Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
MD1 Intro Block Sample Exam
Загружено:
Frank Mbuli EmorolaИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
MD1 Intro Block Sample Exam
Загружено:
Frank Mbuli EmorolaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
MD1 intro block exam
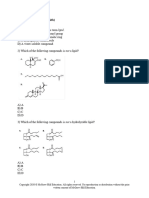
Section I Multiple choice questions Choose the most correct answer: 1 Which of the following set of vitamins has antioxidant function? a) Vitamin K, vitamin D and -carotene b) -carotene, Retinol and Vit.E c) Vit.E, -carotene and vitamin C d) -carotene, Vit C and Vit.D The presence of polyunsaturation in fatty acids imparts: a) tendency to exist in solid state at room temperature b) tendency to exist in liquid state at room temperature c) tendency to exist in cis-conformation at room temperature d) tendency to acquire trans-conformation Cholesterol is an important membrane lipid because: a) it increases the fluidity of the membrane b) it is highly hydrophilic thus acting as a polar head of the phospholipids c) it is so small that it can pack between phospholipid bilayers d) it can be converted to vitamin D Analyse the following structures:
Structure A
Structure B
The difference between A and B in NET CHARGE at pH near 7 is that: a) A will be neutral while B will be negatively charged b) A will be neutral while B will be positively charged c) Both A and B will be neutral d) Both A and B will be negatively charged e) Both A and B will be positively charged 5 Protein kinase-A and Protein kinase-C (PK-A and PK-C) phosphorylate proteins at which of the following amino acids: a) serine and threonine b) tyrosine and phenylalanine c) threonine and tyrosine d) histidine and serine
Absence of dipalmitoyl lecithin in infants leads to: a) hemorrhagic syndrome b) rickets c) keratinisation of mucus secreting epithethia d) respiratory distress syndrome The structure below can best be written as:
a) b) c) d) 8
20:44,8,11,14 20:45,8,11,14 20:46,9,12,15 20:45,8,12,15
Which of the following is an essential fatty acid: a) Stearic acid b) Oleic acid c) Linoleic acid d) Arachidonic acid Which of the following IS NOT a function of bile salts: a) b) c) d) e) Their excretion in the feces represent the only significant mechanism for elimination of excess cholesterol They solubilize cholesterol in the bile, thereby preventing the precipitation of cholesterol in the gallbladder. They facilitate the intestinal absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. They assist in the digestion of carbohydrates by hydrolysing the glycosidic bonds glycine tryptophan serine
10
Which of the following amino acids absorb light at 260nm? a) b) c)
11 a)
the site marked y is a site of hydrolysis by: phospholipase D
b) c) d) 12
phospholipase C phospholipase A1 phospholipase A2
Which one of the following is NOT TRUE about Platelate activating factor (PAF)? a) b) c) d) is synthesized in response to formation of antigen-IgE complexes on surfaces of immune cells it stimulates platelate aggregation it is a mediator of hypersensitivity, acute inflammation and anaphylactic shock it is a sphingolipid of great physiological importance
13
excessive retinol in the body can lead to all of the following EXCEPT: a) b) c) d) presence of free retinol in the cell teratogenic effect to embryos keratinisation of mucus secreting membranes hpervitaminosis A
14
One of the major roles of vitamin A in immunity is: a) b) c) d) cell growth and differentiation growth and maintenance of health epithelial tissues production of antigens production of antibodies
15
Beta carotene is an effective antioxidant scavenging free radicals in which of the following sites most? a) b) c) d) adipose tissue bellow the skin low oxygen partial pressure regions high oxygen partial pressure regions
16
Which one of the following is NOT a free radical? a) b) c) d) superoxide radical (O2-) OH
ROO OH-
17
the role of Calcitonin in calcium homeostasis is: a) b) c) d) to facilitate calcium resorption from bones to facilitate calcium deposition in bones to facilitate calcium transport from maternal to foetal circulation to facilitate absorption of calcium from intestine
18
Vitamin E is stored mostly in which of the following region? a) b) c) d) adipose tissue bellow the skin kidney liver
19
Vitamin E in fighting free radicals it acts in conjunction with which of the following vitamins? a) b) c) d) vitamin C vitamin A vitamin D vitamin K
20
Which of the following drug can induce vitamin K deficiency? a) b) c) d) warfarin tetracycline aspirin gama carboxyglutamate
21
Which of the following is NOT a function of cholesterol? a) b) c) d) it forms vitamin D it forms bile acids it forms steroid hormones it forms blood group antigens
22
Which of the following amino acids is NOT chiral? a) b) c) d) glycine serine alanine tryptophan 4
23
which of the following amino acid is NOT a primary amino acid: a) b) c) d) phenylalanine lysine glutamate hydroxyproline
24
Which of the following amino acids can function as a neurotransmitter? a) b) c) d) phenylalanine lysine glutamate hydroxyproline
25
Which one of the following amino acids is non polar hydrophobic? a) b) c) d) glutamate histidine aspartatic acid alanine
26
Which of the following amino acids CAN NOT act as a phosphorylation site for specific protein kinases? a) b) c) d) tyrosine serine threonine glycine
27
the building block for glycerol phospholipids is: a) b) c) d) phosphatidic acid ceramide sphongosine glycerol
28
the building block for sphingolidis is: a) b) c) d) phosphatidic acid ceramide sphongosine glycerol 5
29
A cerebroside differs from a globoside in that: a) b) c) d) cerebroside contains only one sugar unit while globoside contains more than one sugar units cerebroside contains more than one sugar units while globoside contains only one sugar unit cerebroside contains positively charge sugars while globoside contains neutral sugar units cerebroside contains sialic acid while globoside contains no sialic acid
30
The difference between a globoside and ganglioside is that: a) b) c) d) ganglioside contains only one sugar unit while globoside contains more than one sugar units gangliosides contain more than one sugar units while globoside contains only one sugar unit gangliosides contain positively charge sugars while globoside contains neutral sugar units Gangliosides contain sialic acid while globoside contains no sialic acid
31
Niemann-Pick disease is caused by lack of: a) b) c) d) acid sphingomyelinase sphingomyelin phospholipase A phospholipaseC
32
a sulphatide contains: a) b) c) d) sulphuric acid group phosphoric acid group disulfide bonds a sulpha group
33
Keratinization of mucus secreting epithelia is characteristic feature in the deficiency of: a) b) c) d) vitamin C vitamin D vitamin A vitamin E
34
Tay Sach disease is caused by lack of the following enzyme: a) b) c) d) Hexosaminiades A (HEXA) sphingomyelinase glucocerebroside alpha-galactosidase
35
Excess cholesterol in the body can significantly be removed through: a) b) c) d) formation and secretion of bile salts/acids formation of vitamin D formation of steroid hormones oxidation to CO2 and energy
36
Which of the following molecultes is NOT AMPHIPATHIC? a) b) c) d) cholesterol fatty acid Beta carotene 11-cis retinal
37
Which of the following amino acids is important in for haemoglobin to carry oxygen and act as a buffer? a) b) c) d) Histidine tyrosine alanine arginine
38
One of the following is NOT a rich source of vitamin A a) b) c) d) carrot green cabbage tomatoes fish
39
Which of the following is a rich source of vitamin K? a) b) c) d) green leafy vegetables onions tomato potatoes 7
40
Which of the following is a very good source of retinol form of vitamin A? a) b) c) d) liver tomatoes potatoes carrots
41
Where is vitamin A stored in the body? a) b) c) d) in liver in kidney in adipose tissues below the skin
42
What do we call a fatty acid that is not cannot be synthesized in the body? a) b) c) d) essential primary basic secondary
43
The following substances are all lipids EXCEPT one? a) b) c) d) bee wax cow fat oils hydrophobic protein
44
If a reaction proceeds with elimination of water that reaction can be termed? a) b) c) d) hydrolysis condensation oxidation group transfer
45
If a reaction proceeds with production of heat that reaction can be termed? a) b) hydrolysis Endorgonic 8
c) d) 46
oxidation exergonic
group transfer reactions involve: a) b) c) d) transfer of a group of atoms from one reactant to another joining of two molecules to one product transfer of water to molecule transfer of energy to a molecule
47
phosphorolysis refers to: a) b) c) d) breaking of bonds through addition of a phosphate group addition of phosphate groups to a molecule addition of a phosphate group to glucose lysis of using phosphoric acid
48
Impulse generation during visual perception is a result of: a) hyperpolarisation of retinal membrane b) depolarisation of retinal membrane c) conformational change of retinol d) conformational change of the retinoic acid A mixed TG is one that contains: a) b) c) d) two fatty acids of same type three fatty acids of same type more than one type of fatty acids a glycerol and a phosphate group
49
50
Permeability of the plasma membrane is facilitated by: a) b) c) d) channels and transporters channels and simple diffusion simple diffusion and transporters integral protein and channels
Section II - Short answers questions: Fill all answers in the space provided in this question paper:
In the retina there are three types of cone cells that provide colour vision basing on intensities of the characteristic wavelengths of the light arriving at the retina. These cells are: i) _____________ ii) ________________ i) ___________________ (3 marks) Give a structure of any phospholipid you know and show which part is hydrophobic and which is hydrophilic. (3marks)
phosphotidylcholine
Define a primary amino acid (1 mark) _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ __ List any 3 functional significances of amino acid R-groups (3 marks) a. ____________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ b. ____________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ c. ____________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ Proteins are made by joining of amino acids through condensation reaction. Illustrate how a peptide bond is formed between amino acids. (2 marks)
Define the following terms: (1 marks each)
10
a) zwitterions:_________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________ b) pH:_________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ c) chiral carbon: ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ d) disulfide bond: ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ e) amphipathic molecule ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ f) oxidation and reduction ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ __ g) covalent bonding ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ __ h) Hydrogen bonding ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ __ i) lone pair of electrons ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ __ j) lipids ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ __ 6 The body prefers to store most of the excess calories in form of fats and not as glycogen because of two major reasons: a) ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________(2 marks) b) ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________(2 marks) Give the structure of blood group antigen O. (2 marks)
11
a) Why is blood group O a universal donor? (2 marks) _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ ___ b) Why cant blood group O-person receive blood from other groups like A, B or AB? (2 marks) _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ __ 8 Name the lipid that its lack in premature infants causes respiratory distress syndrome (RDS): _________________________________ (1 marks) During which time this lipid is synthesized in the foetus? ____________________________________________________________ (1 marks) What is the function of this lipid? _______________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ (2 marks) Study the reaction pathway below and answer the questions that follow after:
a) Name the enzymes that act at sites named A, B and C (1 mark each) i)______________ii)__________________________iii)____________________ b) list four sites where the last reaction at C occurs in the human body (1 mark each) c) i)_______________ii)__________________iii)________________iv)__________ d) What are the deficiency symptoms of the above substance in adults and children? (1 mark each)
12
Adults; ________________________________________________________ Children: _______________________________________________________ e) what is the name and function of the substance above (1 mark) ____________________________________________________________________ 10 list any four function of vitamin A including one function for each of the four functions of vitamin A: (1 mark each) i) ________________________________________________________________ ii) _________________________________________________________________ _ iii) _________________________________________________________________ _ iv) _________________________________________________________________ _
13
Вам также может понравиться
- Smith6e Chapter29 TBДокумент12 страницSmith6e Chapter29 TBandrew.gregory978Оценок пока нет
- Exam On Proteins & Enzymes and Lipids: I. Multiple Choice. Submit All Your Answers To Google Classroom in PDF FormatДокумент7 страницExam On Proteins & Enzymes and Lipids: I. Multiple Choice. Submit All Your Answers To Google Classroom in PDF Formatsylv ackermanОценок пока нет
- 12 Chem CH 10 MCQSДокумент12 страниц12 Chem CH 10 MCQSSaran.kОценок пока нет
- Gpat Question Paper 2018Документ23 страницыGpat Question Paper 2018Pawan Kumar khushwahaОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry MCQs: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, VitaminsДокумент10 страницBiochemistry MCQs: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, VitaminsDrug Viral100% (1)
- NIPER JEE Question Paper 2018 PDF DownloadДокумент24 страницыNIPER JEE Question Paper 2018 PDF Downloadsaurabh chaturvediОценок пока нет
- Biotechnologya Todos Los HOДокумент27 страницBiotechnologya Todos Los HOHanan AmarkiОценок пока нет
- BIiomolecules MCQДокумент6 страницBIiomolecules MCQsshadmaniОценок пока нет
- Biomolecules PEARSONДокумент7 страницBiomolecules PEARSONSujata UpadhyeОценок пока нет
- Chemistry of FoodДокумент25 страницChemistry of FoodSubhankar MaityОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 Test BankДокумент24 страницыChapter 5 Test Bank陳禹誌Оценок пока нет
- BiochemДокумент10 страницBiochemRehan MalikОценок пока нет
- Biochem McqsДокумент7 страницBiochem McqsMuhammadsiddique khanОценок пока нет
- 1st AssignmentДокумент9 страниц1st AssignmentRashid MehmoodОценок пока нет
- Microbial Question DR - Shams.Документ32 страницыMicrobial Question DR - Shams.Dr. Mohamed ShamsОценок пока нет
- Biochem 1Документ11 страницBiochem 1Muhammadsiddique khanОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry MLT EXAMДокумент8 страницBiochemistry MLT EXAMLeonel NkwetiОценок пока нет
- Amino Acids:: B SC Semester-VI Unit-Iii Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins & Nucleic AcidsДокумент4 страницыAmino Acids:: B SC Semester-VI Unit-Iii Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins & Nucleic AcidsHarsh KavirajwarОценок пока нет
- BiochemistryДокумент9 страницBiochemistryjosphat mukukaОценок пока нет
- LIPID MCQsДокумент4 страницыLIPID MCQsAhmed Ali SofyОценок пока нет
- Lipid MetabolismДокумент11 страницLipid MetabolismKlint Leyesa100% (1)
- Biochemistry Gpat Exam Question PaperДокумент9 страницBiochemistry Gpat Exam Question PaperPadmavathi C100% (1)
- Komitte 3Документ30 страницKomitte 3Gizem S.Оценок пока нет
- Biochemistry MCQ Module 1Документ60 страницBiochemistry MCQ Module 1ZZ_14U100% (3)
- Chapter 1,2,3 MCQДокумент2 страницыChapter 1,2,3 MCQAbdul qadoosОценок пока нет
- Biomolecule (MCQ)Документ8 страницBiomolecule (MCQ)ΑᲫげφα Κυ๓αན ᄋ1Оценок пока нет
- Understanding Nutrition Canadian 2nd Edition Whitney Test BankДокумент48 страницUnderstanding Nutrition Canadian 2nd Edition Whitney Test Bankradleydiepwxq100% (22)
- MCQs for Pharmacy Technician StudentsДокумент16 страницMCQs for Pharmacy Technician StudentsEntertainment StatusОценок пока нет
- Biochem PreproffДокумент6 страницBiochem PreproffaroobaОценок пока нет
- IARI PHD Entrance Question Paper 2011 - BiochemistryДокумент13 страницIARI PHD Entrance Question Paper 2011 - BiochemistryAbhay KumarОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry Self CreatedДокумент11 страницBiochemistry Self Createdkirklandanderson197Оценок пока нет
- 4th ExamДокумент19 страниц4th ExamAYMUN NAEEMОценок пока нет
- Understanding Nutrition Canadian 2Nd Edition Whitney Test Bank Full Chapter PDFДокумент32 страницыUnderstanding Nutrition Canadian 2Nd Edition Whitney Test Bank Full Chapter PDFdaniel.rodriguez971100% (11)
- BP203T Bichemistry 100 MCQsДокумент16 страницBP203T Bichemistry 100 MCQsShubhrat MaheshwariОценок пока нет
- Final Term Bio 2 MedicineДокумент10 страницFinal Term Bio 2 Medicineأم أحمدОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 The Structure and Function of Large Biological MoleculesДокумент20 страницChapter 5 The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules蔡旻珊Оценок пока нет
- MCQ CHAPTE 13 BIOMOLECULE CBSE Reduced SyllabusДокумент2 страницыMCQ CHAPTE 13 BIOMOLECULE CBSE Reduced SyllabusSavien BrandanОценок пока нет
- Mcqs BiochemДокумент10 страницMcqs Biochemzonishaadan2Оценок пока нет
- Plant RespirationДокумент4 страницыPlant RespirationSoumit PaulОценок пока нет
- Biochem PreproffДокумент7 страницBiochem PreproffKumail LakraОценок пока нет
- Cell & WaterДокумент6 страницCell & Waterminte kingОценок пока нет
- Swarnim Startup & Innovation University Hematology: Objective Question (MCQ) MarksДокумент15 страницSwarnim Startup & Innovation University Hematology: Objective Question (MCQ) MarksDattatray Gote100% (1)
- Quizlet Chapter 5Документ9 страницQuizlet Chapter 5EUNAH LimОценок пока нет
- FeasgsДокумент14 страницFeasgsjan2072650Оценок пока нет
- Accumulative Test 1Документ14 страницAccumulative Test 1hely shahОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Test #9Документ3 страницыChemistry Test #9dania.siddiqui195Оценок пока нет
- Medical exam questions and answersДокумент10 страницMedical exam questions and answersAhmed Abdel-naserОценок пока нет
- Nutrition MCQs MJJKДокумент14 страницNutrition MCQs MJJKarbazОценок пока нет
- MC Chapter 5 TestДокумент13 страницMC Chapter 5 TestGyu Tae JinОценок пока нет
- biomolecules questions waДокумент10 страницbiomolecules questions waYoussef AliОценок пока нет
- Basic Nutrition MC Questions With AnswersДокумент4 страницыBasic Nutrition MC Questions With AnswersAbo SoltanОценок пока нет
- Revision Aminoacids Proteins MCQ StudentДокумент4 страницыRevision Aminoacids Proteins MCQ StudentpatkaОценок пока нет
- Test Biological Molecules Mcqs 2023Документ8 страницTest Biological Molecules Mcqs 2023amsal200416Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 10 PRACTICE QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS PDFДокумент5 страницChapter 10 PRACTICE QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS PDFloserpantz100% (1)
- Chapter 11 Prractice Questions With AnswersДокумент12 страницChapter 11 Prractice Questions With AnswersloserpantzОценок пока нет
- Pak International Nursing College Biochemistry MCQS: (A) Cnh2NonДокумент19 страницPak International Nursing College Biochemistry MCQS: (A) Cnh2NonShimmering MoonОценок пока нет
- 1st Year Paper 1 WhiteДокумент6 страниц1st Year Paper 1 WhiteMuhammad WaseemОценок пока нет
- Exam1 S14Документ33 страницыExam1 S14Asad Javed MehmoodОценок пока нет
- MCQs Dr. Laila - Lipogenesis - Lipolysis - FA OxidationДокумент26 страницMCQs Dr. Laila - Lipogenesis - Lipolysis - FA OxidationYoussef Mohamed100% (2)
- Types of Dietary Fat and Risk of Coronary Heart Disease: A Critical ReviewДокумент15 страницTypes of Dietary Fat and Risk of Coronary Heart Disease: A Critical ReviewMegan KnightОценок пока нет
- Experiment 5 1Документ49 страницExperiment 5 1Angela MagnoОценок пока нет
- Biological Molecules OverviewДокумент39 страницBiological Molecules OverviewJennifer FabiaОценок пока нет
- BiochemistryДокумент4 страницыBiochemistryPriya DhanaОценок пока нет
- Lipids and Proteins Are Associated in Biological Membranes: © 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights ReservedДокумент70 страницLipids and Proteins Are Associated in Biological Membranes: © 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reservedendang dian lestariОценок пока нет
- Witten Exam - FloresДокумент7 страницWitten Exam - FloresJinky AydallaОценок пока нет
- Liposomes A Review of Manufacturing Techniques and Targeting StrategiesДокумент18 страницLiposomes A Review of Manufacturing Techniques and Targeting StrategiesIrini Fountouli - LadopoulouОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Comes Alive: Chapter 2 Part BДокумент67 страницChemistry Comes Alive: Chapter 2 Part Bterryortiz825Оценок пока нет
- Lipid BiosynthesisДокумент187 страницLipid BiosynthesisThanh NguyenОценок пока нет
- Biols102 (Q&a)Документ111 страницBiols102 (Q&a)z5kywx68xkОценок пока нет
- Role of The Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4 in Heart Failure and Cardiovascular DiseaseДокумент12 страницRole of The Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4 in Heart Failure and Cardiovascular DiseaseW CnОценок пока нет
- Mind maps Topic 1 and 2: Cell Biology and Molecular BiologyДокумент19 страницMind maps Topic 1 and 2: Cell Biology and Molecular BiologySusi Meier100% (8)
- Organic Compounds Student Worksheet - Teacher KeyДокумент2 страницыOrganic Compounds Student Worksheet - Teacher KeyYhangale Tactay SociasОценок пока нет
- Experiment 6 - Post LabДокумент3 страницыExperiment 6 - Post LabRyan RiblezaОценок пока нет
- Chem 237 Course Outline Spring 2019 PDFДокумент6 страницChem 237 Course Outline Spring 2019 PDFjoseph al haddadОценок пока нет
- History of Industrial Microbiology PDFДокумент11 страницHistory of Industrial Microbiology PDFOni Port43% (7)
- Exam 1 NotesДокумент54 страницыExam 1 NotesAnonymous If9p21kwZKОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 2-Lipid, ProteinДокумент4 страницыTutorial 2-Lipid, ProteinEngОценок пока нет
- Flavour Academy Presentation 2019Документ187 страницFlavour Academy Presentation 2019datdcb100% (1)
- Curriculum Guide: Instructional PlanningДокумент2 страницыCurriculum Guide: Instructional PlanningRitz Anton LimОценок пока нет
- I & Ii Year Food Chemistry: Semester Course Code Name of The CourseДокумент93 страницыI & Ii Year Food Chemistry: Semester Course Code Name of The CourseEgah GodwinОценок пока нет
- 2003 Nutrition of Marine Fish Larvae KanazawaДокумент42 страницы2003 Nutrition of Marine Fish Larvae KanazawaItzi GuzmánОценок пока нет
- Garcia - Organic Chemistry and BiochemistryДокумент18 страницGarcia - Organic Chemistry and BiochemistryPrince SanjiОценок пока нет
- Gambaran Hasil Pemeriksaan Kadar Trigliserida pada Petugas Perawatan Lantai 4 RSU Wisata UIT Makassar 2018Документ6 страницGambaran Hasil Pemeriksaan Kadar Trigliserida pada Petugas Perawatan Lantai 4 RSU Wisata UIT Makassar 2018nicholas martiosoОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Biochemistry Life at The Molecular Level 4th Edition Voet Test BankДокумент25 страницFundamentals of Biochemistry Life at The Molecular Level 4th Edition Voet Test Bankmaximusthang6iiz100% (21)
- Macromolecule ProjectДокумент3 страницыMacromolecule Projectapi-240096234100% (2)
- Bureau and Cho 1999 Introduction To Nutrition and Feeding of FishДокумент36 страницBureau and Cho 1999 Introduction To Nutrition and Feeding of FishAditiya NugrahaОценок пока нет
- Concept MapДокумент3 страницыConcept MapShenequa LivingstonОценок пока нет
- BIOLOGY FORM 4 Chapter 4 Chemical Composition of The CellДокумент11 страницBIOLOGY FORM 4 Chapter 4 Chemical Composition of The CellMohd IyadRaissa HijazОценок пока нет
- Lipids ExperimentДокумент5 страницLipids ExperimentZheldinan Nicole CruzОценок пока нет