Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Maths Cs Form 5
Загружено:
juriah binti ibrahimИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Maths Cs Form 5
Загружено:
juriah binti ibrahimАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
SEKOLAH MENENGAH TEKNIK SEPANG, 43800 DENGKIL, SELANGOR
FORM 5 MATHEMATICS SCHEME OF WORK 2009
WEEK LEARNING AREAS & LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1 Number Bases 1.1 Understand and use the concept of number in bases two, eight and five. LEARNING OUTCOMES
i. State zero, one, two, three, as a number in base (a)
two; (b) eight; (c) five. ii. State the value of a digit of a number in base (a) two, (b) eight; (c) five. iii. Write a number in base (a) two; (b) eight; (c) five in expanded notation. iv. Convert a number in base (a) two; (b) eight; (c) five; to a number in base ten and vice versa. v. Convert a number in a certain base to a number in another base. vi. Perform computations involving (a) addition; (b) subtraction of two numbers in base two. i. Draw the graph of a a. linear function: y= ax+ b where a and b are constants; b. quadratic function: y = ax 3 + bx + c where a, b and c are constants, a 0; c. cubic function: y= ax 3 + bx2 + cx+ d where a, b, c and d are constants, a 0 d. reciprocal function: y = a/x , where a is a constant, a 0. ii. Find from a graph , a. the value of y given a value of x, b. the value(s) of x, given a value of y. iii. Identify a. the shape of graph given a type of function; b. the type of function given a graph; c. the graph given a function and vice versa. iv. Sketch the graph of a given linear, quadratic, cubic or reciprocal function.
1&2
2 Graphs of Functions II 2.1 Understand and use the concept of graph of functions
2&3
CHINESE NEW YEAR & EVENT HOLIDAY 2.2 Understand and use i. Find the point(s) of intersection of two graphs. the concept of the ii. Obtain the solution of an equation by finding the solution of an points(s) of intersection of two graphs. equation by graphical iii. Solve problems involving solution of an equation by method graphical method. 2.3 Understand and use the concept of the region representing inequalities in two variables i. Determine whether a given point satisfies a. y= ax + b; or b. y > ax + b; or c. y < ax + b. ii. Determine the position of a given point relative to the graph y = ax + b. iii. Identify the region satisfying y > ax + b or y < ax + b. iv. Shade the regions representing the inequalities a. y > ax+b or y<ax+b; b. y > ax+b or y ax +b. v. Determine the region which satisfies two or more simultaneous linear inequalities.
3 Transformations III 3.1 Understand and use the concept of combination of two transformations.
i. Determine the image of an object under combination of
two isometric transformations.
ii. Determine the image of an object under combination of ,
6, 7, &8
a. two enlargements; b. an enlargement and an isometric transformation. iii. Draw the image of an object under combination of two transformations. iv. State the coordinates of the image of a point under combined transformation. v. Determine whether combined transformation AB is equivalent to combined transformation BA. vi. Specify two successive transformations in a combined transformation given the object and the image. vii. Specify a transformation which is equivalent to the combination of two isometric transformations. viii. Solve problems involving transformation.
4 Matrices 4.1 Understand and use the concept of matrix.
i. Form a matrix from given information. ii. Determine a. the numbers of rows; b. the number of columns; c. the order of a matrix. iii. Identify a specific element in a matrix TEST 1 FIRST MID-TERM BREAK i. Determine whether two matrices are equal. ii. Solve problems involving equal matrices Determine whether addition or subtraction can be performed ' on two given matrices. Find the sum or the difference of two matrices. Perform addition and subtraction on a few matrices. Solve matrix equation involving addition and subtraction. i. Multiply a matrix by a number. ii. Express a given matrix as multiplication of a matrix by a number. iii. Perform calculation on matrices involving addition, subtraction and scalar multiplication. iv. Solve matrix equations involving addition, subtraction and scalar multiplication. i. Determine whether two matrices can be multiplied and state the order of the product when the two matrices can be multiplied. ii. Find the product of two matrices. iii. Solve matrix equations involving multiplication of two matrices. i. Determine whether a given matrix is an identity matrix by multiplying it to another matrix. ii. Write identity matrix of any order. iii. Perform calculation involving identity matrices.
10 11 12 4.2 the Understand and use concept of equal matrices. 4.3 Perform addition and subtraction on matrices.
12
4.4 Perform multiplication of a matrix by a number. 12
13
4.5 Perform multiplication of two matrices.
4.6 the 13
Understand and use
concept of identity matrix.
4.7 the 13
Understand and use
i. Determine whether a 2 x 2 matrix is the inverse matrix of
another 2 x 2 matrix.
concept of inverse matrix.
ii. Find the inverse matrix of a 2 x 2 matrix by using
a. method of solving simultaneous linear equations; b. formula.
13
4.8 Solve simultaneous linear equations by using matrices.
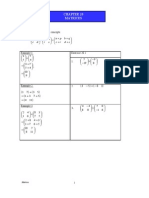
i. Write down simultaneous linear equations in matrix form. ii. Find the matrix in q c d q = k by using inverse
p a b p h
matrix. iii. Solve simultaneous linear equations by using the matrix method. iv. Solve problems involving matrices.
5 Variations 5.1 Understand and use the concept of direct variation.
i. State the changes in a quantity with respect to changes
ii. in another quantity, in everyday life situations involving direct variation. Determine from given information whether a quantity varies directly as another quantity. Express a direct variation in the form of equation involving two variables. Find the value of a variable in a direct variation when sufficient information is given. Solve problems involving direct variation for the following cases.
14
iii. iv. v.
y x, y x 2 , y x 3 , y x 2
1
5.2 Understand and use the concept of inverse variation.
14
i. State the changes in a quantity with respect to changes in another quantity, in everyday life situations involving inverse variation. ii. Determine from given information whether a quantity varies inversely as another quantity. iii. Express an inverse variation in the form of equation involving two variables. iv. Find the value of a variable in an inverse variation when sufficient information is given. v. Solve problems involving direct variation for the following cases. 1 1 1 1 y , y 2 , y 3 , y x x x x i. Represent a joint variation by using the symbol for thefollowing cases. a. Two direct variations b. Two inverse variations c. A direct variation and an inverse variation ii. Express a joint variation in the form of equation. iii. Find the value of a variable in a joint variation when sufficient information is given. iv. Solve problems involving joint variation.
5.3 Understand and use the concept of joint variation. 15
16
6 Gradient and Area Under a Graph 6.1 Understand and use the concept of quantity represented by the
i. State the quantity represented by the gradient of a graph. ii. Draw the distance-time graph, given a. a table of distance-time values; b. a relationship between distance and time.
gradient of a graph.
iii. Find and interpret the gradient of a distance-time graph. iv. Find the speed for a period of time from a distance-time graph. v. Draw a graph to show the relationship between two variables representing certain measurements and state the meaning of its gradient. i. State the quantity represented by the area under a graph. ii. Find the area under a graph. iii. Determine the distance by finding the area under the following types of speed-time graphs. a. v = k (uniform speed) b. v= k t c. v=kt+h d. A combination of the above iv. Solve problems involving gradient and area under a graph. i. Determine the sample space of an experiment with equally likely outcomes. ii. Determine the probability of an event with equiprobable sample space. iii. Solve problems involving probability of an event. i. State the complement of an event in a. words; b. set notation. ii. Find the probability of the complement of an event. i. List the outcomes for events a. A or B as elements of the set A B B b. A and 8 as elements of the set A ii. Find the probability by listing the outcomes of the combined event a. A or B b. A and B iii. Solve problems involving probability of combined event. MID-TERM EXAMINATION FIRST TERM BREAK
6.2 Understand the concept of quantity represented by the area under a graph. 17
18
7 Probability 11 7.1 Understand and use the concept of probability of an event. 7.2 Understand and use the concept of probability of the complement of an event.
18
19
7.3 Understand and use the concept of probability of combined event.
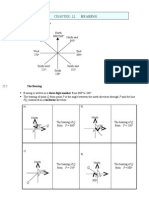
20 & 21 22 & 23 8 Bearing 8.1 Understand and use the concept of bearing. 24 & 25
i. Draw and label the eight main compass directions. a. north, south, east, west b. north-east, north-west, south-east, south-west ii. State the compass angle of any compass direction. iii. Draw a diagram which shows the direction of B relative to A , given the bearing of B from A. iv. State the bearing of point A from point B based on given information. v. Solve problems involving bearing. i. ii. iii. iv. Sketch a great circle through the north and south poles. State the longitude of a given point. , Sketch and label a meridian with the longitude given. Find the difference between two longitudes.
26
9 Earth as a Sphere 9.1 Understand and use the concept of longitude. 9.2 the Understand and use
26
i. Sketch a circle parallel to the equator. ii. State the latitude of a given point.
26
27
28
28 & 29
iii. Sketch and label a parallel of latitude. iv. Find the difference between two latitudes. i. State the latitude and longitude of a given place. 9.3 Understand the ii. Mark the location of a place. concept of location iii. Sketch and label the latitude and longitude of a given of a place. place. 9.4 Understand and use i. Find the length of an arc of a great circle in nautical mile, the given the subtended angle at the centre of the earth and concept of distance on vice versa. the ii. Find the distance between two points measured along a surface of the earth to meridian, given the latitudes of both points. solve iii. Find the latitude of a point given the latitude of another problems. point and the distance between the two points along the same meridian. iv. Find the distance between two points measured along the equator given the longitudes of both points. v. Find the longitude of a point given the longitude of another point and the distance between the two points along the equator. vi. State the relation between the radius of the earth and the radius of a parallel of latitude. vii. State the relation between the length of an arc on the equator between two meridians and the length of the corresponding arc on a parallel of latitude. viii. Find the distance between two points measured along a parallel of latitude. ix. Find the longitude of a point given the longitude of another point and the distance between the two points along a parallel of latitude. x. Find the shortest distance between two points on the surface of the earth. xi. Solve problems involving a. distance between two points; b.travelling on the surface of the earth. , 10 Plan and Elevation i. Identify orthogonal projection. 10.1 Understand and use ii. Draw orthogonal projection, given an object and a the plane. concept of iii. Determine the difference between an object and its orthogonal orthogonal projection with respect to edges and projection. angles i. Draw the plan of a solid object. ii. Draw a. the front elevation; b.the side elevation; 10.2 Understand and use of a solid object. the iii. Draw concept of plan and a. the plan; elevation. b.the front elevation; c. the side elevation; of a solid object to scale. iv. Solve problems involving plan and elevation. concept of latitude. REVISION (PREPARATION FOR TRIAL SPM EXAMINATION) FIRST TRIAL SPM DISCUSSION OF FIRST TRIAL SPM PAPER SECOND MID-TERM BREAK REVISION (PREPARATION FOR SPM EXAMINATION) HARI RAYA AIDILFITRI & EVENT HOLIDAY
30 31 & 32 33 34 35 37 38
39 44 4546 47 52 Prepared by
REVISION (PREPARATION FOR SPM EXAMINATION) SPM EXAMINATION SCHOOL HOLIDAYS
Checked by
Certified by
Pn. Juriah Binti Ibrahim Head of Mathematics Panel SMTeknik Sepang
Pn. Zainab bt. Mohd Shah Head of Science and Mathematics Department SMTeknik Sepang
Pn. Hajah Siti Fatimah bt. Abd. Manan Senior Assistant of Administration SMTeknik Sepang
Вам также может понравиться
- L. Michael Hall - Wealth Genius Manual (OCR & Non-OCR)Документ284 страницыL. Michael Hall - Wealth Genius Manual (OCR & Non-OCR)chris443197% (32)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorДокумент15 страниц6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Preparing For The ACTДокумент64 страницыPreparing For The ACTNoemie P MarconОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 II The Straight Line ENHANCEДокумент22 страницыChapter 7 II The Straight Line ENHANCEjuriah binti ibrahimОценок пока нет
- Chapter 15 I Trigonometry II ENHANCEДокумент45 страницChapter 15 I Trigonometry II ENHANCEjuriah binti ibrahim100% (1)
- 1hrm-1-Prelims-Mathematics in The Modern World-50copies-BillonesДокумент4 страницы1hrm-1-Prelims-Mathematics in The Modern World-50copies-BillonesInvincibleReineОценок пока нет
- Famous Problems of Geometry and How to Solve ThemОт EverandFamous Problems of Geometry and How to Solve ThemРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- Commonly used MATLAB functions and variablesДокумент36 страницCommonly used MATLAB functions and variablesHadjer zit100% (1)
- ME2353 Finite Element Analysis Lecture NotesДокумент34 страницыME2353 Finite Element Analysis Lecture Notespgkaero100% (2)
- Explorations and Discoveries in Mathematics, Volume 1, Using The Geometer's Sketchpad Version 4От EverandExplorations and Discoveries in Mathematics, Volume 1, Using The Geometer's Sketchpad Version 4Оценок пока нет
- Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form 5Документ10 страницYearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form 5ryeОценок пока нет
- YLP Form 5 MathematicsДокумент18 страницYLP Form 5 MathematicsRisma RobinОценок пока нет
- Yearly Lesson Plan f5 2007Документ10 страницYearly Lesson Plan f5 2007hazwani_sОценок пока нет
- RPT Maths f4 2013Документ16 страницRPT Maths f4 2013Kang CkОценок пока нет
- PLANNING MATHEMATICS LESSONS FORM 4Документ10 страницPLANNING MATHEMATICS LESSONS FORM 4hazwani_sОценок пока нет
- Rancangan Tahunan Matematik 2012Документ39 страницRancangan Tahunan Matematik 2012Zuraidah MustaffaОценок пока нет
- Yearly Math Lesson Plan (2012) Form 5Документ19 страницYearly Math Lesson Plan (2012) Form 5Nie Anthon100% (1)
- Form 4 Modern Mathematics SyllabusДокумент9 страницForm 4 Modern Mathematics Syllabusjuriah binti ibrahim100% (2)
- Rancangan Tahunan P&P Mathematics Form 4Документ25 страницRancangan Tahunan P&P Mathematics Form 4Mohd Sani Abd HamidОценок пока нет
- RPT : MATHEMATICS FORM 5 YEARLY PLAN 2010Документ14 страницRPT : MATHEMATICS FORM 5 YEARLY PLAN 2010Madiah JaafarОценок пока нет
- RPT - Add Math F5Документ12 страницRPT - Add Math F5supbarОценок пока нет
- Sheme of Work Mat F5Документ17 страницSheme of Work Mat F5mpuziahОценок пока нет
- F4 Maths YPДокумент10 страницF4 Maths YPKelvinYongОценок пока нет
- 2014 Annual Scheme of Work: SMK Penangah Telupid Form 5 Additional MathematicsДокумент9 страниц2014 Annual Scheme of Work: SMK Penangah Telupid Form 5 Additional Mathematicsjosnih bin murniОценок пока нет
- RPH m3 f3Документ19 страницRPH m3 f3Lynne JbОценок пока нет
- Understanding Number Bases in Different Numeral SystemsДокумент17 страницUnderstanding Number Bases in Different Numeral Systemsriesya1206Оценок пока нет
- Form 4 Modern Mathematics SyllabusДокумент9 страницForm 4 Modern Mathematics SyllabusBenjamin HiОценок пока нет
- Yearly Plan Maths F 5 2011Документ20 страницYearly Plan Maths F 5 2011ysheng98Оценок пока нет
- Scheme of Work Mathematics Form 2Документ16 страницScheme of Work Mathematics Form 2Stephanie Kimi100% (2)
- Yearly Plan 2012 Mathematics Form 2Документ14 страницYearly Plan 2012 Mathematics Form 2FikriSalimОценок пока нет
- SMK Lutong Sekolah Kluster Kecemerlangan Yearly Teaching Plan - 2014 Mathematics Form 4Документ16 страницSMK Lutong Sekolah Kluster Kecemerlangan Yearly Teaching Plan - 2014 Mathematics Form 4KelvinYongОценок пока нет
- Yearly Lesson Addmathsf413Документ10 страницYearly Lesson Addmathsf413SasiKalaRamayahОценок пока нет
- RPT Math F4 2013Документ34 страницыRPT Math F4 2013ummuinsyirahОценок пока нет
- Add Maths Form 4Документ10 страницAdd Maths Form 4Azrul AkmarОценок пока нет
- Chapter 14 Notes-1Документ14 страницChapter 14 Notes-1Regina LinОценок пока нет
- Math lesson plan for Form 2 studentsДокумент18 страницMath lesson plan for Form 2 studentsChe'ras IbrahimОценок пока нет
- Yearly Teaching PlanДокумент7 страницYearly Teaching PlanSean GomezОценок пока нет
- Curriculum Pacing Chart 2014 - 2015 Subject: Algebra I Middle School 1st Nine WeeksДокумент4 страницыCurriculum Pacing Chart 2014 - 2015 Subject: Algebra I Middle School 1st Nine WeekspamhuskeyОценок пока нет
- Yearly Plan Form 5,2013 (Terkini)Документ18 страницYearly Plan Form 5,2013 (Terkini)Chen ChiuwenОценок пока нет
- f5 Add Maths Annual Scheme (2008)Документ6 страницf5 Add Maths Annual Scheme (2008)Abdul ManafОценок пока нет
- Additional Math Form 5Документ8 страницAdditional Math Form 5Jeyaletchumi JeyaОценок пока нет
- Yearly Teaching Plan 2011-Mathsf4Документ13 страницYearly Teaching Plan 2011-Mathsf4Nor SyahidatulnisaОценок пока нет
- Scheme of Work Mathematics Form 2 2013Документ31 страницаScheme of Work Mathematics Form 2 2013Puteri NorhanaОценок пока нет
- Math F4 (2013)Документ49 страницMath F4 (2013)Mohd Azizi Mohd NoorОценок пока нет
- RPT - Add Math F4 - 2015Документ12 страницRPT - Add Math F4 - 2015supbarОценок пока нет
- For: Second Engineer 3000kW Class 1 Fishing Engineer Yacht 2 Chief Engineer (Y2)Документ19 страницFor: Second Engineer 3000kW Class 1 Fishing Engineer Yacht 2 Chief Engineer (Y2)Rakesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Math Yearly Plan f4 2012Документ14 страницMath Yearly Plan f4 2012Soh Tyan JiinОценок пока нет
- Matematik Tambahan Tingkatan 5 2015 Yearly PlanДокумент9 страницMatematik Tambahan Tingkatan 5 2015 Yearly PlanSuziana MohamadОценок пока нет
- Yearly Lesson Plan - Form2Документ16 страницYearly Lesson Plan - Form2petersiewОценок пока нет
- RPT Math Form 2Документ16 страницRPT Math Form 2Hartini KosnanОценок пока нет
- Math Progressions and FunctionsДокумент9 страницMath Progressions and Functionsaziahjamaluddin82Оценок пока нет
- 2nd Quarter Least Learned Competencies - MathematicsДокумент1 страница2nd Quarter Least Learned Competencies - MathematicsERICK HUTAMARESОценок пока нет
- Chapter-9 1Документ4 страницыChapter-9 1durgakalyani.dОценок пока нет
- RPT Mathematics FORM4Документ18 страницRPT Mathematics FORM4mrmatrikОценок пока нет
- Math 8 - Q2 Remedial ActivityДокумент2 страницыMath 8 - Q2 Remedial ActivityHenry ArenaОценок пока нет
- Title Marine Engineering MathematicsДокумент10 страницTitle Marine Engineering MathematicsgunapalshettyОценок пока нет
- Learning Area: 1) Number Bases Mathematics: Form 5 Week/Date Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes Generics Ccts Moral Value NotesДокумент17 страницLearning Area: 1) Number Bases Mathematics: Form 5 Week/Date Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes Generics Ccts Moral Value NotesNur BainiОценок пока нет
- Additional Maths Scheme of Work for Form 5Документ15 страницAdditional Maths Scheme of Work for Form 5Green QingОценок пока нет
- Nptel 1 NewДокумент49 страницNptel 1 NewRajashree DateОценок пока нет
- Form 5Документ21 страницаForm 5dirza82Оценок пока нет
- RPT Add Math Form 4Документ9 страницRPT Add Math Form 4Norhapidah Mohd SaadОценок пока нет
- Math 234 TextДокумент173 страницыMath 234 TextAaron CottrellОценок пока нет
- Yearly Plan Add Math f4 2013Документ17 страницYearly Plan Add Math f4 2013Ayu Lil'princessОценок пока нет
- Quarter 2 Post-TestДокумент4 страницыQuarter 2 Post-TestRoberto Del CarmenОценок пока нет
- Lec #2-Curve Fitting-1Документ4 страницыLec #2-Curve Fitting-1Zaheen00 FatimaОценок пока нет
- Mathematics: Section I: Number and Numeration. 1. Number BasesДокумент7 страницMathematics: Section I: Number and Numeration. 1. Number BasesAisha ShuaibuОценок пока нет
- Math 7 4thДокумент4 страницыMath 7 4thTITO FERNANDEZОценок пока нет
- Trial SPM TRG Math K2Документ32 страницыTrial SPM TRG Math K2Adriana AidaОценок пока нет
- 10 JPNT Trial Mat k1Документ36 страниц10 JPNT Trial Mat k1Assraf JamaliОценок пока нет
- Paper2 Marking Scheme SBP Trial 09Документ9 страницPaper2 Marking Scheme SBP Trial 09idawatieОценок пока нет
- Trial SBP SPM Math 2010Документ65 страницTrial SBP SPM Math 2010Amira ZainudinОценок пока нет
- Jabatan Pelajaran Negeri Sabah: Sijil Pelajaran Malaysia Tahun 2008Документ27 страницJabatan Pelajaran Negeri Sabah: Sijil Pelajaran Malaysia Tahun 2008juriah binti ibrahimОценок пока нет
- Transformation ObjectiveДокумент17 страницTransformation ObjectiveKugahn AesenОценок пока нет
- Chapter 22 I Bearing EnhanceДокумент10 страницChapter 22 I Bearing EnhanceEC1127Оценок пока нет
- Jabatan Pelajaran Negeri Sabah: Sijil Pelajaran Malaysia Tahun 2008Документ18 страницJabatan Pelajaran Negeri Sabah: Sijil Pelajaran Malaysia Tahun 2008juriah binti ibrahimОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 I Transformation I, II ENHANCEДокумент12 страницChapter 2 I Transformation I, II ENHANCEjuriah binti ibrahimОценок пока нет
- Paper1 Question SBP Trial 09Документ30 страницPaper1 Question SBP Trial 09idawatieОценок пока нет
- Chapter 20 I Matrices ENHANCEДокумент18 страницChapter 20 I Matrices ENHANCEjuriah binti ibrahimОценок пока нет
- Chapter 21 I Variations ENHANCEДокумент21 страницаChapter 21 I Variations ENHANCEjuriah binti ibrahimОценок пока нет
- Chapter 17 I Lines & Planes in 3D ENHANCEДокумент29 страницChapter 17 I Lines & Planes in 3D ENHANCEjuriah binti ibrahimОценок пока нет
- Chapter 16 I Angles of Elevation & Depressions ENHANCEДокумент21 страницаChapter 16 I Angles of Elevation & Depressions ENHANCEjuriah binti ibrahimОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 II Stastitic III ENHANCEДокумент55 страницChapter 6 II Stastitic III ENHANCESin YeeОценок пока нет
- Chapter 18 I Number Bases ENHANCEДокумент18 страницChapter 18 I Number Bases ENHANCEjuriah binti ibrahimОценок пока нет
- Chapter 11 I Sets EnhanceДокумент33 страницыChapter 11 I Sets Enhancejuriah binti ibrahimОценок пока нет
- Chapter 13 I Probability ENHANCEДокумент13 страницChapter 13 I Probability ENHANCENorsu'aidah Bt AmirОценок пока нет
- CircleДокумент20 страницCirclejuriah binti ibrahimОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9 II Lines & Planes in 3D ENHANCEДокумент21 страницаChapter 9 II Lines & Planes in 3D ENHANCEjuriah binti ibrahimОценок пока нет
- Chapter 12 I The Straight Line ENHANCEДокумент9 страницChapter 12 I The Straight Line ENHANCEjuriah binti ibrahimОценок пока нет
- Chapter 10 I Quadratic Expressions ENHANCEДокумент12 страницChapter 10 I Quadratic Expressions ENHANCEjuriah binti ibrahimОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 I Polygon EnhancementДокумент11 страницChapter 1 I Polygon EnhancementadibahazОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 I Polygon ENHANCEДокумент10 страницChapter 1 I Polygon ENHANCEayepingpongОценок пока нет
- Mathematical ReasoningДокумент27 страницMathematical ReasoningKugahn AesenОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 II Quadratic Equations EnhanceДокумент11 страницChapter 4 II Quadratic Equations EnhanceGnesan De RajjОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 II Set EnhanceДокумент14 страницChapter 5 II Set Enhancejuriah binti ibrahimОценок пока нет
- Innovation Concept For Measurement Gross Error Detection and Identification in Power System State EstimationДокумент6 страницInnovation Concept For Measurement Gross Error Detection and Identification in Power System State Estimationc_u_r_s_e_dОценок пока нет
- Groups PDFДокумент414 страницGroups PDFArafat Hinju TzОценок пока нет
- Static and Dynamic Analysis of Collapse Behaviour of Steel StructuresДокумент14 страницStatic and Dynamic Analysis of Collapse Behaviour of Steel StructuresmikollimОценок пока нет
- Omputer Cience: 3. ArraysДокумент48 страницOmputer Cience: 3. ArraysHassan TariqОценок пока нет
- Engineering Mathematics Syllabus BreakdownДокумент3 страницыEngineering Mathematics Syllabus BreakdowngopichandallakaОценок пока нет
- Gtu 4th It Question PaperДокумент19 страницGtu 4th It Question Papercomputer myОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3Документ44 страницыChapter 3afrah chelbabiОценок пока нет
- Regression Analysis BasicsДокумент63 страницыRegression Analysis BasicsAmal SutradharОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Scilab Functions And PlottingДокумент11 страницIntroduction To Scilab Functions And PlottingRitesh SharmaОценок пока нет
- Gerson J. Ferreira: Introduction To Computational PhysicsДокумент99 страницGerson J. Ferreira: Introduction To Computational PhysicsDwight ThothОценок пока нет
- Developer's Note On Quantum EspressoДокумент39 страницDeveloper's Note On Quantum EspressoMatsushima KhodaijiОценок пока нет
- Analysis of Stripline-Fed Slot-Coupled Patch Antennas With Vias For Parallel-Plate Mode SuppressionДокумент8 страницAnalysis of Stripline-Fed Slot-Coupled Patch Antennas With Vias For Parallel-Plate Mode SuppressionnaranjitoОценок пока нет
- Lab. Manual PDFДокумент310 страницLab. Manual PDFZedrik MojicaОценок пока нет
- Adaptive Control Design and AnalysisДокумент45 страницAdaptive Control Design and Analysishind90Оценок пока нет
- Invariant SubspacesДокумент7 страницInvariant SubspacesDipro MondalОценок пока нет
- Class 12 Revision Notes MatricesДокумент8 страницClass 12 Revision Notes MatricesAbinash katochОценок пока нет
- HouseholderДокумент9 страницHouseholderKhairil Sangbima100% (1)
- Transmission: SystemsДокумент48 страницTransmission: SystemsAlain JimeneaОценок пока нет
- OPTIMAL TITLEДокумент7 страницOPTIMAL TITLEkrbiotechОценок пока нет
- Chapter-1: 1.1 Control Design ProcedureДокумент23 страницыChapter-1: 1.1 Control Design ProcedureWildan MumtazОценок пока нет
- 0912 Kuliah 12 MatrixДокумент91 страница0912 Kuliah 12 MatrixfellandoОценок пока нет
- Direct Methods For Solving Linear Equations SystemsДокумент15 страницDirect Methods For Solving Linear Equations Systemspedroquiroga7100% (2)
- Sympy-0 7 2Документ1 520 страницSympy-0 7 2Luis Oliveira Silva100% (1)