Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
The Staining Characterization of A Bacterial Unknown: Background
Загружено:
FacesituationИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
The Staining Characterization of A Bacterial Unknown: Background
Загружено:
FacesituationАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
E X E R C I S E
The Staining Characterization of a Bacterial Unknown
15
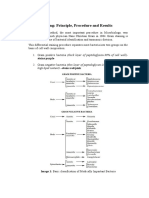
then use the information provided in figure 15.1 and table 15.1 to guide you through the characterization of your unknown. Perform only those staining procedures required as you work your way through the scheme. When you are finished, you should be able to correctly identify your bacterial unknown based on its staining characteristics.
Grampositive
Background
This exercise will allow you to apply what you have learned in previous exercises to the identification of a bacterial unknown. First, you will select or have assigned to you one of the bacterial cultures from the materials list, but you will not know which one. You will
Gram stain (Exercise 11) Gramnegative
Morphology (Exercises 9, 10, 11) Rod Capsule stain (Exercise 14) Coccus Neisseria sicca
Morphology (Exercises 9, 10, 11) Rod Acidfast stain (Exercise 12) Coccus Arrangement (Exercises 10, 11)
()
(+)
Clusters
Short chains
Alcaligenes denitrificans
Enterobacter aerogenes
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Enterococcus faecalis
()
(+)
Spore stain (Exercise 13) () (+)
Mycobacterium phlei*
Corynebacterium pseudodiphtheriticum
Bacillus cereus*
*45-day cultures will yield some Gram-negative cells.
Figure 15.1 Identification scheme for eight bacterial unknowns. You can use this
scheme when identifying your staining unknown. 101
102
SECTION II
Staining Techniques
Table 15.1 Cell Size, Shape, and Arrangement of Bacterial Staining Unknowns
Bacterial culture
Alcaligenes denitrificans Bacillus cereus Corynebacterium pseudodiphtheriticum Enterobacter aerogenes Enterococcus faecalis Mycobacterium phlei Neisseria sicca Staphylococcus epidermidis
Cell size (m)
0.5!12 1!35 0.5!12 0.5!12 0.51 0.2!12 0.51 0.51.5
Cell shape
Rod Rod Rod Rod Coccus Rod Coccus Coccus
Cell arrangement
Single cells or pairs Streptobacilli Single cells or V-shapes Single cells or pairs Single cells, pairs, or short streptococci Single cells or cords Single cells or diplococci Single cells, pairs, or staphylococci
Materials
Cultures (1824-hour agar or broth) Alcaligenes denitrificans Bacillus cereus Corynebacterium pseudodiphtheriticum Enterobacter aerogenes Enterococcus faecalis Mycobacterium phlei Neisseria sicca Staphylococcus epidermidis
All agents in red are BSL2 bacteria.
Spore stain Malachite green Safranin Capsule stain Acidic stain: india ink Basic stain: crystal violet Equipment Hot plate (optional) Light microscope Miscellaneous supplies Bibulous paper Bunsen burner and striker Clothespin Disposable gloves (optional) Egg albumin solution Glass slides Immersion oil Inoculating loop or needle Lens paper Ocular micrometer Stage micrometer slide Staining tray Wash bottle with tap water Wax pencil
Stains Gram stain Crystal violet Grams iodine Ethanol (95%) Safranin Acid-fast stain Carbolfuchsin Acid-alcohol Methylene blue
The Staining Characterization of a Bacterial Unknown
EXERCISE 15
103
Procedure
1. You will select or have assigned to you an unknown from the materials list. Record your unknown number in the laboratory report. 2. Examine the information provided in figure 15.1 and table 15.1. Notice that the Gram stain must be done first to determine Gram reaction and cell morphology (figure 15.1). A negative stain or simple stain may be used in conjunction with a
Gram stain to verify cell size, shape, and arrangement (table 15.1). Notice that Grampositive and Gram-negative cocci will require no additional staining, but Gram-positive and Gramnegative rods will require one or more additional stains for identification. So, whatever your Gram stain results, continue to follow the identification scheme downward until you identify your unknown based on staining characteristics. 3. As you perform whatever stains are required, record your results in the laboratory report.
E X E R C I S E
L A B O R AT O RY R E P O RT
NAME LAB SECTION DATE
15
The Staining Characterization of a Bacterial Unknown
Unknown no. 1. Follow the information provided in figure 15.1 and table 15.1 to identify your staining unknown. Perform only the stains required to identify your unknown. 2. Required staining results: Gram stain (See Exercise 11.) Acid-fast stain (See Exercise 12.)
Magnification Cell size Cell shape Cell arrangement Cell color Gram reaction Magnification Cell shape Cell arrangement Cell color Acid-fast?
105
106
SECTION II
Staining Techniques
Spore stain (See Exercise 13.)
Capsule stain (See Exercise 14.)
Magnification Cell shape Cell arrangement Vegetative cell color Endospores? If yes, color? If yes, location in cell Free spores? If yes, spore color? 3. Summary of the staining characteristics of my unknown:
Unknown no. Cell shape
Magnification Color of background Color of cells Cell shape Capsule? If yes, capsule color?
Cell arrangement
Gram reaction
Acid-fast?
Spores?
Capsules?
4. After examining the information provided in figure 15.1 and table 15.1 and recording the results of required stains, I conclude that my staining unknown is .
The Staining Characterization of a Bacterial Unknown
EXERCISE 15
107
5. Based on the information provided in figure 15.1 and table 15.1, fill in the following table for the eight unknown cultures.
Unknown culture Cell shape Cell arrangement Gram reaction Acidfast Spores Capsules
Alcaligenes denitrificans
Bacillus cereus
Corynebacterium pseudodiphtheriticum
Enterobacter aerogenes
Enterococcus faecalis
Mycobacterium phlei
Neisseria sicca
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Вам также может понравиться
- Poultry ParasitesДокумент164 страницыPoultry ParasitesGiselle Castro Sabino100% (1)
- J201 Quiz IIДокумент5 страницJ201 Quiz IItimweaveОценок пока нет
- Bacteriology Sample ExamДокумент4 страницыBacteriology Sample ExamNathan James Guino-oОценок пока нет
- Systemic Fungal InfectionДокумент43 страницыSystemic Fungal InfectionDarian DavinОценок пока нет
- Gram Staining: Key Bacterial Identification MethodДокумент6 страницGram Staining: Key Bacterial Identification MethodSuci Yulia HartiОценок пока нет
- StainigДокумент38 страницStainigyuppie_raj2175Оценок пока нет
- Antihuman Globulin TestsДокумент6 страницAntihuman Globulin TestsElla OrtegaОценок пока нет
- Special StainsДокумент15 страницSpecial StainsEl Marie SalungaОценок пока нет
- Isoflavonoids and Alfalfa Sprouts: "Put A Sprout On It"Документ15 страницIsoflavonoids and Alfalfa Sprouts: "Put A Sprout On It"tiffanyleecraigОценок пока нет
- Bacteria Lab WorksheetДокумент5 страницBacteria Lab WorksheetharrisonОценок пока нет
- Gram Positive CocciДокумент6 страницGram Positive Coccitamiqua1Оценок пока нет
- ELISAДокумент53 страницыELISAbrijesh100% (10)
- Maggotkin of NurgleДокумент39 страницMaggotkin of NurgleAlessio Conversano100% (1)
- CVC ManualДокумент27 страницCVC ManualNurul Hidayah100% (2)
- Mark Schemes: Quick Quiz Matching End of Unit Test Marks To NC LevelsДокумент2 страницыMark Schemes: Quick Quiz Matching End of Unit Test Marks To NC LevelsVictor Barber Sanchis50% (10)
- Ensure Continuity of Learning During PandemicsДокумент4 страницыEnsure Continuity of Learning During PandemicsHerbert IboОценок пока нет
- 112 Ex3Документ20 страниц112 Ex3Francis SullanoОценок пока нет
- Microbiology Tests and Culture MediaДокумент19 страницMicrobiology Tests and Culture MediaMashal WakeelaОценок пока нет
- Acid Fast StainingДокумент17 страницAcid Fast StaininglemuelОценок пока нет
- Identification of UnknownsДокумент7 страницIdentification of UnknownsAhmed ZiyadОценок пока нет
- Identifying Unknown Bacterium-GuideДокумент13 страницIdentifying Unknown Bacterium-GuideShaezarah MohamudallyОценок пока нет
- LAB 11 Biochemical TestsДокумент15 страницLAB 11 Biochemical TestsDeena Hajj QasemОценок пока нет
- Cell Staining: The Simple StainДокумент4 страницыCell Staining: The Simple StainAitlas KhanОценок пока нет
- Exp7 PrelabДокумент7 страницExp7 Prelab임성민Оценок пока нет
- Exercise 8Документ3 страницыExercise 8Merve Nur GülerОценок пока нет
- Lesson 3 Quality Control Sterilization and Disinfection ModuleДокумент23 страницыLesson 3 Quality Control Sterilization and Disinfection ModuleTinОценок пока нет
- Coombs TestДокумент17 страницCoombs Testnativeman2221Оценок пока нет
- Pex 12 01Документ5 страницPex 12 01Gonzalo LaricoОценок пока нет
- Pex 12 01Документ6 страницPex 12 01Ciera Smith71% (7)
- BIO 223 Lab Report 1Документ7 страницBIO 223 Lab Report 1sara.a.alabdulkarimОценок пока нет
- Learn Microbiology Online Medical Microbiology Guide: News TickerДокумент19 страницLearn Microbiology Online Medical Microbiology Guide: News TickerCecilia MukototsiОценок пока нет
- Bacteriology S23 WorksheetДокумент6 страницBacteriology S23 WorksheetblahОценок пока нет
- Practical Session Two Guide-1Документ9 страницPractical Session Two Guide-1Andrease WandazОценок пока нет
- Dot-ELISA Practical Manual 2Документ4 страницыDot-ELISA Practical Manual 2Anusua RoyОценок пока нет
- Chapter II - 1Документ18 страницChapter II - 1Smiley LettersОценок пока нет
- Lab 3 Bacterial Staining Techniques IIДокумент10 страницLab 3 Bacterial Staining Techniques IIErreneoОценок пока нет
- Group 5 - Experiment No.9 - Preparation of Bacterial Smear and Gram StainingДокумент10 страницGroup 5 - Experiment No.9 - Preparation of Bacterial Smear and Gram StainingPMG BrightОценок пока нет
- 2021 Lab 6 GeneticsДокумент10 страниц2021 Lab 6 GeneticsGurleen KaurОценок пока нет
- The Fundamentals of Scientific Research: An Introductory Laboratory ManualОт EverandThe Fundamentals of Scientific Research: An Introductory Laboratory ManualОценок пока нет
- Lab Class 3 - Detection of Specified Organisms and Identification of BacteriaДокумент3 страницыLab Class 3 - Detection of Specified Organisms and Identification of BacteriakomalramОценок пока нет
- Methods and Materials For Aqua Magt LabДокумент3 страницыMethods and Materials For Aqua Magt LabJon Irish AquinoОценок пока нет
- StainingДокумент5 страницStainingyuppie_raj2175Оценок пока нет
- BIO6LabExam2StudyGuide LimДокумент9 страницBIO6LabExam2StudyGuide Limthu_vu_29Оценок пока нет
- LAB 2: Staining and Streaking: Series of Stains and Chemical Reagents To Increase Contrast and Reveal Information AboutДокумент10 страницLAB 2: Staining and Streaking: Series of Stains and Chemical Reagents To Increase Contrast and Reveal Information AboutrabkaОценок пока нет
- Identify Macromolecules Using Qualitative TestsДокумент4 страницыIdentify Macromolecules Using Qualitative TestsPam SОценок пока нет
- Gram Stain Lab (Keystone Anchor Bio.A.1.2.1) : PA StandardsДокумент3 страницыGram Stain Lab (Keystone Anchor Bio.A.1.2.1) : PA StandardsNicole SanchezОценок пока нет
- Lec 2Документ18 страницLec 2Thomas SantosaОценок пока нет
- Lab ReportДокумент24 страницыLab Reportwol aldo0% (1)
- Mid TermДокумент17 страницMid TermTamoghna NaskarОценок пока нет
- Practical lab 3: Gram staining and bacterial identificationДокумент5 страницPractical lab 3: Gram staining and bacterial identificationSilvia UngureanuОценок пока нет
- Identification of Bacteria Using Gram Staining MethodДокумент7 страницIdentification of Bacteria Using Gram Staining MethodDani MughalОценок пока нет
- Practical 6 Identification of Gram Ve BacteriaДокумент8 страницPractical 6 Identification of Gram Ve BacteriaMona MostafaОценок пока нет
- Gram Staining ProtocolДокумент19 страницGram Staining ProtocolmourighoshОценок пока нет
- MLT 415 Fundamentals of Microbiology Gram StainДокумент7 страницMLT 415 Fundamentals of Microbiology Gram StainYo YaОценок пока нет
- BIO 171 Lab Activity No 2Документ5 страницBIO 171 Lab Activity No 2たこ ゆきОценок пока нет
- Practical MKS ModuleДокумент12 страницPractical MKS ModuleMohammed HashemОценок пока нет
- Bacterial Morphology & Staining TechniquesДокумент6 страницBacterial Morphology & Staining TechniquesTuli UguluОценок пока нет
- Biochemical TestsДокумент41 страницаBiochemical TestsChinthikaОценок пока нет
- Gram Stain Procedure ExplainedДокумент6 страницGram Stain Procedure ExplainedJFcp VazquezОценок пока нет
- Microscope Lab Report and Identification of MicroorganismsДокумент19 страницMicroscope Lab Report and Identification of MicroorganismsWILLIAM BOWERYОценок пока нет
- MICROBIOLOGY & PARASITOLOGY - Basic - Microbiological - ProceduresДокумент75 страницMICROBIOLOGY & PARASITOLOGY - Basic - Microbiological - ProceduresSchola De san joseОценок пока нет
- To Resume Micro ExpeДокумент1 страницаTo Resume Micro ExpeBAJA, GWYNETH ALLYZZA U.Оценок пока нет
- Drug Study BAIAEДокумент5 страницDrug Study BAIAEDAOman09Оценок пока нет
- Clean Hands Hand Hygiene PDFДокумент21 страницаClean Hands Hand Hygiene PDFWina BenaОценок пока нет
- Anti-Vaccine IssueДокумент6 страницAnti-Vaccine IssueKisshenrau Vijayan ArenaОценок пока нет
- Dentist-Patient Communication and Relationship BuildingДокумент38 страницDentist-Patient Communication and Relationship BuildingBhanuji Naidu100% (3)
- Mbagathi Child Health Rotation MBCHB V Revised 110417Документ12 страницMbagathi Child Health Rotation MBCHB V Revised 110417okwadha simionОценок пока нет
- H52839 Oliver Odd Sock InteractiveДокумент20 страницH52839 Oliver Odd Sock InteractiveIulia GramaОценок пока нет
- Pediatric TB and HIV: The Potential of New TB VaccinesДокумент27 страницPediatric TB and HIV: The Potential of New TB VaccinesBarnabasNatambaОценок пока нет
- Effectiveness of Gallus Gallus Domesticus Eggshells As An Antibacterial Component of Hand SoapДокумент71 страницаEffectiveness of Gallus Gallus Domesticus Eggshells As An Antibacterial Component of Hand SoapGabriel Christopher MembrilloОценок пока нет
- 2011 Veterinary Vaccinesand Their Importanceto Animal Healthand Public HealthДокумент11 страниц2011 Veterinary Vaccinesand Their Importanceto Animal Healthand Public HealthCARLOTA DIAZ AGUILARОценок пока нет
- Explain The ImportanceДокумент6 страницExplain The Importanceapi-607897433Оценок пока нет
- 3rd Mid Term Exam - Assignment BSc. 2nd Semester 2023Документ1 страница3rd Mid Term Exam - Assignment BSc. 2nd Semester 2023anisaanОценок пока нет
- Data Diagnosa P-CareДокумент458 страницData Diagnosa P-CarerinaОценок пока нет
- Deaths Involving COVID-19 by Vaccination Status, England Deaths Occurring Between 1 April 2021 and 31 May 2023Документ7 страницDeaths Involving COVID-19 by Vaccination Status, England Deaths Occurring Between 1 April 2021 and 31 May 2023Mihai MotorgaОценок пока нет
- Pil 13082Документ2 страницыPil 13082raul sinatoОценок пока нет
- Dengue TriviaДокумент2 страницыDengue TriviaSamuel Luz Barquia, Jr.100% (1)
- HIV/AIDS Term Paper Provides Insights Into Causes, Prevention & TreatmentДокумент23 страницыHIV/AIDS Term Paper Provides Insights Into Causes, Prevention & TreatmentCindyОценок пока нет
- Treatment: Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) (Документ15 страницTreatment: Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) (akku_m1991Оценок пока нет
- Disseminated Pulmonary TuberculosisДокумент29 страницDisseminated Pulmonary TuberculosisbrightagbotuiОценок пока нет
- The Role of Community Health Nurses During The Pandemic-FinalДокумент27 страницThe Role of Community Health Nurses During The Pandemic-FinalSri WahyuniОценок пока нет
- Management of Herpangina: Denta, Jurnal Kedokteran GigiДокумент5 страницManagement of Herpangina: Denta, Jurnal Kedokteran GigirizadОценок пока нет
- BREAKING NHS Director Confirms Doctors Lied About Cause of Death To Create The Illusion of A COVID-19Документ12 страницBREAKING NHS Director Confirms Doctors Lied About Cause of Death To Create The Illusion of A COVID-19WAYLOR MusicОценок пока нет
- Otitis MediaДокумент34 страницыOtitis MediaEdson Reinier Joseph EnriquezОценок пока нет
- The EPIДокумент14 страницThe EPIMartin Dazel Martin DazelОценок пока нет
- List of Publications Horst R. Thieme: Schrift 157 (1977), 141-154Документ11 страницList of Publications Horst R. Thieme: Schrift 157 (1977), 141-154api-553587843Оценок пока нет