Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Fizik k2 f4 Akhir 06
Загружено:
Cikgu SinАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Fizik k2 f4 Akhir 06
Загружено:
Cikgu SinАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
4531/2 Fizik Kertas 2 Nov 2006 2 jam
Nama:...
Tingkatan:.
SEKTOR SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH BAHAGIAN SEKOLAH KEMENTERIAN PELAJARAN MALAYSIA PEPERIKSAAN AKHIR TAHUN 2006 TINGKATAN 4 FIZIK KERTAS 2 Dua jam tiga puluh minit (Anda dinasihatkan untuk memperuntukkan masa 90 minit untuk Bahagian A, 30 minit untuk Bahagian B dan 30 minit untuk Bahagian C) JANGAN BUKA KERTAS SOALAN INI SEHINGGA DIBERITAHU. 1. 2. Kertas soalan ini mengandungi tiga bahagian : Untuk Kegunaan Pemeriksa Bahagian A, Bahagian B dan Bahagian C Jawab semua soalan dalam bahagian A, satu soalan Bahagian Soalan Markah 1 daripada Bahagian B dan satu soalan daripada 2 Bahagian C. Jawapan kepada ketiga-tiga bahagian ini hendaklah 3 diserahkan bersama-sama. 4 Jawapan kepada bahagian A hendaklah ditulis A 5 dalam ruang yang disediakan dalam kertas soalan. Jawapan kepada Bahagian B dan Bahagian C 6 hendaklah dituliskan pada ruang jawapan yang 7 disediakan dalam kertas soalan ini. Walau 8 bagaimanapun kertas tulis tambahan sekiranya digunakan, perlulah diikat bersama dengan buku soalan ini. Dalam jawapan anda, persamaan, 1 gambar rajah, jadual, graf dan cara lain yang sesuai B 2 untuk menjelaskan jawapan anda boleh digunakan. Rajah tidak dilukis mengikut skala kecuali 1 dinyatakan. C 2 Markah maksimum yang diperuntukkan ditunjukkan dalam kurungan pada hujung tiap-tiap soalan atau Jumlah Besar bahagian soalan. Penggunaan kalkulator saintifik yang tidak boleh diprogramkan
Kertas ini mengandungi 17 halaman bercetak
3. 4. 5.
6. 7.
8.
4531/2
Maklumat berikut mungkin berfaedah (simbol-simbol mempunyai makna yang biasa)
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Momentum = mv F = ma Tenaga kinetik = mv2 Tenaga keupayaan = mgh =
m V Tenaga Masa
6. 7.
Kuasa = P=F/A
8.
Haba, Q = mc Haba Pendam, Q2 = mL
9. 10. 11. 12.
PV = Pemalar
T g = 10 ms-2
I = Ft = mv - mu P = gh
[Lihat sebelah] SULIT
4531/2 Section A (60 marks) Answer all questions in this secton. . The suggested time allocated for you to answer this section is 90 minutes. 1. The figures below show a vernier caliper used to measure the diameter of a metal ball.
Figure 1.1
Figure 1.2
Figure 1.1 shows the position of the vernier scale when the jaws are closed. Figure 1.2 shows the position of the vernier scale when a metal ball is put between the jaws of the vernier calipers. a) What is the zero error of the vernier calipers? [ 1 mark] b) What is the reading of the vernier calipers as shown in Figure 2.2? [ 1 mark] c) Calculate the diameter of the metal ball. [ 1 mark] d) If the device used is replaced by a micrometer screw gauge, which device is more sensitive?
[ 1 mark] 2. The diagram below shows the volume of water in a measuring cylinder before and after an object, Q of mass 50 g is placed inside it. ( Volume of water before putting in the object is 150 cm3 3 [Lihat sebelah] SULIT
4531/2 Volume of water after putting in the object is 230 cm3 )
Q Figure 2 a). Why does the object Q sink to the bottom of the measuring cylinder? .. [1 mark] b). What is the volume of the object Q. .. [1 mark] c). Calculate the density of block Q
[2 marks] d). State one application of density in everyday life.
[1 mark]
3.
[Lihat sebelah] SULIT
4531/2 area 10 cm2 area 40 cm2
oil
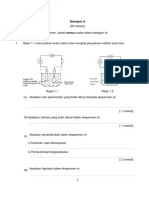
Figure 3 Figure 3 above shows the structure of a hydraulic system where a small force is used to produce a bigger force. A and B are the cross-sectional areas of the pistons. a). A force of 20 N is applied to the smaller piston. i. Calculate the pressure on the smaller piston?
[1 mark] ii. Calculate the force, F exerted on the larger piston.
[1 mark] iii. Find the ratio of the pressure on the smaller piston to pressure on the larger piston.
[1 mark] iv. Name the principle applied in (a)ii. [1 mark] b). Piston P is pushed and moved to the right through a distance of 15 cm and this has resulted in the piston Q moving a bit to the right. i. How much has the piston Q moved? [2 marks] ii. What is the assumption made in obtaining the answer in (b)i. 5 [Lihat sebelah] SULIT
4531/2
[1 mark] iii. State one important property of the liquid used in the hydraulic brake.
[1 mark]
4. oC 140
120
Y X
100 80 60 40 20
3 Figure 4
Time/min
Two solid materials both with the same mass 800 g are heated up with a heater of 1000 W. a) What is the meaning of the melting point of a material. ... [1 mark] b) Based on the graph above, compare i. the specific heat capacity of both materials. [1 mark] ii. their heat capacity ... [1 mark] c) i. State the melting points of X and Y 6 [Lihat sebelah] SULIT
4531/2
[1 mark] ii Calculate the specific latent heat of Y
[2 marks] 5. In a laboratory experiment, students investigate the relationship between the object distance, u and the image distance, v for a convex lens. From the data obtained, a graph is plotted as shown below. 1/v (cm-1)
1.6
1.2
0.8
0.4
1/u (cm-1)
0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 16
a). i. State the value of the intercept at the 1/v axis when 1/u = 0 and therefore find the value of the focal length of the lens.
[2 marks] ii. Name the quantity obtained from the reciprocal of the intercept at the 1/u axis when 1/v = 0. 7 [Lihat sebelah] SULIT
4531/2
.. [1 mark]
b). Calculate the gradient of the graph.
[2 marks] c). Obtain the characteristics of the image produced when i. The object distance u is 0.5 cm. [1 mark] ii. The object distance u is more than 1.0 cm. [1 mark]
6. Figure 6 below shows two masses 3 kg and 5 kg which are connected by a light inextensible string through a smooth pulley.
5 kg
3 kg
Figure 6
[Lihat sebelah] SULIT
4531/2 a). In the figure above, mark and label the forces acting on the string and the two masses
[2 marks] b). In what direction does the 3 kg mass move? .. [1 mark] c). If T is the tension in the string, a is the acceleration of the masses, m1 = 5 kg, m2 = 3 kg, g is the acceleration due to gravity i. Write down two equations relating T, a, m1, m2 dan g for each mass.
[2 marks] ii. Calculate the acceleration of both of the two masses and the tension of the string.
[2 marks] d). State one characteristic of the motion of the two masses.
[2 marks]
7. Figure 7.1 shows a bus moving with a velocity of 70 km/h and shows the condition of a passenger standing in the bus when the brakes are suddenly applied. 9 [Lihat sebelah] SULIT
4531/2 Figure 7.2 shows a cook trying to shake the sauce out of a bottle.
Figure 7.1
Figure 7.2
a.). Based on both of the figures above, state one characteristic experienced by the passenger and the sauce . ... [2 mark] b). What is the velocity of the passenger. i. before the bus driver brakes? . [1 mark] ii. after the bus driver brakes? .. [1 mark] c) What is the velocity of the bottle when the sauce comes out? . [1 mark] d) i. based on the answer to b) ii, write a statement on the motion of the bus and its passenger.
. [2 mark] ii. name the physics concept involved here. .. ... [1 mark]
e) If you are chased by a baby elephant, how would you run away to save yourself. Explain.
10
[Lihat sebelah] SULIT
4531/2 .. .. [2 marks]
8. P
10 m Q
4m
Figure 8 Figure 8 shows a woman skater descending a hill slope. a) i. State the energy changes occurring when the skater descends the hill slope. [1 mark] ii. If the skaters mass is 70 kg, calculate the change in potential energy when the skater moves from P to Q
[2 mark] b) If 70% of the energy in a) ii. is changed into kinetic energy at position Q, calculate i. the kinetic energy at Q.
[2 mark]
ii. the velocity at Q 11 [Lihat sebelah] SULIT
4531/2
[2 mark] iii. what happens to 30% of the energy that is lost?
[1 mark]
(c) i. Assuming that the hill slope is frictionless, explain the motion of the skater as she skates down the hill. .. .. [2 marks] ii. State the principle of conservation of energy. .. [1 mark]
Bahagian B [20 marks] 12 [Lihat sebelah] SULIT
4531/2
Answer any one question in this section. You are advised to spend 30 minutes on this section 1. 110oC
100oC
Pipe water
sea water
Diagram 1
Diagram 2
1. a). Diagram 1 shows pipe water being heated until it is boiling and its temperature is recorded. Diagram 2 shows sea water being heated at the same rate until it is boiling and its temperature is recorded. i). Define what is boiling point. [2 marks]
ii). Compare the difference between the boiling point of pipe water and the boiling point of sea water. Explain the relationship between boiling point and the presence of impurities in water. [4 marks] iii. State other factors that influences the boiling point of water. b). Explain why water is not used as a thermometric liquid. [2 mark] [2 marks]
c). If you are required by a factory that manufactures thermometers commonly found in laboratories to measure the temperature of a substance, explain how you can make an efficient thermometer. In your explanation, emphasize the following aspects: :
i. Strength of the thermometer ii. Choice of the thermometric liquid 13 [Lihat sebelah] SULIT
4531/2 iii. Sensitivity of the thermometer iv. Design of the thermometer so that the scale can easily be read v. Calibration of the thermometer [10 marks]
2. Force
A student carries out an investigation to determine the strength of a spring by arranging the spring and the wooden block on an inclined plane as seen in the above diagram. He compresses the spring by exerting a force on the spring. When the force is removed, the distance traveled by the block up the slope is measured with a measuring tape. a. Explain what is meant by elastic potential energy. [1 mark]
b. Explain why the spring needs to be compressed with a large force to produce a large displacement of the block. [3 marks] c. If a stone of mass 20 g is placed at the end of the spring and a force of 30 N is applied to compress the spring a distance of 5 cm, calculate, i. the elastic potential energy of the spring ii. the kinetic energy of the stone when the spring is released. iii. the velocity of the stone ejected. [2.marks] [2 marks] [2 marks]
d. Using an appropriate concept in physics, explain the modification required in this experiment so that it is more efficient and the block is ejected a longer distance away. [10 marks]
Bahagian C [20 marks] Answer any one question in this section. 14 [Lihat sebelah] SULIT
4531/2 You are advised to spend 30 minutes on this section
3. The figure above shows the arrangement of apparatus to determine the external diameter of a metal pipe. (a) i. What is meant by diameter? [1 mark] ii Explain the function of the wedges used in the set up of the apparatus shown in the figure above [2 marks]
(b) The table below shows the characteristics of some instruments of measurement K, L, M, and N that are used for measuring a quantity of length.
Characteristic Instrument Smallest division on the scale Range of measurement Ability to measure diameter Level of sensitivity
K L M N
0.1 cm 0.01 mm 0.1 cm 0.01 cm
a few metres less than 2 cm up to 1 m up to 10 cm
Able, with the help of set squares Able Able, with the help of set squares Able
Low High Low Average
Based on the table, explain the suitability of the characteristics of the instruments for measuring the internal diameter of a beaker. Determine which instrument is most suitable for measuring the internal diameter of a beaker. Justify your choice. [10 marks] (c) You are given a piece of copper wire, glass rod and a meter rule. i. Explain how the diameter of the copper wire can be determined. [4 marks] ii A few turns of the copper wire produced a displacement of water of volume 0.5 cm3 when the wire is placed in water. Calculate the length of copper wire used if the diameter of wire is 0.1 mm [3 marks]
15
[Lihat sebelah] SULIT
4531/2
4. A researcher is studying four materials P, Q, R and S that have been shaped in the form of a wing. The shape of their cross-sections are shown in the table below.
*assume that the shape is fixed and cannot be inverted. (a) i. Explain the meaning of fluid. ii State Bernoullis principle. [1 mark] [2 marks]
(b) Study the material and their characteristics in relation to their suitability to be made into a wing of a light-weight plane. Determine the most suitable material for this purpose and give the reasons for your answer. [10 marks] (c) i Explain the advantages of having a light-weight racing car with a powerful engine. [3 marks]
ii A light-weight racing car with a powerful engine may have a risk of skidding unless a big downward force presses it on the road. Which of the four materials in the above table is most suitable to be fitted in a racing car? Explain your answer. [4 marks]
16
[Lihat sebelah] SULIT
DIAGNOSTIC TEST FORM 4 - 2006 MARKING SCHEME : PHYSICS PAPER 2 Section A Sec Mrk Answer Remarks
Question 1 (a) (b) (c) (d) Total 1 1 1 1 4 0.02 cm 1.73 cm 1.73 0.02 = 1.71 cm Micrometer screw gauge
Queston 2 (a) 1 (b) (c) (d) Total (a) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (b) (i) (ii) (iii) Total (a) (b) (i) (ii) (c) (i) (ii) 1 1 Total 6 1 1 1 1 5 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 8 1 1 1 1
Density of object > density of water 230 150 = 80 cm3 50/80 = 0.625 g cm-3 to test the purity of materials/buoyancy/hydrometer
Other relevant answers
Queston 3 P = 20/10 = 2.0 N cm-2 F = 40(20/10) = 80 N Ratio = 2.0/2.0 = 1 Pascals Principle 15(10) = 40 x x = 3.75 cm
The pressure of the smaller piston is fully transmitted to the larger piston Not compressible / does not evaporate easily/ is not corrosive
Question 4 The temperature at which the solid changes into liquid cX > c Y Heat capacity of Y > X X = 80 0C, Y = 100 0C
pt = ml 1000(4 1.5)60 = 0.8 l l = 18750 J/kg
Correct substitution ans & unit
Queston 5 (a) (i) 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 7 1.4 f = 1/1.4 = 0.714 cm focal length - 1.4/1.4 - 1.0 Virtual, upright, magnified Real, inverted, magnified or other correct values read from graph no units any two any two
(ii) (b)
(c) (i) (ii) Total
Question 6 (a) 1
T, tension W, weight
Label for both masses
1 (b) (c) (i) 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 9 Upwards
m1 g - T = m1 a T m2 g = m2 a
20 = 8 a a = 2.5 m s-2
(ii) (d) Total
move with the same acceleration in opposite directions
Question 7 (a) 1 1 1 1 1 1 The passenger moves forward and the chilli sauce comes out from the bottle 70 km/h the same velocity that is 70 km/h zero velocity when the bus brakes, the velocity of the bus decreases suddenly 1 (ii) (e) 1 1 1 Total 10 the passenger continues to move with its initial velocity inertia I must run in a zig zag manner The baby elephant continues to move in a straight line when I change my direction suddenly
(b) (i) (ii) (c) (d) (i)
Question 8 (a) (i) (ii) 1 Potential energy changes to kinetic energy E = mg(h2 h1) 1 1 1 1 = 70(10)(10 4) = 4200 J EQ = (70/100)(4200) = 2940 J m v2 = EQ 1 1 1 1 1 1 (70) v2 = 2940 v = 9.165 m s1 the energy has been changed to heat her velocity is higher than the situation before because there is no loss of energy converted to heat The total energy in a closed system is constant/ energy is neither created nor destroyed. Total 11
(b) (i)
(ii)
(iii) (c) (i)
(ii)
Bahagian B SOALAN 1 Bhgn Markah Skema (a) i 2 the boiling point is the temperature at which a liquid produces saturated vapor pressure equals to the atmospheric pressure. ii. 1 sea water contains salt /impurities causing boiling point to be higher 1 because sea water is difficult to vaporize 1 more energy is required to change sea water to vapor 1 therefore a higher temperature is required to boil iii 1 atmospheric pressure 1 type of liquid (b) 1 water evaporates easily causing reading to be inaccurate/ 1 water sticks to the walls of the tube/ higher specific heat capacity (c) 1 thermometer is made from transparent glass that is strong 1 so that it is not easily broken 1 the thermometric liquid chosen is mercury 1 because it easily expands uniformly 1 the capillary tube is made narrow and thin 1 so that it is more sensitive 1 the shape of the thermometer is round 1 so that it has a magnifying effect 1 the thermometer is placed in melting ice to obtain the lower
catatan
Any two of three
1 Jum 20 SOALAN 2 (a). 1 (b) 1 1 1 (c) i 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 20
point the thermometer is placed in steam from boiling water to obtain the upper point
ii..
iii. (d)
is the energy stored in a spring when it is extended or compressed Larger compression produces bigger elastic potential energy Elastic potential energy is changed to kinetic energy Larger kinetic energy produces higher velocity Elastic P E = Fx = 30(0.05) = 0.75 J K E = elastic P E = 0.75 J (0.02)v2 = 0.75 v = 8.66 m/s use a spring with a bigger diameter so that k is bigger the spring is made from steel because the type of material influences k a larger k produces a bigger elastic P E elastic P E changes to K E spring is greatly compressed so that elastic PE is bigger slope of inclined plane is 45 degrees so that distance is maximum
Jum
Bahagian C Bhg Mrk Soalan 3 (a) i 1 ii 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Jawapan The distance between two sides of a sphere through the centre of the sphere To bring the sides of the pipe closer to one another To show that the reading of the side of the pipe is vertically straight to the scale of the ruler The small reading of scale 0.01 cm is chosen Because it is suitable for the internal diameter of the beaker to be measured The range of measurement from 0 to 10 cm is the suitable range for the use to measure diameter of the beaker able to measure the diameter directly without the help of set squares the level of sensitivity is average therefore suitable to measure the diameter therefore the choice of the measuring instrument that is
Catatan
(b)
(c) i
1 1 1 1
suitable is N. This is because its range of measuement is 0 10 cm, it is able to measure the diameter without the help of set squares, the level of sensitivity is average and the smallest division on the scale is 0.01 cm which is not too big. A piece of wire round closely to the glass rod until its length is big enough Using a meter rule measure the length of wire wound at the glass rod, say x cm Then calculate the number of wire wound around the glass rod, say y circumference The diameter of the wire can be determined , x/y cm Using the formula V = (d/2)2l V = 0.5 cm3 (0.01/2)2l = 0.5 l = 6.37 X 103 cm
ii 1 1 1 20
Jum
Bhg Mrk Soalan 4 (a) i 1 ii 1 1 (b) 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 (c) i 1 1 1 ii 1 1 1 1 20
Jawapan Fluid is either liquid or gas When the speed of a fluid increases its pressure decreases When the speed of a fluid decreases its pressure increases The density of the material should be low So that its weight is low The melting point should be high To be able to withstand high temperature achieved during flight The material must be very strong To be able to withstand very strong force exerted on the wing during flight Shaped with a curved surface at the top and a flat surface at the bottom To achieve an upward lifting force when moving at high speed The most suitable is Q Because of its relatively low density, high melting point, high strength and correct shape of aerofoil Acceleration of the car is directly proportional to the force acting on the car Inversely proportional to its mass Hence a light weight racing car with a powerful engine will achieve a higher acceleration Material R Its shape will result in a downward force That prevents the car from being lifted up Its high melting point allows it to withstand high temperature when the car is moving at high speed
Catatan
Jum
Вам также может понравиться
- Fizk 2 Midyearf 52007Документ24 страницыFizk 2 Midyearf 52007Noorleha Mohd YusoffОценок пока нет
- Fizik 2 Trial SPM SBP 2006Документ31 страницаFizik 2 Trial SPM SBP 2006yhan7980Оценок пока нет
- Physics f5p2Документ33 страницыPhysics f5p2Eimma FatimahОценок пока нет
- Fizik Ting 4 (k2)Документ29 страницFizik Ting 4 (k2)TS Shong100% (1)
- Fizik Soalan Kertas 2Документ16 страницFizik Soalan Kertas 2shahrulОценок пока нет
- Trial SBP Physics SPM 2013 Paper 2Документ28 страницTrial SBP Physics SPM 2013 Paper 2Cikgu Faizal50% (2)
- Set 1 Kertas 2Документ20 страницSet 1 Kertas 2Haizul AzliОценок пока нет
- TRIALKEL2010PAPER2Документ34 страницыTRIALKEL2010PAPER2nik mohamad solehinОценок пока нет
- Paper 2 PPT Muar KimiaДокумент24 страницыPaper 2 PPT Muar KimiaCt NurОценок пока нет
- Midterm Paper 2 T4Документ18 страницMidterm Paper 2 T4Red KiteОценок пока нет
- Fizik Kertas 2Документ28 страницFizik Kertas 2Nadia Saidon0% (2)
- Trial SBP Physics SPM 2013 Paper 2 WordsДокумент38 страницTrial SBP Physics SPM 2013 Paper 2 Wordshelmi_tarmiziОценок пока нет
- P 2 Midterm 2015 F 4Документ21 страницаP 2 Midterm 2015 F 4Johari JusohОценок пока нет
- Peperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun Kertas 2 Kimia Tingkatan 5Документ24 страницыPeperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun Kertas 2 Kimia Tingkatan 5Azie Nurul Akhtar100% (3)
- Kertas 2 SC 1st TrialДокумент15 страницKertas 2 SC 1st TrialakmarmataliОценок пока нет
- Physics 2013 P2 Set BДокумент27 страницPhysics 2013 P2 Set BaNNa_RaiHaNОценок пока нет
- Trial Kedah SPM 2014 Physics K2 Modul 2Документ25 страницTrial Kedah SPM 2014 Physics K2 Modul 2NALLATHAMBYОценок пока нет
- Fizik Kertas 2 Trial PerlisДокумент34 страницыFizik Kertas 2 Trial PerlisenasizukaОценок пока нет
- Trial SPM - Fiz K2 SBP 2011Документ38 страницTrial SPM - Fiz K2 SBP 2011ruslawatiОценок пока нет
- SPM Fiz Kertas2set3Документ18 страницSPM Fiz Kertas2set3Azman Bin JaehОценок пока нет
- Fizik p2 MelakaДокумент23 страницыFizik p2 MelakaNAJMILОценок пока нет
- Physics Paper 2 Form 4 2013Документ19 страницPhysics Paper 2 Form 4 2013MadAm JaJa100% (1)
- Fizik Modul T4 Kertas 2 2014Документ28 страницFizik Modul T4 Kertas 2 2014aufa_xfile8784Оценок пока нет
- Fizik Paper 2Документ14 страницFizik Paper 2Pak TehОценок пока нет
- JUJ Pahang 2014 Physics SPM K2 Set BДокумент29 страницJUJ Pahang 2014 Physics SPM K2 Set BCikgu FaizalОценок пока нет
- Kertas 2 FizikДокумент36 страницKertas 2 FizikHajar Norasyikin Abu BakarОценок пока нет
- Percubaan MuarSPM Fizik Paper 2 2016Документ29 страницPercubaan MuarSPM Fizik Paper 2 2016Wong ChinОценок пока нет
- 12 Fiz K2 (Soalan)Документ28 страниц12 Fiz K2 (Soalan)Zaini Abd AzizОценок пока нет
- Physics Trial KedahP22009Документ30 страницPhysics Trial KedahP22009Rushdi RosniОценок пока нет
- SMKMM Phy p2Документ10 страницSMKMM Phy p2Tutor EvonОценок пока нет
- Fizik Kertas 2Документ24 страницыFizik Kertas 2abnu980% (1)
- Fizik K2 Trial 2016 SMK RMMДокумент25 страницFizik K2 Trial 2016 SMK RMMIlya Ismail0% (1)
- Fizik Kertas 2 Peperiksaan Akhir Tahun SBP 2011 Ting 4Документ30 страницFizik Kertas 2 Peperiksaan Akhir Tahun SBP 2011 Ting 4nurul atiqah91% (11)
- TRIAL SPM Paper 2Документ22 страницыTRIAL SPM Paper 2871226Оценок пока нет
- Trial Fizik KBSMДокумент15 страницTrial Fizik KBSMNurul Nabisah Haji MohamadОценок пока нет
- 2011 PSPM Kedah Chemistry 2 W AnsДокумент32 страницы2011 PSPM Kedah Chemistry 2 W Ansjee2kkОценок пока нет
- Soalan Trial Perlis 2011 p2Документ25 страницSoalan Trial Perlis 2011 p2jaaizahkamalОценок пока нет
- Bahagian AДокумент19 страницBahagian AZarina ShОценок пока нет
- Kertas 2 Pep Percubaan SPM SBP 2007 - SoalanДокумент25 страницKertas 2 Pep Percubaan SPM SBP 2007 - SoalanAidil HazwanОценок пока нет
- Skema Soalan Ramalan K2 SPM Set 1 2023Документ25 страницSkema Soalan Ramalan K2 SPM Set 1 2023Gan Hock KiamОценок пока нет
- Modul Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 Physics - (Set 2) Paper 2 (N)Документ47 страницModul Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 Physics - (Set 2) Paper 2 (N)Srp KaMie LooОценок пока нет
- Mid Year Physics f4 p2Документ17 страницMid Year Physics f4 p2MadAm JaJaОценок пока нет
- Kedah Trial Fizik Kertas 2 SPMДокумент22 страницыKedah Trial Fizik Kertas 2 SPMfarahibbОценок пока нет
- Kertas 2 Fizik Trial 2013 PHG PDFДокумент30 страницKertas 2 Fizik Trial 2013 PHG PDFNurhijjah's TerritoryОценок пока нет
- Paper 2 Set 15Документ11 страницPaper 2 Set 15jesunathan44@yahoo.comОценок пока нет
- Trial Pahang SPM 2013 Physics k2Документ30 страницTrial Pahang SPM 2013 Physics k2Mazuva JaparОценок пока нет
- 2011 PSPM Kedah Physics 2 W AnsДокумент34 страницы2011 PSPM Kedah Physics 2 W Ansjee2kk100% (1)
- 01 T 2018 Kebaikan Permainan TradisionalДокумент2 страницы01 T 2018 Kebaikan Permainan TradisionalCikgu Sin100% (1)
- 01 T Kebaikan Aktiviti SukanДокумент2 страницы01 T Kebaikan Aktiviti SukanCikgu SinОценок пока нет
- 01 T Langkah memupuk semangat patriotik 2018Документ2 страницы01 T Langkah memupuk semangat patriotik 2018Cikgu SinОценок пока нет
- 01 T Langkah Menjayakan Kitar Semula 2018Документ2 страницы01 T Langkah Menjayakan Kitar Semula 2018Cikgu Sin33% (3)
- 01 T Langkah Menggalakkan Orang Ramai Bermain Permainan Tradisional 2018Документ1 страница01 T Langkah Menggalakkan Orang Ramai Bermain Permainan Tradisional 2018Cikgu SinОценок пока нет
- Novel F1 2016 CaraДокумент1 страницаNovel F1 2016 CaraCikgu SinОценок пока нет
- Usaha-Usaha Menggalakkan Permainan TradisionalДокумент8 страницUsaha-Usaha Menggalakkan Permainan TradisionalCikgu SinОценок пока нет
- Peribahasa 2Документ2 страницыPeribahasa 2Cikgu SinОценок пока нет
- Sang Kancil Dan KerbauДокумент7 страницSang Kancil Dan KerbauCikgu SinОценок пока нет
- Kebaikan InternetДокумент1 страницаKebaikan InternetCikgu Sin67% (3)