Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
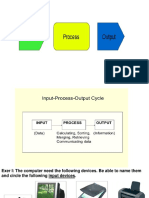
Input, Output, Storage
Загружено:
anjoooyИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Input, Output, Storage
Загружено:
anjoooyАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Lesson 3: Input, Output, and Storage
I. Input Devices Enable a user to input data and commands for the computer to be processed
A. THE KEYBOARD
➢Most widely used input device
➢Electric signals: represent a key that is sent to the computer
➢ Divided into sections:
1. Typewriter Keys: These are the standard alphabetic and numeric characters.
2. Function Keys: are special keys that perform specific function for application.
3. Numeric Keypad: used for mathematical operations
4. Directional keys: used to move the cursor around the screen
B. THE MOUSE:
i. It is a pointing device, that rolls around a flat surface and controls the location of the pointer on the
screen.
ii.Performs the following functions:
1. Pointing: placing the on-screen pointer at a specific place
2. Clicking: Pressing and releasing the mouse button
3. Dragging: holding down the mouse button and drag objects to new location
4. Double Clicking: Pressing and releasing twice.
5. Right-Clicking: pressing the right mouse button
iii.Other devices that control the on-screen pointer:
1. The trackball:
a. This is like a mouse turned upside down. You roll a ball around with fingers to control
the location of the pointers. Mostly found in notebook computers.
2. Joystick and wheel: Joysticks consist of a metal or plastic handle mounted on a base
a. Used for video games
b. Have buttons that can be pushed to control input/output
c. POINTING STICK: A pressure-sensitive device that resembles a pencil eraser, mostly on notebook computers
d. GRAPHICS TABLET: A flat drawing surface and the figure or writing can be input to the computer for processing
e. TOUCH DISPLAY: Screens that contain pictures or shapes that the user can press to input the data
f. TOUCHPAD: Used mostly in notebooks or laptops.
g. AUDIO/VOICE INPUT: usually require a microphone and special voice recognition software to be installed. Use to
input sound/voice.
h. SCANNERS: they can convert a graphical image into a digital image and input it to the computer
i. Image Scanners: images and text
ii.Bar Code Scanners: read product codes
iii.Magnetic Scanners: read the magnetic strip in a credit card. Images can be input directly to the
computer.
i. VIDEO INPUT: Input from a camcorder or VCR using video capture cards.
j. BIOMETRIC INPUT: Uses fingerprint, face, handwriting, voice for identification
k. MAGNETIC STORAGE DEVICES:
i. Small, portable disks that hold limited amount of data
ii.Hard disks: large capacity and fast access storage devices
iii.Zip disks: Auxiliary storage devices that hold large quantities of data/ portable
iv.Magnetic Tape Drives: Used to make system backups and to store large quantities of data.
L. SOLID-STATE STORAGE MEDIA
i. Non-volatile removable media
ii.Miniature mobile media
1. Uses integrated circuits
iii.USB flash drive
1. Connects to the computer via a USB port
M. OPTICAL STORAGE DEVICES
i. CD-DA: Audio Cd
ii.CD-R: allows you to read and write it to a compact disk
iii.CD-ROM: hold large amounts of data, but is read-only access
iv.CD-RW: Can be written on several times
v.DVD-ROM: Read-only DVD format
vi.DVD-R: Similar to CD, but holds more data; read-only
vii.DVD-RW: Can be written on several times
viii.PhotoCD: Used for storing digital photographs on a CD
II. Caring for storage media:
n. Keep away from magnetic fields.
o. Avoid extreme temperatures.
p. Never try to disassemble the case.
q. Remove media from drive when not being used.
r. Write-protect important data.
s. Hold optical disks at their edges.
t. Never remove the media from the drive if the access light is on.
u. Keep disks in a sturdy case when transporting them.
III. Output Devices enable the computer to give or show the results of its processing
v. MONITORS:
i. This is used to display video output to a user.
ii.This produces soft copy
iii.Monitors may be monochromatic or color.
1. Monochromatic monitors display output in a single-color display.
iv.Factors that influence the quality of monitors:
1. Screen size: The diagonal measurement in inches of the display area
2. Resolution: The number of pixels that can be displayed in the display area
3. Dot pitch: The distance between each pixel in the display area
W. PRINTERS
i. Used to create a hard copy of a document or image.
ii.Printers vary by speed, quality, and price.
iii.The most popular types of printers:
1. Laser: Produce images using the same techniques as copier machines
2. Ink jet: Use fine nozzles to spray ink onto the page as the paper passes through
3. Dot matrix: Work similarly to a typewriter in that ink is transferred to the paper by some part of
the printer striking a ribbon to transfer an image
X. SPEAKERS AND HEADSETS
Y. FAX MACHINES AND FAX MODEMS
Z. MULTIFUNCTIONAL DEVICES
AA. CONTAIN A VARIATION OF OUTPUT OPTIONS
ab. DATA PROJECTOR
IV. Connecting I/O Devices to the computer:
➢ Input and output devices must be connected to the computer before they can be used.
i. Plug the device into an existing socket or port on the back of the computer.
ii.Install an expansion card with the port you need included on the back of the card.
iii.Connect wirelessly.
Вам также может понравиться
- INFO SHEET 4.3 - 4.4 Input Output Storage DevicesДокумент3 страницыINFO SHEET 4.3 - 4.4 Input Output Storage DevicesGeh Deng NolealОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Computers Question Bank: Data Information Knowledge Processed ProcessedДокумент12 страницIntroduction To Computers Question Bank: Data Information Knowledge Processed ProcessedSyed Muhammad Ijlal HussainОценок пока нет
- Computer Science L 2Документ13 страницComputer Science L 286d9nfdccqОценок пока нет
- Computer SystemsДокумент27 страницComputer SystemsNaomi NyambasoОценок пока нет
- Computer ApplicationДокумент5 страницComputer ApplicationSayidAli Cadceed MuhumedОценок пока нет
- Grade 12: Ict - Computer Systems ServicingДокумент14 страницGrade 12: Ict - Computer Systems ServicingBea EtacОценок пока нет
- Tle-Ict Computer Systems Servicing: Quarter 1 - Module 3Документ10 страницTle-Ict Computer Systems Servicing: Quarter 1 - Module 3Jeo MillanoОценок пока нет
- TOPIC 2 A COMPUTER SYSTEMS RДокумент22 страницыTOPIC 2 A COMPUTER SYSTEMS RAlex MwendwaОценок пока нет
- ComputerДокумент3 страницыComputerVince BulayogОценок пока нет
- DevicesДокумент19 страницDevicesRaidon JantanataОценок пока нет
- Lesson 3 External Hardware QuastionsДокумент5 страницLesson 3 External Hardware QuastionsPSYCHO DNAОценок пока нет
- Module 6 Page 68-74Документ7 страницModule 6 Page 68-74Junar James Mahinay AbellarОценок пока нет
- Csec It Work Book Answers 01Документ4 страницыCsec It Work Book Answers 01Jada CameronОценок пока нет
- ICT Notes IGCSE - BlogspotДокумент1 страницаICT Notes IGCSE - BlogspotIGCSE and IBDP NotesОценок пока нет
- Computer System, Input, and Output Device: Lesson 2Документ4 страницыComputer System, Input, and Output Device: Lesson 2Ameera Yazmin DiegoОценок пока нет
- Input & Output WorksheetДокумент5 страницInput & Output WorksheetSasha BurkeОценок пока нет
- Second Monthly Exam in Computer 4 Sy-2018-2019Документ2 страницыSecond Monthly Exam in Computer 4 Sy-2018-2019Dhe LandichoОценок пока нет
- Activity Research Log Input DevicesДокумент6 страницActivity Research Log Input DevicesAndrew JamesОценок пока нет
- 1st Unit Test Grade 7 TLE 2nd QuarterДокумент3 страницы1st Unit Test Grade 7 TLE 2nd QuarterCristel Anne A. Llamador100% (1)
- EPAS 9 - Q1 - W4 - Mod4Документ25 страницEPAS 9 - Q1 - W4 - Mod4Rosalie RebayОценок пока нет
- Digital Planet 8 Teachers ManualДокумент44 страницыDigital Planet 8 Teachers Manualur mom100% (2)
- CSS10 Week2-3Документ19 страницCSS10 Week2-3Jevan Hope BaltazarОценок пока нет
- 915-1586267792654-Unit 1.3 HardwareElementsДокумент24 страницы915-1586267792654-Unit 1.3 HardwareElementsDj NinjaОценок пока нет
- Theory Input & Output DevicesДокумент3 страницыTheory Input & Output DevicesMarco Antonio SirpaОценок пока нет
- Input Devices: 1.keyboardДокумент7 страницInput Devices: 1.keyboardRowza HaqueОценок пока нет
- Bits - BytesДокумент2 страницыBits - BytesRuth EstherОценок пока нет
- SWE112 FinalДокумент49 страницSWE112 FinalChe BorisОценок пока нет
- Final Notes Class 9 CSДокумент25 страницFinal Notes Class 9 CSEr Pankaj SharmaОценок пока нет
- Com - Science q1 Wk1 2Документ10 страницCom - Science q1 Wk1 2Coren Jane M. TupanОценок пока нет
- Multiple Choice: Read The Statement and Answer The Following QuestionsДокумент4 страницыMultiple Choice: Read The Statement and Answer The Following QuestionsHomer SotoОценок пока нет
- General Characteristics of It SystemsДокумент12 страницGeneral Characteristics of It SystemsTintinententen Christine TintinОценок пока нет
- L2 Input Device CHSДокумент13 страницL2 Input Device CHSRoxan AbanОценок пока нет
- Book 2 - Emerging Technology, Input Devices, SensorsДокумент21 страницаBook 2 - Emerging Technology, Input Devices, SensorsHAIS Dan MaguireОценок пока нет
- All About BasicsДокумент4 страницыAll About BasicsJumar Divinagracia DimpasОценок пока нет
- Learners Activity Sheet 3Документ10 страницLearners Activity Sheet 3John Raymund MabansayОценок пока нет
- Quiz Mid TestДокумент3 страницыQuiz Mid Testnadiya saputriОценок пока нет
- Written Works 1ST Quarter CSS9Документ7 страницWritten Works 1ST Quarter CSS9Yne AhuninОценок пока нет
- ENDTERM 2nd Semester (NCM110NIF LAB)Документ9 страницENDTERM 2nd Semester (NCM110NIF LAB)Abigail RegaladoОценок пока нет
- Computer Input and Output Devices I. Computer Input Devices A. DefinitionДокумент3 страницыComputer Input and Output Devices I. Computer Input Devices A. DefinitionRachelle GandaОценок пока нет
- SLK TLE CHS Grade 10 1st Quarter Lesson 2Документ10 страницSLK TLE CHS Grade 10 1st Quarter Lesson 2JaysonGayumaОценок пока нет
- Name: Muhammad Hassaan ID: 22020005-003 Program: BBA Resource Person: MR - Farhan Subject: Computer Applications Date: 14-4-23Документ6 страницName: Muhammad Hassaan ID: 22020005-003 Program: BBA Resource Person: MR - Farhan Subject: Computer Applications Date: 14-4-23Barndon KawinskyОценок пока нет
- Assessment: Educate, Empower, ExcelДокумент3 страницыAssessment: Educate, Empower, Excelkelliy annieОценок пока нет
- T.L.E 7 and 8 Week 3Документ13 страницT.L.E 7 and 8 Week 3Eleonor DistrajoОценок пока нет
- 10 Input Devices - GonzalosДокумент3 страницы10 Input Devices - GonzalosshaungonzalosОценок пока нет
- Computer 6 - ReviewerДокумент4 страницыComputer 6 - ReviewerAng PinakaОценок пока нет
- Lab 1 SSK 3000Документ9 страницLab 1 SSK 3000Nasrullah roslanОценок пока нет
- COMPUTER APPLICATION I - Lesson 4Документ6 страницCOMPUTER APPLICATION I - Lesson 4Hack FinОценок пока нет
- Computing Essentials Intro 2014 24th Edition Oleary Test BankДокумент40 страницComputing Essentials Intro 2014 24th Edition Oleary Test Bankvictoriaperkinsrzksfyjacx100% (35)
- Chapter 1 Intro To CompДокумент19 страницChapter 1 Intro To CompRomeo BagunuОценок пока нет
- Computer PeripherlasДокумент32 страницыComputer PeripherlasREYNEL BISTAОценок пока нет
- Input and Output DevicesДокумент6 страницInput and Output DevicesLEESHMAОценок пока нет
- Computer Notes PDFДокумент69 страницComputer Notes PDFAyush SharmaОценок пока нет
- Multimedia Technology LabДокумент21 страницаMultimedia Technology LabishratОценок пока нет
- TVL CSS G11-Q1-DW6Документ4 страницыTVL CSS G11-Q1-DW6JeanaLicas-GocoОценок пока нет
- CompДокумент39 страницCompabcdefОценок пока нет
- Online Entry: Input and Output DevicesДокумент19 страницOnline Entry: Input and Output DevicesHalf-God Half-ManОценок пока нет
- Computer Peripherals: Renante Q. Bista JRДокумент32 страницыComputer Peripherals: Renante Q. Bista JRREYNEL BISTAОценок пока нет
- Lesson 13: Input, Output, Storage Device: Ailene Sibayan - Bobier Faculty, Computer Studies DepartmentДокумент19 страницLesson 13: Input, Output, Storage Device: Ailene Sibayan - Bobier Faculty, Computer Studies DepartmentPanes GrenadeОценок пока нет
- 3rd Quarter ICF 7Документ9 страниц3rd Quarter ICF 7teodora.tuppilОценок пока нет
- Backend Design FlowДокумент33 страницыBackend Design FlowsudeepОценок пока нет
- AC 21-46 v3.0Документ7 страницAC 21-46 v3.0JОценок пока нет
- HOOSEKI Campur 1Документ12 страницHOOSEKI Campur 1Anugrah Prihantoro Amd T100% (3)
- Application Note 135 April 2012 Implementing Robust Pmbus System Software For The Ltc3880Документ12 страницApplication Note 135 April 2012 Implementing Robust Pmbus System Software For The Ltc3880HahdОценок пока нет
- Amplifier: Electronics & SoftwareДокумент3 страницыAmplifier: Electronics & SoftwareJose M. RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Somi Khan: Personal ObjectiveДокумент2 страницыSomi Khan: Personal ObjectivesomiОценок пока нет
- Fox515 Technical DataДокумент2 страницыFox515 Technical DatasyedpandtОценок пока нет
- EDS - NDrive ManualДокумент115 страницEDS - NDrive Manuallfba_16Оценок пока нет
- White Paper - Mineral Oils, White Oils and Engineered Synthetic Dielectric Fluids 20180426.1aДокумент14 страницWhite Paper - Mineral Oils, White Oils and Engineered Synthetic Dielectric Fluids 20180426.1aDavid SundinОценок пока нет
- UHD UF680T 43.49.55.65 Spec 150907 PDFДокумент2 страницыUHD UF680T 43.49.55.65 Spec 150907 PDFfreemayОценок пока нет
- Info Iec60062 (Ed5.0) enДокумент5 страницInfo Iec60062 (Ed5.0) enWagner MirandaОценок пока нет
- WH627 Diagrama Elec.Документ7 страницWH627 Diagrama Elec.iker56777Оценок пока нет
- Module DatasheetДокумент2 страницыModule DatasheetaadilОценок пока нет
- Es - 101Документ8 страницEs - 101Subrata PaulОценок пока нет
- Kathrein 80010310v01 - Technical DocumentДокумент1 страницаKathrein 80010310v01 - Technical DocumentMindaugas PepperОценок пока нет
- GNU Radio lab: Instructor: Proff Do Trong Tuan Group: Kim Trung Hiếu Đỗ Thu Hà Tạ Thị Thanh Lâm DinaliДокумент36 страницGNU Radio lab: Instructor: Proff Do Trong Tuan Group: Kim Trung Hiếu Đỗ Thu Hà Tạ Thị Thanh Lâm DinaliThanh LâmОценок пока нет
- Solutions For Decapsulation, Substrate Thinning and PolishingДокумент12 страницSolutions For Decapsulation, Substrate Thinning and PolishingSee Toh GeraldОценок пока нет
- HT CatalogueДокумент48 страницHT CatalogueHydrotechnik UK LtdОценок пока нет
- 1st YEAR TimeTable BCAДокумент6 страниц1st YEAR TimeTable BCAIshWayTimeОценок пока нет
- Operating Instructions DB-033-961017 E: FH 40 G Dose Rate Measuring UnitДокумент98 страницOperating Instructions DB-033-961017 E: FH 40 G Dose Rate Measuring Unitbiruk girma100% (1)
- Question For Manager Test in Ksfe PDFДокумент11 страницQuestion For Manager Test in Ksfe PDFRajimol RОценок пока нет
- Electric Vehicle Charging Interoperability Test & EvaluationДокумент4 страницыElectric Vehicle Charging Interoperability Test & EvaluationDouglas GohiОценок пока нет
- Components:: R1 R2 R3 R4 C1 C2 D1 D2Документ3 страницыComponents:: R1 R2 R3 R4 C1 C2 D1 D2Anton Pers100% (1)
- Race Condition in J-K LatchДокумент14 страницRace Condition in J-K LatchTejas DharaniОценок пока нет
- WCDMA System Architecture 3G WCDMA Cellular NetworkДокумент13 страницWCDMA System Architecture 3G WCDMA Cellular NetworkThang TranОценок пока нет
- ACS55 ABBmicrodrivesFlyer REVF ENДокумент2 страницыACS55 ABBmicrodrivesFlyer REVF ENHugo Patricio Roco CastroОценок пока нет
- Downloaded From Manuals Search EngineДокумент62 страницыDownloaded From Manuals Search EnginezorktronicsОценок пока нет
- JNTUA JNTUH JNTBasic Electrical and Electronics Engineering BEEE NoteДокумент93 страницыJNTUA JNTUH JNTBasic Electrical and Electronics Engineering BEEE Notejiyija2465Оценок пока нет
- Lm-Emea EngДокумент4 страницыLm-Emea EngsyОценок пока нет
- EE 271 Digital Circuits and Systems: Course Specification (Syllabus)Документ41 страницаEE 271 Digital Circuits and Systems: Course Specification (Syllabus)R.R.S. SavichevaОценок пока нет
- iPhone 14 Guide for Seniors: Unlocking Seamless Simplicity for the Golden Generation with Step-by-Step ScreenshotsОт EverandiPhone 14 Guide for Seniors: Unlocking Seamless Simplicity for the Golden Generation with Step-by-Step ScreenshotsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (4)
- Chip War: The Fight for the World's Most Critical TechnologyОт EverandChip War: The Fight for the World's Most Critical TechnologyРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (82)
- Chip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyОт EverandChip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (229)
- Cyber-Physical Systems: Foundations, Principles and ApplicationsОт EverandCyber-Physical Systems: Foundations, Principles and ApplicationsHoubing H. SongОценок пока нет
- CompTIA A+ Certification All-in-One Exam Guide, Eleventh Edition (Exams 220-1101 & 220-1102)От EverandCompTIA A+ Certification All-in-One Exam Guide, Eleventh Edition (Exams 220-1101 & 220-1102)Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra User Guide For Beginners: The Complete User Manual For Getting Started And Mastering The Galaxy S22 Ultra Android PhoneОт EverandSamsung Galaxy S22 Ultra User Guide For Beginners: The Complete User Manual For Getting Started And Mastering The Galaxy S22 Ultra Android PhoneОценок пока нет
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102От EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- iPhone Unlocked for the Non-Tech Savvy: Color Images & Illustrated Instructions to Simplify the Smartphone Use for Beginners & Seniors [COLOR EDITION]От EverandiPhone Unlocked for the Non-Tech Savvy: Color Images & Illustrated Instructions to Simplify the Smartphone Use for Beginners & Seniors [COLOR EDITION]Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (4)
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam Core 1 220-1001 and Exam Core 2 220-1002От EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam Core 1 220-1001 and Exam Core 2 220-1002Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- CompTIA A+ Complete Practice Tests: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102От EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Practice Tests: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Оценок пока нет
- iPhone X Hacks, Tips and Tricks: Discover 101 Awesome Tips and Tricks for iPhone XS, XS Max and iPhone XОт EverandiPhone X Hacks, Tips and Tricks: Discover 101 Awesome Tips and Tricks for iPhone XS, XS Max and iPhone XРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (2)
- Cancer and EMF Radiation: How to Protect Yourself from the Silent Carcinogen of ElectropollutionОт EverandCancer and EMF Radiation: How to Protect Yourself from the Silent Carcinogen of ElectropollutionРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- Jensen Huang's Nvidia: Processing the Mind of Artificial IntelligenceОт EverandJensen Huang's Nvidia: Processing the Mind of Artificial IntelligenceОценок пока нет
- Raspberry PI: Learn Rasberry Pi Programming the Easy Way, A Beginner Friendly User GuideОт EverandRaspberry PI: Learn Rasberry Pi Programming the Easy Way, A Beginner Friendly User GuideОценок пока нет
- A Beginner's Guide To IPhone 14 Pro Max Mastering: The Comprehensive User Guide And Illustrated Owner's Manual With Tips And Advanced Tricks For New BeОт EverandA Beginner's Guide To IPhone 14 Pro Max Mastering: The Comprehensive User Guide And Illustrated Owner's Manual With Tips And Advanced Tricks For New BeОценок пока нет
- iPhone Photography: A Ridiculously Simple Guide To Taking Photos With Your iPhoneОт EverandiPhone Photography: A Ridiculously Simple Guide To Taking Photos With Your iPhoneОценок пока нет
- Debugging Embedded and Real-Time Systems: The Art, Science, Technology, and Tools of Real-Time System DebuggingОт EverandDebugging Embedded and Real-Time Systems: The Art, Science, Technology, and Tools of Real-Time System DebuggingРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- The User's Directory of Computer NetworksОт EverandThe User's Directory of Computer NetworksTracy LaqueyОценок пока нет

































































































![iPhone Unlocked for the Non-Tech Savvy: Color Images & Illustrated Instructions to Simplify the Smartphone Use for Beginners & Seniors [COLOR EDITION]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/audiobook_square_badge/728318688/198x198/f3385cbfef/1715431191?v=1)