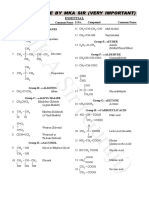
Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Experiment Sadur
Загружено:
Apik SuhimiИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Experiment Sadur
Загружено:
Apik SuhimiАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Problem statement: How is electrolysis used to electroplate an iron spoon with copper metal?
Hypothesis: Electroplating of an iron spoon with copper occurs if the iron spoon is used as the cathode, copper metal is used as the anode and aqueous copper(II)sulphate solution as the electrolyte. Variables: a) Manipulated variable: The position of the iron spoon as an Electrode. b)Responding variable: The deposition of copper on the iron spoon c) Controlled variable : Types of electrolyte and arrangement of Apparatus. Apparatus:
Materials: 1.0 mol dm-3 copper(II)sulphate solution, copper plate Procedure:
1.
About cm3 of 1.0 mol dm-3 copper(II)sulphate solution is poured into a beaker.
2. An iron spoon is polished using sandpaper and is connected to the negative terminal of the power supply. The spoon acts as the cathode. 3. The piece of copper metal, as the anode, is connected to the positive terminal of the power supply 4. The iron spoon and the copper metal are immersed in the copper(II)sulphate solution. The solution is electrolysed for 30 minutes using small current (0.5 A) 5. Steps 1 to 4 of the experiment are repeated by interchanging the positions of the iron spoon and copper metal, whereby the iron spoon is made the anode and the copper metal is made the cathode. Set Set 1: Iron spoon as the cathode, copper metal as the anode Observation At the cathode: A brown metal is deposited on the surface of the iron spoon . At the Anode: The copper anode become thinner Colour of the electrolyte: Colour intensity of the blue solution does not Inference The iron spoon is plated with copper metal The copper anode dissolves to form Cu2+ ions. Concentration of Cu2+ ions in the electrolyte remains constant
change
Set 2: Copper metal as the cathode, iron spoon as the anode
At the cathode: The copper plate becomes thicker.
Copper metal is deposited on the copper electrode.
At the anode: No noticeable change in the appearance of the iron spoon. Colour of the electrolyte : The blue colour of the solution becomes paler. Discussion:
Electroplating of copper on the iron spoon does not take place Concentration of Cu2+ ions in the electrolyte decreases
1. The brown metal deposited on the iron spoon is copper metal.
a)
At the anode : Copper dissolves from the anode by releasing electrons to form Cu2+ ions. Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
b)
At the cathode : Cu2+ ions are discharged by accepting electrons to form copper atoms. Copper metal is deposited on the surface of iron spoon. Cu2+ + 2e- Cu
2.
In this process, Cu2+ ions are transferred from the anode to the cathode ( Iron spoon ) and are deposited as a thin and even layer of copper metal. The colour intensity of the blue solution does not change because the concentration of Cu2+ ions remains constant throughout the electroplating process.
3.
4. A slow electrolysis process using a small current will ensure that the layer of copper sticks firmly to the surface of the iron spoon. Conclusion:
1.
In electroplating an iron spoon with copper using electrolysis, the iron spoon is made the cathode and a piece of copper metal is made the anode.
2. Copper metal is transferred from the copper anode to the iron spoon and is deposited as a thin layer of copper metal 3. Electroplating does not take place if the iron spoon is made the anode. The hypothesis is accepted.
Вам также может понравиться
- Solutions Manual to accompany Engineering Materials ScienceОт EverandSolutions Manual to accompany Engineering Materials ScienceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Electroplating: M6 Section-6 Group-AДокумент25 страницElectroplating: M6 Section-6 Group-AMunib KhanОценок пока нет
- LR 1 Electrolysis of Copper SulphateДокумент6 страницLR 1 Electrolysis of Copper SulphateCloud D. LuffyОценок пока нет
- Anodes and Cathodes in Corrosion ReactionsДокумент10 страницAnodes and Cathodes in Corrosion ReactionsSyed50% (4)
- Rutherford (1911) - StructureOfTheAtom (Original Paper) PDFДокумент24 страницыRutherford (1911) - StructureOfTheAtom (Original Paper) PDFMuhammad Aqso MaulanaОценок пока нет
- Electrolytic Refining of CooperДокумент2 страницыElectrolytic Refining of CooperAslam PAОценок пока нет
- IGCSE CoordSci Electricity and Chemistry L2Документ35 страницIGCSE CoordSci Electricity and Chemistry L2dung luongtuanОценок пока нет
- Electrochemical Cell.Документ9 страницElectrochemical Cell.Maku MichaelОценок пока нет
- Uses of ElectrolysisДокумент3 страницыUses of ElectrolysisM.zuhair asifОценок пока нет
- SudhanshuДокумент14 страницSudhanshusudhanshumishra8090Оценок пока нет
- Voltaic CellДокумент32 страницыVoltaic CellMahijar Jarullhayati Hassan50% (2)
- Electrochemical Cell OriginalДокумент7 страницElectrochemical Cell OriginalShajathi MОценок пока нет
- Electrolysis 090618180154 Phpapp01Документ20 страницElectrolysis 090618180154 Phpapp01jiivi87Оценок пока нет
- ECCДокумент4 страницыECCSanat ChopraОценок пока нет
- Electolysis ElectroplatingДокумент4 страницыElectolysis ElectroplatingSmartPurdyОценок пока нет
- Electolysis ElectroplatingДокумент4 страницыElectolysis ElectroplatingDentist soon to beОценок пока нет
- Electrolysis: Term MeaningДокумент22 страницыElectrolysis: Term MeaningYeen ChengОценок пока нет
- Peka - Chemistry Form 4 - Student's and Teacher's Manual - 01 - ElectrochemistryДокумент4 страницыPeka - Chemistry Form 4 - Student's and Teacher's Manual - 01 - ElectrochemistryWong Wai Lun75% (8)
- Corrosion Resistance With Electroplating C12!6!11 & 12Документ10 страницCorrosion Resistance With Electroplating C12!6!11 & 12horascanmanОценок пока нет
- 1.principles of Chemistry, E. ElectrolysisДокумент7 страниц1.principles of Chemistry, E. ElectrolysisDr.AndrewMatovuОценок пока нет
- Electrochemsitry NotesДокумент9 страницElectrochemsitry NotesAhmad Shafiq ZiaОценок пока нет
- Finding EMF of Electrochemical CellДокумент4 страницыFinding EMF of Electrochemical CellVivek Singh YadavОценок пока нет
- 4.2 ElectrolysisДокумент5 страниц4.2 Electrolysis211273wОценок пока нет
- Two More Uses of Electrolysis: When Electrodes Are Not InertДокумент2 страницыTwo More Uses of Electrolysis: When Electrodes Are Not InertShahid Ur RehmanОценок пока нет
- Important Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th ElectrolysisДокумент6 страницImportant Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th Electrolysisspurohit1991Оценок пока нет
- Electrolysis Text SolnДокумент38 страницElectrolysis Text Solnhemanth PОценок пока нет
- Danish ChemistryДокумент13 страницDanish ChemistryNaveen Kumar.RОценок пока нет
- Electrolysis HLДокумент34 страницыElectrolysis HLRyan BoukaaОценок пока нет
- Application of electrolysis-DESKTOP-GGTF55HДокумент4 страницыApplication of electrolysis-DESKTOP-GGTF55HMaku MichaelОценок пока нет
- ElectroplatingДокумент17 страницElectroplatingShirlyn HeeОценок пока нет
- Assessment of Sample Experiment - Sample 1 - Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionДокумент3 страницыAssessment of Sample Experiment - Sample 1 - Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionORONGSANTIОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Lab Report 1Документ9 страницChemistry Lab Report 1Imazahra Badaruddin25% (4)
- Electrochemical ProcessesДокумент19 страницElectrochemical Processeshrishikeshdeka18Оценок пока нет
- Introduction 1Документ10 страницIntroduction 1Boss of the worldОценок пока нет
- Voltaic Cell and Electrolytic Cell: by 5S3 Jocelyne LewДокумент9 страницVoltaic Cell and Electrolytic Cell: by 5S3 Jocelyne LewJocelyne LewОценок пока нет
- Chemistry - Notes Icse 10Документ25 страницChemistry - Notes Icse 10Suneet MohanОценок пока нет
- Gcse : H O (L) H (Aq) + OH (Aq)Документ9 страницGcse : H O (L) H (Aq) + OH (Aq)Takudzwa ChademanaОценок пока нет
- ChemistryДокумент15 страницChemistryTGC NINJAОценок пока нет
- ElectroplatingДокумент12 страницElectroplatingVishal SОценок пока нет
- POC Electrolysis Lab Report1Документ8 страницPOC Electrolysis Lab Report1nityaОценок пока нет
- M2 Metal FinishingДокумент13 страницM2 Metal FinishingMalvika RkОценок пока нет
- MM 2008 Version Standard Grade Chemistry Topic 10 Making Electricity Page 1Документ10 страницMM 2008 Version Standard Grade Chemistry Topic 10 Making Electricity Page 1Anant AggarwalОценок пока нет
- ElectrometallurgyДокумент2 страницыElectrometallurgyShivana RagoonananОценок пока нет
- Chemistry - ElectrolysisДокумент51 страницаChemistry - Electrolysisjoannavera2020Оценок пока нет
- Chem InvestigatoryДокумент3 страницыChem InvestigatoryManan SethiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 ElectrochemistryДокумент11 страницChapter 6 ElectrochemistryAshraf Shaharudin100% (1)
- Class13 ChemistryG12 Notes and HomeworkДокумент37 страницClass13 ChemistryG12 Notes and HomeworkAndy Rei KouОценок пока нет
- Project Report 12 BДокумент13 страницProject Report 12 BParth SaxenaОценок пока нет
- CHEMISRTYДокумент16 страницCHEMISRTYAmal AmalОценок пока нет
- AlloysДокумент2 страницыAlloysrincyОценок пока нет
- Esis 2Документ35 страницEsis 2Amir Abd KadirОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Application of Electrolysis PDFДокумент3 страницыChemistry Application of Electrolysis PDFMohammad RussellОценок пока нет
- 12 TH V-I ModifiedДокумент151 страница12 TH V-I ModifiedAkash VigneshwarОценок пока нет
- Chem IpДокумент15 страницChem IpSANAJ BSОценок пока нет
- Applications of ElectrolysisДокумент3 страницыApplications of ElectrolysisShahidan Latif100% (1)
- Galvanic/Voltaic CellsДокумент12 страницGalvanic/Voltaic CellsEve BonellОценок пока нет
- Chemistry PPДокумент20 страницChemistry PPArmaan MunavvariОценок пока нет
- The Study of Elementary Electricity and Magnetism by Experiment: Containing Two Hundred ExperimentsОт EverandThe Study of Elementary Electricity and Magnetism by Experiment: Containing Two Hundred ExperimentsОценок пока нет
- The Study of Elementary Electricity and Magnetism by Experiment: Containing Two Hundred Experiments Performed with Simple, Home-made ApparatusОт EverandThe Study of Elementary Electricity and Magnetism by Experiment: Containing Two Hundred Experiments Performed with Simple, Home-made ApparatusОценок пока нет
- Extractive Metallurgy 2: Metallurgical Reaction ProcessesОт EverandExtractive Metallurgy 2: Metallurgical Reaction ProcessesРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Common Names (Organic Compounds)Документ8 страницCommon Names (Organic Compounds)Tushar100% (5)
- Post16organicsynthesisquizv1 322597Документ19 страницPost16organicsynthesisquizv1 322597diceplayaaОценок пока нет
- 2 Tutorial Pressure Sept19Документ7 страниц2 Tutorial Pressure Sept19hairinnisaОценок пока нет
- Smaw 12 Module 1 Grade 12Документ39 страницSmaw 12 Module 1 Grade 12Francis Rico Mutia Rufon100% (14)
- A Helmholtz Free Energy Formulation of The Thermodynamic Properties of The Mixture (Water + Ammonia)Документ35 страницA Helmholtz Free Energy Formulation of The Thermodynamic Properties of The Mixture (Water + Ammonia)Marcelo SilvosaОценок пока нет
- Civil Engineering MCQ'sДокумент1 страницаCivil Engineering MCQ'sNISHIKANTA MONDALОценок пока нет
- ISC 2013 Chemistry Theory Paper 1 Solved PaperДокумент20 страницISC 2013 Chemistry Theory Paper 1 Solved PaperAakash Singh100% (1)
- FY 2018 Self Identified Generic Drug Facilities Sites and OrganizationsДокумент175 страницFY 2018 Self Identified Generic Drug Facilities Sites and OrganizationsDavid Paul HensonОценок пока нет
- Thermit ReactionДокумент10 страницThermit ReactionAndrei PetreОценок пока нет
- KGL ManualДокумент47 страницKGL ManualAaron Shane IrvinОценок пока нет
- EN - Op.2 - EEE EXP4 - Semi Conductors - LecturesДокумент82 страницыEN - Op.2 - EEE EXP4 - Semi Conductors - LecturesImmaculee BITWAGEBWA VERONIQUEОценок пока нет
- A Review of Heat Exchanger Tube Bundle Vibrations in Two-Phase Cross-FlowДокумент19 страницA Review of Heat Exchanger Tube Bundle Vibrations in Two-Phase Cross-FlowPeerasak ArunОценок пока нет
- Carbon and Alloy Steel Forgings For Rings For Reduction GearsДокумент4 страницыCarbon and Alloy Steel Forgings For Rings For Reduction GearsJerry BeanОценок пока нет
- Stepan: Bio-Terge As-90 BeadsДокумент2 страницыStepan: Bio-Terge As-90 BeadsJerily Alzate TapiasОценок пока нет
- Class X Science Pre Board Sample PaperДокумент23 страницыClass X Science Pre Board Sample PaperNasla ShiyasОценок пока нет
- 2013 Synthesis and Cationic Photopolymerization of A Difunctional Episulfide Monomer PDFДокумент6 страниц2013 Synthesis and Cationic Photopolymerization of A Difunctional Episulfide Monomer PDFMarion ChenalОценок пока нет
- Efficiency of Geothermal Power Plants - A Worldwide Review-AzДокумент13 страницEfficiency of Geothermal Power Plants - A Worldwide Review-Azbitconcepts9781Оценок пока нет
- Van Urk Indole TLC Test PDFДокумент11 страницVan Urk Indole TLC Test PDFabazaba151Оценок пока нет
- Periodic LawДокумент2 страницыPeriodic LawenzoОценок пока нет
- FOB Megaflow AW Hydraulic Oil TDSW 814637aДокумент3 страницыFOB Megaflow AW Hydraulic Oil TDSW 814637aElwin arifinОценок пока нет
- What Has ChangedДокумент132 страницыWhat Has ChangedVanessa VanegasОценок пока нет
- Calculating The True Cost of SteamДокумент2 страницыCalculating The True Cost of Steamisquare77Оценок пока нет
- Gpa 2286-95 PDFДокумент22 страницыGpa 2286-95 PDFaidanОценок пока нет
- Cy 2018Документ16 страницCy 2018ArvindОценок пока нет
- 2004.03 Salmonella en Alimentos ELFAДокумент3 страницы2004.03 Salmonella en Alimentos ELFAJavier muñozОценок пока нет
- Properties Foster Fire Resistive Anti-Abrasion Coating Water BasedДокумент2 страницыProperties Foster Fire Resistive Anti-Abrasion Coating Water BasedMinh BảoОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry Notes - Nucleotide MetabolismДокумент5 страницBiochemistry Notes - Nucleotide MetabolismneedthisforepiОценок пока нет
- Lesson 3 Atomic Structure ModelДокумент3 страницыLesson 3 Atomic Structure ModelRachel VillasisОценок пока нет
- Indian BOE Coaching Services: Gujarat BOE-2016 Paper-2 (Boiler Engg-2) SolutionДокумент7 страницIndian BOE Coaching Services: Gujarat BOE-2016 Paper-2 (Boiler Engg-2) SolutionAlok DoshiОценок пока нет