Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Foodborne Illness Causes, Pathogens, Symptoms and Prevention
Загружено:
Ankita ShirahattiИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Foodborne Illness Causes, Pathogens, Symptoms and Prevention
Загружено:
Ankita ShirahattiАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Food Borne Illness Causes y Pathogens- Bacteria; Campylobacter jejuni, Clostridium perfringens, Salmonella, Escherichia coli O157:H7 y Viruses
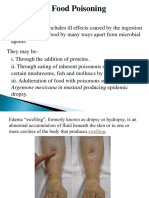
(1/3 of cases in the US) 1-3 incubation days. Hepatitis A (Jaundice) fecal contamination, Hepatitis E, Norovirus, Rotavirus y Parasites- Platyhelminthes, Protozoa, Nematode y Natural Toxins y Prions Common Food Borne Illnesses y Botulism- caused by Clostridium botulinum bacteri that enters through wounds, or they may live in improperly canned or preserved food. Symptoms: dry mouth, nausea, vomiting, paralysis y Campylobacter- fecal-oral, ingestion of contaminated food or water, and the eating of raw meat. It produces an inflammatory, sometimes bloody, diarrhea, periodontitis or dysentery syndrome y E. coli- faecal-oral transmission. Common routes of transmission include: unhygienic food preparation farm contamination due to manure fertilization,. Dairy and beef cattle are primary reservoirs of E. coli O157:H. Food products associated with E. coli outbreaks include cucumber, raw ground beef or spinach, y Listeriosis- Listeriosis is an infection that can occur when a person eats food that has been contaminated with bacteria called Listeria monocytogenes. Vegetables, meats, and other foods you eat can get infected with the bacteria if they come in contact with contaminated soil or manure. Symptoms: stillbirth, vomiting, shock y Norovirus- Noroviruses are transmitted directly from person to person and indirectly via contaminated water and food. Hepatitis A/E, causes Jaundice, vomiting, diarrhea. y Salmonella- infection in the lining of the small intestine caused by Salmonella bacteria. Symptoms: The time between infection and symptom development is 8 - 48 hours. Abdominal pain, chills, diarrhea, vomiting. Eaten improperly prepared or stored food (especially undercooked turkey or chicken, unrefrigerated turkey dressing, undercooked eggs) y Creutzfeldt Jakob disease or CJD is a degenerative neurological disorder that is incurable and invariably fatal. Prion Disease. Symptoms: memory loss, personality change, hallucinations.
Foods Most Associated y Raw meat and poultry y Raw eggs y Unpasteurized milk y Raw shellfish y Raw fruits and vegetables y Unpasteurized fruit juice Reducing the Risk Cook meat, poultry, and eggs thoroughly Separate don t crosscontaminate one food with another Chill refrigerate leftovers promptly Clean wash produce Report suspected food borne illnesses to the local health department
Food Processing Concerns Foods that mingle the products of several individual animals A pathogen in one animal can contaminate may contaminate a whole batch of food mingling the products of several animals as bulk raw milk, pooled raw eggs or groundbeef A single hamburger may contain meat from hundreds of animals A glass of raw milk may contain milk from hundreds of cows A broiler chicken carcass can be exposed to the drippings and juices of many thousands of other birds that went through the same cold water tank after slaughter. Washing fruits and vegetables can decrease but not eliminate contamination Processing food under less than sanitary conditions can cause outbreaks Raw sprouts that are eaten without cooking may contain growing microbes Storage and transport methods for food Formulas Attack rate the rate that a group experienced an outcome or illness = number sick total in that group Relative risk = [a (a+b)] / [c (c+d)] -A relative risk = 1.0 indicates that the incidence rates of disease in the exposed group is equal to the incidence rates in unexposed group. Therefore the data does not provide evidence for an association. -A relative risk >1.0 indicates a positive association or an increased risk. This risk increases in strength as the magnitude of the relative risk increases. Odds Ratio = Odds of exposure in cases= a/c = ad Epidemiology - Studies health of populations instead of individuals. - Outbreak: localized epidemic - Cluster: aggregation of cases over particular period - Pandemic/epidemic/endemic - Fomite: a physical object that serves to transmit an infectious agent from one person to another - Surverlliance: systematic, ongoing collection of data, analysis etc, of health. - Modes of Disease Transmission: Air, Direct Contact, Animal Vector. - Epi Triad: host/agent/environment Types of Studies: - Descriptive Studies: studies without control group used for descriptive purposes. o Case Report/Case Series: report from single patients, series from several patients o Correlative (relationship): Time series (analysis over time), ecologic (ecologic factors), Cross Sec (participants selected despite exposure) - Cohort Studies: based on exposure status, whether or not patients have illness. - Case-control Study: Works backwards from illness to determine a suspected cause.
To Avoid: Clean hands, food contact surfaces, and fruits and vegetables. Meat and poultry should not be washed or rinsed. Separate raw, cooked, and ready-to-eat foods while shopping, preparing, or storing foods. Cook foods to a safe temperature to kill microorganisms. Chill (refrigerate) perishable food promptly and defrost foods properly. Avoid raw (unpasteurized) milk or any products made from unpasteurized milk, raw or partially cooked eggs or foods containing raw eggs, raw or undercooked meat and poultry, unpasteurized juices, and raw sprouts. Cooking meat and poultry to USDA recommended safe minimum temperatures makes them safe to eat: Beef, veal, lamb: steaks & roasts - 145F Fish - 145F Turkey, chicken & duck: whole, pieces & ground - 165F Egg dishes - 160F Beef, veal, lamb: ground 160F
Вам также может понравиться
- Ducks, Chickens, Dogs, and SheepДокумент5 страницDucks, Chickens, Dogs, and SheepChelsea Green PublishingОценок пока нет
- CH 5 Worksheets-Practice CardiovascularДокумент11 страницCH 5 Worksheets-Practice CardiovascularKatie ByarsОценок пока нет
- G. Scanes. Poultry Science, 5th Edition (VetBooks - Ir)Документ490 страницG. Scanes. Poultry Science, 5th Edition (VetBooks - Ir)Nanang Haryadi100% (1)
- 09-016 - Hoy - Calculation Refresher PDFДокумент16 страниц09-016 - Hoy - Calculation Refresher PDFDrmohammed SaifОценок пока нет
- Dr. Joko Wahyu Wibowo MkesДокумент51 страницаDr. Joko Wahyu Wibowo MkesRangga Alam VaneoОценок пока нет
- Atomic Structure and Periodicity PDFДокумент111 страницAtomic Structure and Periodicity PDFGisselleОценок пока нет
- The Magic JuiceДокумент3 страницыThe Magic JuiceBenjamin SteylОценок пока нет
- SciPoultryAndMeatProcessing - Barbut - V01 CompleteДокумент764 страницыSciPoultryAndMeatProcessing - Barbut - V01 CompleteajlinariОценок пока нет
- Root Words Meaning Example AДокумент13 страницRoot Words Meaning Example AAsif Ullah100% (1)
- Fce Writing Full RevisionДокумент16 страницFce Writing Full RevisionCharlie Chap100% (2)
- DiseaseDetectives Cio 2015Документ13 страницDiseaseDetectives Cio 2015Ojasw UpadhyayОценок пока нет
- Disease Detectives B-Answer KeyДокумент14 страницDisease Detectives B-Answer KeyskdfkjlОценок пока нет
- 2020 Disease Detectives 071619Документ71 страница2020 Disease Detectives 071619Sharynn Kew MooreОценок пока нет
- Observational Study DesignДокумент45 страницObservational Study DesignIfanda Ibnu HidayatОценок пока нет
- Business Plan Prepared by Green Bean VenturesДокумент33 страницыBusiness Plan Prepared by Green Bean VenturesMohammed otayokhe100% (2)
- Food PoisoningДокумент16 страницFood PoisoningS RahmnОценок пока нет
- Food Poisoning and IntoxicationsДокумент26 страницFood Poisoning and IntoxicationslakshmijayasriОценок пока нет
- Presentation Products Transglutaminase AlginatesДокумент25 страницPresentation Products Transglutaminase AlginatesBDF Transglutaminase AlginatesОценок пока нет
- Food Safety Awareness For Food HandlersДокумент13 страницFood Safety Awareness For Food HandlersIvee van GoghsiaОценок пока нет
- Food PoisoningДокумент55 страницFood PoisoningAnusikta PandaОценок пока нет
- Epidem. Lecture 1 & 2Документ18 страницEpidem. Lecture 1 & 2sajad abasew100% (1)
- Chapter 6 - Statistical Process Control - APIC Text OnlineДокумент15 страницChapter 6 - Statistical Process Control - APIC Text OnlineManalAbdelazizОценок пока нет
- Nutrition 3 Food SafetyДокумент71 страницаNutrition 3 Food SafetyReda AbolilaОценок пока нет
- My IGPДокумент11 страницMy IGPGladzangel LoricabvОценок пока нет
- Frankenmuth Disease Detective Test 2014 Answer KeyДокумент18 страницFrankenmuth Disease Detective Test 2014 Answer KeyOjasw UpadhyayОценок пока нет
- Infectious Agents James N KCДокумент3 страницыInfectious Agents James N KCapi-344421763Оценок пока нет
- Disease and EpidemiologyДокумент76 страницDisease and EpidemiologyRajОценок пока нет
- 2017 Disease ExamДокумент13 страниц2017 Disease ExamManoj Kumar UpadhyayОценок пока нет
- 1 5EpiCurves SlidesДокумент33 страницы1 5EpiCurves SlidesHéctor Pando SánchezОценок пока нет
- Disease Detectives II Host Agent EnvironmentДокумент48 страницDisease Detectives II Host Agent EnvironmentStella Jeong100% (1)
- In Silico Library Design - Screening and MD Simulation of COX-2 Inhibitors For Anticancer ActivityДокумент12 страницIn Silico Library Design - Screening and MD Simulation of COX-2 Inhibitors For Anticancer ActivitywindragunawanОценок пока нет
- Disease Detectives C ExamДокумент34 страницыDisease Detectives C ExamGustavo Pacheco0% (1)
- CytokinesДокумент12 страницCytokinesclventuriniОценок пока нет
- Clinical CalculationsДокумент42 страницыClinical Calculationsapi-404239289Оценок пока нет
- Clinical Epidemiology Guide 2015Документ23 страницыClinical Epidemiology Guide 2015Archit ChawlaОценок пока нет
- Therapeutic Choices 2011Документ1 365 страницTherapeutic Choices 2011priyarajan007Оценок пока нет
- Antibiotic Resistance Past to Future: Origins, Current Issues and Possible SolutionsДокумент9 страницAntibiotic Resistance Past to Future: Origins, Current Issues and Possible SolutionsPaul QuinnОценок пока нет
- Companion Diagnostics or Theranostics Products in The MarketДокумент3 страницыCompanion Diagnostics or Theranostics Products in The MarkettonnymjohnsonОценок пока нет
- 1 Introduction To Biostatistics PDFДокумент20 страниц1 Introduction To Biostatistics PDFYounas BhattiОценок пока нет
- TEST1 Percentages 05062016Документ5 страницTEST1 Percentages 05062016Sahil KalaОценок пока нет
- Midterm exam questions DNA replication transcription translationДокумент7 страницMidterm exam questions DNA replication transcription translationAZGG75286Оценок пока нет
- E. COLI and IntroductionДокумент28 страницE. COLI and IntroductionKaranja GitauОценок пока нет
- Chap 1 and 2Документ43 страницыChap 1 and 2Kashien Arianna ReglosОценок пока нет
- For A Communicable Disease, Point The 5 Steps of Spreading and The Preventive Measures For Each StepДокумент4 страницыFor A Communicable Disease, Point The 5 Steps of Spreading and The Preventive Measures For Each StepAna MariaОценок пока нет
- Case Analysis 2Документ7 страницCase Analysis 2Shane Fross SeñedoОценок пока нет
- Food Borne DiseasesДокумент88 страницFood Borne DiseasesVidhi RanaОценок пока нет
- Food Borne DiseasesДокумент42 страницыFood Borne DiseasesJesse LeeОценок пока нет
- Common Food-Borne Disease OrganismsДокумент8 страницCommon Food-Borne Disease OrganismsaedrianuyОценок пока нет
- Final Written ReportДокумент5 страницFinal Written ReportJillianne MoyanoОценок пока нет
- Foodborne IllnessДокумент13 страницFoodborne IllnessThảo LinhОценок пока нет
- Foodborne Diseases Can Be Classified Into Two Main TypesДокумент5 страницFoodborne Diseases Can Be Classified Into Two Main TypesSiphamandla MadikizelaОценок пока нет
- Food Poisoning Causes, Symptoms and PreventionДокумент49 страницFood Poisoning Causes, Symptoms and PreventionMazinОценок пока нет
- Pemicu 3 GIT BudiДокумент67 страницPemicu 3 GIT BudiGrace KahonoОценок пока нет
- Plant Sanitation 1Документ11 страницPlant Sanitation 1Mylene Alano PlacidoОценок пока нет
- Food Poison ColoradoДокумент4 страницыFood Poison ColoradoAlpascaFirdausОценок пока нет
- Pemicu 3 GIT GraceДокумент67 страницPemicu 3 GIT GraceGrace KahonoОценок пока нет
- Bacterial Agents:: o Staphylococcus AureusДокумент2 страницыBacterial Agents:: o Staphylococcus Aureussabrina_teng_2Оценок пока нет
- FOOD INFECTIONДокумент20 страницFOOD INFECTIONtesnaОценок пока нет
- Ramsheed V K Silver Arts and Science College PerambraДокумент8 страницRamsheed V K Silver Arts and Science College PerambraATHIRA MОценок пока нет
- What Is E. Coli and Where Does It Come From?Документ3 страницыWhat Is E. Coli and Where Does It Come From?city1212Оценок пока нет
- Microbes and More - Creative LPДокумент28 страницMicrobes and More - Creative LPAshleigh LynОценок пока нет
- Food PoisoningДокумент23 страницыFood PoisoningEsther NyawiraОценок пока нет
- By, Padmaratinam.C.U 3 YearДокумент21 страницаBy, Padmaratinam.C.U 3 YearGOWTHAM GUPTHAОценок пока нет
- Food PoiosoningДокумент21 страницаFood PoiosoningMuneeza ShafiqОценок пока нет
- Food PoisoningДокумент25 страницFood PoisoningNicole FarquharsonОценок пока нет
- MODULE 12 - Foodborne DiseasesДокумент16 страницMODULE 12 - Foodborne DiseasesFil HynneyОценок пока нет
- GastroenteritisДокумент4 страницыGastroenteritisArumDesiPratiwiОценок пока нет
- FDI Mapping With NIC CodeДокумент53 страницыFDI Mapping With NIC CodeRajeev BhambriОценок пока нет
- HorsesДокумент1 страницаHorsesapi-326793280Оценок пока нет
- Hwy 280 - Hamburger HeavenДокумент4 страницыHwy 280 - Hamburger HeavenchefchadsmithОценок пока нет
- Grade 9 Tle ReviewerДокумент4 страницыGrade 9 Tle ReviewerSaara Oxana G. SalcedoОценок пока нет
- Open RTI Petition For Slaughter Houses and Meat Shops in India Under Municipal Corporation's and Committees - Abhishek KadyanДокумент3 страницыOpen RTI Petition For Slaughter Houses and Meat Shops in India Under Municipal Corporation's and Committees - Abhishek KadyanNaresh KadyanОценок пока нет
- FN41.3.04.Meat, Poultry, and SeafoodДокумент28 страницFN41.3.04.Meat, Poultry, and SeafoodGeorgia GrantОценок пока нет
- Marketing ObjecДокумент3 страницыMarketing ObjecAramae Quindoza BiloloОценок пока нет
- Subway pricing strategy focuses on quality foodДокумент1 страницаSubway pricing strategy focuses on quality foodSanil VaghaniОценок пока нет
- Ross Tech Lighting For BroilersДокумент40 страницRoss Tech Lighting For BroilersCaesarОценок пока нет
- Liquid Diet ClearДокумент1 страницаLiquid Diet ClearKenoОценок пока нет
- Food Carbon Footprint ExplainedДокумент3 страницыFood Carbon Footprint ExplainedSathish KumarОценок пока нет
- Croatan Investing in Regenerative Agriculture Infrastructure Across Value Chains - WebДокумент44 страницыCroatan Investing in Regenerative Agriculture Infrastructure Across Value Chains - WebMcKenna SwanОценок пока нет
- Pizza To GoДокумент2 страницыPizza To GoEdgardo MembreñoОценок пока нет
- Alternative Poultry Production Systems and Outdoor Access - ATTRAДокумент24 страницыAlternative Poultry Production Systems and Outdoor Access - ATTRAAnonymous FvXjyF4cT4Оценок пока нет
- Challenge Yourself: Beginner Mens Challenge Preparation GuideДокумент23 страницыChallenge Yourself: Beginner Mens Challenge Preparation GuideUni TabberОценок пока нет
- Our Meatless Future: How The $1.8T Global Meat Market Gets DisruptedДокумент17 страницOur Meatless Future: How The $1.8T Global Meat Market Gets DisruptedThanaratana AkarakulОценок пока нет
- Revised Syllabus - Meat Pros - New FinalДокумент7 страницRevised Syllabus - Meat Pros - New FinalDaniel Jorolan Baldoz Jr.Оценок пока нет
- A Systematic Comparison of The US and EU Startup Ecosystems of Cultivated MeatДокумент92 страницыA Systematic Comparison of The US and EU Startup Ecosystems of Cultivated MeatDriesОценок пока нет
- Investment Office ANRSДокумент27 страницInvestment Office ANRSSHASHI SHEKARОценок пока нет
- Roh TeewurstДокумент1 страницаRoh TeewurstMichael LeydarОценок пока нет
- Islamic Ruling On Using Skins of Impure and Prohibited To Eat Animals Like Pigs EtcДокумент2 страницыIslamic Ruling On Using Skins of Impure and Prohibited To Eat Animals Like Pigs EtcIbn SadiqОценок пока нет
- NSSP Guide for Safe ShellfishДокумент516 страницNSSP Guide for Safe ShellfishpedroloxxxОценок пока нет