Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Flowchart 2
Загружено:
Jordan BelkeИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Flowchart 2
Загружено:
Jordan BelkeАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
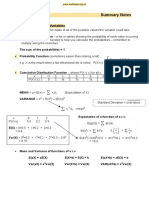
Probability of Observing a Quantity or Proportion
Quantity
State a quantity or proportion
Proportion
Excel functions standard deviation of quantities = stdev(data) area to the left of t-score = t.dist(t-score, degrees of freedom, TRUE) area to the left of z-score = norm.s.dist(z-score, TRUE)
t-score =
Calculate the score
stated quantity sample mean standard deviation z-score =
Calculate the score
stated proportion sample proportion standard deviation
Find the area to the left of the score
The shaded area is the probability of observing a quantity or proportion less than or equal to the stated quantity or proportion.
Hypothesis Test for a Single Proportion
H0 < HA >
State the hypothesis
Comparing a sample proportion to a fixed quantity H0 : population proportion = standard error =
H0 > HA <
H0 = HA
(1 )
N
Calculate the score
z-score = sample proportion standard error
Confidence Interval p ( critical value ) p (1 p ) N
Find the area to the left of the score (standard normal distribution)
Find the p-value (standard normal distribution)
Excel functions area = norm.s.dist(z-score, TRUE) z-score = norm.s.inv(area)
p-value = 1 norm.s.dist(z-score, TRUE)
p-value = 2 x (1 norm.s.dist(abs(z-score), TRUE))
p-value = norm.s.dist(z-score, TRUE)
State the conclusion
p-value approach: The probability of the null hypothesis being true is the p-value. Significance approach: If p-value < significance level, reject the null hypothesis.
Hypothesis Test for Comparing Proportions
H0 < HA >
State the hypothesis
H0 > HA <
H0 = HA
Comparing two sample proportions H0 : population proportion 1 = population proportion 2 standard error = p1 ( 1 p1 ) p2 (1 p2 ) + N1 N2
Calculate the score
z-score = sample proportion standard error
Find the area to the left of the score (standard normal distribution)
Find the p-value (standard normal distribution)
Excel functions area = norm.s.dist(z-score, TRUE) z-score = norm.s.inv(area)
p-value = 1 norm.s.dist(z-score, TRUE)
p-value = 2 x (1 norm.s.dist(abs(z-score), TRUE))
p-value = norm.s.dist(z-score, TRUE)
State the conclusion
p-value approach: The probability of the null hypothesis being true is the p-value. Significance approach: If p-value < significance level, reject the null hypothesis.
Hypothesis Test for a Single Mean
H0 < HA >
State the hypothesis
H0 > HA <
H0 = HA
Comparing a sample mean to a fixed quantity H0 : population mean = s2 N degrees of freedom = N 1 standard error =
Calculate the score
t-score = sample mean standard error
Confidence Interval x ( critical value ) s2 N
Find the area to the left of the score (t distribution)
Find the p-value (t distribution)
Excel functions area = t.dist(t-score, degrees of freedom, TRUE) t-score = t.inv(area, degrees of freedom)
p-value = 1 t.dist(t-score, df, TRUE)
p-value = 2 x (1 t.dist(abs(t-score), df, TRUE))
p-value = t.dist(t-score, df, TRUE)
State the conclusion
p-value approach: The probability of the null hypothesis being true is the p-value. Significance approach: If p-value < significance level, reject the null hypothesis.
Hypothesis Test for Comparing Means
H0 < HA >
State the hypothesis
H0 > HA <
H0 = HA
Comparing two sample means H0 : population mean 1 = population mean 2 standard error =
2 2 s1 s2 + N1 N2
Calculate the score
t-score = sample mean 1 sample mean 2 standard error
degrees of freedom N1 + N2 2
Find the area to the left of the score (t distribution)
Find the p-value (t distribution)
Excel functions area = t.dist(t-score, degrees of freedom, TRUE) t-score = t.inv(area, degrees of freedom) area to the nearest tail = t.test(data set 1, data set 2, 1, 3)
p-value = 1 t.dist(t-score, df, TRUE)
p-value = 2 x (1 t.dist(abs(t-score), df, TRUE))
p-value = t.dist(t-score, df, TRUE)
State the conclusion
p-value approach: The probability of the null hypothesis being true is the p-value. Significance approach: If p-value < significance level, reject the null hypothesis.
Hypothesis Test for a Single Variance
H0 < HA >
State the hypothesis
Comparing a variance to a fixed quantity H0 : population variance = 2 degrees of freedom = N 1
H0 > HA <
H0 = HA
Calculate the score
2 -score =
( N 1 ) s2
2
Find the area to the left of the score (Chi-squared distribution)
Find the p-value (Chi-squared distribution)
Excel functions area = chisq.dist(score, degrees of freedom, TRUE)
p-value = 1 chi.dist(x-score, df, TRUE)
p-value = 2 x min(1 chi.dist(x-score, df, TRUE), chi.dist(x-score, df, TRUE))
2 -score = chisq.inv(area, degrees of freedom)
p-value = chi.dist(x-score, df, TRUE)
State the conclusion
p-value approach: The probability of the null hypothesis being true is the p-value. Significance approach: If p-value < significance level, reject the null hypothesis.
Hypothesis Test for Comparing Variances
H0 < HA >
State the hypothesis
H0 > HA <
H0 = HA
Comparing two variances H0 : population variance 1 = population variance 2 degrees of freedom smaller variance = Nsmaller variance 1 degrees of freedom larger variance = Nlarger variance 1
Calculate the score
F-score =
2 ssmaller variance 2 slarger variance
Find the area to the left of the score (F distribution)
Find the p-value (F distribution)
Excel functions area = f.dist(f-score, df for smaller variance, df for larger variance, TRUE) F-score = f.inv(area, df for smaller variance, df for larger variance)
State the conclusion
p-value approach: The probability of the null hypothesis being true is the p-value. Significance approach: If p-value < significance level, reject the null hypothesis.
Вам также может понравиться
- Statistics Formula Sheet: Summarising DataДокумент3 страницыStatistics Formula Sheet: Summarising DatacinnamonalbeeОценок пока нет
- Formula SheetДокумент3 страницыFormula SheetLevi CliffordОценок пока нет
- Summary Advanced StatisticsДокумент11 страницSummary Advanced StatisticstjОценок пока нет
- Multiple Regression Analysis - InferenceДокумент34 страницыMultiple Regression Analysis - InferenceAndre Mitsuo AkamineОценок пока нет
- EC-512EC512 LecNotes Pt2Документ29 страницEC-512EC512 LecNotes Pt2Nagmani KumarОценок пока нет
- CFA Level 1 Review - Quantitative MethodsДокумент10 страницCFA Level 1 Review - Quantitative MethodsAamirx6450% (2)
- Statistics Cheat SheetДокумент23 страницыStatistics Cheat Sheetcannickg100% (2)
- Cheating Formula Statistics - Final ExamДокумент4 страницыCheating Formula Statistics - Final ExamM.Ilham PratamaОценок пока нет
- Stat SymbolsДокумент8 страницStat SymbolsjanmalexxОценок пока нет
- Interpreting and Calculating P-Values - MinitabДокумент4 страницыInterpreting and Calculating P-Values - MinitabDhaka SylhetОценок пока нет
- Non - Parametic TestДокумент5 страницNon - Parametic TestHASHMI SUTARIYAОценок пока нет
- S2 Summary: Formulae To LearnДокумент2 страницыS2 Summary: Formulae To LearnredderdatОценок пока нет
- HypothesisEvaluationДокумент19 страницHypothesisEvaluationadafqОценок пока нет
- Math 115 - Summary PacketДокумент10 страницMath 115 - Summary PacketBella DouglasОценок пока нет
- Evaluating Hypotheses: Jayanta Mukhopadhyay Dept. of Computer Science and EnggДокумент17 страницEvaluating Hypotheses: Jayanta Mukhopadhyay Dept. of Computer Science and EnggUtkarsh PatelОценок пока нет
- STA101 Formula SheetДокумент4 страницыSTA101 Formula SheetOlawale AwedaОценок пока нет
- Statistical Inference: Dr. Mona Hassan AhmedДокумент34 страницыStatistical Inference: Dr. Mona Hassan Ahmedkareem3456Оценок пока нет
- Hypothesis TestingДокумент41 страницаHypothesis TestingvisitantaiОценок пока нет
- Jfuture 202005025Документ2 страницыJfuture 202005025devi kumarОценок пока нет
- Tests For A Population Mean The Critical Region and The P-ValueДокумент8 страницTests For A Population Mean The Critical Region and The P-ValueDamini ThakurОценок пока нет
- Linear Equations in Two Variables: Quick Reference, STD: X 1Документ4 страницыLinear Equations in Two Variables: Quick Reference, STD: X 1Sarbu GeorgeОценок пока нет
- TohДокумент53 страницыTohY20me135 V.LokeshОценок пока нет
- OverviewДокумент1 страницаOverviewgobu269104Оценок пока нет
- Hypothesis Statistics-1-1Документ35 страницHypothesis Statistics-1-111- NikunjОценок пока нет
- 1 Statistical Project: 2.1 1 Qualitative VariableДокумент8 страниц1 Statistical Project: 2.1 1 Qualitative VariablehelinОценок пока нет
- Math Supplement PDFДокумент17 страницMath Supplement PDFRajat GargОценок пока нет
- Concept of Data Depth and ApplicationsДокумент9 страницConcept of Data Depth and ApplicationsMCSlocolocoОценок пока нет
- Analysing and Presenting Data: Practical Hints: Daniele CEI, Giorgio MATTEIДокумент53 страницыAnalysing and Presenting Data: Practical Hints: Daniele CEI, Giorgio MATTEIAdi DanuОценок пока нет
- Eva Uation Methods 273 A Spring 09Документ17 страницEva Uation Methods 273 A Spring 09Lena MohameedОценок пока нет
- s2 Revision NotesДокумент5 страницs2 Revision NotesAlex KingstonОценок пока нет
- Revision - Elements or Probability: Notation For EventsДокумент20 страницRevision - Elements or Probability: Notation For EventsAnthony Saracasmo GerdesОценок пока нет
- AQA S2 Revision NotesДокумент8 страницAQA S2 Revision NotesLscribd15Оценок пока нет
- Cheat Sheet FinalДокумент2 страницыCheat Sheet FinalFrancis TanОценок пока нет
- Statistics Hypothesis TestingДокумент7 страницStatistics Hypothesis TestingWasif ImranОценок пока нет
- ELEG 5633 Detection and Estimation Detection Theory I: Jing YangДокумент27 страницELEG 5633 Detection and Estimation Detection Theory I: Jing YangJames Espinoza100% (1)
- Goodness of Fit Test DFДокумент2 страницыGoodness of Fit Test DFcutedesi8585Оценок пока нет
- Basics of Inference: Department of Statistics Ram Lal Anand CollegeДокумент34 страницыBasics of Inference: Department of Statistics Ram Lal Anand CollegeshanОценок пока нет
- Statistics Training IIT KGPДокумент96 страницStatistics Training IIT KGPVinay DuttaОценок пока нет
- Chi Square Test of Independence Dennis GacesДокумент17 страницChi Square Test of Independence Dennis GacesRheanne CervezaОценок пока нет
- Review of StatisticsДокумент36 страницReview of StatisticsJessica AngelinaОценок пока нет
- STA101 Formula SheetДокумент4 страницыSTA101 Formula SheetConner BiekerОценок пока нет
- Lab Sheet-1Документ8 страницLab Sheet-1rj OpuОценок пока нет
- Statistika: Hypothesis TestingДокумент50 страницStatistika: Hypothesis TestingSuryati PurbaОценок пока нет
- Non-Parametric TestДокумент12 страницNon-Parametric Testhansdeep479Оценок пока нет
- Probability and Statistics in ExcelДокумент11 страницProbability and Statistics in ExcelJaroslav PokornyОценок пока нет
- 5.1.1 SSK5210 Examples On Hypothesis Testing - 2Документ10 страниц5.1.1 SSK5210 Examples On Hypothesis Testing - 2Sarveshwaran BalasundaramОценок пока нет
- Review 2 SummaryДокумент4 страницыReview 2 Summarydinhbinhan19052005Оценок пока нет
- Statistics - 160: The Normal Probability DistributionДокумент17 страницStatistics - 160: The Normal Probability DistributionALLAPARTHI SHANMUKHA PRIYA RAMA ABHILASH 15MIS0077Оценок пока нет
- Minimax: 1 The Parks-Mcclellan Filter Design MethodДокумент11 страницMinimax: 1 The Parks-Mcclellan Filter Design MethodCristóbal Eduardo Carreño MosqueiraОценок пока нет
- Background For Lesson 5: 1 Cumulative Distribution FunctionДокумент5 страницBackground For Lesson 5: 1 Cumulative Distribution FunctionNguyễn ĐứcОценок пока нет
- Testing of Hypothesis: 1 Steps For SolutionДокумент8 страницTesting of Hypothesis: 1 Steps For SolutionAaron MillsОценок пока нет
- Formula SheetДокумент2 страницыFormula SheetBlythe ButlerОценок пока нет
- Chapter 8Документ21 страницаChapter 8Ciobanu GheorgheОценок пока нет
- Chi SquareДокумент35 страницChi SquarePravab DhakalОценок пока нет
- Two-Sample T-Tests Using Effect SizeДокумент11 страницTwo-Sample T-Tests Using Effect SizescjofyWFawlroa2r06YFVabfbajОценок пока нет
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsОт EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (8)
- 2.1. Artikel 1 - The Value Relevance of Accounting Information - Empirical Evidence From JordanДокумент14 страниц2.1. Artikel 1 - The Value Relevance of Accounting Information - Empirical Evidence From JordanMonica Ratu LeoОценок пока нет
- Class 10 Multilevel ModelsДокумент42 страницыClass 10 Multilevel Modelshubik38Оценок пока нет
- STAB22 FinalExam 2013F PDFДокумент23 страницыSTAB22 FinalExam 2013F PDFexamkillerОценок пока нет
- Adrijana TorbovskaДокумент6 страницAdrijana Torbovskav9991 v9991Оценок пока нет
- W11 - Mitchell & Jolley - ''Research Design Explained''Документ744 страницыW11 - Mitchell & Jolley - ''Research Design Explained''gina khairunnisaОценок пока нет
- Uniformidadcontenido Troubleshooting Pharm TechДокумент12 страницUniformidadcontenido Troubleshooting Pharm Techjcoccio2Оценок пока нет
- Asphalt Pavement Acoustic Performance Model: SustainabilityДокумент15 страницAsphalt Pavement Acoustic Performance Model: SustainabilityNuno FerreiraОценок пока нет
- We Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsДокумент41 страницаWe Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsGustavoОценок пока нет
- Financial Time Series ModelsДокумент11 страницFinancial Time Series ModelsAbdi HiirОценок пока нет
- Applied Econometrics PDFДокумент224 страницыApplied Econometrics PDFalemayehu tameneОценок пока нет
- Multiple Regression AnalysisДокумент27 страницMultiple Regression AnalysisEmmy SukhОценок пока нет
- CS5691:Programming Assignment 1 15 M Arch 2019 Team 25 M Sriram (EE16B027), P Venkat (CS16B017) Indian Institute of Technology, MadrasДокумент13 страницCS5691:Programming Assignment 1 15 M Arch 2019 Team 25 M Sriram (EE16B027), P Venkat (CS16B017) Indian Institute of Technology, MadrasSriram MudunuriОценок пока нет
- Multiple Regression & Canonical Correlation Analysis: Reynel T. RevillaДокумент18 страницMultiple Regression & Canonical Correlation Analysis: Reynel T. RevillaChristine Cubar PallarОценок пока нет
- Religare Commodities Metals and Energy ResearchДокумент12 страницReligare Commodities Metals and Energy Researchninoy_johnterryОценок пока нет
- Assingment6 512Документ6 страницAssingment6 512Sai AОценок пока нет
- SEM - Schreiber 2006 Reporting Structural Equation Modeling and Confirmatory Factor Analysis Results A ReviewДокумент15 страницSEM - Schreiber 2006 Reporting Structural Equation Modeling and Confirmatory Factor Analysis Results A ReviewhoorieОценок пока нет
- Intermediate Statistics Test Sample 2Документ19 страницIntermediate Statistics Test Sample 2muralidharan0% (1)
- Student FilesolДокумент5 страницStudent Filesolsubash1111@gmail.comОценок пока нет
- 31 61 1 PBДокумент15 страниц31 61 1 PBGhina SalsabilaОценок пока нет
- VelPAK TutorialДокумент95 страницVelPAK TutorialKURTОценок пока нет
- The Case:: Shahid GulzarДокумент4 страницыThe Case:: Shahid GulzarShahid JugnooОценок пока нет
- Carlson X-Port PDFДокумент60 страницCarlson X-Port PDFAmorim SilvaОценок пока нет
- Mufita2016 Sas LogДокумент2 страницыMufita2016 Sas LogmuffitaraniОценок пока нет
- Randomized Block DesignДокумент7 страницRandomized Block DesignPurani SwethaОценок пока нет
- Sampling Methods and The Central Limit TheoremДокумент30 страницSampling Methods and The Central Limit TheoremNadia TanzeemОценок пока нет
- FactorДокумент40 страницFactoraraksunОценок пока нет
- Modeling of The Equilibrium Moisture ContentДокумент6 страницModeling of The Equilibrium Moisture ContentOscar TorresОценок пока нет
- Impact of Human Resource Planning On Organizational PerformanceДокумент14 страницImpact of Human Resource Planning On Organizational Performanceimrul khanОценок пока нет
- ResSimCh7 PDFДокумент48 страницResSimCh7 PDFoilkgas31Оценок пока нет
- General Physics 1 - Budget of WorkДокумент11 страницGeneral Physics 1 - Budget of Workanon_145781083Оценок пока нет