Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Trex 00009
Загружено:
OSDocs2012Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Trex 00009
Загружено:
OSDocs2012Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Critical Questions
I General
1. Tell me about your oilfield experience.
2. How long on OW Horizon? I low long in current role? When did you arrive on th e
rig?
3. Where were you located? What was your room assig;nment
4. When did you come on tour and go off tour on the 20th April?
5. Could you tell me what happened during that shift?
6. Where and when were fluids released?
a. Please identify any lot:acions where you saw fluids (gas, water, mud) escaping.
7. Can you describe what yon saw and heard leading up to the explosion? And when?
8. \\!hen did you realize something was wrong?
9. Where and when were tlames observed?
10. Did you smell any fumes or vapors? What were they?
11 . Did you explosions? From which direction did any blast pressure \V;l'I.'C
come?
12. Did you observe any collateral damage to the rig? What and where?
13. Do you know where anyone else was located on the rig near the time of the event?
14. Did you hear or see any gas or fire alarms?
15. When was your last training on well event response?
16. What training and competency processes do you have and could we have a copy of
any associated records
17. \\!hat's your general knowledge of risks associated with your activities? \X'hy is it
important to monitor whM you do?
18. What was your frame of mind? Understanding o f well starus? What your next
programme of work?
EXHIBIT #_....,),___ __ _
WIT: _ _ ___ _ _
BP-HZN-BLY00061243
EXHIBIT TREX-00009
Critical Questions
I MI Swaco- Mud Engineers
1. Do you know who put the clisplacement program together?
2. was your understanding of the riser clisplacement procedure) (In asking this question
I'd be looking to know how well they understood the need to get the spacer above the stack,
if they understood the densities and volumes of the clifferenr fluids, and what rhe objecri,e
was)
3. \Vhar was the procedure for mi..xing rhe spacer w irs final volume of -430 bbl?
(Confirmation of composition, fluid transfers and densities.
a. Was the last volume increase prior ro displacemenr "dusring up" the vis and density
prior to pumping)
4. Was the FAS XL used? (aga.in, confirmation of what we've heen rold)
5. Was using the FAS AK/FA SQUEEZE as a spacer a standard practice?
a. Did it align with the approved Mud Program? Well Program?
b. If the answer is no. Was any MoC and or risk assessment done? was your
understanding of the desire w OYer board the LCM materials?
6. Who, on the rig, made the decision on what fluids and volumes to pump?
7. Do you know if mud was being back to the boat during the displacement?
a. Is this standard practice?
8. Were you aware of the risk of moving mud around during the displacement when unable to
record volumes?
9. Do you know how volumes were being monitored during the displacement?
10. Cbrify uur untlC:'.r>tanding th;lt the:: pilb mi.xe::d together 'l.vhy that was dnnt'.?
11. Where were you during the disphKement?
12. Were you involved in the Negative test?
13. Were you at any meetings prior to the Negative test or displacement?
a. \X'ho else ;1ttcnckd these meetings:>
b. Did you talk to the :\1ut.lloggers?
14. Who was in charge of the operation?
15. Did you hear a discussion about pressure on the Drill Pipe?
a. \X.'hat were the pressures?
16. !\ re rou aware of any fluicls being bled off- do you know ro which pits the fluicls went?
17. Did you notice anything unusual duri ng the events btding up ro the incident? (Fluid
vnltuncs, rar.cs, etc.)
a. Wcrc yon romfortablc with the fluid transfers, inYentory of mud on the rig ere)
h. volumes measurc.rl?
18. Were you there for the sheen test rhat was done?
19. How is a test conducted?
20. 1\fter the sheen test do you know who was watching t he flow line?
21. How was rhc divertcr system aligned?
22. How was rhc mud system ahgned?
a. \X.11at is t11c system layout
23. How was rhe overboard disposal sysrem aligned:>
24. Was the cliverrer closed? If so, when \v;tS it closed?
BP-HZN-BLY00061244
Critical Questions
I TransOcean- Toolpushers & Driller
I . How long on DW Horizon? How long in current role'! When did you arrive on the rig?
2. lf you were there can you tell me about the wiper trip/ recovering the wear bushing I
running the casing I cementing the casing?
3. Can you recall the weight and volume of the spacer that was pumped?
4. Can you recall the displacement volume pumped?
5. What did the line up on the rig floor look like for the negative test?
6. How were the different pressures being monitored?
7. Can you recall what the DP pressures were?
8. Were any pressures I fluids bled off from the well?
9. How was the pressure on the well bled off- which pits did the returns go to- what was
the line up, how were the volumes measured?
I 0. Do you know how fast the bleed offs were flowing?
I I. Which annular was used for the negative test?
12. Did the annular leak when it was closed for the negative test?
13. Was the annulus topped up- if so with how much fluid and how often?
14. Tell me in as much detail as you can about the negative test.
15. Who decided to do the bleed offs?
I 6. Do you know how many bleed offs there were?
17. Who was on the rig floor at that time?
18. Who was operating the BOP/ kill valve etc?
19. Who was communicating with the cementer?
20. Who was directing the rig floor operations?
21. Did you pump down the kill line to check it was full?
22. What is the line volume between the cement unit and rig floor?
23. How much pressure did that put on the kill line?
24. What conversations took place on the rig floor?
25. Who was in attendance during these conversations?
26. Did you hear a discussion about pressure on the DP?
27. Can you describe these phenomena to me (Bladder effect)?
28. Do you know if anyone calculated what the differential pressures should. be during the
negative test?
29. Did you attend a meeting to discuss the displacement to sea water?
30. Did you talk to the mud logger during your shift?
31. Did you know mud was being back loaded?
32. Was mud being back loaded to the boat- when did this start and when did it finish?
33. Were yoLt aware of the risk of moving mud arow1d during the displacement when unable to
recnrd vnhtmes?
34. Was tl1e trip taok being cleaned out - when did that start and finish?
35. Was fluid being dumped overboard during the displacement?
36. Do you know when the dump line was opened?
37. Who was monitoring the mud volumes during the displacement- how was that being
done?
38. Look at Discovery Wells data - annotate the chart
a. Do you know why there was a pressure increase on the cemcntlinc at 1752?
b. Do ymt koow when the IBOP was closed?
BP-HZN-BLY00061245
c. Do you know why the DP pressure was just bled to 273 psi at 1700?
d. What do you think was happening between 2100 and 2200?
e. Do you know what the pressure blip at 1842 could be?
39. If you got a sudden flow of mud at surface what would you and your crew's response be?
a. Is there a procedure for such an event?
b. Which annular would you normally close?
40. How was the pipe spaced out across the BOP? (Tolerance of the Dynamic Position
diversions wave-action and heave compensator)
41. Is there a standard space out across the BOP and when is it used?
42. Could you describe to me how the Diverter was lined up on that day?
a. How arc the valves operated?
43. If the Divcner is lined up to the small gas buster- how is it changed to the overboard
line?
44. Where is the vent line from the small gas buster?
45. Where is the gas buster situated'?
46. How is the BOP and Diverter panels configured -is it all green for open and red for
closed?
47. How many BOP panels are there on the rig?
48. Can you describe lhe flow line I divener I overboard lines and valves configuration?
49. Did you gel daily wriuen instructions- what did they include?
50. Do you know of any hydraulic leaks or other issues with the BOP Stack?
51 . Do you know the last time Lhc ROY Hot Stab was used on Lhe BOP?
52. What telephone calls did you receive after you left the rig floor'>
53. When did you realise that something was wrong'?
54. What did you see and hear leading up to and during the explosions?
55. When was your last training on well event response?
56. Where are the flow meter sensors situated and how accurate are they?
57. Do you have any hand written logs of events on the day of the event? Do you have any in
your possession?
Did they have any concerns about the 1400 psi on the drill pipe gauge and equalising the
pressure across the IBOP?
a. \'Vlm was going on when there was on the drill pipe?
59. Can you describe what the "bladder effect" is?
60. From time you >tuppcd pumpinp;, please rake us rhrot1gh yo11r actions ru rhe time of
b. TcU us what you can remember? What did you sec and hear?
61. \\!hat. the Eme.rgenL)' Respome design philosophy
62. \X'hat the design philosophy of the Fire & Gas system
63. \\'hat processes are used to manage alarms, interlocks, and by passes?
BP-HZN-BLY00061246
Critical Questions
I TransOcean- Master & OIM
1. :\re you aware of any hot "vork or other work activities on deck or below deck?
2. Which were nmning at the time of r.he incident?
3. What is the Emergency Response design philosophy
4. What is the design philosophy of the Fire & Gas system
5. Where any fire and gas detection overridden?
6. What processes are used to manage alarms, interlocks, and by passes?
7. Was any sa fery equipment (TISD, TIDS, P&.G) our of service ar rhe of the
incident?
8. \\/hat are used to manage changes to operating and procedures?
9. Thn1sters \\,.hat dots that mean? How do they work with EDS?
a. Oo you have to MOC emergency disconnect?
b. \\'hat's the disconnect ti me?
c. Does that change protocol for EDS at aU?
d. What's the linkage between thrusters and EDS?
10. What was the EDS setting on the Rig that day:
a. How was it managed?
11. When did you tirst initiate the EDS?
12. \V'ere there any external audi t actions out standing?
13. Emergency Response Plan
a. T-P will inform the OIM if an imminent well-control situation. OIM tells
the Master to prep for evacuation?
b. When did this notitication take place?
c. \'\'hen did you implement rhe Emergency Plan? What was
involved?
14. Where are you back-up drawings held? r\re As buil t drawings available?
15. \vhu sorr of back-ups do you have for your Data Systems?
a. How regularly do you back up
b. Who your rerons go to?
c. t\ re these reports accessible?
BP-HZN-BLY00061247
Critical Questions
j TransOcean Subsea Engineers, OIM & Drillers
1. What are the test procedures used to verify the operation of all the emergency back-up
(AMF, EDS, Autoshear ami ROV inte.rvt'nt.ion) on the BOP, and what were rhe
results of these tests the last time they were done? What is the test procedure for the
cond.it.ion of the A.\1F batteries to demonstrate they are fit for purpose?
2. How do you verify that the AMF and Autoshe;u systems were armed?
3. On what funct.ion was the hydraulic leak on the yeUow pod reported on 23 February
2010, w;1s it investig<Hed and what were the findings?
4. Do you have storage of the BOP control application and if so,
can you provide a copy?
5. Did you have a robust BOP maintenance management system implemented on the
Deepwater Horizon, and what is the outstanding maintenance back log (hours and jobs)?
6. Who maintains or repairs ROP components and systems, and what is your process for
qu;;tlity vecificiltion? What hilve been the most frequc::nt problems on Ult' hydraulic sysrc::m
and the control pods?
7. During the berv.:een BOP period at the end of January 20 10, what repair
am.! maintenance work was performed on the pod solenoid valves and was it cl one under
()EM procedures and condi tions?
R. When w;ls the bst timf' tht' bl ind shear mms were changed, ;llld what maintenance I
inspection routine has been performed since?
9. What modifications have been made to the ROV intervention system on the Deepwater
Horizon BOPs?
BP-HZN-BLY00061248
Critical Questions
I Halliburton Cementing & Mud Logging
1. Explain all che inputs into OptiCem?
2. \\i'har was che main focus of the OptiCem modeling runs)
3. was i$sue ;trounu muu cumprt!ssil>iliry when you were nmning t he OptiCc.-m
model? How did you g<'"t the OptiCt"m morld ro hydrostatic
by the MDT logging tool?
4. \'Vhat were the mechanical specificatiom of the centralizers used in the OptiCem model?
5. Did you read version 18, gas flow potential when you sent the report to BP?
6. Did you notify anyone of the serious risk of gas flow potential?
7. How do you calibrate the OptiCem hydraulic model to actual conditions? (Cementing
Engineer)
8. What input parameter s in OpriCem model create the largest modeling errors? (Cementing
Engineer)
9. Explain how the open hole calliper data was used in the OptiCem modeling?
10. are the differences between the OptiCem hydraulic model and Halliburton's drilling
fluids Hydraulic model? Wh:n is che accuracy of che models? (Cementing Engineer)
11. How l-l;dl iburron test nitrified cement slurry at <tcnt<t l welll.1ore conditions? (Cementing
Engineer)
12. \\1m is 1-lal.liburton's QA/QC procedure for cement and cement additives? (Cementer,
Cementing Engineer)
13. f-low do you ensure cement slurry pumped meet design criteria? (Cementer, Cementing
bngineer)
14. What is the calibration process for sensors on the cement unit- pressure, volume density,
additive Yolumes? \'\'hen was the last time the unit was calibrated? Do you have rt!cords of
the calibrations? (Cementer)
15. Describe how the cement w'li t and che nitrogen unit were rigged up on the D\XiJ-1 for the
fo>lmecl cemen r job? \\.'hat the size and volume of the cemenring line from the unit 10 the
rig floor? From the nitrogen rie in point 10 the remenring head? (Cementer)
16. Has p::-rfurmt"d any post-job tt">ting using mueri:ds from tht> D\X'l-1 job?
Testing to simulate the D\X'H cement job? \'V'hat tests were performed? were the
results? (Cementer, Cementing Engi.nec::r)
17. Did you compare the actual job to rhe pre-job OpriCem model? I low did you feel this job
went? (Cementing Engineer)
1l:L What )'our experience in using Nitriticu t:ement for J eep water production intervals? How
many jobs have you pumped under these types of conuirions? How Joes che complexity of
this job compare w others? (Cementer, Cc:: menring Engineer)
19. is the perCI:!ll t of failure> ior nitrified cement jobs? \X'hat is the primary failure mode?
What is the nature of the failure? \'\'hat are the success factors? How did this job compare?
(Cementer, Cementing Engineer)
20. Mud Logging- (Halliburton Mud Logger)
a. \X'h;n is tltt" proeedu re fur t nuniroring the vulume of fluids pumped
during riser dispbtcements;.
b. \'\!hat sensors were rou monitoring during thr riser displacement and at time of
incic.knr? r\nything srrangt:?
21. Do you calculate thr decrease in St>lndpipc pressure when displacing the riser with seawater?
Do you compare the calculated results ro actual results?
22. Wh;lt sensors have alarm serrmgs dunng riser displacements? Were t hey turned on during
the riser cl isplneemcn t?
23. How is flow out sensor calibr:nccl? How ;rccurate is the flow out rare in
BP-HZN-BLY00061249
Critical Questions
j Cameron- Driller & Controls System Engineer
1. If the well is flowing and the blind shear ram closes. what ca.n the blind shear ram
rolera te a.ntl still seaP
2. With knowledge of the system leaks, what affect would they have on the BOP to
perform it's primarily function?
3. With knowl<::dge of the system modifications, \\ hat affect. would they have on the
HOP to per form it's primar(ly function;:
4. Describe in cierail , how rhe .AMP system loss nf power,
communication and hydraulic pressure?
5. Based on the service work you have performed on the Deepwater Horizon, what are
the most problematic components?
BP-HZN-BLY00061250
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- DOJ Pre-Trial Statement On QuantificationДокумент14 страницDOJ Pre-Trial Statement On QuantificationwhitremerОценок пока нет
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- To's Proposed FOF and COLДокумент326 страницTo's Proposed FOF and COLOSDocs2012Оценок пока нет
- 2013-9-18 Aligned Parties Pre-Trial Statement Doc 11411Документ41 страница2013-9-18 Aligned Parties Pre-Trial Statement Doc 11411OSDocs2012Оценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- 2013-9-11 BPs Phase II PreTrial Reply Memo For Source Control Doc 11349Документ13 страниц2013-9-11 BPs Phase II PreTrial Reply Memo For Source Control Doc 11349OSDocs2012Оценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- To's Post-Trial BriefДокумент57 страницTo's Post-Trial BriefOSDocs2012Оценок пока нет
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- BP's Proposed Findings - Combined FileДокумент1 303 страницыBP's Proposed Findings - Combined FileOSDocs2012Оценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- BP Pre-Trial Statement On QuantificationДокумент13 страницBP Pre-Trial Statement On Quantificationwhitremer100% (1)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- 2013-09-05 BP Phase 2 Pre-Trial Memo - Source ControlДокумент13 страниц2013-09-05 BP Phase 2 Pre-Trial Memo - Source ControlOSDocs2012Оценок пока нет
- USAs Proposed Findings Phase I (Doc. 10460 - 6.21.2013)Документ121 страницаUSAs Proposed Findings Phase I (Doc. 10460 - 6.21.2013)OSDocs2012Оценок пока нет
- HESI's Proposed FOF and COLДокумент335 страницHESI's Proposed FOF and COLOSDocs2012Оценок пока нет
- HESI's Post-Trial BriefДокумент52 страницыHESI's Post-Trial BriefOSDocs2012Оценок пока нет
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- BP's Post-Trial BriefДокумент72 страницыBP's Post-Trial BriefOSDocs2012Оценок пока нет
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- USAs Post Trial Brief Phase I (Doc. 10461 - 6.21.2013)Документ49 страницUSAs Post Trial Brief Phase I (Doc. 10461 - 6.21.2013)OSDocs2012Оценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- State of LAs Post Trial Brief Phase I (Doc. 10462 - 6.21.2013)Документ23 страницыState of LAs Post Trial Brief Phase I (Doc. 10462 - 6.21.2013)OSDocs2012Оценок пока нет
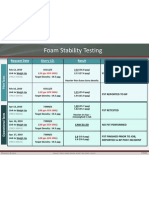
- Foam Stability Testing: Request Date Slurry I.D. Result CommentsДокумент1 страницаFoam Stability Testing: Request Date Slurry I.D. Result CommentsOSDocs2012Оценок пока нет
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Exterior: Circa 2003Документ1 страницаExterior: Circa 2003OSDocs2012Оценок пока нет
- Plaintiffs Proposed Findings and Conclusions (Phase One) (Doc 10459) 6-21-2013Документ199 страницPlaintiffs Proposed Findings and Conclusions (Phase One) (Doc 10459) 6-21-2013OSDocs2012Оценок пока нет
- State of ALs Post Trial Brief Phase I (Doc. 10451 - 6.21.2013)Документ22 страницыState of ALs Post Trial Brief Phase I (Doc. 10451 - 6.21.2013)OSDocs2012Оценок пока нет
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- PSC Post-Trial Brief (Phase One) (Doc 10458) 6-21-2013Документ72 страницыPSC Post-Trial Brief (Phase One) (Doc 10458) 6-21-2013OSDocs2012100% (1)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Macondo Bod (Basis of Design)Документ23 страницыMacondo Bod (Basis of Design)OSDocs2012Оценок пока нет
- Arnaud Bobillier Email: June 17, 2010: "I See Some Similarities With What Happened On The Horizon"Документ5 страницArnaud Bobillier Email: June 17, 2010: "I See Some Similarities With What Happened On The Horizon"OSDocs2012Оценок пока нет
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Driller HITEC Display CCTV Camera System: Source: TREX 4248 8153Документ1 страницаDriller HITEC Display CCTV Camera System: Source: TREX 4248 8153OSDocs2012Оценок пока нет
- Circa 2003Документ1 страницаCirca 2003OSDocs2012Оценок пока нет
- DR Gene: CloggedДокумент1 страницаDR Gene: CloggedOSDocs2012Оценок пока нет
- Laboratory Results Cement Program Material Transfer TicketДокумент13 страницLaboratory Results Cement Program Material Transfer TicketOSDocs2012Оценок пока нет
- Circa 2003Документ1 страницаCirca 2003OSDocs2012Оценок пока нет
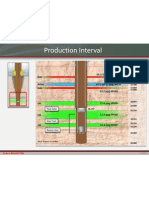
- Production Interval: 14.1-14.2 PPG M57B Gas Brine GasДокумент1 страницаProduction Interval: 14.1-14.2 PPG M57B Gas Brine GasOSDocs2012Оценок пока нет
- April 20, BLOWOUT: BP Misreads Logs Does Not IdentifyДокумент22 страницыApril 20, BLOWOUT: BP Misreads Logs Does Not IdentifyOSDocs2012Оценок пока нет
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- End of Transmission: Transocean Drill Crew Turned The Pumps Off To InvestigateДокумент1 страницаEnd of Transmission: Transocean Drill Crew Turned The Pumps Off To InvestigateOSDocs2012Оценок пока нет
- Webster:: Trial Transcript at 3975:2-4Документ1 страницаWebster:: Trial Transcript at 3975:2-4OSDocs2012Оценок пока нет
- Nitrogen TriiodideДокумент8 страницNitrogen Triiodidesharklaser009Оценок пока нет
- Emergency Preparedness ManualДокумент6 страницEmergency Preparedness ManualOferations Suffort DefartmentОценок пока нет
- IgneousrocksДокумент20 страницIgneousrocksapi-289539870Оценок пока нет
- Ilinox Atex LineДокумент13 страницIlinox Atex LineDidit AndiatmokoОценок пока нет
- TaalДокумент24 страницыTaalFranc Ventura0% (1)
- Green Book, Methods For The Determination of Possible Damage, CPR 16EДокумент337 страницGreen Book, Methods For The Determination of Possible Damage, CPR 16Ejeremyg998100% (8)
- Composition A 5Документ3 страницыComposition A 5Frank Der-BesteОценок пока нет
- HM CompilationsДокумент8 страницHM CompilationsDarkoОценок пока нет
- Anarchist Cookbook 2004 (Part-2)Документ2 страницыAnarchist Cookbook 2004 (Part-2)Jagmohan JagguОценок пока нет
- Volcaniclastic Sediments - Composition, Classification and DiagenesisДокумент45 страницVolcaniclastic Sediments - Composition, Classification and DiagenesisDavid A. Cuéllar100% (3)
- Dystopian Short StoryДокумент9 страницDystopian Short Storyapi-269395151Оценок пока нет
- Failure Analysis of Engineering Structures Methodology and Case HistoriesДокумент206 страницFailure Analysis of Engineering Structures Methodology and Case Historiesdennis_dizon_6100% (4)
- Cryogenic GrindingДокумент21 страницаCryogenic GrindingRahul Yadav100% (1)
- Major Accidents in Process IndustriesДокумент18 страницMajor Accidents in Process IndustriesAnonymous 1XHScfCIОценок пока нет
- CLB FC 0X Se Rep 0096 - C1Документ193 страницыCLB FC 0X Se Rep 0096 - C1jeddijОценок пока нет
- Beyond Misinformation 2015Документ52 страницыBeyond Misinformation 2015Jim Jones100% (4)
- Testimony of Yasuhiko Taketa A Survivor of Hiroshima GENSUIKIN PDFДокумент6 страницTestimony of Yasuhiko Taketa A Survivor of Hiroshima GENSUIKIN PDFThe Dangerous OneОценок пока нет
- From ENEMIES WITHIN: Inside the NYPD’s Secret Spying Unit and Bin Laden’s Final Plot Against America by Matt Apuzzo and Adam Goldman. Copyright © 2013 by A&G Books, Inc. Reprinted by permission of Touchstone, a Division of Simon & Schuster, Inc.Документ2 страницыFrom ENEMIES WITHIN: Inside the NYPD’s Secret Spying Unit and Bin Laden’s Final Plot Against America by Matt Apuzzo and Adam Goldman. Copyright © 2013 by A&G Books, Inc. Reprinted by permission of Touchstone, a Division of Simon & Schuster, Inc.wamu8850Оценок пока нет
- Abrams Oif PDFДокумент20 страницAbrams Oif PDFsolnegro7100% (1)
- Chemistry of High Energy Materials: R.A. RodriguezДокумент8 страницChemistry of High Energy Materials: R.A. RodriguezCarlos Hernandez MontesОценок пока нет
- Coc ExcelДокумент4 страницыCoc ExcelJan Melchor AglibotОценок пока нет
- Gamma World - Water Rights (Mass CONFusion 1984) (2nd Ed)Документ15 страницGamma World - Water Rights (Mass CONFusion 1984) (2nd Ed)tommy fletcher100% (4)
- Incident Reporting Form (Ir 01) : Fatality Lti I RWC Accident NEAR MissДокумент1 страницаIncident Reporting Form (Ir 01) : Fatality Lti I RWC Accident NEAR Missmuhammadumar412296Оценок пока нет
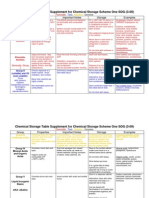
- Chemical Storage TableДокумент4 страницыChemical Storage TableMin Si ThuОценок пока нет
- Blasting Technology - Chemistry of ExplosivesДокумент27 страницBlasting Technology - Chemistry of ExplosivesBenjamin AmoahОценок пока нет
- Hunter S. Thompson BiographyДокумент323 страницыHunter S. Thompson BiographyangelrizoОценок пока нет
- Oisd GDN 165Документ20 страницOisd GDN 165sgh1355Оценок пока нет
- Squig GobbaДокумент2 страницыSquig GobbaPatrick Högye100% (1)
- Report Tex WritingДокумент6 страницReport Tex WritingshevaachandraОценок пока нет
- Mystara CSДокумент28 страницMystara CSmadison76100% (7)
- Machine Learning Guide for Oil and Gas Using Python: A Step-by-Step Breakdown with Data, Algorithms, Codes, and ApplicationsОт EverandMachine Learning Guide for Oil and Gas Using Python: A Step-by-Step Breakdown with Data, Algorithms, Codes, and ApplicationsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (4)
- Practical Reservoir Engineering and CharacterizationОт EverandPractical Reservoir Engineering and CharacterizationРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- Internal Combustion: How Corporations and Governments Addicted the World to Oil and Subverted the AlternativesОт EverandInternal Combustion: How Corporations and Governments Addicted the World to Oil and Subverted the AlternativesРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (2)
- Pocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataОт EverandPocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (22)