4
He added two more similar bulbs to his circuit, in parallel. The current through
each bulb was 0.15 A.
Use Peter's conclusion to predict the current at A4 with the 5 bulbs in the circuit.
................ A
A4
1 mark
Rainford High Technology College 13
Unit 9I (Energy and Electricity)
(c)
Peter left the circuit connected overnight. He used a datalogger to measure the
current at position A4 at regular intervals of time. The next morning the bulbs
were dim.
Using the axes below, sketch (do not plot) how the current at position A4 might
change with time.
Indicate on the graph:
(i)
The correct labels for each axis, including the correct units.
(ii)
The shape of the graph you would expect to obtain.
0
2 marks
Maximum 5 marks
Rainford High Technology College 14
Unit 9I (Energy and Electricity)
8.
(a)
A pupil makes a small coil of copper wire and passes an electric current through
it.
The pupil places a small magnet near the coil.
c o il
m agnet
The magnet is attracted towards the coil. The pupil turns the magnet around so
that the South pole is nearest the coil.
What effect, if any, will this have?
.
.
1 mark
(b)
The pupil uses the coil and the magnet to make a simple ammeter to measure
the current through a bulb.
s c a le
s tra w
p a p e r c lip
p iv o t
m agnet
c o il
not to scale
Rainford High Technology College 15
Unit 9I (Energy and Electricity)
(i)
The paper clip is used to balance the weight of the magnet.
Why is the paper clip further away from the pivot than the magnet is?
1 mark
(ii)
Explain how a current in the coil makes the straw pointer move.
2 marks
(iii)
The pupil places a piece of soft iron in the middle of the coil.
Describe and explain how this will affect the reading on the scale when
the same current flows through the coil.
2 marks
Maximum 6 marks
Rainford High Technology College 16
Unit 9I (Energy and Electricity)
9.
A flywheel is a rotating wheel which is used to store energy.
(a)
Energy must be transferred to a flywheel to make it rotate. How is the
energy in the rotating flywheel classified?
Tick the correct box.
as chemical energy
as kinetic energy
as potential energy
as thermal energy
1 mark
(b)
A flywheel is rotating at a high speed. No energy is being supplied to it. The
flywheel is used to turn a dynamo, and the energy from the dynamo is used to
light a bulb.
(i)
The bulb is left connected until the flywheel stops rotating. Not all the
energy stored in the flywheel is transferred to the bulb. Some of it is lost.
Give two places from which it is lost, and explain how it is lost.
1. ...........................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................
2. ...........................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................
2 marks
(ii)
The experiment is repeated using a different bulb which gives out more
energy each second. Compared to the first light bulb, describe how the
second light bulb will affect the motion of the flywheel, and explain your
answer.
.................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................
Rainford High Technology College 17
Unit 9I (Energy and Electricity)
2 marks
Maximum 5 marks
10.
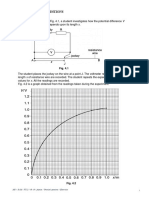
John used an electrical heater to heat a cup of water. He kept stirring the water. When
the temperature reached 20C, he started his stopwatch and measured the temperature
of the water every half minute.
He switched off the heater after 4 minutes, but continued to record the temperature.
His results are shown in the table.
One measurement is missing and another appears to be wrong.
Time (minutes)
Temperature (C)
0.0
20
0.5
26
1.0
31
1.5
36
2.0
41
2.5
46
3.0
3.5
57
4.0
56
4.5
58
5.0
59
5.5
59
Rainford High Technology College 18
Unit 9I (Energy and Electricity)
(a)
Use the results in the table to draw a graph on the grid.
Label the axes.
Plot the points and draw a smooth curve of best fit.
)
4 marks
(b)
From your curve, estimate the temperature of the water after three minutes.
............C
1 mark
maximum 5 marks
Rainford High Technology College 19
Unit 9I (Energy and Electricity)
11.
a t in y w h ite h o t s p a r k
fr o m a s p a r k le r
a fr e s h ly b o ile d e g g
(a)
a h e a v y ir o n p o k e r, h o t e n o u g h
t o g iv e o u t a d u ll r e d g lo w
a g la s s o f c o ld
w a te r in a fr id g e
Each of the four objects shown above started at room temperature.
Now they are all at different temperatures, as described by the labels.
(i)
Which object is at the highest temperature?
..........................................................................................................
1 mark
(ii)
Which object has lost thermal energy?
..........................................................................................................
1 mark
(iii)
Which object has had the largest gain in thermal energy?
..........................................................................................................
1 mark
(b)
Omar puts a hot steel ball into a beaker of cold water. He waits until the
temperatures of the ball and the water are the same.
From his results, he calculates that:
the thermal energy stored in the steel ball has fallen by 3770 J;
the thermal energy stored in the water has risen by 2940 J.
The energy stored in the water rose by less than 3770 J. What has
happened to the other 830 J?
....................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................
1 mark
Maximum 4 marks
Rainford High Technology College 20
Unit 9I (Energy and Electricity)
12.
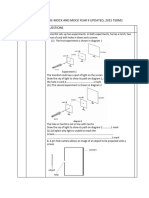
Anita has arranged a horseshoe magnet with a long bar magnet pivoted above it.
p iv o t
N
S
N
bar m agnet
S
h o rs e s h o e
m agnet
(a)
Whenever Anita tips the bar magnet, it always moves back to the position shown
in the diagram. Explain why this happens.
.
.
.
.
2 marks
(b)
When a current is passed through a coil, it produces magnetic poles as shown in
the diagram below.
Rainford High Technology College 21
Unit 9I (Energy and Electricity)
Anita winds a coil around each end of the horseshoe magnet as shown below.
p iv o t
N
S
N
bar m agnet
h o rs e s h o e
m agnet
(i)
Describe what will happen to the bar magnet when she closes the switch.
Explain your answer.
3 marks
(ii)
Anita reverses the battery. Suggest what happens to the bar magnet.
1 mark
(iii)
Anita replaces the battery with a power supply which changes the direction
of the current every second. Suggest what happens to the bar magnet.
1 mark
Maximum 7 marks
Rainford High Technology College 22
Unit 9I (Energy and Electricity)
Rainford High Technology College 23
Вам также может понравиться
- Section 2 Electricity - UnlockedДокумент54 страницыSection 2 Electricity - UnlockedjesudassajОценок пока нет
- Year 8 - Heating Nand Cooling - Magnets and ElectromagnetsДокумент11 страницYear 8 - Heating Nand Cooling - Magnets and ElectromagnetssarahhОценок пока нет
- Repaso Fisbi 3 5 22Документ32 страницыRepaso Fisbi 3 5 22Bruna TrastoОценок пока нет
- 8 Energy TransfersДокумент12 страниц8 Energy TransfersЖеня МарченкоОценок пока нет
- 2009 IB Physics - SL FieldsДокумент17 страниц2009 IB Physics - SL FieldsGajendraОценок пока нет
- IB Questionbank Physics Work-Energy-PowerДокумент27 страницIB Questionbank Physics Work-Energy-PowerDURU ALTINKAYAОценок пока нет
- GCSE Physics TransformersДокумент34 страницыGCSE Physics Transformerswill bОценок пока нет
- Current, Potential Difference & Resistance 2Документ17 страницCurrent, Potential Difference & Resistance 2Juyeon NamОценок пока нет
- Igcse e Waves With MSCДокумент82 страницыIgcse e Waves With MSCaliОценок пока нет
- Internal ResistanceДокумент4 страницыInternal Resistancenewabrown1012Оценок пока нет
- FORM-1-TOPIC-10.-CELLS-AND-SIMPLE-CIRCUITS-QUESTIONS-Teacher.co_.ke_Документ7 страницFORM-1-TOPIC-10.-CELLS-AND-SIMPLE-CIRCUITS-QUESTIONS-Teacher.co_.ke_bryanodhiambo25Оценок пока нет
- Year 7 Science Exam Practice Questions 2016Документ58 страницYear 7 Science Exam Practice Questions 2016Sarah KKC100% (1)
- Waves 1 QPДокумент18 страницWaves 1 QPBunnyОценок пока нет
- 4437 6H Que 20071031Документ24 страницы4437 6H Que 20071031parbhoos1610Оценок пока нет
- Alternating Currents ExplainedДокумент42 страницыAlternating Currents ExplainedmixilopotstlyОценок пока нет
- 3.5.1.1 Basics of ElectricityДокумент76 страниц3.5.1.1 Basics of ElectricityqekosaduОценок пока нет
- Ks - 3 - Energy - Questions 2Документ8 страницKs - 3 - Energy - Questions 2cmilfra646Оценок пока нет
- Living With Electricity Past Papers ANSWERS - PPTMДокумент14 страницLiving With Electricity Past Papers ANSWERS - PPTM2144639220Оценок пока нет
- 2007 iGCSE Physics Written Paper Question PaperДокумент28 страниц2007 iGCSE Physics Written Paper Question Paperoscar wildeОценок пока нет
- Electricity - Level 4 - QuestionsДокумент14 страницElectricity - Level 4 - Questionselizabeth100% (1)
- Current, Potential Difference & Resistance 2 QPДокумент17 страницCurrent, Potential Difference & Resistance 2 QPXuan HouОценок пока нет
- Current Electricity TEST: Name: ClassДокумент3 страницыCurrent Electricity TEST: Name: ClassRobbie TurnerОценок пока нет
- Current-Voltage Characteristics QPДокумент12 страницCurrent-Voltage Characteristics QPJohnОценок пока нет
- (Total 1 Mark) (Total 1 Mark) (Total 1 Mark)Документ8 страниц(Total 1 Mark) (Total 1 Mark) (Total 1 Mark)Allan GunawanОценок пока нет
- Topic 7 Magnetism FДокумент17 страницTopic 7 Magnetism FsaadОценок пока нет
- 2C Current and Voltage Exam QuestionsДокумент12 страниц2C Current and Voltage Exam QuestionsMalooka AlyОценок пока нет
- Energy Style Examination QuestionsДокумент16 страницEnergy Style Examination QuestionsLobo LoОценок пока нет
- 2005 June: Section 6 Magnetism and ElectromagnetismДокумент43 страницы2005 June: Section 6 Magnetism and ElectromagnetismMecid AliyevОценок пока нет
- 4 7 3InducedPotentialTransformersandtheNatGrid PDFДокумент69 страниц4 7 3InducedPotentialTransformersandtheNatGrid PDFlОценок пока нет
- P1 2 Energy and Efficiency Foundation QuestionsДокумент73 страницыP1 2 Energy and Efficiency Foundation QuestionsjesudassajОценок пока нет
- Nihira Munde - Gr-8 Term 1 Physics QP 21-22Документ10 страницNihira Munde - Gr-8 Term 1 Physics QP 21-22yuvika gargОценок пока нет
- A2 Fields Part IVДокумент38 страницA2 Fields Part IVmata4cholОценок пока нет
- FT 12 Gr10 P4 Qs (Electricity)Документ8 страницFT 12 Gr10 P4 Qs (Electricity)Kiron SheiqОценок пока нет
- Year 8 EOY RevisionДокумент9 страницYear 8 EOY RevisionAbisam8Оценок пока нет
- p5 Electricity in The Home Exam QsДокумент28 страницp5 Electricity in The Home Exam Qsmuhammedinshal04Оценок пока нет
- Year-7-Science-revision 2Документ17 страницYear-7-Science-revision 2Cally ChewОценок пока нет
- Suzhou Foreign Language School 2nd Monthly Class Test for IGCSE 2– December 2014 PhysicsДокумент10 страницSuzhou Foreign Language School 2nd Monthly Class Test for IGCSE 2– December 2014 PhysicsrehanОценок пока нет
- Chap 7 Electrity & MagnetismДокумент5 страницChap 7 Electrity & Magnetismchristina teoОценок пока нет
- Assessment Test (Electricity) Marks-55 Duration: 1 HourДокумент8 страницAssessment Test (Electricity) Marks-55 Duration: 1 HourMehedi hasan TonmoyОценок пока нет
- Fields - QP IBDP PhysicsДокумент9 страницFields - QP IBDP PhysicsArham ShahОценок пока нет
- Electrical Circuits Revision QuestionsДокумент17 страницElectrical Circuits Revision QuestionsOrlando ScottОценок пока нет
- 46.2 Electromagnetic Effects Cie Igcse Physics Ext Theory QPДокумент14 страниц46.2 Electromagnetic Effects Cie Igcse Physics Ext Theory QPKk. DdОценок пока нет
- Magnetism and Electromagnetism QuestionsДокумент17 страницMagnetism and Electromagnetism QuestionseОценок пока нет
- QB Topic 2 - 3 Work Energy Power AДокумент11 страницQB Topic 2 - 3 Work Energy Power AmarufinoОценок пока нет
- PHYSICS PREmock and MockДокумент5 страницPHYSICS PREmock and MockSoala WaribokoОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetism HigherДокумент12 страницElectromagnetism HigherThea Cassius FernandezОценок пока нет
- James Ruse Agricultural High School: PhysicsДокумент12 страницJames Ruse Agricultural High School: PhysicsLisWeiОценок пока нет
- Electricity - Level 5 - QuestionsДокумент19 страницElectricity - Level 5 - QuestionsThe PassionОценок пока нет
- Madeley High School Q1 Physics Circuit and Resistance QuestionsДокумент23 страницыMadeley High School Q1 Physics Circuit and Resistance QuestionsmadhujayanОценок пока нет
- 3 7 3 3-Electric-PotentialДокумент68 страниц3 7 3 3-Electric-Potentialwakoaisha2Оценок пока нет
- Magnetic fields and forces in physics experimentsДокумент12 страницMagnetic fields and forces in physics experimentsjohn12044912Оценок пока нет
- 46.3-Electromagnetic Effects-Cie Igcse Physics Ext-Theory-QpДокумент13 страниц46.3-Electromagnetic Effects-Cie Igcse Physics Ext-Theory-Qphaardikchpubey10Оценок пока нет
- 14 Science ST Edwards School 2014Документ19 страниц14 Science ST Edwards School 2014ryanbatiОценок пока нет
- Forces and Energy Test ReviewДокумент6 страницForces and Energy Test ReviewYan Naing SoeОценок пока нет
- Electricity QuestionsДокумент23 страницыElectricity QuestionsSteve BishopОценок пока нет
- Thermal Physics CIE IGCSE 0625 PPQДокумент11 страницThermal Physics CIE IGCSE 0625 PPQPeter IsigiОценок пока нет
- Electricity - Level 3 - QuestionsДокумент12 страницElectricity - Level 3 - QuestionselizabethОценок пока нет
- October Half Term Revision 2020 (Edexcel)Документ27 страницOctober Half Term Revision 2020 (Edexcel)turboОценок пока нет
- National Power Corporation Masinloc Power Project: Focus On Social Engineering - Case StudyДокумент18 страницNational Power Corporation Masinloc Power Project: Focus On Social Engineering - Case StudyMack ConcepcionОценок пока нет
- DM0565RДокумент20 страницDM0565RSURESH CHANDRA ROUTОценок пока нет
- Eng 1201 Literature Review 1Документ6 страницEng 1201 Literature Review 1api-609701143Оценок пока нет
- Meiden Power Conversion SystemДокумент17 страницMeiden Power Conversion SystemaddinОценок пока нет
- Modes of TurbineДокумент20 страницModes of Turbinenabil160874Оценок пока нет
- Maintenance On Unit 5Документ10 страницMaintenance On Unit 5Mazhar UddeenОценок пока нет
- Economic Analysis of The German Regulation For Electrical Generation Projects From Biogas Applying The Theory of Real OptionsДокумент10 страницEconomic Analysis of The German Regulation For Electrical Generation Projects From Biogas Applying The Theory of Real OptionsHEGEL JOHAN RINCON LAURENSОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan Earth ScienceДокумент2 страницыLesson Plan Earth ScienceValerie MiguelОценок пока нет
- Interleaved Power Converter With Current Ripple Cancelation at A Selectable Duty CycleДокумент6 страницInterleaved Power Converter With Current Ripple Cancelation at A Selectable Duty CycleTiago CostaОценок пока нет
- White Collar FactoryДокумент14 страницWhite Collar FactoryAnder AndersenОценок пока нет
- ERC Philippines power plant inspection standardsДокумент4 страницыERC Philippines power plant inspection standardsAubry GarciaОценок пока нет
- Data Sheet: PIKO 5.5 10AДокумент2 страницыData Sheet: PIKO 5.5 10ADuško TovilovićОценок пока нет
- FisherДокумент2 страницыFisherleslie.lp2003Оценок пока нет
- Green CitiesДокумент33 страницыGreen CitiesAina AyieОценок пока нет
- Book EV Charging Stations Near YouДокумент22 страницыBook EV Charging Stations Near YouJerry SinghОценок пока нет
- Technical ProposalДокумент4 страницыTechnical ProposalolescootОценок пока нет
- Geothermal EnergyДокумент28 страницGeothermal EnergyJello PanaguitonОценок пока нет
- Panasonic SLA HandbookДокумент73 страницыPanasonic SLA HandbookzocanОценок пока нет
- Guidelines GHG Conversion Factors 07jul2011Документ50 страницGuidelines GHG Conversion Factors 07jul2011Atanas StoykovОценок пока нет
- Ebara Vertical Inline Evm - EngДокумент35 страницEbara Vertical Inline Evm - EngAseem Vivek MasihОценок пока нет
- The New Gas Turbine Portfolio To Meet The Market Requirements For Distributed GenerationДокумент17 страницThe New Gas Turbine Portfolio To Meet The Market Requirements For Distributed Generationimant197812gmail.comОценок пока нет
- Guidelines for Erection, Testing and Commissioning of Small Hydro Power PlantsДокумент73 страницыGuidelines for Erection, Testing and Commissioning of Small Hydro Power PlantsoctatheweelОценок пока нет
- Grundfosliterature NB NBE NK NKE 60HzДокумент20 страницGrundfosliterature NB NBE NK NKE 60HzCarla RamosОценок пока нет
- Sulzer Running Direction Fuel InterlockДокумент3 страницыSulzer Running Direction Fuel InterlockKarthik Reddiar100% (1)
- How To Choose An EPC Contractor For PV ProjectsДокумент14 страницHow To Choose An EPC Contractor For PV Projectsavnish_parashar9292Оценок пока нет
- Comfosystems Prices 2013 Ventilation and Air DistributionДокумент21 страницаComfosystems Prices 2013 Ventilation and Air DistributionWPenrithОценок пока нет
- Modular Transfomer Substation PDFДокумент12 страницModular Transfomer Substation PDFrakacyuОценок пока нет
- 17 SML Smart Construction Products and Processes - en PDFДокумент16 страниц17 SML Smart Construction Products and Processes - en PDFEkky CecilОценок пока нет
- 300 Series PTДокумент2 страницы300 Series PTbhaskarbabaiОценок пока нет
- Energy (R) Evolution: A Sustainable Energy Outlook For CanadaДокумент120 страницEnergy (R) Evolution: A Sustainable Energy Outlook For Canadarto2951100% (1)