Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
CHAPTER 5-Modul Bimbingan SPM
Загружено:
Novah GurulooИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CHAPTER 5-Modul Bimbingan SPM
Загружено:
Novah GurulooАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CHAPTER 5: CHEMICAL BONDS
CHAPTER 5: CHEMICAL BONDS
A FORMATION OF COMPOUNDS
Activity 1: Formation of chemical bonds Choose the correct answer from the table. Sharing monoatomic ionic stable chemical bonds arrangement inert covalent duplet
Noble gases are gases. They exist as.. gases and are chemically unreactive . They have ... octet or .. electron
2 3
.. Other atoms besides noble gases tend to achieve the stable electron through the formation of . Two types of chemical bonds : (i) (ii) ... bond - formed when atoms join together by transferring of electrons ... bond - formed when atoms join together by ..of electrons
arrangement
Form 4^^Modul Bimbingan SPM 5
Page 1
CHAPTER 5: CHEMICAL BONDS
B Ionic Bonds
Activity 2 : Formation of ions 1 Underline the correct answer. To achieve a stable electron arrangement : (i) A metal atom (donates / accepts) electrons, forming a (positive / negative) ion (ii) 2 (a) called cation. A (non-metal / metal) atom accepts electrons, forming a (positive / negative)
ion called anion. Complete the diagram below.
(b)
(Refer to page 84 85 - F4 Chemistry text book)
Activity 3 : Formation of ionic bonds
Form 4^^Modul Bimbingan SPM 5
Page 2
CHAPTER 5: CHEMICAL BONDS
Fill in the blanks with the correct words. 1 Formation of ionic compound, sodium chloride ( )
NaCl
Electron arrangement of sodium atom is ............................................................. A sodium atom ..one electron to achieve the electron
arrangement which is 2.8.
Sodium ion, .......... is formed Electron arrangement of chlorine atom is.. Electron from sodium atom is transferred to a .atom A chlorine atom electron from sodium atom to .. the stable electronwhich is 2.8.8
Chloride ion, .. is formed The sodium ion, and chloride ion, formed are ..to one another
+
Na
Cl
to form an ionic compound ..,
NaCl
The strong .forces between the opposite-charged ions is called .bond.
(Refer to page 86 - F4 Chemistry text book)
2 Complete the diagram below.
2.8.1 Sodium atom,Na
2.8.7 Chlorine atom,Cl
............. Sodium ion,
............... Chloride ion, ..
Form 4^^Modul Bimbingan SPM 5
Page 3
CHAPTER 5: CHEMICAL BONDS
3 (a)
Fill in the blanks with the correct answers. Formation of ionic compound magnesium chloride, MgCl2 . Electron arrangement of magnesium atom is ..................................................
A magnesium atom .two electrons to achieve the electron arrangement which is, 2.8.
Magnesium ion, .......... is formed Electron arrangement of chlorine atom is Electrons from magnesium atom is transferred to two .atoms A chlorine atom electron from magnesium atom to .. the stable electron which is 2.8.8.
Chloride ion,.. is formed The magnesium ion,Mg2+ and two chloride ions, formed are to one
Cl
another to form an ionic compound ., MgCl2 The strong .forces between the opposite-charged ions is
called ..bond
(Refer to page 86 - F4 Chemistry text book)
(b) Complete the diagram below.
(Refer to page 86 - F4 Chemistry text book)
Form 4^^Modul Bimbingan SPM 5
Page 4
CHAPTER 5: CHEMICAL BONDS
C Covalent Bonds Activity 4 : Formation of covalent bonds Fill in the blanks with the correct words. 1 Covalent bonds are formed when .. atoms .. electrons to achieve 2 . electron arrangements . Types of covalent bonds:(i) (ii) (iii) A single bond is formed when of electrons is shared between two atoms. A double bond is formed when ..of electrons is shared between two atoms. A triple bond is formed when .of electrons is shared between two atoms. Formation of hydrogen molecules, H2 :-
A hydrogen atom has valence electron, with an electron arrangement of... It needs .. more electron to achieve the .. electron arrangement ..hydrogen atoms one electron each for Shared-paired electrons forms a .. bond in the hydrogen molecule, H2 Single bond holds the two hydrogen atoms together because the shared-pair of
5 (a)
electrons is attracted to the.. of both atoms Complete the diagram below.
(b) A covalent bond can be illustrated by using.
Form 4^^Modul Bimbingan SPM 5
Page 5
CHAPTER 5: CHEMICAL BONDS
Activity 5 : Formation of covalent bonds 1 Formation of oxygen molecules, O2 : An oxygen atom has valence electron, with an electron arrangement of..
It needs .more electrons to achieve the .. electron arrangement
.....oxygen atoms sharepairs of electrons forming a..bond 2 Draw the electron arrangement for the formation of oxygen molecule. (a) [Proton number : O, 8 ;]
(b) Illustrate the formation of oxygen molecule using the Lewis structure.
Formation of a nitrogen molecule, N2 : A nitrogen atom has valence electron, with an electron arrangement .....
It needs more electrons to achieve the .. electron arrangement ..nitrogen atoms sharepairs of electrons forming a covalent
bond Draw the electron arrangement for the formation of nitrogen molecule. [Proton number : N, 7]
(b) Illustrate the formation for nitrogen molecule using the Lewis structure.
Form 4^^Modul Bimbingan SPM 5
Page 6
CHAPTER 5: CHEMICAL BONDS
Activity 6 1 Draw the electron arrangements for the formation of the following ionic compounds: [Proton number : Li, 3 ; Ca, 20 ; O, 8 ; Cl, 17 ] (a) Lithium oxide,
Li2 O
(b)
Calcium chloride,
CaCl2
Draw the electron arrangements for the formation of the following covalent compounds [Proton number : C, 6 ; Cl, 17, : O, 8] (a) Tetrachloromethane, CCl4
(b)
Carbon dioxide molecule, CO2
Form 4^^Modul Bimbingan SPM 5
Page 7
CHAPTER 5: CHEMICAL BONDS
Complete the table below to compare the characteristics for the formation of ionic and covalent bonds. Ionic bond Valence electrons Characteristic Electrons involved Elements Electron transfer to achieve stable electron arrangement Bond formation Particles Non-metals atom and non metal atoms Covalent bond
D PROPERTIES OF IONIC AND COVALENT BONDING Activity 7 : Physical properties of ionic and covalent compounds 1. Complete the table of the properties of ionic and covalent compounds, using the words given in the box : conduct electricity in aqueous solution or molten state all state low solid high solid, liquid, gas Ionic compound Properties Physical states at room temperature Melting points Boiling points Electrical Conductivity Solubility in water Solubility in organic solvent 2 Explain why ionic compounds are able to conduct electricity in aqueous solution or in molten state but not in solid state. ... 3 Explain why covalent compound do not conduct electricity in all states. . 4 Explain why ionic compounds have higher melting points than covalent compounds.
Page 8
do not conduct electricity at insoluble soluble
Covalent compound
Form 4^^Modul Bimbingan SPM 5
CHAPTER 5: CHEMICAL BONDS
. 5 .. Example of covalent compounds ;-............................................................................................................................................ Uses of covalent compounds as solvent in our daily lives: .................................................................................................................................... (Refer to page 90 - 91 - F4 Chemistry text book) Activity 8 1
Atom A (a)
Atom B
Write the electron arrangement for atom A. ..
(b) A and B can form a compound (i) What type of bond holds atom A and B together? .. (ii) What will happen to atom A during the formation of the compound with atom B? .. (iii) Draw the electron arrangement of the compound formed in (b)(ii).
(iv) (c)
State one physical property of the compound formed. .. Carbon atom, C, with an electron arrangement of 2.4 can combine with atom B to form a compound. (i) What is the molecular formula of the compound formed? . If the relative atomic masses of carbon is 12 and B is 32, what is the relative molecular mass of the compound in c(i).
(ii)
Form 4^^Modul Bimbingan SPM 5
Page 9
CHAPTER 5: CHEMICAL BONDS
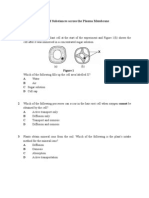
.. Activity 9 1 The diagram below shows the proton number and the nucleon number for three atoms of elements, E, G and W. The letters used do not represent the actual symbols of the elements.
12 6
(a)
23
35
11
17
The reaction between atoms of element G and W forms an ionic compound whereas the reaction between atoms of element E and W forms a covalent compound. Explain how these ionic and covalent compounds are formed.
Ionic compound
Electron arrangement of an atom of element G is ................................................... Atom G .one electron to achieve the electron arrangement which is 2.8 G ion, .......... is formed Electron arrangement of atom W is.. Electron from atom G is transferred to an atom of Atom W receives .electron from atom G to achieve the .. electron arrangement which is 2.8.8 W ion,.. is formed The G ion, .. and W ion, ..formed are ..to one another to form an .compound, . The strong .forces between the opposite-charged ions is called .. bond.
Covalent bond
Atom E has ... valence electrons, with an electron arrangement of..... It needs .. more electrons to achieve the .. electron arrangement One atom of E contributes four electrons for Atom W has valence electrons, with an electron arrangement of. It needs .more electron to achieve the.electron arrangement One atom of E share a pair of electrons with .atoms of W Covalent compound of is formed
Page 10
Form 4^^Modul Bimbingan SPM 5
CHAPTER 5: CHEMICAL BONDS
Form 4^^Modul Bimbingan SPM 5
Page 11
Вам также может понравиться
- Skincare Routine Order Cheat SheetДокумент10 страницSkincare Routine Order Cheat SheetYel Salenga100% (3)
- Chapter 5: Chemical Bonds: A Formation of Compounds Learning OutcomesДокумент9 страницChapter 5: Chemical Bonds: A Formation of Compounds Learning OutcomesWong Wai Lun100% (1)
- Mantras Om or Aum and The Gayatri MantraДокумент131 страницаMantras Om or Aum and The Gayatri MantraFrancis Lobo67% (3)
- Stopping by Woods On A Snowy EveningДокумент9 страницStopping by Woods On A Snowy EveningJulia Garces100% (2)
- Critical Analysis of W.H Auden Poems The PDFДокумент8 страницCritical Analysis of W.H Auden Poems The PDFMöĤämmĔd äĹ-ŚäÁdï100% (1)
- Revision - Additional Mathematics F4.1 - FunctionsДокумент4 страницыRevision - Additional Mathematics F4.1 - FunctionsJiaRenTeohОценок пока нет
- Biology SPM RevisionДокумент16 страницBiology SPM RevisionNoor Hidayah Sambli100% (1)
- CHAPTER 2 BiologyДокумент10 страницCHAPTER 2 BiologyMohamad ShukriОценок пока нет
- Instructor'S Manual To Accompany Charles Kittel Introduction To Solid State PhysicsДокумент62 страницыInstructor'S Manual To Accompany Charles Kittel Introduction To Solid State Physicsn4meОценок пока нет
- 1 Matter & The Atomic Structure ModulДокумент43 страницы1 Matter & The Atomic Structure Modulryder1man6433100% (1)
- Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 1Документ27 страницChemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 1ZekZanaОценок пока нет
- Alkane Alkene QuestionsДокумент10 страницAlkane Alkene QuestionsormattОценок пока нет
- Cell Structure and OrganisationДокумент26 страницCell Structure and OrganisationNor Hafiza AhmadОценок пока нет
- Gondola CalculationДокумент6 страницGondola CalculationBudi SusantoОценок пока нет
- Polymers and Polymerization - Worksheet: Monomer Polymer StructureДокумент2 страницыPolymers and Polymerization - Worksheet: Monomer Polymer StructureLam Hoang0% (1)
- 22precise Advanced Level Chemistry Practical Guide PDFДокумент92 страницы22precise Advanced Level Chemistry Practical Guide PDFCorina Stanculescu100% (1)
- 7.3 (B) Preparing Standard SolutionДокумент18 страниц7.3 (B) Preparing Standard SolutionNovah GurulooОценок пока нет
- Chem U5 A2 EdexcelДокумент48 страницChem U5 A2 EdexcelReez SinhaОценок пока нет
- SPM Chemistry Paper 2 ExerciseДокумент16 страницSPM Chemistry Paper 2 ExerciseMohd HaidilОценок пока нет
- 5 Chemical BondsДокумент10 страниц5 Chemical BondsNor Fairul Bin SudarmanОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 2011 No LogoДокумент96 страницChemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 2011 No Logohome8008100% (2)
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Oxidation and Reduction (Part 1)Документ22 страницыSPM Chemistry Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Oxidation and Reduction (Part 1)Ck OoiОценок пока нет
- Ecological Quality RatioДокумент24 страницыEcological Quality RatiofoocheehungОценок пока нет
- Tokyo Guidelines 2018Документ115 страницTokyo Guidelines 2018Alik Razi100% (1)
- Chemistry Paper 2 Questions PDF August 24 2011-12-50 PM 472kДокумент22 страницыChemistry Paper 2 Questions PDF August 24 2011-12-50 PM 472kJamaludin Abu KassimОценок пока нет
- Underground Equipment SelectionДокумент44 страницыUnderground Equipment SelectionCherotich Silas cheboseiОценок пока нет
- Reaction Kinetics Question PDFДокумент8 страницReaction Kinetics Question PDFdanielmahsa0% (1)
- Structured Question: Analysis of Past Year Questions From 2003 - 2008Документ27 страницStructured Question: Analysis of Past Year Questions From 2003 - 2008Nazreen NashruddinОценок пока нет
- Pahang STPM Trial 2011 Chemistry Paper 2 (W Ans)Документ21 страницаPahang STPM Trial 2011 Chemistry Paper 2 (W Ans)plouffle100% (1)
- Folio Biology A+Документ67 страницFolio Biology A+Nina IsmailОценок пока нет
- Redox Reaction (Past Year)Документ5 страницRedox Reaction (Past Year)Kuryu ZuherlyОценок пока нет
- Kimia Module 1 5 Diagnostik f4 PDFДокумент70 страницKimia Module 1 5 Diagnostik f4 PDFJuan DavisОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Paper 3 SampleДокумент3 страницыChemistry Paper 3 Samplerihdus2100% (2)
- XII Past Papers (Maths)Документ48 страницXII Past Papers (Maths)Behroz Usman SiddiquiОценок пока нет
- Cls Jeead-17-18 Xii Che Target-5 Set-2 Chapter-1Документ34 страницыCls Jeead-17-18 Xii Che Target-5 Set-2 Chapter-1abhi0% (2)
- 3 (Movement of Substances Across Plasma Membrane)Документ16 страниц3 (Movement of Substances Across Plasma Membrane)Jia YueОценок пока нет
- Chemistry SPM 2016 SaltДокумент2 страницыChemistry SPM 2016 SaltAzie Nurul AkhtarОценок пока нет
- Redox MCQ Cie + AnswersДокумент1 страницаRedox MCQ Cie + Answersby7777Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 Teacher S Guide 2009Документ33 страницыChapter 4 Teacher S Guide 2009Chen ShyanОценок пока нет
- 49 Question Trial SPM ChemistryДокумент1 страница49 Question Trial SPM ChemistrychongpeisiОценок пока нет
- Industrial Wastewater Treatment Via PhotocatalysisДокумент34 страницыIndustrial Wastewater Treatment Via PhotocatalysisAlok GargОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3Документ7 страницChapter 3api-3841154Оценок пока нет
- Summer Task Mathematics-VIДокумент5 страницSummer Task Mathematics-VIUmair IslamОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic InductionДокумент5 страницElectromagnetic InductionfaisalsmkpnОценок пока нет
- Biology Chapter 2 Topical ExerciseДокумент3 страницыBiology Chapter 2 Topical ExerciseAlan WangОценок пока нет
- Matriculation Chemistry (Electrochemistry)Документ77 страницMatriculation Chemistry (Electrochemistry)ridwan100% (3)
- Chap1 StoichiometryДокумент42 страницыChap1 StoichiometryAndré QianОценок пока нет
- MSC. - Chemistry - 2013Документ179 страницMSC. - Chemistry - 2013Anonymous kT0ONWОценок пока нет
- COM123Документ44 страницыCOM123Mùbãrâk MøhàmmãdОценок пока нет
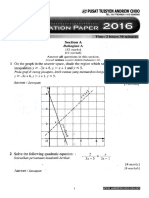
- 2016 SPM Maths - Paper 2 PDFДокумент16 страниц2016 SPM Maths - Paper 2 PDFwww.tuitionking763780% (5)
- Stoichiometry Questions & AnswersДокумент2 страницыStoichiometry Questions & Answersnosirat aladeОценок пока нет
- Organic Chemistry Assignment 1 - SCH4U h5, Chemistry, 12, UniversityДокумент4 страницыOrganic Chemistry Assignment 1 - SCH4U h5, Chemistry, 12, UniversityAnonymous iadge07t0% (3)
- CHAPTER 7 Light, Sight and ColourДокумент43 страницыCHAPTER 7 Light, Sight and ColourAkmar MataliОценок пока нет
- Algebraic Method To Balance Chemical EquationДокумент3 страницыAlgebraic Method To Balance Chemical EquationBruce WalkerОценок пока нет
- Format of Lab Report Example 8609Документ14 страницFormat of Lab Report Example 8609herrk167% (3)
- H2 Biology - Notes On Genetics of VirusesДокумент10 страницH2 Biology - Notes On Genetics of VirusesSefLRhoОценок пока нет
- 1.0 Title of Experiment: BKF2741 Chemical Reaction Engineering Laboratory IДокумент11 страниц1.0 Title of Experiment: BKF2741 Chemical Reaction Engineering Laboratory IElaine PuiОценок пока нет
- 1 - Activity Coefficent CalculatorДокумент7 страниц1 - Activity Coefficent CalculatordhavaleshОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9Документ13 страницChapter 9Nadira AtiqahОценок пока нет
- Predicting Redox Reactions (No MS)Документ1 страницаPredicting Redox Reactions (No MS)AsadОценок пока нет
- Physics Chapter 5 Revision Notes For ExamДокумент2 страницыPhysics Chapter 5 Revision Notes For ExammrdarkknighificationОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Final Study Guide: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionДокумент22 страницыChemistry Final Study Guide: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The Questionsrahimi@verizon.netОценок пока нет
- SPM Checklist For ChemistryДокумент23 страницыSPM Checklist For Chemistryadella75100% (3)
- Tipo Test Tilley PDFДокумент7 страницTipo Test Tilley PDFJesus27Оценок пока нет
- Manual-4 6 7Документ412 страницManual-4 6 7Nina Brown100% (1)
- AS Chemsitry UNIT 1 Class Test Edexcel Exam PapersДокумент26 страницAS Chemsitry UNIT 1 Class Test Edexcel Exam Papersecs90603Оценок пока нет
- Section #1: All Atoms Are Electrically NeutralДокумент2 страницыSection #1: All Atoms Are Electrically NeutralJanelyn GarinОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 5 Chem BondДокумент6 страницTutorial 5 Chem BondaribniminnakОценок пока нет
- Acids and Bases MenuДокумент32 страницыAcids and Bases MenuNovah GurulooОценок пока нет
- Chemistry F4: Theme 3: Interaction Between Matters Chapter 6: Acid, Base & Salt (6.8 - 6.11)Документ29 страницChemistry F4: Theme 3: Interaction Between Matters Chapter 6: Acid, Base & Salt (6.8 - 6.11)Novah GurulooОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7: Acid and Base 7.4: NeutralisationДокумент30 страницChapter 7: Acid and Base 7.4: NeutralisationNovah GurulooОценок пока нет
- 7.3 (A)Документ21 страница7.3 (A)Novah GurulooОценок пока нет
- Chemistry F4: Theme 3: Interaction Between Matters Chapter 6: Acid, Base & Salt (6.1 - 6.7)Документ18 страницChemistry F4: Theme 3: Interaction Between Matters Chapter 6: Acid, Base & Salt (6.1 - 6.7)Novah GurulooОценок пока нет
- Effect of Osmosis Crossword Puzzle AnswerДокумент2 страницыEffect of Osmosis Crossword Puzzle AnswerNovah GurulooОценок пока нет
- Paper On SUPERSTITIONS WOMEN by Santosh Takale at NCSM Kolkata-LibreДокумент7 страницPaper On SUPERSTITIONS WOMEN by Santosh Takale at NCSM Kolkata-LibreNovah GurulooОценок пока нет
- Scheme of Work Kelab Siaraya 2016Документ2 страницыScheme of Work Kelab Siaraya 2016Novah GurulooОценок пока нет
- Chem Form 4 Yearly Plan 2014Документ30 страницChem Form 4 Yearly Plan 2014Novah GurulooОценок пока нет
- Worksheet 6.3 The Factor Concentration of IonДокумент3 страницыWorksheet 6.3 The Factor Concentration of IonNovah GurulooОценок пока нет
- Latest Novah (Edited by TPC & Ysp) RPT Chem Form 5 2015Документ31 страницаLatest Novah (Edited by TPC & Ysp) RPT Chem Form 5 2015Novah GurulooОценок пока нет
- International Specification For Orienteering Maps 2000Документ18 страницInternational Specification For Orienteering Maps 2000MapaybrujulaОценок пока нет
- Worksheet 7.2 The Relationship Between Different Concentrations of Hydrochloric Acid and PH ValuesДокумент4 страницыWorksheet 7.2 The Relationship Between Different Concentrations of Hydrochloric Acid and PH ValuesNovah GurulooОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4Документ171 страницаChapter 4Novah GurulooОценок пока нет
- Effect of Osmosis Crossword Puzzle AnswerДокумент2 страницыEffect of Osmosis Crossword Puzzle AnswerNovah GurulooОценок пока нет
- Worksheet 8 An Ionic Equation For The Formation of Lead (II) IodideДокумент3 страницыWorksheet 8 An Ionic Equation For The Formation of Lead (II) IodideNovah Guruloo0% (1)
- Worksheet 9.1 Hardness of Alloy and Pure MetalДокумент2 страницыWorksheet 9.1 Hardness of Alloy and Pure MetalNovah GurulooОценок пока нет
- Worksheet 9.2 Resistance To Rust of Alloy and Pure MetalДокумент2 страницыWorksheet 9.2 Resistance To Rust of Alloy and Pure MetalNovah GurulooОценок пока нет
- Worksheet 7.1 The Role of Water in Showing The Properties of AcidsДокумент2 страницыWorksheet 7.1 The Role of Water in Showing The Properties of AcidsNovah GurulooОценок пока нет
- Worksheet 7.1 The Role of Water in Showing The Properties of AcidsДокумент2 страницыWorksheet 7.1 The Role of Water in Showing The Properties of AcidsNovah GurulooОценок пока нет
- Worksheet 6.4 To Construct An Electrochemical CellДокумент3 страницыWorksheet 6.4 To Construct An Electrochemical CellNovah GurulooОценок пока нет
- C2 Body CoordinationДокумент17 страницC2 Body CoordinationNovah GurulooОценок пока нет
- Worksheet 7.3 The Strength of Ethanoic Acid and Nitric Acid of The Same ConcentrationДокумент3 страницыWorksheet 7.3 The Strength of Ethanoic Acid and Nitric Acid of The Same ConcentrationNovah GurulooОценок пока нет
- Worksheet 6.1 The Factor of The Position of IonsДокумент6 страницWorksheet 6.1 The Factor of The Position of IonsNovah GurulooОценок пока нет
- Worksheet 6.2 The Factor of Specific ElectrodesДокумент4 страницыWorksheet 6.2 The Factor of Specific ElectrodesNovah GurulooОценок пока нет
- Worksheet 6.2 The Factor of Specific ElectrodesДокумент4 страницыWorksheet 6.2 The Factor of Specific ElectrodesNovah GurulooОценок пока нет
- Worksheet 5.1 Compare The Physical Properties of The Ionic and Covalent CompoundsДокумент3 страницыWorksheet 5.1 Compare The Physical Properties of The Ionic and Covalent CompoundsNovah GurulooОценок пока нет
- Worksheet 4.1 Compare The Reactivity of The Group 1 ElementsДокумент2 страницыWorksheet 4.1 Compare The Reactivity of The Group 1 ElementsNovah GurulooОценок пока нет
- Optik: Original Research ArticleДокумент6 страницOptik: Original Research ArticlesimarpreetОценок пока нет
- ACR39U-U1: (USB Type A) Smart Card ReaderДокумент8 страницACR39U-U1: (USB Type A) Smart Card Readersuraj18in4uОценок пока нет
- YoungMan EN131 GUIDEДокумент16 страницYoungMan EN131 GUIDErcpawar100% (1)
- 8-General Rules For Erection ProcedureДокумент4 страницы8-General Rules For Erection ProcedurePrijin UnnunnyОценок пока нет
- Exam 3 DynamicsДокумент7 страницExam 3 DynamicsJulioОценок пока нет
- Javanese PeopleДокумент22 страницыJavanese PeopleDenisaОценок пока нет
- Surface Finish Measurement NotesДокумент32 страницыSurface Finish Measurement NotesAneez ShresthaОценок пока нет
- SOPДокумент16 страницSOPjerome marquezОценок пока нет
- 1.1.3.12 Lab - Diagram A Real-World ProcessДокумент3 страницы1.1.3.12 Lab - Diagram A Real-World ProcessHalima AqraaОценок пока нет
- MSDS DowthermДокумент4 страницыMSDS DowthermfebriantabbyОценок пока нет
- Discrete Wavelet TransformДокумент10 страницDiscrete Wavelet TransformVigneshInfotechОценок пока нет
- ANG DELAVEGA FinalPositionPaperДокумент6 страницANG DELAVEGA FinalPositionPaperZane IbalaОценок пока нет
- Crma Unit 1 Crma RolesДокумент34 страницыCrma Unit 1 Crma Rolesumop3plsdn0% (1)
- Etoricoxib - Martindale 39thДокумент2 страницыEtoricoxib - Martindale 39thCachimbo PrintОценок пока нет
- 15 Benefits of CyclingДокумент8 страниц15 Benefits of CyclingJoycs PintoОценок пока нет
- Minimalist KWL Graphic OrganizerДокумент2 страницыMinimalist KWL Graphic OrganizerIrish Nicole AlanoОценок пока нет
- V. Jovicic and M. R. Coop1997 - Stiffness, Coarse Grained Soils, Small StrainsДокумент17 страницV. Jovicic and M. R. Coop1997 - Stiffness, Coarse Grained Soils, Small StrainsxiangyugeotechОценок пока нет
- 3397 - Ciat LDC 300VДокумент71 страница3397 - Ciat LDC 300VPeradОценок пока нет
- MMW ReviewerДокумент3 страницыMMW ReviewerMarcSaloj NeryОценок пока нет
- Coding DecodingДокумент21 страницаCoding DecodingAditya VermaОценок пока нет
- ECE199R-C12 Final Document OJTДокумент48 страницECE199R-C12 Final Document OJTRigel ZabateОценок пока нет
- Reading Part 2Документ14 страницReading Part 2drama channelОценок пока нет
- 12-Week Off-Season Training Programme Junior Rugby (U18 - U21)Документ5 страниц12-Week Off-Season Training Programme Junior Rugby (U18 - U21)LeBron JamesОценок пока нет