Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Solomon S2 E MS
Загружено:
Arjun MohindraИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Solomon S2 E MS
Загружено:
Arjun MohindraАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
GCE Examinations Advanced Subsidiary / Advanced Level
Statistics Module S2
Paper E
MARKING GUIDE
This guide is intended to be as helpful as possible to teachers by providing concise solutions and indicating how marks should be awarded. There are obviously alternative methods that would also gain full marks. Method marks (M) are awarded for knowing and using a method. Accuracy marks (A) can only be awarded when a correct method has been used. (B) marks are independent of method marks.
Written by Shaun Armstrong & Chris Huffer
Solomon Press
These sheets may be copied for use solely by the purchasers institute.
S2 Paper E Marking Guide
1. (a) (b) advantage e.g. more accurate disadvantage e.g. takes longer e.g. getting views of shop staff on changing opening hours as small no. involved and will affect all so need views of all let X = no. of bags in F.P. with scratchcard X ~ B(10, P(X = 0) = 0.3487 (b) (c) P(X > 2) = 1 P(X 2) = 1 0.9298 = 0.0702 let Y = no. of bags in box with scratchcard Y ~ B(50, H0 : p =
1 10 1 10 1 10
B1 B1 B2 M1 A1 M1 A1 ) M1 B1 M1 A1 B1 M1 (8) (4)
2.
(a)
H1 : p <
1 10
P(X 2) = 0.1117 more than 10% not significant, insufficient evidence of lower propn 3. (a) (b) continuous uniform F(t) = = F(x) =
t -4
1 8
t
dx
1 8
1 8
0, 1 (x + 4), 8 1,
[x] 4 =
(t + 4) x < 4, 4 x 4, x > 4.
M1 A1 A1
(c)
= P( 1 .5 x 1.5) 3 =3 1 = 8 8 e.g. gives zero prob. of more than 4 cm error and doesnt suggest higher prob. density near 0 as would be likely binomial, n = 10, p = p would vary (i) (ii) let X = no. of blue beads X ~ B(10,
1 2 1 2
M1 M1 A1 B2 B2 B1 ) M1 A1 M1 M1 M1 A1
1 8
(d)
(10)
4.
(a) (b) (c)
P(X = 5) = 0.6230 0.3770 = 0.2460 [0.2461 (4sf) using 10C5..] let Y = no. of red beads Y ~ B(10, 1 ) 8 P(X > 0) = 1 P(X = 0) = 1 ( 7 )10 = 0.7369 (4sf) 8
(d)
let R = no. of red beads in n picks R ~ B(n, P(R > 0) > 0.99 P(R = 0) < 0.01 (
7 8
) M2 A1 (12)
) <
1 100
S2E MARKS page 2
Solomon Press
5.
(a)
let X = no. of donations over 10 000 per year X ~ Po(25) P(X = 30) =
e 25 2530 30!
M1 M1 A1 M1 M1 M1 A1 A1 M1 M1 M1 A1 A1 M1 M1 A1 M1 M1 A1 M1 A1 A1 (13)
= 0.0454 (3sf)
(b)
25 let Y = no. of donations over 10 000 per month Y ~ Po( 12 )
P(Y < 3) = P(Y 2) = e
25 12
(1 +
25 12
25 ( 12 ) 2 2
= 0.6541 (4sf) (c) let D = no. of donations over 10 000 per 2 years D ~ Po(50) N approx. E ~ N(50, 50) P(D > 45) P(E > 45.5) = P(Z > 45.5 50 ) = P(Z > 0.64)
50
= 0.7389 6. (a) = P(T > 2) = 1 F(2) 1 = 1 135 (108 + 36 32) =
23 135
(b)
F(m) = 1 2 F(1.1) = 0.4812; F(1.2) = 0.5248 1.1 < m < 1.2 median between 11 and 12 minutes f(t) = F (t) = f(t) =
2 45 1 135
(c)
(54 + 18t 12t2)
2
(9 + 3t 2t ), (3 4t)
0, (d) f (t) =
2 45
0 t 3, otherwise.
M1
3 4 3 4
S.P. when f (t) = 0 t =
M1 10 = 7.5 mins M1 A1 B1 B1 B2 M1 A1 A1 M1 A1 B1 M1 B1 M1 A1 A1 Total (14)
some justification e.g. ve quadratic mode = (e) 7. (a)
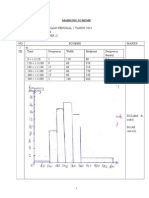
e.g. assumes patients never wait for more than 30 mins Poisson e.g. reasonable to suggest bicycles passing will occur singly, at random and at constant rate n = 36, fx = 54, mean =
2
(b)
54 36
= 1.5
fx = 0 + 14 + 40 + 18 + 16 + 50 = 138 variance = 138 1.52 = 1.58 (3sf) 36 values support Poisson as expect mean variance (c) let X = no. of bicycles passing per 30-mins X ~ Po(9) H0 : = 9 H 1 : > 9 P(X 16) = 1 P(X 15) = 1 0.9780 = 0.0220 less than 5% significant, evidence of more bicycles
(14) (75)
Solomon Press
S2E MARKS page 3
Performance Record S2 Paper E
Question no. Topic(s)
1
sampling
2
binomial, hyp. test
3
rect. dist., c.d.f.
4
binomial
5
Poisson, N approx.
6
c.d.f., median, p.d.f., mode
7
Poisson, hyp. test.
Total
Marks Student
10
12
13
14
14
75
S2E MARKS page 4
Solomon Press
Вам также может понравиться
- Solomon S2 D MSДокумент4 страницыSolomon S2 D MSArjun MohindraОценок пока нет
- Actl 20025101 Finalexamsolutions 2006Документ15 страницActl 20025101 Finalexamsolutions 2006柯颖Оценок пока нет
- 2010 JJC Prelim P2 SolutionsДокумент12 страниц2010 JJC Prelim P2 Solutionsnothingtodo1992Оценок пока нет
- p2 SMKBM Percubaan p2 2014 (A)Документ8 страницp2 SMKBM Percubaan p2 2014 (A)masyatiОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Probability and Statistics SOLUTION PDFДокумент22 страницыIntroduction To Probability and Statistics SOLUTION PDFwiwolo8536Оценок пока нет
- Business Statistics BUS120 Fall 2018/2019 Assignment: Submitted ToДокумент5 страницBusiness Statistics BUS120 Fall 2018/2019 Assignment: Submitted Toaboubakr soultanОценок пока нет
- Solutions Manual To: An Introduction To Mathematical Finance: Options and Other TopicsДокумент65 страницSolutions Manual To: An Introduction To Mathematical Finance: Options and Other TopicsHanh VuОценок пока нет
- 2011 IJC Prelims P2 Soln PDFДокумент13 страниц2011 IJC Prelims P2 Soln PDFmath3matics3Оценок пока нет
- Chapter #19 Solutions - Engineering Economy, 7 TH Editionleland Blank and Anthony TarquinДокумент15 страницChapter #19 Solutions - Engineering Economy, 7 TH Editionleland Blank and Anthony TarquinMusa'bОценок пока нет
- Pahang Paper 2 AnswerДокумент10 страницPahang Paper 2 AnswerChan Tak KiengОценок пока нет
- Solucionario Segundo Quimestre DPДокумент16 страницSolucionario Segundo Quimestre DPAndres FernandoОценок пока нет
- Scheme Sem II 20082009Документ12 страницScheme Sem II 20082009Sharifah Shahida Syed IdrusОценок пока нет
- 16 M4 January 2003 Mark SchemeДокумент5 страниц16 M4 January 2003 Mark SchemeraaaaaawrОценок пока нет
- 2014 Calculus AB Free Response Questions (Answers and Explanations) 4Документ7 страниц2014 Calculus AB Free Response Questions (Answers and Explanations) 4ericОценок пока нет
- Credit Past Paper Questions - SolutionsДокумент28 страницCredit Past Paper Questions - SolutionsknoxmathsОценок пока нет
- (Solutions Manual) Probability and Statistics For Engineers and ScientistsДокумент51 страница(Solutions Manual) Probability and Statistics For Engineers and ScientistsAmy Parker100% (1)
- (Solutions Manual) Probability and Statistics For Engineers and Scientists Manual HaylerДокумент51 страница(Solutions Manual) Probability and Statistics For Engineers and Scientists Manual HaylerRondell Sinanan100% (1)
- Pure Mathematics Module P4: Marking GuideДокумент4 страницыPure Mathematics Module P4: Marking GuideThilina Kalhara PanduwawalaОценок пока нет
- Paperdos Ed33 For Science HurgleДокумент4 страницыPaperdos Ed33 For Science HurglesdadОценок пока нет
- Solomon B MS - S1 EdexcelДокумент4 страницыSolomon B MS - S1 EdexcelabhayОценок пока нет
- Trial SPM MT 2014 Jawapan K2Документ12 страницTrial SPM MT 2014 Jawapan K2Mohd Ellif SarianОценок пока нет
- Brilliant'S Progressive Test: Our One/Two-Year Postal Courses All India Engineering Entrance Examination, 2012Документ11 страницBrilliant'S Progressive Test: Our One/Two-Year Postal Courses All India Engineering Entrance Examination, 2012sanskarid94Оценок пока нет
- TRIAL ADDMATE SPM 2011 Pahang Paper 2 AnswerДокумент11 страницTRIAL ADDMATE SPM 2011 Pahang Paper 2 AnswerwaichunkoОценок пока нет
- Homework 7 SolutionДокумент7 страницHomework 7 SolutionTACN-2T?-19ACN Nguyen Dieu Huong LyОценок пока нет
- Targate'16: Answer Keys: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10Документ19 страницTargate'16: Answer Keys: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10Mahesh ChoudharyОценок пока нет
- 4 < − 1 2 ≤ ≤ θ θ θ θ θ θ (2sin) 4 (2 sin) 2 1 (2 sin) 4 − + + ≥ + 2sin 4 < − 2si 2 1 n ≤ ≤ θДокумент6 страниц4 < − 1 2 ≤ ≤ θ θ θ θ θ θ (2sin) 4 (2 sin) 2 1 (2 sin) 4 − + + ≥ + 2sin 4 < − 2si 2 1 n ≤ ≤ θNg Shu QingОценок пока нет
- Solomon A MSДокумент4 страницыSolomon A MSgranadeclamoОценок пока нет
- JJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsДокумент14 страницJJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongОценок пока нет
- Course 1 May 2001 Answer KeyДокумент25 страницCourse 1 May 2001 Answer KeyAnisah NiesОценок пока нет
- Iit Jee 2012 Paper1-Final SolnДокумент9 страницIit Jee 2012 Paper1-Final SolnPedamallu SrinivasОценок пока нет
- 19 (Anal Add Math CD)Документ10 страниц19 (Anal Add Math CD)q998Оценок пока нет
- Exam Style PaperДокумент5 страницExam Style PaperRaiyan RahmanОценок пока нет
- Answer Key: Paper-2Документ14 страницAnswer Key: Paper-2vishal110085Оценок пока нет
- Nyjc h2 Math p2 SolutionДокумент11 страницNyjc h2 Math p2 SolutionjimmytanlimlongОценок пока нет
- RT Solutions-17!07!2011 XII ABCD Paper II Code BДокумент15 страницRT Solutions-17!07!2011 XII ABCD Paper II Code Bvishal110085Оценок пока нет
- TRIAL STPM Mathematics M 2 (JOHOR) SMK TunHussienOnnДокумент8 страницTRIAL STPM Mathematics M 2 (JOHOR) SMK TunHussienOnnSKОценок пока нет
- 12 06 2011 Xii Abcd Paper II Code BДокумент14 страниц12 06 2011 Xii Abcd Paper II Code Bvishal110085Оценок пока нет
- Assignment 2 MAS291Документ6 страницAssignment 2 MAS291Mê Chơi GameОценок пока нет
- 2012 Edexcel Higher A Paper 2 Mark SchemeДокумент6 страниц2012 Edexcel Higher A Paper 2 Mark SchemeBrenda WaltersОценок пока нет
- U U U U: Be The Statement ThatДокумент9 страницU U U U: Be The Statement Thatnothingtodo1992Оценок пока нет
- 2012 GCE A Level Solution H2 Math Paper 2Документ8 страниц2012 GCE A Level Solution H2 Math Paper 2Amos YapОценок пока нет
- Answer Key: Full Syllabus TestДокумент12 страницAnswer Key: Full Syllabus TestchakshuishanОценок пока нет
- RT Solutions-09!10!2011 XIII VXY Paper I Code BДокумент16 страницRT Solutions-09!10!2011 XIII VXY Paper I Code Bvishal27042233Оценок пока нет
- X Xy X: 2010 HCI H2 Mathematics Preliminary Examination Paper 2 Solution QN SolutionsДокумент11 страницX Xy X: 2010 HCI H2 Mathematics Preliminary Examination Paper 2 Solution QN Solutionsnothingtodo1992Оценок пока нет
- Full Topics Form 4 Test 2Документ12 страницFull Topics Form 4 Test 2Sazlin A GhaniОценок пока нет
- Solution All PaperДокумент21 страницаSolution All PaperSanjay Verma75% (4)
- Homework 6Документ5 страницHomework 6Ashish MalikОценок пока нет
- LT D, U K.: Model Paper - 01 Answers (EM)Документ3 страницыLT D, U K.: Model Paper - 01 Answers (EM)ngor1111Оценок пока нет
- Term 3 Week 6 Revision Exercises - Statistics Suggested SolutionsДокумент5 страницTerm 3 Week 6 Revision Exercises - Statistics Suggested SolutionsWen Berry JiahuiОценок пока нет
- Bab 3Документ39 страницBab 3dedy28Оценок пока нет
- Batu Pahat Sem 3 (A)Документ9 страницBatu Pahat Sem 3 (A)Justice WongОценок пока нет
- Mindful Maths 1: Use Your Algebra to Solve These Puzzling PicturesОт EverandMindful Maths 1: Use Your Algebra to Solve These Puzzling PicturesОценок пока нет
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesОт EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesОценок пока нет
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageОт EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageОценок пока нет
- Introductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)От EverandIntroductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)Оценок пока нет
- ATI TEAS Calculation Workbook: 300 Questions to Prepare for the TEAS (2023 Edition)От EverandATI TEAS Calculation Workbook: 300 Questions to Prepare for the TEAS (2023 Edition)Оценок пока нет
- UCAS - Personal Statement - How To GuideДокумент5 страницUCAS - Personal Statement - How To GuideArjun MohindraОценок пока нет
- Solomon S2 F QPДокумент4 страницыSolomon S2 F QPArjun MohindraОценок пока нет
- Solomon S2 E QPДокумент4 страницыSolomon S2 E QPArjun MohindraОценок пока нет
- Solomon S2 D QPДокумент4 страницыSolomon S2 D QPArjun MohindraОценок пока нет
- Solomon S2 A MSДокумент4 страницыSolomon S2 A MSArjun MohindraОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Unit 4 Structured QuestionsДокумент3 страницыChemistry Unit 4 Structured QuestionsArjun MohindraОценок пока нет
- Solomon S2 C QPДокумент4 страницыSolomon S2 C QPArjun MohindraОценок пока нет
- Solomon S2 B QPДокумент4 страницыSolomon S2 B QPArjun MohindraОценок пока нет
- Solomon S2 A QPДокумент4 страницыSolomon S2 A QPArjun MohindraОценок пока нет
- EDEXCEL A2 CHEMISTRY UNIT 4 January 2011 MARK SCHEMEДокумент22 страницыEDEXCEL A2 CHEMISTRY UNIT 4 January 2011 MARK SCHEMEGhaleb W. MihyarОценок пока нет
- UCAS - Personal Statement - How To GuideДокумент5 страницUCAS - Personal Statement - How To GuideArjun MohindraОценок пока нет
- Edexcel Mathematics C2 January 2008 QPДокумент6 страницEdexcel Mathematics C2 January 2008 QPArjun MohindraОценок пока нет
- 05 Poisson DistributionДокумент22 страницы05 Poisson Distributiondhanesh150% (1)
- ch03 PDFДокумент57 страницch03 PDFNadya AzzanОценок пока нет
- RM2Документ102 страницыRM2Anonymous eWMnRr70qОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER3 - Discrete Random VariablesДокумент28 страницCHAPTER3 - Discrete Random VariablesDustin WhiteОценок пока нет
- Binomial Distribution AND Its ApplicationsДокумент16 страницBinomial Distribution AND Its ApplicationsViolet ColorОценок пока нет
- Chapter13slides PoissonДокумент18 страницChapter13slides PoissoneugenezainОценок пока нет
- Chap6 Some Probability Distributions - LectureДокумент21 страницаChap6 Some Probability Distributions - LectureJoegenekaye CutadОценок пока нет
- The Normal Distribution MSДокумент7 страницThe Normal Distribution MSManav MaistryОценок пока нет
- Statistics Midterms NotesДокумент8 страницStatistics Midterms Noteskt. rznОценок пока нет
- Interpret The Key Results For Binomial Capability Study AnalysisДокумент7 страницInterpret The Key Results For Binomial Capability Study AnalysisCloud RedfieldОценок пока нет
- Qar Lab ManualДокумент44 страницыQar Lab ManualSanketh SОценок пока нет
- Equivalence Tests For The Ratio of Two Negative Binomial Rates PDFДокумент12 страницEquivalence Tests For The Ratio of Two Negative Binomial Rates PDFscjofyWFawlroa2r06YFVabfbajОценок пока нет
- Probability DistributionДокумент32 страницыProbability DistributionUrieОценок пока нет
- Binomial DistributionДокумент14 страницBinomial DistributionDr Vishwas ParlikarОценок пока нет
- Distribution AssignmentДокумент3 страницыDistribution AssignmentAbhishek KumarОценок пока нет
- Random VariablesДокумент23 страницыRandom VariablesashviniОценок пока нет
- My Learning From Data Science ClassesДокумент16 страницMy Learning From Data Science ClassesSunny DograОценок пока нет
- Course Outline StatisticsДокумент4 страницыCourse Outline StatisticsNurin IzadОценок пока нет
- Poisson Distribution Explained - Intuition, Examples, and Derivation - Towards Data ScienceДокумент10 страницPoisson Distribution Explained - Intuition, Examples, and Derivation - Towards Data ScienceQurban khaton HussainyarОценок пока нет
- Final Term Assessment FALL 2020: Student's Name Noor Nabi Shaikh Registration Number 1711125Документ8 страницFinal Term Assessment FALL 2020: Student's Name Noor Nabi Shaikh Registration Number 1711125Noor Nabi ShaikhОценок пока нет
- Binomial TheoryДокумент20 страницBinomial TheoryAmar SinhaОценок пока нет
- Poisson DistributionДокумент12 страницPoisson DistributionBtd DefendОценок пока нет
- Fig. 1 The Process Yield HistogramДокумент10 страницFig. 1 The Process Yield HistogramALIKNFОценок пока нет
- Math Commerce 2Документ182 страницыMath Commerce 2Manoj Ghagas100% (1)
- Review of Sessions 1-7 PUBH 614 Spring 2019Документ68 страницReview of Sessions 1-7 PUBH 614 Spring 2019welcome martinОценок пока нет
- Some Important Discrete Probability Distributions: Powerpoint To AccompanyДокумент8 страницSome Important Discrete Probability Distributions: Powerpoint To AccompanyDevaky_Dealish_182Оценок пока нет
- Exercise ProbabilityДокумент87 страницExercise ProbabilityMalik Mohsin IshtiaqОценок пока нет
- Special Parametric Families of Univar. DistributionДокумент18 страницSpecial Parametric Families of Univar. DistributionDan DaveОценок пока нет
- Binomial Theorem: IIT JEE (Main) ExaminationДокумент56 страницBinomial Theorem: IIT JEE (Main) ExaminationHanuman VermaОценок пока нет