Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
MED Pnemonics
Загружено:
bsms1482Исходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
MED Pnemonics
Загружено:
bsms1482Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Posted: Thu Feb 10, 2005 9:30 pm MNEMONICS. ENJOY!!!!
Post subject: VERY USEFUL
I hope u guys enjoy the following mnemonics. Thanks
Causes of acute Pancreatitis BAD SHIT Black scorpion bite Alcohol ( or autoimmune : PAN ) Drugs ( tetracycline, azothioprin, sulfa, diuretics ) Stones ( gallstones or steroid ) Hyperlipidemia Infection ( mumps ) Trauma Small Bowel Obstruction "SHAVIT" S - Stone (gallstone ileus) H - Hernia A - Adhesions V - Volvulus I - Intussusception T - Tumor Non-GI Causes of Vomiting ABC's of Non- GI causes of vomiting Acute renal failure Brain (Increased ICP) Cardiac (Inferior MI) DKA Ears (labyrinthitis) Foreign substances (Tylenol, theo, etc) Glaucoma Hyperemesis Gravidarum Infections (pyelonephritis, meningitis) Extraintestinal manifestations of I. B. D. are A PIE SAC Aphthous ulcers, Pyoderma gangrenosum, Iritis, Erythema nodosum, Sclerosing cholangitis, Arthritis, clubbing. Which I. B. D. has C-obblestones on endoscopy - C-rohn's.
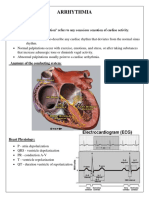
Acute Rheumatic Fever
There are several for the major criteria, I use "JONES" J - Joints O - Obvious (cardiac) - sorry, I know this is kinda weak N - Nodules (subcutaneous nodules) E - Erythema marginatum S - Syndeham's Chorea Causes of ST Elevation "ELEVATION" E - Electrolytes L - LBBB E - Early Repolarization V - Ventricular hypertrophy A - Aneurysm T - Treatment - Pericardiocentesis I - Injury (AMI, contusion) O - Osborne waves (hypothermia) N - Non-occlusive vasospasm
Hyperkalamia causes large T waves on the ECG, Hypokalaemia causes small ones - ie. large pot - lots of tea, small pot - no tea.
If QRS complex is wide, consider bundle branch block. LBBB causes a "W" pattern in V1-2 and a "M" pattern in V5-6. RBBB is the other way round. Remember as WiLLiaM MaRRoW. Elevation of cardiac enzymes after a M.I. is CPK, then AST, then LDH. Remember as - C AST Le. Basal Systolic Murmur: Aortic Stenosis (AS) -The mnemonic key is Arthur Shawcross (AS), a cannibalistic murderer, a key which immediately follows the symbol. -Clinical: Angina pectoris despite normal coronary arteries Arthur Shawcross represents the Angel of death [Angina]. Exertional syncope His victims Swooned [Syncope] with fear when they saw him.
Exertional dyspnea of congestive heart failure Arthur Shawcross claims he left the crime scenes whistling Dixie [Dyspnea]. Sudden cardiac death Arthur Shawcross causes Sudden Death. -Physical findings Loud, harsh, systolic ejection murmur at the upper right sternal border, usually associated with a palpable systolic thrill. Arthur Shawcross is a Base [Basal] Thrill-murderer [Thrill]. He is a Harsh Hardened criminal, who attributed his grotesque actions to incest with his Sister [Systolic]. S4 gallop is common and represents left ventricular hypertrophy and increased left ventricular pressure. His ghoulish tales read like the Four [S4] Horsemen of the Apocalypse. S3 when left ventricular failure is present. As a child, AS displayed the classic homicidal Triad [S3]: animal torture, fire-setting, and bed-wetting. Delayed upstroke in the carotid pulse. Parvus et tardus carotid pulse. His last victim still had a Small but palpable pulse. However, the ambulance was Delayed [upstroke], and, it soon became too Little, too Late [Parvus et Tardus]. Paradoxical splitting of S2 AS sent his victims to Paradise [Paradoxical].
Apical Diastolic Murmur: Mitral Stenosis (MS)
-The mnemonic key is MicroSoft (MS), a key which immediately follows the symbol.
-Physical findings: The thrill at the apex is the diastolic murmur. >> Hopeful applicants at the Apex of their careers are Thrilled to be hired by MicroSoft. The left ventricle (LV) is of normal pressure and size, so the point of maximum impulse is not displaced to the left. >> MS owns a Healthy Windows [Vented: Normal LV] environment, and is Not willing to be Displaced from its location. High-pitched opening snap [OS] following S2, heard best between the second to fourth left intercostal space. >> The new Windows98 Operating System [OS] sold at a High-pitched pace. S1 is loud and snapping. >> MicroSoft 1-sound is Bill Gates [S1], who barks out Loud Snapping orders. -Chest x-ray: Kerley B lines (dilated interlobular septa or septal edema) are horizontal, nonbranching lines at the peripheral lower lung fields. >> The Curly-haired [Kerley B lines] computer geek... The large left atrium straightens the left heart border and is suggested by a double density right-heart border, by the posterior displacement of the esophagus, and by an elevated left mainstem bronchus. >> ...stole Double Density [CXR] diskettes to be sold in Los Angeles [large LA]. -Catheterization: The left atrial (LA) pressure pulse reveals a prominent "a wave (LA contraction against the mitral valve). >> Those trying to enter the ranks of MS had to show Prominent A grades ["a wave]
at the Apex [Apical diastolic murmur] of their class.
Symptoms of aortic stenosis are SAD or ASD - Syncope, Angina, Dyspnea. For Causes of A-Fib/Flutter H = cHf, other cardiomyopathies E = Enlargement of the atria A = Alcohol binge drinking R = Rheumatic heart disease T = hyperThyroid Asystole "3 Hypo's & 3 Hyper's" Hypoxia Hypothermia Hypokalemia Hyperkalemia Hyper H (Acidosis) Hyper Rx (Drugs/OD) Submitted by Tag Filley, M.D. Syncope "HEAD, HEART and VESS'LS" H - hypoglycemia hypoxia E - epilepsy A - anxiety [the "swoon"] D - dysfunction of brain stem [i.e. brain stem TIA] H - heart attack E - embolism of pulmonary artery A - aortic obstruction [ Aortic stenosis, myxoma, IHSS ] R - rhythm disturbance T - tachycardia esp VT V - vasovagal E - ectopic i.e. hemorrhage obvious or not S - situational [micturation, defecation...] S - subclavial steal L - low SVR [eg: anaphalaxis] S - sensitive carotid sinus of M.I. is BOOMAR - Bed rest, Oxygen, Opiate, Monitor, Anticoagulate, Reduce clot size Proven MI.. should be met by M.O.N.A. M = morphine O = oxygen
N = nitrates A = aspirin suspected right ventricular MI suspected .. hold the Nitrates. submitted by Chris Mnemonic for remembering antiarrhythmics Class Drug Mnemonic Read as: Professor Quackers "dissed" - Lydia's penny Mexican tacos. - Feeling profaned, - proper Bertha Butt - (amiable British socialite) - virtually dismembered 'im. or Professor Quackers dissed Lydia's Penny Mexican Tacos. Feeling profaned, proper Bertha Butt, (amiable British socialite), virtually dismembered 'im.*Note: "Dissed" is used here as the slang term "dis" from dismiss. I.e., "Don't 'dis' me, man!" Class IA Procainamide Professor Quinidine Quackers Disopyramide "dissed" * Class IB Lidocaine Lydia's Phenytoin penny Mexiletine Mexican Tocainide Tacos Class IC Flecainide feeling Propafenone profaned Class II Propranolol proper Beta Blockers Bertha Butt Class III Amiodarone amiable Bretylium British Solatol socialite Class IV Verapamil virtually Diltiazem dismembered 'im Atropine Adenosine
Endocarditis "FAME" F - FEVER A - ANEMIA M - MURMUR E - ENDOCARDITIS Causes of pericarditis are CARDIAC RIND - Collagen vascular disease, Aortic aneurysm, Radiation, Drugs eg. hydralazine, Infections, Acute renal failure, Cardiac infarction, Rheumatic fever, Injury, Neoplasms, Dressler's
syndrome. 5 T's of early cyanosis in congenital heart disease Tetralogy, Transposition, Truncus, Total anomalous, Tricuspid atresia Sumbitted by Ben Humphreys
95% of hypertension is primary (idiopathic). 5% is secondary and causes include CHAPS - Cushing's syndrome, Hyperaldosteronism (Conn's syndrome) , Aorta coarctation, Pheochromocytoma, Stenosis of the renal arteries.
Takayasu's disease is also called pulseless disease, therefore I can't Tak'a ya's pulse. Henoch-Schonlein Purpura "JARS" J - Joints A - Abdominal pain R - Renal S - Skin Compartment Syndrome "6 p's" pulselessness pain pallor parasthesia poikiolothermia paralysis Predisposing Conditions for Pulmonary Embolism TOM SCHREPFER T--trauma O--obesity M--malignancy S--surgery C--cardiac disease H--hospitalization R--rest (bed-bound) E--estrogen, pregnancy, post-partum P--past hx F--fracture
E--elderly R--road trip
(Cot)Caught by Sin : Cotton BySSinosis Shortness of Breath HAPISOCS H: History of any pulmonary disease A: Activity at onset P: Pain upon inspiration I: Infections fever/chills S: Smoker years/packs O: Orthopnea C: Cough (Persistent) S: Sputum Productive/color Submitted by medmanRRT@aol.com Non-Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema "PONS" P - Phosgene, paraquat, phenothiazines O - Opioids/organophosphates N - Nitrous dioxide S - Salicylates Treatment of acute pulmonary edema As Easy as 'LMNOP' : Remember the mnemonic LMNOP when treating a patient with acute pulmonary edema Lasix (furosemide) intravenous (IV), one to two times the patient's usual dose, or 40 mg if the patient does not usually take the drug. Morphine sulfate. Initial dose, 4 to 8 mg IV (subcutaneous administration is effective in milder cases); may repeat in 2 to 4 hours. Avoid respiratory depression. Morphine increases venous capacity, lowering left atrial pressure, and relieves anxiety, which reduces the efficiency of ventilation. Nitroglycerin IV, 5 to 10 ug/min. Increase by 5 ug/min q 3 to 5 minutes. Reduces left ventricular preload. Caution: may cause hypotension. Oxygen, 100% given to obtain an arterial PO2>60 mm Hg. Position patient sitting up with legs dangling over the side of the bed. This facilitates respiration and reduces venous
return. Beta-1 receptors are in the heart (you have 1 heart) and beta-2 receptors are in the lungs (you have 2 lungs). Decreased Pleural fluid Glucose : "IRAN" I=Infections RA=Rheumatoid arthritis N=Neoplasia Anterior Mediastinal Mass "4 T's" T - Thymoma T - Teratoma T - Thyroid tumor/goiter T - Terrible lymphoma Middle Mediastinal Mass "Habit5" H - Hhernia, hematoma A - Aneurysm B - Bronchogenic cyst/duplication cyst I - Inflammation (sarcoid, histo, coccidio, TB) T5 - Tumors (lung, lymphoma, leukemia, leiomyoma, lymph node hyperplasia) Bilateral Hilar Adenopathy "Please Helen Lick My Popsicle Stick" P - Primary TB H - Histoplasmosis L - Lymphoma M - Metastases P - Pneumoconiosis S - Sarcoidosis Sarcoidosis: SARCOIDOSIS: G-E-R-M-A-N ACE "SCHAUMANN" B-O-E-K G-Granulomas E-Erythema nodosum R-Restrictive lung defect (PFTs) M-Multiple systemic manifestations A-Asteroid bodies (inclusions) N-Noncaseating granuloma, Negative TB test ACE - Angiotensin converting enzyme levels monitor
disease activity and response to therapy. Schaumann's bodies (inclusions) B-Bell's palsy, Bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy, Black females O-Optic nerve dysfunction is a common manifestation of neurosarcoid. E-Eyes: uveitis K-Kveim skin test Rat Poisons "RATS PANIC" I'm sure that you'll easily remember this one! R - Red squill A - Arsenicals T - Thallium S - Strychnine P - PNU/Phosphorus/zn Phosphide A - Alpha naphtha thiurea (ANTU) N - Norbormide I - Indanediones C - Coumadin/cholcalciferol Anion Gap Acidosis: "Mudpiles" M - Methanol U - Uremia D - DKA/AKA P - Paraldehyde/phenformin I - Iron/INH L - Lactic acidosis E - Ethylene glycol S - Salicylates Normal Gap Acidosis "HARDUP" H - Hyperalimentation/hyperventilation A - Acetazolamide R - RTA D - Diarrhea U - Ureteral diversion P - Pancreatic fistula/parenteral saline Osmolar Gaps "ME DIE" M - Methanol
E - Ethanol D - Diuretics (mannitol, sorbitol, glycerol) I - Isopropanol E - Ethylene glycol Respiratory Alkalosis: Asthmatic Sally poisoned POPE's HEN Asthma Salicylate poisoning PO= Pulmonary Oedema PE= Pulmonary Embolism HEN= Hepatic Encephalopathy Hypoglycemia "Reexplain" R - renal failure EX - exogenous P - pituitary L - liver failure A - alcohol I - insulinoma/infection N - neoplasm Hypoglycemia [By Sung Kim] Hypoglycemia - H-U-N-G-E-R: B-E-S-T S-A-U-C-E I-S M-SG H-Hepatic failure (advanced), Hypothermia U-Uremia/renal failure N-Nausea, vomiting G-Growth hormone deficiency E-Ethanol metabolism blunts gluconeogenesis R-Reye's syndrome B-Beta blockers E-Enzyme defects (glycogen storage diseases) S-Sepsis T-Tumors: Islet beta cell tumors (pancreatic): Insulinomas Non-islet cell tumors: Large mesenchymal tumors S-Sulfonylureas A-Adrenal insufficiency U-Under 0.3 (insulin/glucose ratio) to make the diagnosis C-C-peptide measurement to rule out factitious hypoglycemia E-Endocrine: Epinephrine, glucagon deficiencies (counterregulatory hormone deficiencies)
I-Immune disease with insulin or insulin receptor antibodies S-Sarcomas: large retroperitoneal sarcomas M-Maple syrup urine disease, severe Malaria S-Salicylates in children G-Galactosemia (with milk ingestion), disorders of Gluconeogenesis Symptoms of hyperthyroidism Remember the following mnemonic when evaluating patients for hyperthyroidism: S : Sweating T : Tremor or Tachycardia I : Intolerance to heat, Irregular menstruation, and Irritability N : Nervousness G : Goiter and Gastrointestinal (loose stools/diarrhea). CUSHING'S DISEASE is Dependent on (Pituitary) and Depresses ( Cortisol) on Daddy Doses of Dexa(High doses of Dexamethasone). Hypercalcemia "SHAMPOO DIRT" S - Sarcoidosis H - Hyperparathypoidism, Hyperthyroidism A - Alkali-milk syndrome M - Metastases, myeloma P - Paget disease O - Osteogenesis imperfecta O - Osteoporosis D - Vitamin intoxication I - Immobility R - RTA T - Thiazides Hypercalcemia symptoms are Bones (pain), Stones (renal), abdominal Groans (pain) and psychic moans (confusion). Multiple endocrine neoplasia MEN I is 3 P's (Pituitary, Parathyroid, Pancreas). MEN II is 2 C's (Catecholamines ie. pheochromocytome, carcinoma of medulla of thyroid) and Parathyroid (IIa) or Mucocutaneous neuromas (IIb).
The most common thyroid carcinoma is P-apillary (Popular). It also has P-sammona bodies on histology. It causes P-alpable lymph nodes (lymphatic spread). The most common symptoms of PHEochromocytoma begin with the first 3 letters - Palpitations, Headache, Episodic diaphoresis (sweating). Tumors that go to bone "Kinds Of Tumors Leaping Primarily To Bone" K - Kidney O - Ovarian T - Testicular L - Lung P - Prostate T - Thyroid B - Breast Causes of joint pain are SOFTER TISSUE - Sepsis, Osteoarthritis, Fractures, Tendon/muscle, Epiphyseal, Referred, Tumour, Ischaemia, Seropositive arthritides, Seronegative arthritides, Urate, Extra-articular rheumatism (eg. polymyalgia). Ossification centers of the elbow There are two that I know of (most people use "CRITOE"): C - Capitellum R - Radial head I - Internal (medial epicondyle) T - Trochlea O - Olecranon E - External (lateral epicondyle) These appear at 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, and 12 years of age in order and go away two years later. The other mnemonic I know for the ossification centers is "Come Rub My Tree Of Love" where the "M" is medial epicondyle and the "L" is the lateral epicondyle. Wrist Bones "Never Loosen Tillies Pants, Mother Might Come Home" Proximal row: N - Navicular L - Lunate T - Triquetrium P - Pisiform
Distal row: M - greater Multiangular (trapezium) M - lesser Multiangular (trapezoid) C - Capitate H - Hamate Also: "Some Lovers Try Positions That They Can't Handle" Rotator Cuff Muscles "SITS" S - Supraspinatus I - Infraspinatus T - Teres minor S - Subscapularis The Salter Classification: "SALTR" S - Slip of physis A - Above physis L - Lower than physis T - Through physis R - Rammed physis NEPHROTIC SYNDROME (NS) is characterized by the following: [By Shweta] N = Na + water retention This occurs due to several factors, including compensatory secretion of aldosterone in response to hypovolemiamediated release of ADH. E = Edema Due to hypoproteinemia + Na, water retention. Edema is soft, pitting and starts in the periorbital region. P = Proteinuria >3.5gm/1.74sq. ml/24hrs H = Hypertension + hyperlipidemia (due to increased lipoprotein synthesis in liver, abnormal transport of circulating lipoproteins, decreased catabolism.) R = Renal vein thrombosis O = "Oval fat bodies" in the urine. Lipiduria follows hyperlipidemia. Albumin as well as lipoproteins are lost. Lipoproteins are reabsorbed by tubular epithelial cells and they shed along with degenerated cells- this appears as "oval fat bodies" in urine.
T = Thrombotic + thromboembolic complications owing to loss of anticoagulant factors (eg. anti-thrombin III ) I = Infection. These patients are prone to infection, especially with staphylococci and pneumococci. Vulnerability is due to loss of immunoglobulins. C = hyperCoagulable state Henoch-Schonlein Purpura "JARS" J - Joints A - Abdominal pain R - Renal S - Skin Causes of hematuria Use the mnemonic SITTT as an aid in evaluating the cause of hematuria: S: Stone I: Infection T: Trauma T: Tumor T: Tuberculosis Causes of secondary nephrotic syndrome ie. not of direct renal origin are DAVID - Diabetes mellitus, Amyloidosis, Vasculitis, Infections, Drugs. Causes of acute and reversible forms of urinary incontinence The following mnemonic aids in remembering the causes of acute and reversible forms of urinary incontinence - DRIP D: Delirium R: Restricted mobility, retention I: Infection, inflammation, impaction (fecal) P: Polyuria, pharmaceuticals Hereditary cystic disorders: Polycystic kidney disease Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is associated with cysts in the kidneys and, in many cases, in the brain (berry aneurysms), liver, spleen, pancreas, and lungs.
Halley Berry AKA Dorothy (Dandridge) Portrayed Carmen Jones. Halley ?Hematuria: Gross and microscopic Berry -Berry aneurysms AKA ?ADPKD D-Dominant (autosomal) inheritance O-Obstruction of the urinary tract by stones, blood clots RRenal failure O-Oxalate: calcium oxalate and uric acid stones T-renal Tubular defects H-Hemorrhagic cysts Y-Year 1 - Most cases are diagnosed in the first year of life, presenting as bilateral abdominal masses. Portrayed ?Polycystic: continued enlargement of the cysts often leads to progressive renal failure. Carmen ?CT scanning: Enlarged kidneys with multiple bilateral cysts are diagnosed using ultrasound, IVP, or CT scanning. Jones - Juvenile nephronophthisis (JN) and medullary cystic disease (MCD) are in the DDx. -Cardiac valvular disorders: Mostly mitral valve prolapse (MVP) and aortic regurgitation -Salt-wasting nephropathy, renal tubular acidosis (RTA) -Chronic flank pain due to the mass effect of the enlarged kidneys Lusty Carmen Jones powdered her nose, using her Bivalve [MVP] mirror compact, -then she slowly raised her Saltrimmed [Salt-wasting nephropathy] MargaRiTA [RTA], and seductively placed her other hand on her Hip [Flank pain]. -Hyperchloremic acidosis -Salt-wasting nephropathy causing hyponatremia It was said that Dorothy was not allowed to swim in the hotels Chlorinated pool [Hyperchloremic acidosis]. When she defiantly swam in the pool, they Drained it [Saltwasting nephropathy, Hyponatremia]. -Hypertension
-End-stage renal disease (ESRD) Dorothy was forced to enter through the back door, even while she was contracted to sing under The Big Tent [Hypertension]. Dorothy was only 41 when she was found DEAD [ESRD]. Review: Dx: Positive family history (autosomal dominant inheritance) Gross and microscopic hematuria Ultrasound, IVP, or CT scanning detect the enlarged kidneys with multiple bilateral cysts
Renal Pathology Buzz words Lupus = wire LOOP lesion (LUPUS=LOOP) goodPASTURE = a pasture is FLAT so is the immunoflouresence for GP Membraneous GN = spike and DOME appearance (think membrane = dome) (held up by spikes) Membranoproliferative GN = M P GN = Tram Track think of MP's (military police riding on Trams) Post streptococcal GN= Lumpy Bumpy think Strep aerobics Lumpy people Bumping around doing aerobics WBC Count "Never Let Mom Eat Beans" and "60, 30, 6, 3, 1" Neutrophils 60% Lymphocytes 30% Monocytes 6% Eosinophils 3% Basophils 1% Hem - PT, PTT: To remember the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways in
relation to what blood test is affected: PiTT (I for Intrinsic pathway) - PiTTsburgh PeT (E for Extrinsic pathway) Vitamin K-dependent proteins and warfarin sodium [by Sung Kim and S. Levine, MD, PhD.] Warfarin sodium is a vitamin K antagonist. -Vitamin K-dependent proteins C and S. -Vitamin K-dependent clotting factors II, VII, IX, and X of the extrinsic pathway. --> The Korean [vitamin K] War [Warfarin] was fought Outdoors [Extrinsic --> pathway]. The American PT boats [PT, Protime, or prothrombin time], --> whose access had been limited by the rough Seas [protein C], quickly sent out SOS [protein S] messages. Microcytic Anemia "TICS"Thalasemia Iron deficiency Chronic disease Sideroblastic anemia Submitted by Jeff Rodgerson M.D. HCMC Medical Center Eosinophilia "NAACP" N - Neoplasm A - Allergy A - Addison's C - Cirrhosis, CVD P - Parasite (visceral larva migrans), Periarteritis nodosa Submitted by Tag Filley, M.D. Thalassemia major is the most Severe -thalassemia [BBeta-Bad]. -Major B-A-D M-A-F-I-A guys have the typical gangster appearance: Short [Microcytic hypochromic anemia] and
Ugly [distortion of facial, skull, and long bones] B-Basophilic stippling A-Anemia, Anisocytosis D-Deferoxamine M?MCV is low A-HbA is decreased F-HbF is increased I-Ineffective erythropoiesis A?HbA2 is increased
Cooley's anemia (beta-thalassemia major) is the homozygous state. -The key is Denton A. Cooley, M.D., Texas Heart Institute (THI).
D-Deferoxamine therapy to prevent hemochromatosis A-Anemia - In beta-thalassemia major or intermedia, anemia is due to a combination of ineffective erythropoiesis and hemolysis of circulating cells. C-Congestive heart failure is a cause of death in the first years of life if the patient is not transfused.
M-MCV is low; Microcytic hypochromic anemia D-Diagnosis, prenatal T-Tower skull (also frontal bossing, chipmunk facies, and distortion of long bones) H-Hemolytic anemia with Hepatosplenomegaly in the first year of infant life IIntermedia - Beta-thalassemia intermedia presents with abnormalities similar to those of thalassemia major.
Increased susceptibility to infections Peripheral blood smear: Basophilic stippling Helmet cells Nucleated target cells Anisocytosis (RBCs of different size/volume) X-ray: Hair-on-end skull
Serum hemoglobin electrophoresis: HbA is decreased. HbA2 is increased. HbF is increased --> Dr. Cooley performed Major surgery [thalassemia Major] as a --> Cardiothoracic surgeon [Cardiac failure] live on the Internet [Infections]. --> His skilled hands can perform Microsurgery [Microcytic hypochromic --> anemia] on Fetuses [HbF]. --> His surgical cap [Helmet cells] fit loosely over his Crew cut --> [Hair-on-end skull]. --> He proceeded to make an incision along the Blue Stippled line --> [Basophilic Stippling] drawn on the skin. --> Dr. Cooley's Target [Target cells] academic score had always been an --> A+ [HbA2 is increased]. --> He would Not accept a simple A [HbA is decreased]. --> The surgical staff is a close knit community, like a B-AD M-A-F-I-A --> (see below), quick to dispose of weak, Ineffective [Ineffective erythropoiesis] residency candidates.
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
D-I-S-S-E-M-I-N-A-T-E-D D-Dx: D dimer I-Immune complexes S-Snakebite, shock, heatstroke S-SLE E-Eclampsia, HELLP syndrome M-Massive tissue damage I-Infections: viral and bacterial N-Neoplasms
A-Acute promyelocytic leukemia T-Tumor products: Tissue Factor (TF) and TF-like factors released by carcinomas of pancreas, prostate, lung, colon, stomach E-Endotoxins (bacterial) D-Dead fetus (retained) Characteristic features of multiple myeloma on X-ray are ABCDE - Asymmetry, Border irregular, Colour irregular, Diameter usually > 0.5cm, Elevation irregular. 9 Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a monoclonal malignancy, usually of B lymphocytes. -Incidence: CLL is the most common adult leukemia in the United States. Males>Females 50-70 years of age Songwriter Phil CoLLins [CLL] is Male and probably over 50 years of age. He recently won an Oscar for his "Tarzan" song. Clinical and diagnosis Lymphocytosis >15,000/mm3 Generalized lymphadenopathy Tarzan can spring from Limb [Lymphocytosis] to Limb [Lymphadenopathy] above the tree tops Splenomegaly, hepatomegaly Low serum immunoglobulins (immunosuppression) --> where the Splendid [Splenomegaly] Moonlight [imMunosuppression] --> streams through the branches. Diffuse bone marrow infiltration and replacement of cellular elements cause: Anemia Thrombocytopenia Granulocytopenia
--> Walt Disney Pictures produced the Animated Animal [Anemia] adventure --> "Tarzan". --> The "Tarzan" [Thrombocytopenia] song earned CoLLins an Oscar [Osteo, --> bone marrow failure] award for the best original song. --> Tarzan had Little need for Plates [Platelets <100,000/L] in the --> jungle. --> Phil CoLLins is a Grammy [Granulocytopenia] Awardwinning singer and --> songwriter. Occasionally extravascular hemolysis: warm-antibody autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AHA) --> An African jungle [Autoimmune extravascular] APE [AHA] had Warmly --> [Warm-antibody] adopted baby Tarzan. Differential diagnosis Malignant lymphoma Infectious mononucleosis --> Tarzan is Lord [Lymphoma] of the Jungle and friend of the Monkeys --> [Mononucleosis]. Phil CoLLins was born in London [Lymphoma].
Treatment Chlorambucil (an alkylating agent), with or without prednisone Fludarabine --> Some may imagine a Ram [ChloRambucil] scrambling about, but others --> will --> recall that Clayton [Chlorambucil] is the villainous jungle guide
--> who was hired by Professor [Prednisone] Porter, not knowing that --> Clayton [Chlorambucil] had his captured Prey [Prednisone] --> immediately Flown [Fludarabine] out for profit.
References: 1. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 14/e Edition, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1998. 2. Maximum access to diagnosis and therapy (MAXX), Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, New York, 1999. 3. Scientific American Medicine (SAM-CD), Scientific American Inc, New York, 1997. Hodgkin's lyphoma classification - A = Asymptomatic, B = Bad. Risk of underlying malignancy with dermatomyositis or polymyositis is 30% at age 30, 40% at age 40 etc. Malignant Monoclonal Gammopathies: Multiple myeloma -The mnemonic key for multiple myeloma (MM) is Marilyn Monroe (MM), a key which immediately follows the >> symbol. -Clinical: Weakness and fatigue due to normochromic normocytic anemia. >> MM's original name was Norma [Normochromic normocytic] Jean. Bone pain and pathologic fractures: predominantly osteolytic tumors and osteoporosis. >> MM's name was illuminated in marquee Lights [osteoLytic], but she >> secretly longed for an Oscar award [Osteoporosis]. Susceptibility to bacterial infections. >> MM was Susceptible to Toxic [infections] relationships. Acute renal failure (ARF) due to the effects of filtered lightchain proteins,
hypercalcemia, and amyloid deposits in the kidney. >> MM's Lightly-Chained ARF dog barked when MM's death was said to be >> related to her JFK Army-Lord [Amyloid]. -Laboratory Hypercalcemia >> MM fluffed White Talcum [hypercalcemia] powder on her delicate white >> skin... Hypergammaglobulinemia >> ...to protect it from the movie industry's Large hot Camera >> lights[hyperGammaglob]. Serum electrolytes: Low anion gap >> MM wore gowns with Low [Low anion gap] revealing necklines. Rouleaux on peripheral blood smear. Occasionally Coombs(+) hemolytic anemia. >> MM used hair Rollers [Rouleaux] and Combs [Coombs] to create her >> famous hairdo. Leukocyte alkaline phosphatase (LAP) staining reaction: High LAP score. >> MM used her Great LAP to her advantage because.... Normal levels of Serum Alkaline Phosphatase (SAP) >> ...she was Not a SAP.
Antineoplastic agents & Adverse effects
Male testicular tumors: "S-E-C sac T-I-C-S S-Seminoma: most common E-Embryonal carcinoma C-Choriocarcinoma Sac-Yolk sac tumor (endodermal sinus tumor)
T-Teratoma, Teratocarcinoma I-C-Interstitial (Leydig) cell tumor S-Sertoli cell tumor Paraneoplastic syndromes and their associated cancers: Your diagnosis can be "Highly S-C-R-A-M-B-L-E-D." Highly-Hypercalcemia (squamous cell carcinoma) S-SIADH, hyponatremia (SCLC) C-Clubbing (adenocarcinomas) R-Retinal blindness (SCLC) A-ACTH (SCLC) M-Myasthenia gravis (thymoma) B-Bone - hyperosteoarthropathy (adenocarcinomas) L-Limbic encephalitis (SCLC) E-Eaton-Lambert myasthenic syndrome (SCLC) D-Dermatomyositis (cancer of the lung, ovary, breast, stomach; NHL)
SIADH: Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion SCLC: Small cell lung cancer NHL: non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
Microbiology The first two mnemonics are modifications of well-known mnemonics. -Gram-positive, spore-forming, rods: Bacillus and Clostridium Some love stay home forming spores: Basically Claustrophilic (Bacilli and Clostridia)
-Other gram-positive rods: Others love to belong: C-L-A-N
C-Corynebacterium L-Listeria A-Actinomyces N-Nocardia
All species within the Enterobacteriaceae family are gramnegative enteric bacilli and are facultative anaerobes that can ferment glucose to acid. When microorganisms compete with humans for glucose, they are Nasty CURSESS." Nasty-Neisseria (N. gonorrhoeae and N. meningitides) C-Curved: Vibrio and C-Campylobacter species UR-Urease-positive SE-Serratia SS-Salmonella, Shigella Urease(+): Y. enterocolitica, Y. pseudotuberculosis, P. mirabilis, P. vulgaris, M. morgani
Clinically significant Anaerobes "A Closed Box For Pepsi." A-Actinomyces G+ C-Clostridia- G+ B-Bacteroides GFor Fusobacterium GPepsi Peptostreptococci G+ Bloody diarrhea Bloody diarrhea may be caused by invasive bacteria or parasites, including: Campylobacter, Shigella, Salmonella, Yersinia, and Trichuris (whipworm). The Cutting edge of the Campbell's [Campylobacter] soup can was Bloody. The Shaggy [Shigella] surface was Abrasive [Bloody]. The Salmon [Salmonella] scales were Abrasive [Bloody].
The Jersey [Yersinia] sweatshirt was rough and Abrasive [Bloody]. The Bullwhip [Whipworm] drew Blood.
Bordetella pertussis: Whooping cough Bordetella pertussis is the etiologic agent of whooping cough. -Laboratory: Absolute lymphocytosis in children (a reportedly recent USMLE Step 2 question). >> Many crossed the Border [Bordetella] for their Green* cards [lymphocytosis]. *In our color-coding scheme of mnemonics, green will represent lymphocytes. B-O-R-D-E-T-E-L-L-A B-Bordet-Gengou agar culturing a nasopharyngeal swab is the standard diagnostic test ordered during the first 2 weeks of onset. O-whOoping cough R-Rod: B. pertussis is a small, gram-negative pleomorphic rod D-DFA - Direct fluorescent antibody test of nasopharyngeal secretions results in frequent false-positives. E-Erythromycin for therapy and prophylaxis. T-Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole is an alternative antibiotic choice. E-ELISA is the diagnostic test ordered after the first 2 weeks of onset. L-Leukocytosis: 10,000 - 50,000 cells/uL with 50-75% mature lymphocytes L-Lymphocytosis in children
A-Adult lymphocytosis is rare.
Organisms that Spread from Blood to Urine CASH CML C - candida A - aureus staph S - salmonella H - histoplasma C - cytomegalo virus M - mycobacteria L - leptospira Submitted by Ousama Dabbagh M.D Acute Rheumatic Fever There are several for the major criteria, I use "JONES" J - Joints O - Obvious (cardiac) - sorry, I know this is kinda weak N - Nodules (subcutaneous nodules) E - Erythema marginatum S - Syndeham's Chorea Kawasaki's "scream fever" S - sausage fingers C - conjunctival redness R - rash E - extremity involvement A - adenopathy M - mucosal erythema FEVER - fever Causes of post op fever Remember the following mnemonic when determining the possible cause(s) of fever in a patient who has recently undergone a surgical procedure: the 5 W's (or 6 W's) Wind : the pulmonary system is the primary source of fever in the first 48 hours. ( Atelectasis, pneumonia ect.) Wound : there might be an infection at the surgical site. Water : check intravenous access site for signs of phlebitis. Walk : deep venous thrombosis and pulmonay embolism can develop due to pelvic pooling or restricted mobility Whiz : a urinary tract infection is possible if urinary catheterization was required.
Also Wonder drugs - drug fevers. (added by Calvin Lee)
Classification of hypersensitivity reactions "ACID" Type I Anaphylaxis Type II Cytotoxic - mediated Type III Immune - complex Type IV Delayed hypersensitivity
Criteria for Lupus SOAP BRAIN MD Serositis (pleuritis, pericarditis) Oral Ulcers Arthritis Photosensitivity Blood (all are low - anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia) Renal (protein) ANA Immunologic (DS DNA etc.) Neurologic (psyc, seizures) Submitted by Mike Ritter, MD FAAEM, San Diego, CA Risk of underlying malignancy with dermatomyositis or polymyositis is 30% at age 30, 40% at age 40 etc. Blue Sclera: "MIXED" M = Marfans , I = Imperfecta ( Osteogenesis ) XE =(pseudo) Xanthoma elasticum ED = Ehlers Danlos Altered Mental Status "AEIOU TIPS" A - Alcohol/drugs E - Endocrine I - Insulin O - Opiates U - Uremia T - Toxins/trauma I - Infections P - Psych/porhyria S - SAH, shock, stroke, seizure, space occupying lesion MIDAS : States to exclude as cause of coma.
Meningitis Intoxication Diabetes Air - respiratory failure Subdural or subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Level of consciousness "AVPU" A - alert V - resonds to verbal stimuli P - responds to painful stimuli U - unconscious Vertebral/Basilar Ischemia 4Ds dizziness (nystagmus) diplopia (skew deviation) dysarthria dysphagia Submitted by: Ronald H. Miller, OD, The Ohio State University Cerebellar lesions lead to VANISHeD - Vertigo, Ataxia, Nystagmus, Intention tremor, Slurred speech, Hypotonic reflexes, Dysdiadochokinesia. ( or Dementia ) Marcus Gunn Pupil Marcus Welby, M.D. "knows". Robert Young was also in "Father Knows Best". D-R K-N-O-W-S D-Deafferentation of the pupillary light reflex R-Retrobulbar optic neuritis K-Kan't kick inward: afferent limb defect N-No constriction to direct light stimulation O-Optic nerve (CN II) damaged unilaterally W-swinging flashlight test S-consensual reflex intact
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH): Rupture of an aneurysm releases blood directly into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) under arterial pressure.
Clinical manifestations: CSF ~ FDR F-D-R's Last Words: O! CAN'T W-H-I-P 'E-M F-Focal signs: limb weakness, dysphagia, CN III palsy D-Depression of consciousness with headache R-Retinal (subhyaloid) hemorrhage Last-Lucidity with headache is the usual pattern of onset. Words-Warning leak sign of impending rupture (controversial sign). O-(looks like eyes) CN III palsy Can't extend knees (Kernig's sign) W-circle of Willis H-Headache: sudden onset of severe headache ("the worst headache of my life") I-Increased ICP P-Papilledema E-Epileptic seizures M-Meningismus
Subarachnoid hemorrhage : Ruptured berry aneurysm A-Adult polycystic kidney disease, Anterior communicating artery B-Berry aneurysm C-Circle of Willis D-Danlos-Ehlers and Marfan's syndromes
Causes of Syncope: F-A-D-E-O-U-T F-Faint simple vasovagal fainting A-Arrhythmia causing cardiac syncope D-Drugs: alcohol, illicit drugs, nitrates, antihypertensives, sympathetic blockers E-Eyeball pressure O-Orthostatic hypotension: dysautonomias
U-Undiagnosed seizures T-Takayasu's arteritis: reduced cerebral blood flow due to involvement of the carotid and vertebral arteries.
Causes of Vertigo: revolving, P-I-V-O-T-I-N-G M-E-N P-Petrositis, benign Positional vertigo I-Ischemic attacks: transient vertebrobasilar ischemic attacks V-Vestibular neuronitis O-Other Otogenic causes: Otosclerosis, herpes zoster Oticus, Obstructed external auditory canal T-Tumors of the middle ear, labyrinth, pons, cerebellopontine angle, CN VIII I-Internal auditory artery occlusion N-Neuronitis: acute vestibular neuronitis G-Giant cell arteritis - internal auditory artery occlusion M-Meniere's disease E-Ear: otitis media, labyrinthitis, barotrauma N-Neuromas: acoustic neuromas
Headache: S-T-O-I-C M-P S-Sentinel headache that precedes a major subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) T-Temporomandibular joint dysfunction, Tension-type headache, Tumors O-Other: pressure, traction, or displacement of extracerebral structures. I-Indomethacin-responsive headache C-Cluster headache M-Meningitis, Migraine headache P-Posttraumatic headache, Paranasal sinuses _______________________________________________ _____________________________________________ Intracerebral hemorrhage: T-I-P Ur H-A-T to M-Ds T-Trauma I-Idiopathic P-Penia ? thrombocytopenia
Ur-Vasculitis H-Hypertension A-Amyloid angiopathy T-Tumors associated with bleeding M-Malformations: AV D-blood Dyscrasias
Subdural hemorrhage: subconsciously dying -Elderly -Slowly dying -Alcohol -Brain injury _______________________________________________ _____________________________________________ Cerebrovascular I-N-F-A-R-C-T-S I-Infections: septic heart valve vegetations N-Neoplasms; Nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis F-Fracture of the long bone A-Atherosclerosis, Atrial fibrillation-related emboli R-Reperfusion -> infarct -> hemorrhage C-Carotid atheromas or mural thrombi T-Thrombotic occlusions S-Sylvan fissure: MCA is a particularly common site.
Lacunar infarct: "Lacunar" from the Latin for G-A-P or- D-IS-P-A-R-I-T-Y G-deep Gray matter: basal ganglia A-Atherosclerosis P-hyPertension D-Dysarthria and a contralateral clumsy hand or arm due to infarction in the base of the pons or in the genu of the internal capsule. (20%) I-Internal Capsule: Lacunae in the posterior limb of the Internal capsule may cause pure motor hemiplegia involving the face, arm, leg, foot. (60%) S-Subcortical, capsular, or thalamic lacunae
P-Pontine lesions A-Ataxic hemiparesis due to an infarct in the base of the pons R-Rare: Lacunae in the anterior limb of the Internal capsule may cause severe dysarthria with facial weakness. I-Ipsilateral ataxia (arm/leg) with leg weakness: Pontine lesion (rare) T-Thalamus: Lacunae in the Thalamus may cause pure sensory stroke (10%) y-V-Ventrolateral Thalamic lacunae
Anterior cerebral artery (A*C*A) occlusion: *C*-Contralateral Crural (leg) monoplegia *C*-Crest of Cerebral hemispheres and medial hemispheric walls represent the leg area of the motor strip
Middle cerebral artery (MCA) occlusion: "Difficulty with AB-Cs in M-C-A" A-Apraxia B-Blindness in corresponding half of the visual field (contralateral homonymous hemianopsia) C-Contralateral Clumsiness of arm, face. -- Leg is somewhat spared. M-Memorization difficulties C-Calculation difficulties A-Aphasia with language-dominant hemispheral involvement. Posterior cerebral artery (PCA) occlusion: P-O-S-T P-Proximal fling movements O-Occipital lobe infarction results in contralateral homonymous hemianopsia which may be complete S-Speech and Spelling maintained, but unable to read fluently T-Thalamic syndrome _______________________________________________ _____________________________________________ A well-known mnemonic regarding occlusion of the vertebral-basilar circulation: 4D
-Dizziness -Diplopia -Dysarthria -Dysphagia _______________________________________________ _____________________________________________ Types of Stroke Stroke "H-I-T" you! H-Hemorrhagic I-Ischemic T-TIA (Transient Ischemia Attack)
T.I.A (Transient Ischemic attack) Patients often describe it as a shade being pulled over their eyes: S-H-A-D-E-D S-Sensory loss; TIA may herald a stroke H-Hypertension, Hyperlipidemia A-Amaurosis fugax (transient monocular blindness) D-DDx: seizures, neoplasms, migraine, vertigo E-Extrinsic factor is monitored for warfarin administration; E-Endarterectomy D-Diabetes Root values of reflexes are 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8 - S1-2 ankle, L3-4 knee, C5-6 biceps/supinator, C7-8 triceps. Argyle Robertson Pupil Accomodation Reflex Present - Pupillary Reflex Absent.
Neurosyphilis [By jsara] -Symptomatic Neurosyphilis: The small, irregular Argyll Robertson pupil reacts to accommodation but not to light. -Tabes dorsalis: Argyl-Robertson Pupil (ARP) in syphlis - Accomodation Reflex Present (ARP)
but the light reflex is absent, so ARP=ARP. -General paresis: P-A-R-E-S-I-S* P-Personality A-Affect R-Reflexes are hyperactive E-Eye: Argyll Robertson pupils S-Sensorium: illusions, delusions, hallucinations I-Intellect: decrease in recent memory, orientation, calculations S-Speech Reference: *From Harrison Principles of Internal Medicine, 14/e Edition, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1998.
Pattern of Weakness in UMN lesions FLUE weakness FUELs Contractures F=Flexion,L=Lower Limb,U=Upper Limb E= Extensors Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Demented (Memory Loss) Dribbles (Urinary Incontinence) Disbalanced (Gait disorder)
TRAP to identify parkinson's disease Tremor at rest (pill-rolling tremor) Rigidity Akinesia Posture typical of a Parkinson's patient
Progressive Cerebellar Ataxias: Bassen-Kornzweig Acanthocytosis (Abetalipoproteinemia)
Abetalipoproteinemia is a rare autosomal recessive disorder that occurs primarily in Ashkenazi Jews during their childhood years (6-12 years of age). -The key is Bette [aBeta] Midler, who is Jewish [Ashkenazi Jews] by birth, but hardly shy or Recessive. -Clinical:
Lack of intestinal apolipoprotein B causes mild malabsorption (notably of fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, K), steatorrhea, and low serum chylomicrons, VLDL, IDL, and LDL. - Did you know that Bette is computer-savvy? Know that she created her own web page on a PC, and Not on an Apple [No Apolipoprotein-B] computer. Progressive neuromuscular disease of the peripheral nervous system (PNS) and of the cerebellum (ataxia of gait, trunk, and limbs). - Bette wanted to be featured on serious PBS [PNS] television, but instead her trash with flash persona was interviewed for E! Celebrity [Cerebellum] Profile. - Bette paid heavy Taxes [aTaxia] after starring in "That Old Feeling" [sensory ataxia] with Dennis Farina. - The concert tour: As the tail-wagging mermaid, Bette motored around the stage in a Wheelchair [muscle weakness]. Retinitis pigmentosa -Then she donned her mermaid Goggles [retinitis pigmentosa] and grinned. -Diagnosis: Ataxia plus acanthocytes in peripheral blood smear. The low cholesterol gives rise to deformed or spiky red blood cells called acanthocytes. Low apolipoprotein B, low vitamin E Low plasma triglyceride (TG) and cholesterol levels - The Jewish Cantor [aCanthocytosis] disapproved of the bawdy stiletto Spike [Spiky RBC] heels she wore to holy day services. Small bowel biopsy: Foamy epithelial cells and lacy villus tips. - The mermaid character was set in a Foamy [epithelial cells] sea backdrop.
- Under her Lacy [Lacy villus tips] mermaid costume, Bette had to wear a tightly laced corset. She was still No Twiggy [low TGs]. -Treatment: Low fat diet, fat-soluble vitamins such as vitamins A and E. - Bette tried to lose weight on a Low Fat Diet in preparation for her A&E [vitamins A and E] interview.
Radiopaque Ingestants "Chipes" C - Cocaine condoms/ chloral hydrate/ calcium H - Heavy metals I - Iron/ iodides P - Psychotropics (TCA, phenothiazines) E - Enteric coated/BA S - Solvents (CCl4)
Drugs that can go into an ET tube "lane" L - lidocaine A - atropine N - naloxone E - epi Some like NAVEL, which includes Valium. Others have commented that valium should not go in an ET tube.
History taking in EMS "sample" S - signs/symptoms A - allergies M - medications P - past medical history L - last oral intake E - events leading to injury or illness
Pain scale: "OPQRST" O - onset P - provocation Q - quality R - radiation S - severity T - time
Pain Scale (Revisited) PQRSTAPPP P - palliates/provokes Q - quality R - region/radiation S - severity (on a 1-10 scale) T - timing (onset, frequency, duration) A - associated symptoms P - prior P - persists P - progression (stable, better, worse) Submitted by Omar A. Blanco
More on Pain Evaluation LOCI" (Latin for places) and the "Daughters of the American Revolution" L - Location O- Onset C- Character I- Intensity D- Duration A- Aggravation A- Alleviation A - Association R - Radiation
One More Pain Mnemonic P - period of pain A - area of pain I - intensity of pain
N - nullify ( what makes pain go away, if any) Submitted by Greg Van Hook Concretions: "Big Mess" B - Barbituates I - Iron G - Glutethemide M - Meprobamate E - Extended release theophylline SS - Salicylates
X linked Bleeder, Blind, Becker and Duch, B cell others : G6PD,NDI,SCID,CGD
_________________ H-DOCTOR Winners never quit, Quiters never win!!!!!!!!!!
Back to top
Guest
Posted: Wed Apr 25, 2007 8:40 pm subject:
Post
causes of hepatomegaly massive = CRAM Cancer - primary and secondary Right heart failure Alcoholic liver disease with fatty infiltration Myeloproliferative diseases (ie Chronic myeloid laekaemia, PRubraVera,Essential
Throbocythaemia) moderate = FAILL all of the above plus Fatty liver - from DM, obesity Amyloidosis Iron - haemochromatosis Lymphoma Laeukaemia - chronic mild H3B all of the above plus Hepatitis HIV Hydatid Biliary duct obstruction
Back to top Guest
Posted: Fri Jul 06, 2007 5:05 pm subject: Post
Thanks for them, they are very useful!
Back to top Gladwin
Guest Posted: Wed May 27, 2009 11:36 pm subject: Causes of Nephritic Syndrome Memonics Post
Causes of Nephritic Syndrome Memonics: RABID RPGN, Alport's Syndrome, Berger's disease, Infections, DPGN
Вам также может понравиться
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtОт EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Neurology Multiple Choice Questions With Explanations: Volume IIОт EverandNeurology Multiple Choice Questions With Explanations: Volume IIРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- MnemonicsДокумент23 страницыMnemonicsJot grewalОценок пока нет
- Emergency Medicine CardiovascularДокумент4 страницыEmergency Medicine CardiovascularxaileenxОценок пока нет
- Cardiology and Medical MnemonicsДокумент4 страницыCardiology and Medical MnemonicshawkreadОценок пока нет
- 4 Valvular Heart Disease ICMPD (Autosaved)Документ30 страниц4 Valvular Heart Disease ICMPD (Autosaved)mus zaharaОценок пока нет
- DR Mohamed A. Fathi Cardiology Specialist and Tutor GMCHRCДокумент76 страницDR Mohamed A. Fathi Cardiology Specialist and Tutor GMCHRCMohamed Ahmed FathiОценок пока нет
- CardiovascularДокумент51 страницаCardiovascularhanthuanОценок пока нет
- K7 - Penyakit Jantung Katub-ANNДокумент38 страницK7 - Penyakit Jantung Katub-ANNXeniel AlastairОценок пока нет
- Summary CVS Davidson 23rdДокумент5 страницSummary CVS Davidson 23rdDeshi SportsОценок пока нет
- Clinical ... ىلمعلاДокумент12 страницClinical ... ىلمعلاLinto JohnОценок пока нет
- Cardiology Plabable PDFДокумент22 страницыCardiology Plabable PDFTirtha Taposh100% (1)
- Valvular Heart Disease: Departemen Kardiologi Dan Kedokteran Vaskular FK UsuДокумент38 страницValvular Heart Disease: Departemen Kardiologi Dan Kedokteran Vaskular FK UsuDumora FatmaОценок пока нет
- Helpful MnemonicsДокумент44 страницыHelpful MnemonicsAdvaita Susarla0% (1)
- Ngaji Arrythmia Cordis 3Документ122 страницыNgaji Arrythmia Cordis 3Dhita Dwi NandaОценок пока нет
- TM 9 TM 9 Only Clinical Exam of Heart and Circulatory System AGWEnglishДокумент73 страницыTM 9 TM 9 Only Clinical Exam of Heart and Circulatory System AGWEnglishcellin rubianti azzharaОценок пока нет
- 2021-Lecture 4-Cardiac Cell and PhysiologyДокумент24 страницы2021-Lecture 4-Cardiac Cell and PhysiologyMajd HusseinОценок пока нет
- 2 5404863613531850140 PDFДокумент51 страница2 5404863613531850140 PDFzaid auglaОценок пока нет
- DR Abdulkareem Al Othman Valvular HDДокумент10 страницDR Abdulkareem Al Othman Valvular HDDarawan MirzaОценок пока нет
- MS ReviewerДокумент158 страницMS ReviewerDexan Juridico100% (2)
- Cardiology MnemonicsДокумент11 страницCardiology Mnemonicsadibestara0% (1)
- Cardiology Mnemonics PDFДокумент22 страницыCardiology Mnemonics PDFEliza SparkОценок пока нет
- Medical Surgical Nursing Outline B - Joshua DiaoДокумент17 страницMedical Surgical Nursing Outline B - Joshua DiaoLevi Rae CLerigo EstiponaОценок пока нет
- Ischemic Heart DiseaseДокумент67 страницIschemic Heart Diseasealfaz lakhani80% (5)
- Cardiology Basic QuestionsДокумент9 страницCardiology Basic QuestionsSunita PooniaОценок пока нет
- Mitral StenosisДокумент25 страницMitral StenosisPradeepa Hari100% (1)
- In The Name of ALLAH, The Most Beneficent, The Most Gracious, The Most Merciful !Документ24 страницыIn The Name of ALLAH, The Most Beneficent, The Most Gracious, The Most Merciful !Wan HafizОценок пока нет
- Cardiology Cardiovascular: Aortic Stenosis CharacteristicsДокумент11 страницCardiology Cardiovascular: Aortic Stenosis CharacteristicsxaileenxОценок пока нет
- Ficits: Wernicke-Korsakoff's Psychosis: FindingsДокумент36 страницFicits: Wernicke-Korsakoff's Psychosis: FindingsfarazОценок пока нет
- Lesson9 Cardiovascular AssessmentДокумент21 страницаLesson9 Cardiovascular AssessmentDennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RMОценок пока нет
- Cardiology-6 CADДокумент20 страницCardiology-6 CADMahmoud RamadanОценок пока нет
- Lecture 3 - Stroke - Highlights On Pathophysiology, Clinical PresentationДокумент39 страницLecture 3 - Stroke - Highlights On Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentationepic sound everОценок пока нет
- Arrhythmia: PalpitationДокумент36 страницArrhythmia: PalpitationHala BahaaОценок пока нет
- Valvular Heart Disease 2Документ46 страницValvular Heart Disease 2Topea BogdanОценок пока нет
- Cardiology MneumonicsДокумент14 страницCardiology Mneumonicsadwait marhattaОценок пока нет
- 07 - 01 - Assessment of Cardiovascular SystemДокумент55 страниц07 - 01 - Assessment of Cardiovascular SystemSalman Habeeb100% (1)
- Guidelines For Examination of Cardiovascular System: Bendehiba Latroche, MD, DIS, DIUДокумент22 страницыGuidelines For Examination of Cardiovascular System: Bendehiba Latroche, MD, DIS, DIUkskamkalpanaОценок пока нет
- ECG NotesДокумент7 страницECG NotesShams NabeelОценок пока нет
- Emergencies in GP DR Ibrahim AlmoosaДокумент70 страницEmergencies in GP DR Ibrahim Almoosaموسى التميميОценок пока нет
- Cvs MnemonicsДокумент3 страницыCvs MnemonicsSuneel Kaushik KОценок пока нет
- Congenital Heart Disease (CHD) : Kussia Ayano (MD)Документ54 страницыCongenital Heart Disease (CHD) : Kussia Ayano (MD)Yemata HailuОценок пока нет
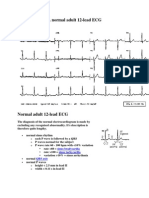
- A Normal Adult 12-Lead ECG: Sinus Bradycardia Sinus Tachycardia QRS AxisДокумент4 страницыA Normal Adult 12-Lead ECG: Sinus Bradycardia Sinus Tachycardia QRS AxisSharan SandhuОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular MneumonicsДокумент10 страницCardiovascular MneumonicsKaly RieОценок пока нет
- Rheumatic Heart DiseaseДокумент30 страницRheumatic Heart DiseaseDhiraj PantОценок пока нет
- CardiologyДокумент14 страницCardiologyBlescy Raros CarreonОценок пока нет
- Alcapa SyndromeДокумент38 страницAlcapa SyndromeZiaОценок пока нет
- RTC ShockДокумент16 страницRTC ShockMarcelОценок пока нет
- Cardiology MnemonicsДокумент14 страницCardiology MnemonicsAimee Gutierrez100% (1)
- Ninja NerdДокумент3 страницыNinja NerdSalsabila HMОценок пока нет
- Valvular Heart Disease: Dr. Nigussie BerihunДокумент43 страницыValvular Heart Disease: Dr. Nigussie Berihunsisay tigabuОценок пока нет
- Lec 4 A - StrokeДокумент9 страницLec 4 A - StrokeEmily MurrayОценок пока нет
- Pemicu 1A Blok KGD - FK UNTARДокумент72 страницыPemicu 1A Blok KGD - FK UNTARaindrawantoОценок пока нет
- Problem 5 - Emergency Medicine: Group 11Документ68 страницProblem 5 - Emergency Medicine: Group 11Panji Dify AkbarОценок пока нет
- Mnemonic For Emergency MedsДокумент16 страницMnemonic For Emergency MedsAl-nazer Azer AlОценок пока нет
- MnemonicsДокумент9 страницMnemonicsJhey MalanyaonОценок пока нет
- Immediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideОт EverandImmediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideОценок пока нет
- Mnemonics for Medicine: Differential Diagnoses and Other PearlsОт EverandMnemonics for Medicine: Differential Diagnoses and Other PearlsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- AnalgesicДокумент62 страницыAnalgesicAnjum IslamОценок пока нет
- Employee Health Declaration FormДокумент3 страницыEmployee Health Declaration FormKajal KumariОценок пока нет
- Kolon CancerДокумент14 страницKolon CancerzalinaОценок пока нет
- Uretritis GonoreДокумент16 страницUretritis GonoreUswatun HasanahОценок пока нет
- Alkalosis RespiratoryДокумент9 страницAlkalosis RespiratoryJack Eugene LiowОценок пока нет
- 2019 Nbde Partıı GuideДокумент29 страниц2019 Nbde Partıı GuideBinayak UpadhyayaОценок пока нет
- Rosai DiseaseДокумент9 страницRosai DiseaseIrina Gabriela VizureanuОценок пока нет
- Group 10, VitaminsДокумент12 страницGroup 10, VitaminsALCORUОценок пока нет
- Preston Test 3Документ4 страницыPreston Test 3Aleksandra StasiakОценок пока нет
- Asynchronous Activity MiceДокумент3 страницыAsynchronous Activity MiceTrixie Cayetano LopintoОценок пока нет
- ORWH MMM Booklet 508C 1Документ16 страницORWH MMM Booklet 508C 1Manar ShamielhОценок пока нет
- Introduction To DiabetesДокумент13 страницIntroduction To DiabetesNEW GENERATIONSОценок пока нет
- The Uranium Series The Actinides in Homeopathy Ulrich Welte.22975Документ25 страницThe Uranium Series The Actinides in Homeopathy Ulrich Welte.22975Velu SubramanianОценок пока нет
- Rad Rle: Chief ComplaintДокумент17 страницRad Rle: Chief ComplaintAngelo MadjosОценок пока нет
- PDPH Stevenage 2014Документ6 страницPDPH Stevenage 2014Karyadi PrayananggaОценок пока нет
- Neuro-Ophthalmology Review: by Peter Mark G. Chao, MD May 5, 2011Документ48 страницNeuro-Ophthalmology Review: by Peter Mark G. Chao, MD May 5, 2011JL BillsОценок пока нет
- Pathology Restaurant: Menu Pathologic Diagnosis / AppearancesДокумент2 страницыPathology Restaurant: Menu Pathologic Diagnosis / AppearancesNirosha ArulОценок пока нет
- Ectopic EruptionДокумент4 страницыEctopic EruptionBhumika SharmaОценок пока нет
- XenotransplantationДокумент8 страницXenotransplantationEesha FawadОценок пока нет
- Signature Assignment Culminating Argument (PTSD) : Capstone 401 Professor Jose Candelario July 30 2020Документ24 страницыSignature Assignment Culminating Argument (PTSD) : Capstone 401 Professor Jose Candelario July 30 2020klm klmОценок пока нет
- AppendixC - Nutrient Chart PDFДокумент7 страницAppendixC - Nutrient Chart PDFMaria Christina LagartejaОценок пока нет
- Royal Medical Services Professional Training Division Logbook For Surgery ResidentsДокумент58 страницRoyal Medical Services Professional Training Division Logbook For Surgery ResidentsMohammed SameerОценок пока нет
- Flyer 3 Page R1Документ3 страницыFlyer 3 Page R1Fazilah ShahromОценок пока нет
- An Anti-Racist Approach To Achieving Mental Health Equity in Clinical Care - Legha 2020Документ19 страницAn Anti-Racist Approach To Achieving Mental Health Equity in Clinical Care - Legha 2020EricОценок пока нет
- G R Duncanson-Veterinary Treatment of Llamas and Alpacas-CABI (2012)Документ269 страницG R Duncanson-Veterinary Treatment of Llamas and Alpacas-CABI (2012)David Peña TriviñoОценок пока нет
- Can The World Health Organization Meet The Challenge of The Pandemic - DER SPIEGELДокумент9 страницCan The World Health Organization Meet The Challenge of The Pandemic - DER SPIEGELveroОценок пока нет
- Final For Net English M Oh FW 040222Документ466 страницFinal For Net English M Oh FW 040222Abdullah100% (1)
- Cerebral Palsy Practice Essentials: Signs and SymptomsДокумент11 страницCerebral Palsy Practice Essentials: Signs and SymptomsTahsinur RahmanОценок пока нет
- The Epilepsies: Support For Education and Learning: Clinical Case Scenarios-Children and Young People With EpilepsyДокумент42 страницыThe Epilepsies: Support For Education and Learning: Clinical Case Scenarios-Children and Young People With EpilepsyNinia MОценок пока нет
- Ethnomedicinal Plants Used by The Subanen Tribe in Two Villages in Ozamis City Mindanao PhilippineДокумент15 страницEthnomedicinal Plants Used by The Subanen Tribe in Two Villages in Ozamis City Mindanao PhilippineDjamaeОценок пока нет