Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Biology Form 5 Chapter 3
Загружено:
Hasan YusofАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Biology Form 5 Chapter 3
Загружено:
Hasan YusofАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
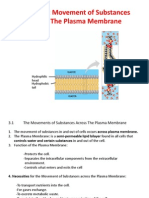
PUSAT TUISYEN RIMBA ILMU BIOLOGY FORM 5 CHAPTER 3 : MOVEMENT ACROSS PLASMA MEMBRANE 1. Three types of passive transport.
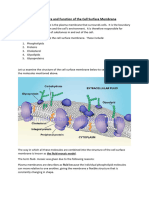
i. Simple diffusion ii. Osmosis iii. Facilitated diffusion 2. TRANSPORT i. Active Transport ii. Passive Transport Simple Diffusion: The movement of molecules from region of high concentration to low concentration. The movement of molecules from region of high concentration to a region of low concentration with the help of carrierproteins. Osmosis: The movement of water molecules from dilute solution to a concentrated solution across a Semi permeable membrane. 3. The figure below shows the model of the plasma membrane. Label L, M, N, and O shows four types of nutrients. P1, P2 and P3 show three types of protein.
(i)
Processes labelled L, M, N, O. L : Simple diffusion M : Fasilitated diffusion N : Fasilitated diffusion O : Active transport
(ii) Protein labelled P1, P2 and P3. P1 : Pore protein P2 : Carrier protein P3 : Carrier protein (iii) Two characteristics of the molecules that are transported into the cell by process L. 1. Small 2. Soluble in lipid 4. The figure shows a model of the active transport system that depends on several carrier proteins found in the cell membrane.
(i) What is active transport: Movement of particles across the plasma membrane by carrier proteins, against the concentration gradient and requires energy. (ii) An example of active transport in plants. Ion or mineral uptake by plant root hairs. (iii) Two differences between active transport and diffusion. Any two differences energy, gradient concentration, living membrane.
5. The table below shows the effect of hypotonic, isotonic and hypertonic solution on spinach strips, red blood cells and plant cells.
Hypotonic solution
Isotonic solution
Hypertonic solution Spinach strip in 30% sucrose solution
Spinach strip in distill water
Distill water is hypotonic compared to the cell sap. Water enters into spinach cell through cut surface by osmosis . Epidermis is water proof. The epidermis layer curved inward. Red blood cell in distill water.
Spinach strip in 5% sucrose solution The rate of water entering and leaving the spinach cell through semi permeable mambrane is the same. The shape of spinach strip remains the same
Red blood in 30% sodium chloride solution
Plant cell in distill water
Red blood cell in isotonic solution Plant cell in isotonic solution
Plant cells in 30% sucrose solution
1. Which of the following cell structures cannot be seen under a light microscope? a. Cell wall b. Nucleolus c. Chloroplast d. Plasma membrane 1. Which of a. b. c. d. the following components gives elasticity to cell membranes? Glucose Protein Cellulose Cholesterol
1. Cell X uses active transport extensively to move substances. What organelle exists is unusually large numbers in cell X? a. Chloroplast b. Ribosome c. Vacuole d. Mitochondrion 1. The functions of enzyme are specific because of the. a. Sentively of all catalysts of temperature b. Structure of protein molecules c. Presence of inhibitors d. Effects of coenzymes 1. Mitochondrion is used for a. Secretion of substances b. Release of energy c. Cell division d. Photosynthesis
1. Cell membrane is composed mainly of a. Inorganic molecules b. Protoplasm c. Cytoplasm d. Lipids 1. .. is the maintanance of a stable biological environment in organisms. a. Regulatory mechanism
b. Biocontrol c. Homeostasis d. Internal control system
1. Top of Form
1. "It has a system of sacs and tubes that transports substances within the
cytoplasm." The statement above is a description of...
a. b. c. d.
Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus Ribosome vacuole
1. .. is the organelle that performs cellular respiration.Bottom of Form
a. b. c. d.
Vacuole Chloroplast Mitochondrion Golgi apparatus
1. This enzyme can be used to tenderise meat during food processing. a. Trysin b. Pepsin c. Protease d. Amylase
Вам также может понравиться
- Chapter 3: Movement Across The Plasma Membrane: Intervention-Biology Chapter 3 (Answer)Документ4 страницыChapter 3: Movement Across The Plasma Membrane: Intervention-Biology Chapter 3 (Answer)Anonymous 6qork2Оценок пока нет
- Transport MechanismsДокумент30 страницTransport MechanismsApril VeraОценок пока нет
- Cell Processes Study Guide KeyДокумент4 страницыCell Processes Study Guide Keyapi-260817414Оценок пока нет
- The Plasma Membrane: Membranes Cover The Surface of Every Cell, and Also Surround Most OrganellesДокумент11 страницThe Plasma Membrane: Membranes Cover The Surface of Every Cell, and Also Surround Most OrganellesSyeda Kaneez Mohammadi MohammadiОценок пока нет
- Cell Membrane FunctionsДокумент60 страницCell Membrane FunctionsKate Clancy NugaoОценок пока нет
- Cell Structures and Their Functions: Jed Esperidion S. Jumilla II, RMT, MDДокумент98 страницCell Structures and Their Functions: Jed Esperidion S. Jumilla II, RMT, MDJed Esperidion Solivio JumillaОценок пока нет
- The Cell MembraneДокумент23 страницыThe Cell MembraneNaveed AkhterОценок пока нет
- Senior High School: Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (Stem) Specialized SubjectДокумент53 страницыSenior High School: Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (Stem) Specialized Subjectpotato macchiatoОценок пока нет
- Cells: A. Ultrastructure & Function of The CellДокумент9 страницCells: A. Ultrastructure & Function of The CellRhea Lyn LamosteОценок пока нет
- Membrane Structure and FunctionДокумент11 страницMembrane Structure and FunctionShiloh FrederickОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3: Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneДокумент28 страницChapter 3: Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneMohd Asraf90% (10)
- Biol Worksheet 2013 Grade 11thДокумент5 страницBiol Worksheet 2013 Grade 11thendalew damtieОценок пока нет
- Transport Mechanism Lecture BestДокумент9 страницTransport Mechanism Lecture Bestelyza gwenОценок пока нет
- 1-Passive Transport:: Selectively Permeable BarriersДокумент19 страниц1-Passive Transport:: Selectively Permeable Barriersapi-3706483Оценок пока нет
- Transport Across Plasma Membrane PDFДокумент2 страницыTransport Across Plasma Membrane PDFTracie Curry100% (1)
- Mader/Biology, 11/e - Chapter Outline: 5.1 Plasma Membrane Structure and FunctionДокумент4 страницыMader/Biology, 11/e - Chapter Outline: 5.1 Plasma Membrane Structure and Functionapi-455371000Оценок пока нет
- C3Movement Across The Plasma MembraneДокумент14 страницC3Movement Across The Plasma Membranemagdelena100% (1)
- Significance of Lipids in Biological Membranes and Transport MechanismsДокумент9 страницSignificance of Lipids in Biological Membranes and Transport Mechanismsroshan khan100% (2)
- Significance of Lipids in Biological Membranes and Transport MechanismsДокумент9 страницSignificance of Lipids in Biological Membranes and Transport Mechanismsroshan khanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 Study GuideДокумент9 страницChapter 7 Study GuideCesar MontenegroОценок пока нет
- Test Essays January 4Документ7 страницTest Essays January 4Stephanie JenkinsОценок пока нет
- General Biology 1 Self-Learning Packet Preliminaries Module # 4-Cell TransportДокумент9 страницGeneral Biology 1 Self-Learning Packet Preliminaries Module # 4-Cell TransportGi GiОценок пока нет
- Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneДокумент27 страницMovement of Substances Across The Plasma Membranenurhanim ckОценок пока нет
- MCQs and True-FalseДокумент10 страницMCQs and True-Falsehussain AltaherОценок пока нет
- 13-Movement of Substances Across The PДокумент8 страниц13-Movement of Substances Across The PAbbas TalibОценок пока нет
- Histology: Cytology, The Study of The Structure and Function of CellsДокумент48 страницHistology: Cytology, The Study of The Structure and Function of CellsZmeu CristinaОценок пока нет
- 4 Homeostasis and Cell TransportДокумент50 страниц4 Homeostasis and Cell Transportnuria mukaraniОценок пока нет
- KANESS (016-4573342) 10, JLN TPT 10, Taman Puchong Tekali, 47150, Puchong, Selangor Chapter 2: Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneДокумент6 страницKANESS (016-4573342) 10, JLN TPT 10, Taman Puchong Tekali, 47150, Puchong, Selangor Chapter 2: Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneKaness MathzОценок пока нет
- Facilitated Diffusion Is The Process of SpontaneousДокумент3 страницыFacilitated Diffusion Is The Process of SpontaneousashОценок пока нет
- R-Sen Lecture 01aДокумент28 страницR-Sen Lecture 01ahimanshu_agraОценок пока нет
- Cell Membrane Membrane: How Substances Get Across The MembraneДокумент15 страницCell Membrane Membrane: How Substances Get Across The MembraneMariane CarandangОценок пока нет
- 116 - Transport Mechanisms in CellsДокумент4 страницы116 - Transport Mechanisms in Cellslastjoe71100% (1)
- General Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeДокумент10 страницGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeMega CyclopsОценок пока нет
- Cell TransportДокумент19 страницCell TransportOctavio ManciniОценок пока нет
- Cellular Transport ConceptДокумент7 страницCellular Transport ConceptRuhul Qudus NaimОценок пока нет
- Lect 2 Membrane TransportДокумент29 страницLect 2 Membrane Transportramadan100% (1)
- Transport Across Cell Membrane.: DR Nilesh Kate MBBS, MD Associate ProfДокумент67 страницTransport Across Cell Membrane.: DR Nilesh Kate MBBS, MD Associate ProfAspireОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 5 MembranesДокумент7 страницCHAPTER 5 MembranesNadeem IqbalОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 Cellular TransportДокумент3 страницыChapter 5 Cellular TransportBlair100% (1)
- Biology - Module 4Документ6 страницBiology - Module 4ASHLEY MONICA PLATAОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 ModifiedДокумент58 страницChapter 7 ModifiedJohnYooОценок пока нет
- Kertas 1 SPM (Percubaan) 1-10Документ76 страницKertas 1 SPM (Percubaan) 1-10Hazizi HanapiОценок пока нет
- AssignmentДокумент6 страницAssignmentsylvia anneОценок пока нет
- The Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneДокумент30 страницThe Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneNorizan HusainОценок пока нет
- Nota Biologi Tingkatan 4 BAB 3Документ12 страницNota Biologi Tingkatan 4 BAB 3Firas Muhammad50% (4)
- 2 5 Transport MechanismДокумент25 страниц2 5 Transport Mechanismıamnıkolaı 4100% (1)
- The Cell and Its Environment: Biology, Ss 1Документ3 страницыThe Cell and Its Environment: Biology, Ss 1AJAYI PETER100% (1)
- Membrane - FunctionДокумент4 страницыMembrane - Functionphuong anhОценок пока нет
- Bio 4 OsmosisДокумент8 страницBio 4 OsmosisJustin Damian Malaki MalubayОценок пока нет
- Membrane - FunctionДокумент4 страницыMembrane - Functionphuong anhОценок пока нет
- Transport MechanismsДокумент6 страницTransport MechanismsJohn Dave ElloranОценок пока нет
- Cell Membrane Function and StructureДокумент6 страницCell Membrane Function and Structurecris ibarraОценок пока нет
- 1.4a Movement of Substances 1 12BIOДокумент18 страниц1.4a Movement of Substances 1 12BIOedensatire21Оценок пока нет
- Biology Short NoteДокумент10 страницBiology Short NotePatrix ParkerОценок пока нет
- MODULE 1.3 Cell Membrane TransportДокумент11 страницMODULE 1.3 Cell Membrane TransportBrandon James SevillaОценок пока нет
- LESSON - 11 - Gen Biology 1Документ4 страницыLESSON - 11 - Gen Biology 1Jhay Luiz Cajigal ArquinesОценок пока нет
- Cell ConstituentsДокумент8 страницCell ConstituentsSanaa SamkoОценок пока нет
- Cell PhysiologyДокумент15 страницCell PhysiologyHENRY MURIGIОценок пока нет
- Expand High Fidelity PCR System Roche PDFДокумент2 страницыExpand High Fidelity PCR System Roche PDFTeresaОценок пока нет
- Dna ExtractionДокумент3 страницыDna ExtractionNeo Mervyn MonahengОценок пока нет
- Interrelationship Between Carbohydrate Protein Fat MetabolismДокумент12 страницInterrelationship Between Carbohydrate Protein Fat MetabolismShailaja Neaupane100% (5)
- Lesson 1 The Cell Theory Grade 12Документ33 страницыLesson 1 The Cell Theory Grade 12Lunaaaaa100% (1)
- Jigyasa Compendium 20141Документ234 страницыJigyasa Compendium 20141neela kantaОценок пока нет
- GKP 687Документ8 страницGKP 687tamilarasu244165Оценок пока нет
- Membrane ProteinsДокумент47 страницMembrane ProteinsStanley ChikoveОценок пока нет
- Alpha InterferonДокумент7 страницAlpha InterferonLAURA MARCELA BARRENECHE CALLEОценок пока нет
- NET Dec 2016 C PaperДокумент18 страницNET Dec 2016 C PaperNiraj ShethОценок пока нет
- Golden RiceДокумент1 страницаGolden Ricedoris_1987Оценок пока нет
- Test Bank For Molecular Biology Principles and Practice 1st Edition Michael M CoxДокумент6 страницTest Bank For Molecular Biology Principles and Practice 1st Edition Michael M CoxglendavictoriabbkОценок пока нет
- Transcription and Translation: From DNA To RNA To ProteinДокумент35 страницTranscription and Translation: From DNA To RNA To ProteinInjila AhmadОценок пока нет
- Types of Receptors and Their Properties: Noman AnwarДокумент21 страницаTypes of Receptors and Their Properties: Noman AnwarNoman AnwarОценок пока нет
- (20493614 - Endocrine Connections) How Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists WorkДокумент13 страниц(20493614 - Endocrine Connections) How Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists WorkEka RahmawatiОценок пока нет
- Double Immunodiffusion TestДокумент4 страницыDouble Immunodiffusion Testmuddassir attarОценок пока нет
- 4.code of Ethics For Chemical EngineersДокумент103 страницы4.code of Ethics For Chemical EngineersOnyx Xyno100% (1)
- Alkyd Resin Soucek2015Документ83 страницыAlkyd Resin Soucek2015Anchit GhoshОценок пока нет
- Functional MeatДокумент54 страницыFunctional MeatnimraОценок пока нет
- The Effect of Substrate Concentration On The Rate of Reaction of Enzyme ActivityДокумент6 страницThe Effect of Substrate Concentration On The Rate of Reaction of Enzyme ActivityMaan PatelОценок пока нет
- M.sc. Botany2010Документ24 страницыM.sc. Botany2010Vishal AgrahariОценок пока нет
- Compendium of Selected Recent Publications Cell and Molecular Biology ResearchДокумент16 страницCompendium of Selected Recent Publications Cell and Molecular Biology ResearchXyza Kim OlivaОценок пока нет
- 1 s2.0 S0022282816302176 MainДокумент85 страниц1 s2.0 S0022282816302176 MainNia Rukman100% (1)
- Role of Zinc and IronДокумент7 страницRole of Zinc and IronE MeerОценок пока нет
- Instapdf - in Pharmacology and Toxicology Mcqs With Answers 419 PDFДокумент12 страницInstapdf - in Pharmacology and Toxicology Mcqs With Answers 419 PDFDR AbidОценок пока нет
- Activity1 Cancer Gene CardsДокумент14 страницActivity1 Cancer Gene CardsIsmael FernandezОценок пока нет
- Dna Fingerprinting: by Insiya TalwariДокумент12 страницDna Fingerprinting: by Insiya TalwariInsiya TalwariОценок пока нет
- Iso 24276 2006 PDFДокумент24 страницыIso 24276 2006 PDFJonathan MoralesОценок пока нет
- Lyphochek Assayed Chemistry Control Levels 1 and 2: Revision Date 2023-06-12 Indicates Revised InformationДокумент23 страницыLyphochek Assayed Chemistry Control Levels 1 and 2: Revision Date 2023-06-12 Indicates Revised Informationpsychejane100% (2)
- DLL Grade 7 Video LessonДокумент4 страницыDLL Grade 7 Video LessonJr CapanangОценок пока нет
- Learning Activity 1 CarbohydratesДокумент59 страницLearning Activity 1 CarbohydratesMaxine Danielle AlmeroОценок пока нет
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceОт EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (18)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerОт EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (393)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityОт EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsОт EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (6)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisОт EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesОт EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (397)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessОт Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (33)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceОт EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (517)
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseОт EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (52)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueОт EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (38)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomОт EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (216)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainОт EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (65)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)От EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (411)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedОт EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (11)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionОт EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (812)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveОт EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (66)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainОт EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (110)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorОт EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorОценок пока нет
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperОт EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (15)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemОт EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (115)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouОт EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (62)
- Darwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignОт EverandDarwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (39)
- Why We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsОт EverandWhy We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2083)
- The Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightОт EverandThe Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (5)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldОт EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (595)