Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Derma - Skin
Загружено:
Martin Allen BuenaventuraИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Derma - Skin
Загружено:
Martin Allen BuenaventuraАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Dermatology
Skin and Integumentary System
Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water loss Regulates body temperature Houses sensory receptors Contains immune system cells Synthesizes chemicals, including Vitamin D Excretes small amounts of waste Layers of Skin 1. Epidermis - stratum basale - keratinocytes = 90% epidermal cells - melanocytes = 8% epidermal cells - subdivided into layers of stratified squamous epithelium - lacks blood vessels - keratinized - thickest on palms and soles (0.8 1.4 mm) - melanocytes provide melanin - rests on basement membrane Epidermal Differentiation - Increase in cell size and shape - Appearance of new cellular organelles - Change from a generalized cellular metabolism to a more focused metabolism - Alteration in the properties of the plasma membrane cell surface antigen and receptor - Dehydration of cellular organelles - Terminally diff keratinocyte (keratin filaments, matrix proteins, protein reinforced membrane with surface associated lipids Nonkeratinocyte in epidermis Melanocyte pigment producing cell Merkel cell mechanoreceptor Langerhans cell Melanocyte - Dendritic pigment synthesizing cell derived from the neural crest - HISTO: pale staining cytoplasm with ovoid nucleus and the intrinsic color of pigment containing melanosomes - (+) vimectin, (-) keratin filaments
Divides at a rate keeping pace with keratinocyte turnover - EPIDERMAL MELANIN UNIT (36 basal and suprabasal keratinocyte coexist with one melanocyte) Merkel cell - slow adapting type 1 mechanoreceptor - located in sites of high tactile sensitivity e.g. digits - nonkeratinocyte located at the basal layer of the epidermis - HISTO: pale staining cytoplasm, nucleus is lobulated and margins of cell project cytoplasmic spines toward keratinocytes - Sites: hairy and glaborous skin of digits, lips, regions of the oral cavity, outer root sheath of hair follicle Langerhans cell - nonkeratinocyte distributed in basal, spinous and granular layers with preference for the suprabasal position - HISTO: pale staining and have convoluted nuclei - Electron microscopy: with dispersed vimectin filaments and small rod or racket shaped structures called birbeck granules - Responsible for recognition, uptake, processing and presentation of soluble antigens and haptens to sensitized T lymphocytes *Basement membrane - is anchored to the dermis by short fibrils and separates these two layers of skin 2. Dermis - made up of connective tissue, epithelial tissue, smooth muscle tissue, nervous tissue, and blood - on average 1.0 2.0 mm thick - dermal papillae - binds epidermis to underlying tissues - irregular dense connective tissue - muscle cells - nerve cell processes - blood vessels - hair follicles - glands -
kirstie
Dermatology Skin and Integumentary System
a. Papillary region i. superficial dermis with papillae ii. areolar connective tissue b. Reticular region i. deeper four/fifths of dermis ii. dense irregular connective tissue iii. collagen and elastic fibers iv. contains: blood vessels, nerves, glands and hair follicles
Sweat or Sudoriferous Glands widespread in skin deeper dermis or hypodermis eccrine glands types of merocrine gland that secrete fluid (sweat) product released through the cell membrane aprocrine sweat, ceruminous (wax), and mammary (milk) glands types of apocrine glands that secrete cellular product and portion of the free ands of cells Sebaceous Glands usually associated with hair follicles holocrine glands disintegrating cell and its contents for the secretion secrete sebum absent on palms and soles Hair Follicles epidermal cells tube-like depression extends into dermis hair root hair shaft hair papilla dead epidermal cells melanin arrector pili muscle Hair cycle o Anagen growing phase 80-90% of scalp hair, 3-4 years in human scalp o Telogen phase resting phase Average of 3 months o Catagen phase transitory phase Clubhair, average of 3 weeks
3 segments o infundibular portion o isthmus o inferior or matrix 3. Subcutaneous layer Hypodermis Loose connective tissue Adipose tissue Insulates Major blood vessels Skin Color Genetic Factors Varying amounts of melanin Varying size of melanin granules Albinos lack melanin Physiological Factors Dilation of dermal blood vessels Constriction of dermal blood vessels Carotene Jaundice Environmental Factors Sunlight UV light from sunlamps X-rays Mechanics of pigment transfer Fusion and breakdown of plasma membrane of both melanocyte and keratinocyte establishing a communication between the cells Phagocytosis of melanosomes containing the dendritic processes by the keratinocyte called apoptosis *All people have the same number of melanocytes in their skin 2 types of melanin Eumelanin brown or black color, elliptical in shape Pheomelanin red or yellow. With less regular shape *size of melanosomes in black skin are larger than in light skin individuals
kirstie
Dermatology Skin and Integumentary System
Nails Protective coverings Nail plate Nail bed Lunula Life Span Changes Scaly skin Age spots Dermis becomes reduced Loss of fat Wrinkles Sagging Sebaceous glands secret less oil Melanin production slows Hair thins Number of hair follicles decrease Impaired nail growth Sensory receptors decline Inability to control body temperature Less vitamin D production Skin Problems Hair follicle o Alopecia areata, telogen effluvium, androgenetic alopecia Sebaceous gland o Acne vulgaris, sebaceous cyst, steatocystoma multiplex Apocrine gland o Hidradenitis suppurative, Fox fordyces disease Sweat gland o Hyperhidrosis, bromhidrosis, anhidrosis, chromhidrosis o Syringoma Keratinocyte o Psoriasis Melanocyte o Vitiligo, Albinism, Postinflammatory hyper/hypopigmentation
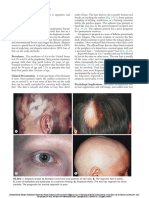
Clinical Application Acne Vulgaris Most common skin disorder Sebum and epithelial cells clog glands Produces whiteheads and blackheads (comedones) Anaerobic bacteria trigger inflammation (pimple) Largely hormonally induced Androgens stimulate sebum production Treatments include antibiotics, topical creams, birth control pills *please refer to the slides for the pictures Asteatotic eczema Sebaceous hyperplasia Psoriasis Chronic Bullous disease in children (epidermo dermal junction) Vitiligo Generalized type Postinflam hypopigmentation (melanocytes) Pigmentary problems (melanocytes) Melasma (melanocytes) Syringoma (eccrine glands) Steatocytoma multiplex (sebaceous glands) Fox fordyces disease (apocrine glands) Alopecia areata (hair follicle) Androgenic alopecia (hair follicle) Female androgenic alopecia Onycholysis in Psoriasis Onychomycosis Xeroderma Pigmentosum extreme freckling and skin cancer due to lack of DNA repair enzymes Squamous and basal cell carcinoma derived from epithelial tissue Malignant melanoma derived from melanocytes
kirstie
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Modul Kulit SsДокумент22 страницыModul Kulit Ssshafiraa29Оценок пока нет
- PortfolioДокумент80 страницPortfolioMicheal McDowellОценок пока нет
- Approach To Non Scarring Alopecia FINALДокумент58 страницApproach To Non Scarring Alopecia FINALSiddharth DashОценок пока нет
- Sphingony Eurocosmetics 2014Документ5 страницSphingony Eurocosmetics 2014Kushal SunilОценок пока нет
- Regrow Hair Protocol v2Документ87 страницRegrow Hair Protocol v2Asad Khan100% (1)
- 1st Quarterly ExamДокумент4 страницы1st Quarterly ExamChristine BalanonОценок пока нет
- Harrison2003 Hair Loss ChildrenДокумент14 страницHarrison2003 Hair Loss ChildrenErnawati HidayatОценок пока нет
- Structure and Chemical Composition of Raw Hides and SkinsДокумент11 страницStructure and Chemical Composition of Raw Hides and SkinsAnushree Bhattacharya75% (4)
- Baicapil™Документ26 страницBaicapil™HarmonyLife100% (6)
- Androgenetic Alopecia Treatment in Asian MenДокумент4 страницыAndrogenetic Alopecia Treatment in Asian MenSeraОценок пока нет
- Chemical Constituents, Pharmacological Effects and Therapeutic Importance of Hibiscus Rosa-Sinensis-A ReviewДокумент20 страницChemical Constituents, Pharmacological Effects and Therapeutic Importance of Hibiscus Rosa-Sinensis-A ReviewhaveanicedayОценок пока нет
- Avicequinone C Isolated From Avicennia Marina ExhiДокумент14 страницAvicequinone C Isolated From Avicennia Marina Exhidogne123456789Оценок пока нет
- Hair Loss Common Causes and TreatmentДокумент8 страницHair Loss Common Causes and TreatmentDesireé González ArzolayОценок пока нет
- The Complete Integumentary System Study GuideДокумент72 страницыThe Complete Integumentary System Study GuideDeborahMcCloudОценок пока нет
- Forensic Hair AnalysisДокумент30 страницForensic Hair Analysismira rambe100% (2)
- HAIR LOSS Myths and Truths When Is It Normal and When Is AlopeciaДокумент5 страницHAIR LOSS Myths and Truths When Is It Normal and When Is Alopeciamaria vastikОценок пока нет
- Ddg.13546.Doc BenerДокумент25 страницDdg.13546.Doc Benernailatul fadhilaОценок пока нет
- Alopecia Areata: Habif's Clinical DermatologyДокумент4 страницыAlopecia Areata: Habif's Clinical DermatologyMasithaОценок пока нет
- ISHRS 21st Abstract Book 2013 SanFran DR Alan Bauman FinalДокумент542 страницыISHRS 21st Abstract Book 2013 SanFran DR Alan Bauman FinalAlan J Bauman MDОценок пока нет
- Anagain™: Stimulating Hair Growth and Fighting Hair LossДокумент12 страницAnagain™: Stimulating Hair Growth and Fighting Hair Losssoul_in_the_dark100% (1)
- Soymilk Reduces Hair Growth and Hair Follicle Dimensions: M. Seiberg, J.-C. Liu, L. Babiarz, E. Sharlow and S. ShapiroДокумент9 страницSoymilk Reduces Hair Growth and Hair Follicle Dimensions: M. Seiberg, J.-C. Liu, L. Babiarz, E. Sharlow and S. ShapiroAragornn ElessarrОценок пока нет
- Neutrophilic Sebaceous Adenitis A Challenger Diagnosis With Favorable Response To Dapsone Contribution of Two News CasesДокумент6 страницNeutrophilic Sebaceous Adenitis A Challenger Diagnosis With Favorable Response To Dapsone Contribution of Two News CasesAthenaeum Scientific PublishersОценок пока нет
- Undetectable Hair Transplants by Dr. Ch. Krishna PriyaДокумент155 страницUndetectable Hair Transplants by Dr. Ch. Krishna PriyaKrishna RayaluОценок пока нет
- KukitДокумент9 страницKukitFarhan RahmadiОценок пока нет
- Der MaДокумент337 страницDer Machendewen77100% (2)
- Review of Ayurvedic Herbs With K Esharanjana Property in The Management of Caniites (Palitya)Документ4 страницыReview of Ayurvedic Herbs With K Esharanjana Property in The Management of Caniites (Palitya)Ujju LabanaОценок пока нет
- Treatment of Alopecia With Platelet-Rich Plasma - AДокумент43 страницыTreatment of Alopecia With Platelet-Rich Plasma - AShivam TyagiОценок пока нет
- Hair Loss TreatmentДокумент12 страницHair Loss TreatmentJaTi NurwigatiОценок пока нет
- Standardized Scalp Massages Literature ExcerptДокумент15 страницStandardized Scalp Massages Literature Excerptlolo jikОценок пока нет
- Lookingbill and Marks' Principles of DermatologyДокумент19 страницLookingbill and Marks' Principles of Dermatologyputri theresia50% (2)