Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Pelvis and Perineum
Загружено:
Sarah Sy-SantosИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Pelvis and Perineum
Загружено:
Sarah Sy-SantosАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Pelvis and Perineum: GIOBUNNNYY, super simple lang ng notes ko.
Hope it helps kahit di detailed and di siya complete :D A. Pelvis and Pelvic Cavity Pelvic Wall: Formed by Pelvic Girdle Pelvic/ Hip Bone: Ilium+Ischium+Pubis Sacroiliac joint: Syndesmosis; attached to iliac tuberosity Pubic Symphysis: Synovial; auricular surface Triradiate Cartilage: separates childs hip bone at acetabulum *Pelvic bone of children is separate until puberty Ilium: Arcuate Line: part of linea terminalis below auricular surface *Linea Terminalis: Arcuate line+pectineal line+pubic crest Ischium: Ischial tuberosity: rough surface behind inferior rami Greater sciatic notch: between PIIS+ ischial spine Pubis: Pectineal Line: continuation of arcuate line Subpubic line: assessment for vaginal delivery Sacrum: Sacral Promontory Coccyx: CLINICAL: Coccydenia: painful coccyx; fracture of coccyx Pelvic Fracture: 2 fractures for displacement/ instability Divisions of Pelvis Greater (False) Pelvis Superior to pelvic inlet Borders: Iliac alae; S1 y Pelvic Inlet/ brim Borders: Promontory+ ala of sacrum
Linea Terminalis Symphysis Pubis Lesser (true) Pelvis Between pelvic inlet and outlet Surfaces of hip bone and coccyx Divided by pelvic diaphragm into pelvic cavity proper and perineum y Pelvic Outlet/ Inferior pubic aperture Tip of coccyx Sacrotuberous Ligament Ischial Tuberosities Pubic Arch CLINICAL: Pelvic Diameters and Conjugates Pelvic Inlet Diameters: Anteroposterior: from pubic symphysis to sacral promontory True Conjugate Obstetric Conjugate: smallest Diagonal conjugate: External measurement Transverse: measurement of pelvic inlet using widest part of linea terminalis Oblique: left/ right; use sacroiliac joint Midpelvis: Plane of greatest dimension Diameters: Anteroposterior: IV disc bet S2-3 to the midpoint of pubic symphysis Transverse: midpoint between obturator foramen
Plane of least dimension
Diameters: Anteroposterior: Anatomical: tip of coccyx to tip of pubic symphysis Transverse/ Bispinous: smallest diameter, bet ischial spines Variations in Male/ Female Pelvis Gynecoid (for females): wide Anteroposterior and transverse diameters Android (for males): small diameters; <3 shaped Anthropoid: contracted transverse diameter Platypelliod: contracted anteroposterior diameter Subpubic angle: Female: > 85 Male: <70 Pelvic Axis: Central point of pelvic cavity Directed downward and posterior Directed downward and anterior Anatomical Position of Pelvis ASIS+ anterior aspect of pubic symphysis lie in the same angle. Symphysis pubis faces posteriorly and backward Pelvic Foramina Pudendal nerve supplies perineum by going through the Greater sciatic Foramen then reenters through the lesser sciatic foramen Obturator nerve exits pelvic cavity via obturator canal to supply mid thigh muscles
Sacroiliac: synovial (auricular)+syndesmosis (tuberosity) Ligaments: Anterior Sacroiliac Interosseous Posterior Sacroiliac Sacrotuberous Sacrospinous Sacrococcygeal Anterior Sacrococcygeal ligament Lateral Sacrococcygeal ligament Posterior Sacrococcygeal ligament Pubic Symphysis: fibrocartilage; interpubic disc Ligaments: Superior interpubic Inferior (arcuate) interpubic Pelvic Wall Muscles: Obturator Internus: exits via Lesser Sciatic Foramen Piriformis: exits via Greater Sciatic Foramen Pelvic Floor Muscles: incomplete anteriorly for urethra and vagina; below pelvic diaphragm= perineum Levator ani: originates from obturator fascia thickening (body of pubis-ischial spine) Anterior fibers: surrounds prostate and vaginal sphincter Intermediate fibers: Puborectalis: Surrounds rectum; holds feces in rectum Pubococcygeus Posterior fibers: Iliococcygeus Perineal Body: anterior connection between puborectalis muscles Posterior connection: anococcygeal ligament
Pelvic joints
Pelvic Cavity: contains distal ureter and urinary bladder, rectum and pelvic genital organs Borders: Superiorly: Pelvic Inlet Inferiorly: Pelvic Floor Posteriorly: Sacrum, coccyx, piriformis Anteriorly: Pubic bone, symphysis Laterally: Hip bone, obturator membrane, internus muscle Pelvic Fascia: Membranous: continuous with transversallis fascia Parietal: covers the wall Visceral: covers the organs inside the pelvis cavity Endopelvic: between parietal and visceral membranous fascia; fatty Pelvic Peritoneum: continuation of parietal peritoneum into the pelvic cavity but doesnt reach the pelvic floor Peritoneal Recess: Depressions of the pelvic peritoneum Peritoneal Reflections: Fascia goes back/ folds on itself Supervesical Fossa: above urinary bladder and connected to abdominal wall Pararectal Fossa: Surrounds rectum Pouches: Male: Rectovesical Female: Uterovesical pouch: uterus/bladder Rectouterine pouch (Douglas Pouch): rectum/ uterus; blood accumulation= sign for ectopic pregnancy Rectovesical: rectum/bladder; only possible after hysterodectomy( removal of uterus)
Pelvic Viscera Urinary Bladder: Posterior to pubic bones separated by potential space ( retropubic space of Retzius) Detrussor Muscle Urethral Orifice/ Surface Uretral Orifice Bladder Trigone: triangular smooth surface of bladder Internal urethral sphincter: involuntary; thickening of muscle in the bladder neck External urethral sphincter: motor Sympathetic: T10-12; Pelvic and Hypogastric Plexus Motor to external sphincter Inhibitory to detrussor and internal Sphincter Parasympathetic: Responsible for micturation S2-S4; Pelvic Splanchnic nerves and Inferior Hypogastric Plexus CLINICAL Catheter: > Rectum: Superior 3rd covered by peritoneum Innervated by S3 Spread tenia coli Abscence of fatty appendices Flexures: Anterior Sacral Anarectel: 800 angulation to hold poop Lateral (valve of Houston) Superior Left Inferior Intermediate: Right Rectal Ampulla: stores feces CLINICAL: Digital Rectal Exam: for prostatic enlargement
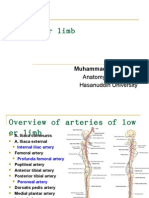
Arteries: Internal Iliac: main blood supply of pelvic cavity Anterior Division: (IIOUVM) Umbilical: distal portion medial umbilical ligament proximal portion superior vesical artery Obturator: passes obturator canal Inferior Vesical (males) Uterine/ Ductus Deferens Vaginal (female) Middle Rectal Inferior Pudendal Inferior Rectal: supplies perineum Inferior Gluteal Posterior Division: Iliolumbar Lateral Sacral Superior Gluteal: direct continuation Ovarian Median Sacral: from Aorta Superior Sacral: from Inferior Mesenteric Blood supply of Rectum: Inferior Mesenteric Artery Superior Rectal Internal Iliac Artery Middle Rectal Inferior Pudendal Inferior Rectal; middle sacral Blood Supply of Bladder: Umbilical: Superior vesical Internal Iliac: Inferior Vesical: also supplies prostate Venous Plexus Caval Circulation: directly to IVC via Internal Iliac Vein Portal Circulation: passes thru liver via Superior Rectal Vein inferior Mesenteric Vein Internal vertebral: drains vertebrae via Lateral Sacral vein
Venous drainage of Rectum Superior Rectal IMV (PORTAL) Middle Rectal Internal Iliac CAVAL Inferior Rectal Inferior Pudendal Venous Drainage of Bladder Vesical Venous Plexus Internal Iliac (Caval) Pelvic Nerves: Lumbosacral and Coccygeal Spinal Nerves: Somatosensory; supplies skin Sacral Sympathetic Periarterial Hypogastric
B. Perineum Standing position:Narrow region between the thighs Abducted Legs: *center of diamond= perineal body Urogential Triangle Anal Triangle
Anal Triangle: Contents: Ischioanal fossa: wedged space beside anal Canal Alcocks Canal: Contains Internal Pudendal Nerve Anal canal: Rectal Ampulla Anus External Sphincter: Deep Superficial: Nerve to Levator Ani Subcutaneous: Nerve to Levator Ani + Inferior Rectal Nerve
Columns of Morgagni: Proximal: Anorectal Line
Distal: Pectinate and Dentate line Transitional Zone Anoderm: Below dentate line Pecten: From dentate line to anocutaneous line Anocutaneous line: non keratinizing to keartinizing Corrugator cutis ani muscle: Surgical canal: anorectal line to anal opening Anatomical canal: dentate line to anal opening
Вам также может понравиться
- MCQ in AbdomenДокумент4 страницыMCQ in AbdomenJayathra Liyanagamage100% (2)
- Abd MCQДокумент3 страницыAbd MCQerisamwaka100% (2)
- Wiki Abdomen Mcqs ExplainedДокумент9 страницWiki Abdomen Mcqs Explainedchemptnk100% (2)
- Sudan Medical Specialization Board 2Документ37 страницSudan Medical Specialization Board 2Dania Zaid100% (1)
- MCQ Head & NeckДокумент5 страницMCQ Head & NeckSyafiqah Ahmad100% (2)
- Anatomy 250Документ50 страницAnatomy 250Abdul MusawerОценок пока нет
- Mcqs in Upper Limb: DR - Khalid MiladДокумент10 страницMcqs in Upper Limb: DR - Khalid MiladOzgan SüleymanОценок пока нет
- 200 Most Important Mcqs With Answers From Past CPSP Papers - Answers After Every 10 McqsДокумент27 страниц200 Most Important Mcqs With Answers From Past CPSP Papers - Answers After Every 10 Mcqsanum ijaz100% (2)
- MCQ PhysiologyДокумент7 страницMCQ Physiologydrng48Оценок пока нет
- Anatomy MCQSДокумент13 страницAnatomy MCQSdrpnnreddyОценок пока нет
- Thigh Mcqs ExplainedДокумент9 страницThigh Mcqs ExplainedRobert EdwardsОценок пока нет
- Anatomy I MCQ PDFДокумент10 страницAnatomy I MCQ PDFRishabhОценок пока нет
- Blood Vessels of Upper LimbДокумент23 страницыBlood Vessels of Upper Limbkhalid_shinasОценок пока нет
- Knee & Leg MCQ - ProProfs QuizДокумент8 страницKnee & Leg MCQ - ProProfs QuizBassamSheryanОценок пока нет
- Anatomy 1800 Multiple Choice Questions B01DRY51AOДокумент1 страницаAnatomy 1800 Multiple Choice Questions B01DRY51AOJoseph NduaguibeОценок пока нет
- Histology of The Digestive SystemДокумент27 страницHistology of The Digestive SystemHarnarayan Jeev Singh Bajaj100% (1)
- Upper Limb, Pectoral RegionДокумент24 страницыUpper Limb, Pectoral Regiongtaha80Оценок пока нет
- 2 MCQ - Autonomic - 2Документ33 страницы2 MCQ - Autonomic - 275qkdkj9mdОценок пока нет
- Histology Exam IV Review Part 2Документ26 страницHistology Exam IV Review Part 2ashdmb217Оценок пока нет
- Anatomy MCQ 1Документ15 страницAnatomy MCQ 1Maria75% (4)
- Upper Limb Solved MCQs (Set-1)Документ6 страницUpper Limb Solved MCQs (Set-1)Fawad KtkОценок пока нет
- 4 - Anatomy MCQs Upper LimbДокумент37 страниц4 - Anatomy MCQs Upper LimbRiaОценок пока нет
- The Lower Limb (Biomedic Unismuh 2012)Документ65 страницThe Lower Limb (Biomedic Unismuh 2012)Sadam_fasterОценок пока нет
- Upper Limb MCQsДокумент12 страницUpper Limb MCQstafi66Оценок пока нет
- All Bat NotesДокумент1 048 страницAll Bat NotesAfk SystemОценок пока нет
- Blue Boxes Lower LimbДокумент4 страницыBlue Boxes Lower LimbZllison Mae Teodoro MangabatОценок пока нет
- Anatomy Abdomen MCQs For DNBДокумент62 страницыAnatomy Abdomen MCQs For DNBPG Aspirant100% (2)
- MCQ - Test 2Документ3 страницыMCQ - Test 2Gaurav SinghОценок пока нет
- Nervemuscle MCQДокумент9 страницNervemuscle MCQNishanthy PirabakarОценок пока нет
- Compiled MSPC 235 Past Questions Volume IIIДокумент15 страницCompiled MSPC 235 Past Questions Volume IIIPaapaErnestОценок пока нет
- 015 Anatomy MCQ ACEM Primary PDFДокумент14 страниц015 Anatomy MCQ ACEM Primary PDFMoiez Ahmad100% (1)
- Anatomy - Anterior Triangle of The Neck PDFДокумент6 страницAnatomy - Anterior Triangle of The Neck PDFAngel KimОценок пока нет
- 1 SEMESTER 18/19: Median Nerve-Carpal Tunnel Weakens Lateral 3 Digits Sensory Loss ParalysisДокумент60 страниц1 SEMESTER 18/19: Median Nerve-Carpal Tunnel Weakens Lateral 3 Digits Sensory Loss ParalysisInsaf AhamedОценок пока нет
- Anatomy Forearm MCQДокумент2 страницыAnatomy Forearm MCQthevampire20104825100% (1)
- Question Chapter 4 Spinal Cord and Ascending, Descending, and Interegmental TractsДокумент17 страницQuestion Chapter 4 Spinal Cord and Ascending, Descending, and Interegmental TractsTrang BuiОценок пока нет
- MCQ Anatomy-thorax-Abdo-PelvisДокумент100 страницMCQ Anatomy-thorax-Abdo-PelvisMatt McCannОценок пока нет
- 25 MCQ NeuroДокумент5 страниц25 MCQ NeuroVaishnavi Singh100% (1)
- GROSS ANATOMY-Review Notes PDFДокумент56 страницGROSS ANATOMY-Review Notes PDFgreen_archerОценок пока нет
- 5 Pulmonary Response To ExerciseДокумент45 страниц5 Pulmonary Response To ExerciseRabia RaufОценок пока нет
- QB-Neurophysiology 1st MidtermДокумент19 страницQB-Neurophysiology 1st MidtermJUANA ELIZABETH LOZA CASTROОценок пока нет
- 30 SEQs of Lower Limb Anatomy by DR RoomiДокумент2 страницы30 SEQs of Lower Limb Anatomy by DR RoomiMudassar Roomi50% (2)
- Histology Lecture: Minerva Diana A. Dichoso, RMTДокумент108 страницHistology Lecture: Minerva Diana A. Dichoso, RMTVernadel ApolloОценок пока нет
- Lymphatic Drainage of Abdomen: Learning ObjectivesДокумент5 страницLymphatic Drainage of Abdomen: Learning ObjectivesUloko ChristopherОценок пока нет
- Anatomy MCQsДокумент41 страницаAnatomy MCQsAzim Arif Hashmi100% (1)
- Upper Limb - Pectoral Region, Scapular Region, Axilla & Brachial PlexusДокумент12 страницUpper Limb - Pectoral Region, Scapular Region, Axilla & Brachial Plexusewijayapala100% (1)
- Upper Limb-MCQ With AnswersДокумент20 страницUpper Limb-MCQ With AnswersMatt McCannОценок пока нет
- MCQ Lower Limb G4Документ14 страницMCQ Lower Limb G4Sajjad HaiderОценок пока нет
- Dr:Khalid MiladДокумент27 страницDr:Khalid MiladMohsen Elzobna0% (1)
- Upper Limb MCQ AnswersДокумент3 страницыUpper Limb MCQ AnswerschiОценок пока нет
- Upper Limb - Clinical AnatomyДокумент19 страницUpper Limb - Clinical AnatomyewijayapalaОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 Embryo Q and A ModuleДокумент76 страницUnit 1 Embryo Q and A ModuleBAYAN NADER YOSRI JABARI 22010404Оценок пока нет
- Nervous System Practice QuestionsДокумент7 страницNervous System Practice QuestionsOsama AlhumisiОценок пока нет
- Abdomen OSPE Charts Questions OnlyДокумент29 страницAbdomen OSPE Charts Questions OnlyRathnaОценок пока нет
- MCQ Question BankДокумент102 страницыMCQ Question BankdrmadaanpiyushОценок пока нет
- Royal's Neurophysiology McqsДокумент17 страницRoyal's Neurophysiology McqsJames IbrahimОценок пока нет
- #Anatomy-Upperlimb Important QuestionsДокумент4 страницы#Anatomy-Upperlimb Important QuestionsSudeepthiОценок пока нет
- Pelvis and Perinium 2019Документ59 страницPelvis and Perinium 2019Vuluwa GeorgeОценок пока нет
- ZOO 4733 - Exam 3 ReviewДокумент21 страницаZOO 4733 - Exam 3 ReviewDaniel PóoОценок пока нет
- OB - TransesДокумент112 страницOB - TransesAldwin BagtasОценок пока нет
- Laboratory Exercise No. 2A. Microscopic Observation of Bacteria - Sep 13Документ6 страницLaboratory Exercise No. 2A. Microscopic Observation of Bacteria - Sep 13Adrian MiguelОценок пока нет
- Test Bank For Essentials of Life Span Development 6th Edition John SantrockДокумент60 страницTest Bank For Essentials of Life Span Development 6th Edition John Santrockhanhvaleriefq7uОценок пока нет
- EDS261Документ8 страницEDS261micasandogu01Оценок пока нет
- Cawis vs. Cerilles - G.R. No. 170207 - April 19, 2010Документ2 страницыCawis vs. Cerilles - G.R. No. 170207 - April 19, 2010Lordy Jessah AggabaoОценок пока нет
- 9028 AccДокумент1 страница9028 Accvarun sklmtvОценок пока нет
- Right On 1Документ2 страницыRight On 1Lingva Lingva BinestОценок пока нет
- Cheiloscopy in Gender Determination: A Study On 2112 IndividualsДокумент5 страницCheiloscopy in Gender Determination: A Study On 2112 Individualsknr crsОценок пока нет
- 7a - Alfa R CBT Training Certificate of CompletionДокумент1 страница7a - Alfa R CBT Training Certificate of Completionapi-355974373Оценок пока нет
- Week 3 CPAR Day 1Документ4 страницыWeek 3 CPAR Day 1zessicrel mejiasОценок пока нет
- Joan of Arc Inspiring Example Barbara BeckwithДокумент4 страницыJoan of Arc Inspiring Example Barbara BeckwithraikibaОценок пока нет
- Creative Works - Main Report - ABCDДокумент65 страницCreative Works - Main Report - ABCDvenkatesh subbaiyaОценок пока нет
- Syllabus For BOSДокумент31 страницаSyllabus For BOSkannanchammyОценок пока нет
- Tagalog Medley 1Документ4 страницыTagalog Medley 1Bon.AlastoyОценок пока нет
- 09Документ69 страниц09Sakshi VermaОценок пока нет
- Values in Decision MakingДокумент24 страницыValues in Decision MakingMr.TarnateОценок пока нет
- Growth of The SocialismДокумент11 страницGrowth of The SocialismHarpreet SinghОценок пока нет
- CentOS Quick Start Guide by Shiwang KalkhandaДокумент313 страницCentOS Quick Start Guide by Shiwang KalkhandaSlaheddineОценок пока нет
- Api 119Документ8 страницApi 119hokhmologОценок пока нет
- Happiness Level 1 - Exercises PDFДокумент2 страницыHappiness Level 1 - Exercises PDFMohamed Amine AkouhОценок пока нет
- Ten Random Fucking ParagraphsДокумент1 страницаTen Random Fucking ParagraphsMason SykesОценок пока нет
- Final Stipulated Judgment Parella Vs Atamian Et Al. United States District Court For Northern OklahomaДокумент3 страницыFinal Stipulated Judgment Parella Vs Atamian Et Al. United States District Court For Northern OklahomaMarc Parella100% (1)
- Case Study ICM Solution For MindTreeДокумент3 страницыCase Study ICM Solution For MindTreevinodОценок пока нет
- Left Brain Right Stuff Rosenzweig en 20830Документ5 страницLeft Brain Right Stuff Rosenzweig en 20830albertОценок пока нет
- The Accounting Equation and Financial StatementsДокумент30 страницThe Accounting Equation and Financial StatementsAlya CandyОценок пока нет
- Teachers' Perception of Their Initial Preparation in Teaching Senior High School PhysicsДокумент11 страницTeachers' Perception of Their Initial Preparation in Teaching Senior High School PhysicsFelipe López GarduzaОценок пока нет
- West Report 6 Mi BemolДокумент4 страницыWest Report 6 Mi BemolDocSunsetОценок пока нет
- Case Digest (Complete)Документ7 страницCase Digest (Complete)Shailah Leilene Arce Briones100% (1)
- Lawang SewuДокумент3 страницыLawang SewuIlo JejacОценок пока нет
- 20 Century Filipino: Traditional ComposersДокумент13 страниц20 Century Filipino: Traditional ComposersMawi AguiluzОценок пока нет
- Tenses MergedДокумент76 страницTenses MergedMihály Bence SzabóОценок пока нет