Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
3 Transfer Processes of Heat: Practice 3.1 (P. 84)
Загружено:
sliversniperИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
3 Transfer Processes of Heat: Practice 3.1 (P. 84)
Загружено:
sliversniperАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
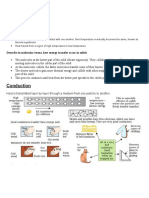
A Heat Chapter 3 Transfer Processes of Heat
3 Transfer Processes of Heat
This ensures even heating.
Practice 3.1 (p. 84)
1 C
A: The fur is not a source of heat. It cannot
raise the temperature of the thermometer. 9 (a) Water is a poor conductor of heat. Heat is
C: The fur can only slow down the rate of conducted slowly from the top of the
heat loss. boiling tube down to the bottom then to
2 C the ice.
3 C (b) We cannot get the same result if we
4 replace the boiling tube by a long metal
Material Example Good Good tube. Since metal is a good conductor of
conductor insulator
heat, this ensures even heating in the
Solid Copper
tube. Heat is conducted faster to the ice.
(metal)
Solid Plastic The ice melts faster.
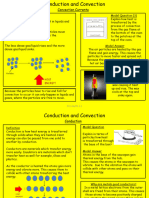
10 In conduction, particles vibrate and transfer
(non-metal) energy when they collide each other. Since
Liquid Water
Gas Air there are very few particle in a vacuum,
conduction does not occur in a vacuum.
5 Metal is a good conductor. Hence, when we
11 The length and the thickness of the metal rods
touch a metal railing, it conducts energy away
should be the same, so that the cross-sectional
from our hands quickly and we feel cold.
areas and the distance between the two ends
However, plastic is a good insulator. When
are constant.
we touch a plastic railing, only very little
The ends of the rods should be placed in the
energy is conducted away from our hands and
same position in the flame so that the
so we feel warm.
temperature difference is constant.
6 Since fat is a good insulator, the fat of fat
people reduces their heat loss by conduction.
Hence, fat people feel warmer than thin
Practice 3.2 (p. 91)
1 A
people in winter.
2 A
7 Goose-down in the jacket traps air. Since air
3 D
is a poor conductor of heat, energy cannot
4 The warm air around the light bulb can flow
easily escape by conduction.
out through the opening.
8 Since copper is a better conductor of heat
5 The air trapped in cotton and feathers can
than stainless steel, it conducts heat faster and
prevent heat loss by conduction. However, a
avoid the accumulation of heat at a point.
New Physics at Work (Second Edition) 14 Oxford University Press 2006
A Heat Chapter 3 Transfer Processes of Heat
hot pan loses energy to the air above it On the other hand, the temperature of the side
through convection. facing the Sun would increase rapidly.
6 Since polystyrene is a good insulator, a 8 Light-coloured surfaces are poor radiators of
polystyrene box reduces heat loss to the heat because they reflect energy away. The
surroundings by conduction. Moreover, the hot air inside the hot air balloon balloons
lid of a polystyrene box reduces heat loss by cools down more slowly. This saves fuel.
convection. 9 Since black paper is a better absorber of
7 The formation of convection current is due to radiation than white paper, snow under the
the rise and the expansion of hot water, and black paper would melt faster than that under
hot water replaced by cold water coming the white paper.
down. If the heating element of an electric
kettle is fixed at the top, the convection Revision exercise 3
current of water cannot form. Heating is more Multiple-choice (p. 107)
slowly. Section A
8 In convection, particles of a fluid carry 1 C
energy from the hot region to the cold region 2 A
and the particles in the cold region would 3 B
move along the convection current to the hot 4 A
region to absorb energy. Since no particles 5 C
exist in a vacuum, no convection occurs in a 6 (HKCEE 2005 Paper II Q7)
vacuum. 7 (HKCEE 2005 Paper II Q8)
Practice 3.3 (p. 100) Section B
1 D 8 B
2 C 9 C
3 D
4 B Conventional (p. 108)
5 C Section A
6 Heat travels from the Sun to the Earth by 1 Black surfaces are good absorbers of
radiation. radiation and get hot under sunlight. (1A)
7 It is very cold in the space. In order to reduce There will be a risk of explosion of the fuel in
heat loss, the spacesuit of astronauts should the storage tanks in the case of a high
be silvery in colour. temperature. (1A)
If it were dull black, astronauts would radiate 2 Black surfaces are good absorbers of
their energy quickly and become very cold. radiation. (1A)
New Physics at Work (Second Edition) 15 Oxford University Press 2006
A Heat Chapter 3 Transfer Processes of Heat
It can absorb the radiation from the Sun more (b) Put the shield on a car window. Since the
effectively. (1A) shield is shiny, when radiation falls on it,
it can reflect the radiation away. Hence, it
can reduce the temperature rise in a car.
3 Air is a poor conductor of heat. (1A) (1A)
It can reduce the absorption of heat from the
outside by the food compartment. (1A) 7 (a) By conduction, heat flows out of a room
4 (a) Aluminium. (1A) through windows. (1A)
(b) Since aluminium conducts heat better For double-glazed windows, in addition
than stainless steel does, it conducts heat to the glass, there is a layer of trapped air.
to the stainless steel layer faster. (1A) (1A)
This can reduce the accumulation of heat Since air is a good insulator, it further
and ensure even heating. (1A) reduces heat loss by conduction. (1A)
Therefore, double-glazed windows are
5 (a) Transparent plate is used so that the much more efficient than single-glazed
radiation from the Sun can pass through. windows.
(1A) (b) Since conduction cannot occur in a
(b) Since a black surface is a good radiation vacuum, (1A)
absorber, (1A) a double-glazed window with a vacuum
between the panes can stop the heat loss
a lower plate with a black surface can be
by conduction. (1A)
heated up by radiation more quickly. (1A)
Hence, a double-glazed window with a
The surface should be dull in colour
vacuum between the panes performs
because a dull surface is a better radiation
better than that with air. (1A)
absorber than a shiny surface. (1A)
8 (a) Radiation. (1A)
6 (a) It is because radiation from the Sun can
(b) Since the specific heat capacity of sea
pass through car windows. (1A)
water is much higher than that of sand,
The radiation warms up the air and other
(1A)
materials inside the car. The warm air and
by E = mc∆T, even if sea water loses
materials emit more infra-red radiation
much more energy than that of sand, the
which cannot escape through the
temperature drop of sea water can be
windows easily. (1A)
mile, while that of sand is huge. (1A)
Also, since all windows of the car are
(Specific heat capacity of sand
closed, the car has no energy loss through
= 835 J kg−1 °C−1
convection. (1A)
Specific heat capacity of water
Hence, the temperature inside the car
= 4200 J kg−1 °C−1)
rises.
New Physics at Work (Second Edition) 16 Oxford University Press 2006
A Heat Chapter 3 Transfer Processes of Heat
(b) When a glass covers the solar water
heater, it creates an environment similar
to a greenhouse for the heater. (1A)
Hence, it raises the temperature of the air
near the heater and allows the water
inside the heater to absorb more energy.
(c) (1A)
(c) Black objects are good absorbers of
radiation. For black pipes, they can
absorb more radiation energy and heat up
the water inside to a higher temperature.
(1A)
(d) Copper is more suitable for making pipes
(For cold and warm regions.) (2A)
(1A)
(For the label of the movement of air.)
because energy is transferred from the
(1A)
pipes to water by conduction and copper
is a good conductor (while plastic is a
Section B
good insulator). (1A)
9 (a) Convection. (1A)
11 (a) Dull surface is better absorber and better
(b) Inside the oven, a convection current is
radiator of radiation than shiny surface.
formed. (1A)
(1A)
The temperature of the air is different at
Therefore, shiny surface should face the
different points along the convection
food when baking because the dull
current. (1A)
surface outside can absorb more energy
A fan can mix the hot and cold air, so that
and reduce the baking time. (1A)
food can be cooked more evenly. (1A)
(b) Yes, it is better to change the arrangement
(c) Vitreous enamel is a good insulator. (1A)
in (a). (1A)
It prevents heat loss to the outside of the
The shiny surface is a poor absorber of
oven. (1A)
heat and a poor radiator. (1A)
(Or it prevents the outside of the oven
The shiny surface outside can reduce heat
being too hot to touch.)
loss of the food by radiation and keep the
(d) Since a shiny surface is a bad radiation
food hot for a longer period of time. (1A)
absorber, (1A)
(c) Evaporation takes away energy from the
it prevents heat loss by radiation. (1A)
food. (1A)
10 (a) (i) Radiation. (1A)
The energy taken is the latent heat of
(ii) Conduction. (1A)
vaporization of water. (1A)
New Physics at Work (Second Edition) 17 Oxford University Press 2006
A Heat Chapter 3 Transfer Processes of Heat
Aluminium foil can reduce the leaving of (ii) Copper is a good conductor of heat,
steam from the food, and thus the heat but plastic is not. (1A)
loss by evaporation. (1A)
(For effective communication.) (1C)
(b) The advantage of using solar panels is
12 The steam of herbal tea rises. Glass plates can that it will not cause pollution to the air.
reduce the heat loss due to evaporation, (1A) (1A)
and the formation of convection current. (1A) The disadvantage is that it can only be
Cold air from freezers sinks and the food in used in day-time and sunny days. (1A)
freezers can be kept frozen even they do not (c) The density of hot water is lower than
have covers. (1A) cold water. Hot water is at the top of the
(For effective communication.) (1C) storage tank, while cold water is at the
13 (a) From land to ocean. (1A) bottom. (1A)
(b) Winter monsoon is caused by convection Therefore, the solar panel takes cold
current. Because of the large specific heat water from the bottom of the storage tank
capacity of water, the land loses heat to heat it up. The radiator takes hot water
more quickly than the sea. (1A) from the top of the storage tank to warm
Warm air rises above the sea and (1A) the house. (1A)
cool air blows in from the land to replace 16 (a) Radiation. (1A)
it. This results in winter monsoon. (1A) The space between the Sun and the Earth
(For effective communication.) (1C) is vacuum. Only radiation transfers heat
14 (a) Black ‘fuel effect’ lumps burn and release without the need of a medium. (1A)
heat. Hot air inside the fire is heated. It (b) Heat from the body is conducted to the
expands and rises. (1A) sweat on the skin. (1A)
Hot air leaves the fire at A, (1A) The sweat evaporates from the skin and
and is replaced by cold air entered from takes away heat. (1A)
C. (1A) Since the sweat is made of water, the
The air forms a convection current energy lost is the latent heat of
flowing from C to A. (1A) vaporization of water. Sweating therefore
(b) (i) Radiation. (1A) cools the runner. (1A)
(ii) Dull black surface. (1A) (c) Foil blanket traps air. (1A)
15 (a) (i) Since black bodies absorb radiation Since air is a poor conductor heat, it
better, (1A) reduces heat loss by conduction. (1A)
pipes painted in black heat water in Shiny surfaces are poor absorbers and
a higher rate. (1A) poor radiators of heat. (1A)
New Physics at Work (Second Edition) 18 Oxford University Press 2006
A Heat Chapter 3 Transfer Processes of Heat
They reduce heat loss by radiation and of the wall.
stop the runner cooling down too quickly. Put the heater away from the walls to the
(1A) outside.
Replace the metal foil between the wall
and the heater with a good insulating
material.
17 (a) (i)
(For correct movement of air.) (1A)
(ii) Convection. (1A)
(iii) The heater heats up the air around it.
The warm air expands, gets less
dense and (1A)
rises. (1A)
As warm air rises, it cools down
gradually (1A)
and falls. (1A)
Then it moves to replace the rising
warm air near the heater. (1A)
(b) Since shiny objects are poor radiation
absorbers and poor radiators, a metal foil,
which has shiny surfaces, absorbs and
radiates little energy. (1A)
Therefore, the metal foil reduces energy
transferred to the wall and hence reduces
heat loss to the outside. (1A)
(c) Any two of the following: (2A)
Use double-glazed window.
Paint the walls of the room with light
colours.
Insert insulating materials between layers
New Physics at Work (Second Edition) 19 Oxford University Press 2006
A Heat Chapter 3 Transfer Processes of Heat
Physics in articles (p. 112)
(a) Convection. (1A)
(b) We will feel hot first and then get burnt
after a long time. (1A)
It is because heat is transferred to our
hand by convection. (1A)
(c) The smaller the size of the hole, the
higher the rate of hot air flowing out.(1A)
In a fixed time, if more hot air passes
through a point, the temperature at that
point will be higher. (1A)
Heat will be more concentrated to the
hanging point, thus making the
temperature higher. (1A)
(For effective communication.) (1C)
(d) Bamboo is a poor conductor of heat, but
metal is a good conductor of heat. (1A)
It takes more time for heat to conduct
from the hanging point to our hand.
Therefore, it is safer to use. (1A)
New Physics at Work (Second Edition) 20 Oxford University Press 2006
Вам также может понравиться
- Simple Experiments in Static Electricity - A Series of Instructive and Entertaining Experiments in Static Electricity for Students and AmateursОт EverandSimple Experiments in Static Electricity - A Series of Instructive and Entertaining Experiments in Static Electricity for Students and AmateursОценок пока нет
- 4 Transfer Processes: Practice 4.1 (p.109)Документ6 страниц4 Transfer Processes: Practice 4.1 (p.109)Oscar TSANGОценок пока нет
- Practice 10401 AnsДокумент1 страницаPractice 10401 AnsPak Yu ChauОценок пока нет
- Heat Transfer Processes in Gases and Down JacketsДокумент1 страницаHeat Transfer Processes in Gases and Down JacketsPak Yu ChauОценок пока нет
- Part2 ch02Документ5 страницPart2 ch02api-3705610Оценок пока нет
- Ch02 SolutionДокумент7 страницCh02 Solutionapi-3700944Оценок пока нет
- Active Physics Full Solutions Chapter 1 Temperature and Heat Transfer ExercisesДокумент2 страницыActive Physics Full Solutions Chapter 1 Temperature and Heat Transfer ExercisesTSE WING HEI謝穎晞Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 Transfer of Thermal Energy-1Документ6 страницChapter 7 Transfer of Thermal Energy-1Boss's I will be a superheroОценок пока нет
- Transfer of Thermal Energy: Test Yourself 10.1 (Page 168)Документ5 страницTransfer of Thermal Energy: Test Yourself 10.1 (Page 168)Jack Kowman100% (8)
- Class 7 ScienceДокумент40 страницClass 7 ScienceQulb e AbbasОценок пока нет
- Answers To End-Of-Chapter Questions For Chapter 9, Conduction, Convection and RadiationДокумент3 страницыAnswers To End-Of-Chapter Questions For Chapter 9, Conduction, Convection and RadiationMencam AsongОценок пока нет
- Heat Transfer and Expansion NotesДокумент8 страницHeat Transfer and Expansion NotesmelissaОценок пока нет
- QuestionsДокумент11 страницQuestionsR MathewОценок пока нет
- Chapter 12 Transfer of Thermal EnergyДокумент15 страницChapter 12 Transfer of Thermal EnergyGiovanni SlackОценок пока нет
- Heat TransferДокумент4 страницыHeat TransferSelwah Hj AkipОценок пока нет
- Chapter Nine Class 9thДокумент10 страницChapter Nine Class 9thShahbaz KhanОценок пока нет
- Transfer of Heat Energy - Check Your UnderstandingДокумент2 страницыTransfer of Heat Energy - Check Your UnderstandingAlyssa Cole100% (1)
- Unit 6 S2Phy Thermal Transfer PracticeДокумент8 страницUnit 6 S2Phy Thermal Transfer PracticeWilly TanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 FLSДокумент30 страницChapter 5 FLSnurul najwaОценок пока нет
- Conduction: Transfer of Thermal EnergyДокумент10 страницConduction: Transfer of Thermal Energyanwar9602020Оценок пока нет
- Notes Transfer of Thermal EnergyДокумент12 страницNotes Transfer of Thermal Energymahrosh mamoon100% (2)
- C08 Transfer of Thermal Energy (Teacher)Документ49 страницC08 Transfer of Thermal Energy (Teacher)a m i rОценок пока нет
- Transfer of Heat: Long Questions & AnswersДокумент7 страницTransfer of Heat: Long Questions & AnswersUsman babarОценок пока нет
- THERMAL TRANSFER-pureДокумент14 страницTHERMAL TRANSFER-pureblueegofxОценок пока нет
- Transfer of Thermal Energy: ConductionДокумент10 страницTransfer of Thermal Energy: ConductionmelissaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 11Документ10 страницChapter 11ranaaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9Документ3 страницыChapter 9ProdeepОценок пока нет
- Y10 C10 Heat Transfer MSДокумент2 страницыY10 C10 Heat Transfer MSShafiqa FitriОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3: Basic PrinciplesДокумент15 страницChapter 3: Basic PrinciplesWengelОценок пока нет
- 11-Transfer of Thermal EnergyДокумент46 страниц11-Transfer of Thermal Energyrodel.verzosaОценок пока нет
- Transfer of Heat: Long Questions & AnswersДокумент7 страницTransfer of Heat: Long Questions & AnswersUsman babarОценок пока нет
- Heat Transfer MethodsДокумент4 страницыHeat Transfer MethodsKartikОценок пока нет
- Chapter-4 QA Section-E&FДокумент4 страницыChapter-4 QA Section-E&FronikОценок пока нет
- 2 Conduction Convection RadiationДокумент24 страницы2 Conduction Convection RadiationSyed Inam UllahОценок пока нет
- Heat Transfer Modes"TITLE"Chemical Heat Transfer Mechanisms" TITLE"Conduction, Convection and Radiation"TITLE"ECH 3023 Heat Transfer FundamentalsДокумент51 страницаHeat Transfer Modes"TITLE"Chemical Heat Transfer Mechanisms" TITLE"Conduction, Convection and Radiation"TITLE"ECH 3023 Heat Transfer FundamentalsBilal AhmedОценок пока нет
- 09 HeatДокумент18 страниц09 HeatJulia AhmadОценок пока нет
- Heat Transfer MethodsДокумент45 страницHeat Transfer MethodsLinaОценок пока нет
- 7th Class ScienceДокумент10 страниц7th Class ScienceM Saadat SaeediОценок пока нет
- Father Agnel School, Noida Assignment Class Vii Ch-HeatДокумент13 страницFather Agnel School, Noida Assignment Class Vii Ch-HeatDeepak KansalОценок пока нет
- PhysicsДокумент2 страницыPhysicsJohn Paul RodriguezОценок пока нет
- IGCSE Physics Chapter on Thermal Energy TransferДокумент26 страницIGCSE Physics Chapter on Thermal Energy TransferAishath Waheeda50% (2)
- 01 Exercise Solutions e PDFДокумент9 страниц01 Exercise Solutions e PDFouo So方Оценок пока нет
- 1-C, 2-D, 3-A, 4-E, 5-BДокумент2 страницы1-C, 2-D, 3-A, 4-E, 5-Blepton1973Оценок пока нет
- PM Test C10 (Student)Документ7 страницPM Test C10 (Student)damonchooОценок пока нет
- 9th Physics CHAPTER 9 S.Q Numerical Problems PDFДокумент3 страницы9th Physics CHAPTER 9 S.Q Numerical Problems PDFMuneer KaleriОценок пока нет
- Assignment Questions - Heat TransferДокумент12 страницAssignment Questions - Heat TransferPratik Walimbe0% (1)
- Heat TransferДокумент29 страницHeat TransferDIANA QUINONESОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics Module 5: Assessment Task 5: Laguna University College of Education A.Y 2020-2021Документ20 страницThermodynamics Module 5: Assessment Task 5: Laguna University College of Education A.Y 2020-2021anembam putobungbongОценок пока нет
- TRANSFER OF THERMAL ENERGY - NewДокумент7 страницTRANSFER OF THERMAL ENERGY - NewKatlo MokgethiОценок пока нет
- Bridge Course Physics SyllabusДокумент49 страницBridge Course Physics SyllabusNAVINRAJ RSОценок пока нет
- PiXL Knowledge Test PowerPoint AQA P1 CORE Science Legacy 2016 and 2017Документ19 страницPiXL Knowledge Test PowerPoint AQA P1 CORE Science Legacy 2016 and 2017Isini sehansa amarathungaОценок пока нет
- Thermal physics worksheetДокумент15 страницThermal physics worksheetilyasheee901100% (2)
- Answers To End-Of-Chapter QuestionsДокумент2 страницыAnswers To End-Of-Chapter QuestionsSanifer PlayzОценок пока нет
- Physics For The Life Sciences 2nd Edition Solution ManualДокумент11 страницPhysics For The Life Sciences 2nd Edition Solution ManualJosephWoodsdbjt100% (38)
- 1 s2.0 S0022311503003179 MainДокумент7 страниц1 s2.0 S0022311503003179 MainkasturiОценок пока нет
- 6.2 Transfer of Thermal EnergyДокумент78 страниц6.2 Transfer of Thermal EnergyHakim AbbasОценок пока нет
- Physics 16 - Thermal ProcessesДокумент19 страницPhysics 16 - Thermal ProcessesSuhaan HussainОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER I: Introduction To Heat Transfer Methods of Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and RadiationДокумент83 страницыCHAPTER I: Introduction To Heat Transfer Methods of Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and RadiationSruthi ChallapalliОценок пока нет
- Thermal Energy TransferДокумент44 страницыThermal Energy Transferp geetha raniОценок пока нет
- Thermal Physics: Kinetic Molecular Model and Thermal PropertiesДокумент18 страницThermal Physics: Kinetic Molecular Model and Thermal PropertiesHakim Abbas Ali Phalasiya100% (1)
- U4Документ16 страницU4api-3826695Оценок пока нет
- PP2Документ11 страницPP2api-3826695Оценок пока нет
- Install The 3cdaemon First, Then Run The 3cdaemonДокумент4 страницыInstall The 3cdaemon First, Then Run The 3cdaemonapi-3826695Оценок пока нет
- The Future For S5 Graduates: 5.1 Pre-ReadingДокумент13 страницThe Future For S5 Graduates: 5.1 Pre-Readingapi-3826695Оценок пока нет
- PP1Документ11 страницPP1api-3826695100% (1)
- PP7Документ11 страницPP7api-3826695Оценок пока нет
- Examination: 1.1 The Aims of The HKCEE Paper 1, Reading (1A) and Writing (1B)Документ13 страницExamination: 1.1 The Aims of The HKCEE Paper 1, Reading (1A) and Writing (1B)api-3826695Оценок пока нет
- 3.1 Vocabulary To Do With Charity WorkДокумент15 страниц3.1 Vocabulary To Do With Charity Workapi-3826695Оценок пока нет
- U2Документ14 страницU2api-3826695Оценок пока нет
- PP6Документ11 страницPP6api-3826695Оценок пока нет
- Pets and AnimalsДокумент10 страницPets and Animalsapi-3826695Оценок пока нет
- Chemistry A Modern View: Exercise Book 3 Suggested AnswersДокумент39 страницChemistry A Modern View: Exercise Book 3 Suggested Answersapi-3826695Оценок пока нет
- PP10Документ11 страницPP10api-3826695Оценок пока нет
- PP8Документ10 страницPP8api-3826695Оценок пока нет
- PP5Документ11 страницPP5api-3826695Оценок пока нет
- The World of WorkДокумент10 страницThe World of Workapi-3826695Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 16 Measures of DispersionДокумент15 страницChapter 16 Measures of Dispersionapi-3732612Оценок пока нет
- PP3Документ11 страницPP3api-3826695Оценок пока нет
- 5ACh14 (Arithmetic and Geometric Sequences and Their Summation)Документ42 страницы5ACh14 (Arithmetic and Geometric Sequences and Their Summation)api-3826695Оценок пока нет
- 5BCh15 (More About Probability)Документ22 страницы5BCh15 (More About Probability)api-3826695Оценок пока нет
- Chemistry A Modern View: Exercise Book 1 Suggested AnswersДокумент34 страницыChemistry A Modern View: Exercise Book 1 Suggested Answersapi-3826695100% (2)
- Chemistry A Modern View: Exercise Book 2 Suggested AnswersДокумент27 страницChemistry A Modern View: Exercise Book 2 Suggested Answersapi-3826695100% (5)
- Chapter 17 Uses and Abuses of StatisticsДокумент2 страницыChapter 17 Uses and Abuses of Statisticsapi-3732612Оценок пока нет
- 5ACh13 (Linear Inequalities in Two Unknowns)Документ33 страницы5ACh13 (Linear Inequalities in Two Unknowns)api-3826695Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 11 Qualitative Treatment of LocusДокумент6 страницChapter 11 Qualitative Treatment of Locusapi-3732612Оценок пока нет
- 5ACh12 (Coordinate Treatment of Simple Locus Problems)Документ43 страницы5ACh12 (Coordinate Treatment of Simple Locus Problems)api-3826695Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 10 VariationsДокумент32 страницыChapter 10 Variationsapi-3732612100% (2)
- 4BCh08 (More About Trigonometry 1)Документ36 страниц4BCh08 (More About Trigonometry 1)api-3826695100% (2)
- 4BCh09 (More About Trigonometry 2)Документ67 страниц4BCh09 (More About Trigonometry 2)api-3826695100% (1)
- 4BCh07 (Basic Properties of Circles 2)Документ25 страниц4BCh07 (Basic Properties of Circles 2)api-3826695100% (1)
- Pressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedОт EverandPressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Einstein's Fridge: How the Difference Between Hot and Cold Explains the UniverseОт EverandEinstein's Fridge: How the Difference Between Hot and Cold Explains the UniverseРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (50)
- Piping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationОт EverandPiping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (18)
- Hyperspace: A Scientific Odyssey Through Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th DimensionОт EverandHyperspace: A Scientific Odyssey Through Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th DimensionРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- Formulas and Calculations for Drilling, Production, and Workover: All the Formulas You Need to Solve Drilling and Production ProblemsОт EverandFormulas and Calculations for Drilling, Production, and Workover: All the Formulas You Need to Solve Drilling and Production ProblemsОценок пока нет
- Basic Alarm Electronics: Toolbox Guides for Security TechniciansОт EverandBasic Alarm Electronics: Toolbox Guides for Security TechniciansJohn SangerРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- The Laws of Thermodynamics: A Very Short IntroductionОт EverandThe Laws of Thermodynamics: A Very Short IntroductionРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (10)
- Control of Power Electronic Converters and Systems: Volume 1От EverandControl of Power Electronic Converters and Systems: Volume 1Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Quantum Mechanics 4: Spin, Lasers, Pauli Exclusion & Barrier PenetrationОт EverandQuantum Mechanics 4: Spin, Lasers, Pauli Exclusion & Barrier PenetrationРейтинг: 1 из 5 звезд1/5 (1)
- Operational Amplifier Circuits: Analysis and DesignОт EverandOperational Amplifier Circuits: Analysis and DesignРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- Design of Foundations for Offshore Wind TurbinesОт EverandDesign of Foundations for Offshore Wind TurbinesРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- 1,001 Questions & Answers for the CWI Exam: Welding Metallurgy and Visual Inspection Study GuideОт Everand1,001 Questions & Answers for the CWI Exam: Welding Metallurgy and Visual Inspection Study GuideРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (7)
- Rolling Bearing Tribology: Tribology and Failure Modes of Rolling Element BearingsОт EverandRolling Bearing Tribology: Tribology and Failure Modes of Rolling Element BearingsОценок пока нет