Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
3 934584 78 0
Загружено:
nguyenhongduongktdtИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
3 934584 78 0
Загружено:
nguyenhongduongktdtАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
6
Contents
Contents
Basics
10 Areas of use for diesel engines 10 Suitability criteria 10 Applications 14 Engine characteristic data 16 Basic principles of the diesel engine 16 Method of operation 19 Torque and power output 20 Engine efficiency 23 Operating statuses 27 Operating conditions 30 Fuel-injection system 31 Combustion chambers 34 Diesel fuels 38 Alternative fuels
76 Fuel supply system (low-pressure stage) 76 Fuel tank 76 Fuel lines 77 Diesel fuel filter 78 Fuel-supply pump 80 Distributor tube 81 Low-pressure pressurecontrol valve 81 ECU cooler 81 Fuel cooler 82 Supplementary valves for in-line fuel-injection pumps 84 Overview of in-line fuelinjection pump systems 84 Areas of application 84 Types 85 Design 85 Control 88 Presupply pumps for inline fuel-injection pumps 88 Applications 89 Design and method of operation 91 Manual priming pumps 91 Preliminary filter 91 Gravity-feed fuel-tank system 92 Type PE standard in-line fuel-injection pumps 93 Fitting and drive system 93 Design and method of operation 102 Design variations 112 Type PE in-line fuel-injection pumps for alternative fuels 113 Operating in-line fuelinjection pumps 114 Governors and control systems for in-line fuel-injection pumps 114 Open and closed-loop control 116 Action of the governor/ control system
116 Definitions 117 Proportional response of the governor 118 Purpose of the governor/ control system 121 Types of governor/ control system 126 Overview of governor types 132 Mechanical governors 158 Calibration devices 171 Type PNAB pneumatic shutoff device 172 Timing devices 174 Electric actuator mechanisms 176 Control-sleeve in-line fuel-injection pumps 177 Design and method of operation 180 Overview of distributor fuel-injection pump systems 180 Areas of application 180 Designs 182 Port-controlled systems 184 Solenoid-valve-controlled systems 188 Helix and port-controlled distributor injection pumps 189 Applications and installation 191 Design 194 Low-pressure stage 197 High-pressure pump with fuel distributor 206 Auxiliary control modules for distributor injection pumps 206 Overview 208 Governors 215 Timing device 218 Mechanical torque-control modules 231 Load switch 231 Potentiometer 232 Delivery-signal sensor
Air supply
40 Cylinder-charge control systems 40 Overview 41 Intake air filters 44 Swirl flaps 44 Turbochargers and superchargers 55 Exhaust-gas recirculation
Diesel fuel injection
56 Basic principles of diesel fuel injection 56 Mixture distribution 58 Start of injection and delivery 60 Injected-fuel quantity 61 Injection characteristics 66 Injection pressure 67 Injection direction and number of injection jets 68 Overview of diesel fuel-injection systems 68 Requirements 70 Designs
Contents
233 Shutoff devices 234 Electronic Diesel Control 237 Diesel-engine immobilizers 238 Solenoid-valve controlled distributor injection pumps 238 Areas of application 238 Designs 240 Fitting and drive system 242 Design and method of operation 244 Low-pressure stage 246 High-pressure stage of the axial-piston distributor injection pump 250 High-pressure stage of the radial-piston distributor injection pump 254 Delivery valves 255 High-pressure solenoid valve 256 Injection timing adjustment 262 Electronic control unit 263 Summary 264 Overview of discrete cylinder systems 264 Single-plunger fuel-injection pumps PF 266 Unit injector system (UIS) and unit pump system (UPS) 270 System diagram of UIS for cars 272 System diagram of UIS/UPS for commercial vehicles 274 Type PF single-plunger fuel-injection pumps 274 Design and method of operation 276 Sizes 278 278 279 282 286 Unit Injector (UI) Installation and drive Design and construction Operating concept High-pressure solenoid valve
288 Unit pump (UP) 288 Design and construction 290 Unit pump for large-size engines 292 Overview of common-rail system 292 Areas of application 292 Design 293 Method of operation 296 System diagram for cars 298 System diagram for commercial vehicles 300 High-pressure components of common-rail system 300 High-pressure pump (pressure generation) 305 Fuel rail (high-pressure accumulator) 308 Nozzle (fuel injection) 312 314 316 320 Nozzles Pintle nozzles Hole-type nozzles Future development of the nozzle Nozzle holders Standard nozzle holders Stepped nozzle holders Two-spring nozzle holders Nozzle holders with needle-motion sensors
335 Helix and-Port-controlled axial-piston distributor pumps 336 Solenoid-valve-controlled axial-piston and radialpiston distributor pumps 337 Common Rail System (CRS) 338 Unit Injector System (UIS) for passenger cars 339 Unit Injector System (UIS) and Unit Pump System (UPS) for commercial vehicles 340 Application-related adaptation of car engines 344 Application-related adaptation of commercial-vehicle engines 349 Calibration tools 352 352 353 354 357 358 359 Sensors Automotive applications Temperature sensors Micromechanical pressure sensors Rail-pressure sensors Inductive engine-speed sensors Rotational-speed (rpm) sensors and incremental angle-of-rotation sensors Hall-effect phase sensors Half-differential shortcircuiting-ring sensors Accelerator-pedal sensors Hot-film air-mass meter HFM5 LSU4 planar broad-band Lambda oxygen sensors
322 324 325 326 327
360 362 364 366 368
328 High-pressure lines 328 High-pressure connection fittings 329 High-pressure delivery lines
370 Electronic Control Unit (ECU) 370 Operating conditions 370 Design and construction 370 Data processing 376 Open and closed-loop electronic control 376 Open and closed-loop electronic control 376 Data processing (DP) 378 Data exchange with other systems
Electronics
332 Electronic Diesel Control EDC 332 Requirements 332 System overview 333 System structure 334 In-line fuel-injection pumps
Contents
380 Fuel-injection control 389 Lambda closed-loop-control for passenger-car diesel engines 395 Further special adaptations 395 Port-and-helix-controlled fuel-injection systems: Triggering 398 Solenoid-valve-controlled injection systems: Triggering 405 Control and triggering of the remaining actuators 406 Substitute functions 407 Torque-controlled EDC systems 410 Data transfer between automotive electronic systems 410 System overview 410 Serial data transfer (CAN) 415 Prospects 416 Actuators 416 Electropneumatic converters 417 Continuous-operation braking systems 417 Fan control function 418 Start-assist systems
440 Nozzle tests 442 Emissions measurement concept 444 Turbidity testing
Background information
13 History of the diesel engine 15 Diesel aircraft engines of the 1920s and 30s 33 M System 54 Pressure-wave superchargers 75 History of diesel fuel injection 99 History of in-line fuel-injection pumps 103 1978 diesel speed records 115 History of the governor 202 Off-road applications 205 Diesel records in 1972 207 History of the mechanically controlled distributor injection pump from Bosch 239 Family tree of Bosch electronically controlled distributor injection pumps 241 1998 Diesel Records 285 The history and the future of the unit injector (UI) 313 Dimensions of diesel fuel-injection technology 321 High-precision technology 331 Caviation in the high-pressure system 348 Engine test bench 363 Measured variables on diesel engines 375 Very severe demands are made on the ECU 379 Where does the word Electronics come from? 382 Race-Trucks 429 Global service 449 Ozone and smog 481 Greenhouse effect
Diesel exhaust gases
446 446 446 448 450 Exhaust emissions Overview Major components Combustion by-products Reduced emissions
452 Exhaust-gas treatment systems 452 Diesel oxidation-type catalytic converter 452 Particulate filter 453 NOX accumulator-type catalytic converter 455 SCR principle 455 Combination systems 456 Emissions-control legislation 456 Overview 458 CARB legislation (Cars/LDT) 462 EPA regulations (Cars/LDT) 464 EU regulations (Cars/LDT) 467 Japanese legislation (cars/LDTs) 468 US legislation (commercial vehicles) 469 EU legislation (commercial vehicles) 471 Japanese legislation (commercial vehicles) 472 US test cycles 474 European test cycle 475 Japanese test cycles for cars and LDTs 476 Test cycles for commercial vehicles 478 Emissions testing for type approval 482 Index of technical terms 482 Technical terms 487 Abbreviations
Servicing and repairs
420 Electronic diagnosis 420 Operating concept 423 On-Board-Diagnosis (OBD) 424 424 426 430 Service technology Overview Testing EDC systems Fuel-injection pump test benches 432 Testing in-line fuel-injection pumps 436 Testing helix and portcontrolled distributor injection pumps
Вам также может понравиться
- Automotive Mechatronics PDFДокумент549 страницAutomotive Mechatronics PDFgo8894% (18)
- Energy Efficiency Electronic Book Version 1548 - PowerGenerationHandbook v1 - 1Документ362 страницыEnergy Efficiency Electronic Book Version 1548 - PowerGenerationHandbook v1 - 1avikrisadОценок пока нет
- Piston Engines, GasTurbine Engines, Propellers PDFДокумент141 страницаPiston Engines, GasTurbine Engines, Propellers PDFAakash SawaimoonОценок пока нет
- 8344x Indx PDFДокумент6 страниц8344x Indx PDFAnsabОценок пока нет
- Nissan Serena c24 Repair Manual IndexДокумент18 страницNissan Serena c24 Repair Manual IndexAditya Pratama0% (2)
- ITube LinksДокумент12 страницITube Linksrahman.alam787Оценок пока нет
- High Performance Single-Engine CourseДокумент5 страницHigh Performance Single-Engine CourseSETAH S. de R.L.Оценок пока нет
- CaterpilarДокумент4 страницыCaterpilarpangestu66100Оценок пока нет
- DiavelДокумент831 страницаDiavelManuel Martinez CarranzaОценок пока нет
- TAD1242GE: Volvo Penta Genset EngineДокумент0 страницTAD1242GE: Volvo Penta Genset EngineJulio Hinostroza AlarconОценок пока нет
- ABB Power Generation GuideДокумент362 страницыABB Power Generation GuideGoncaloBritoNunes100% (1)
- VAG 4.0 TFSiДокумент88 страницVAG 4.0 TFSiBoris KopetschekОценок пока нет
- Cummins ISLДокумент5 страницCummins ISLNoe Arguet50% (2)
- Códigos de Falla Cummins ISX QSX - ISX QSX Cummins Fault CodesДокумент13 страницCódigos de Falla Cummins ISX QSX - ISX QSX Cummins Fault CodesFranco Dennis Catata100% (1)
- SearchДокумент25 страницSearchDaniel Thirtle0% (1)
- LS600hL LS600h (Engine)Документ36 страницLS600hL LS600h (Engine)Minh Nhat Phan100% (2)
- 16H Ats PDFДокумент37 страниц16H Ats PDFMiguel Marquez KongОценок пока нет
- G3608 Spec SheetДокумент4 страницыG3608 Spec SheetTu Pham100% (1)
- 2016 Ducati Xdiavel 67364Документ360 страниц2016 Ducati Xdiavel 67364SANTOSDIOSOОценок пока нет
- PLTMG Prabumulih 18V34SG Rev.3 OperasiДокумент66 страницPLTMG Prabumulih 18V34SG Rev.3 OperasiOctavianus Harahap100% (2)
- QSK19 Engine Fuel System Familiarization2Документ73 страницыQSK19 Engine Fuel System Familiarization2Tiagohowpy Ramos100% (1)
- g3520c Natural Gas For 1950Документ6 страницg3520c Natural Gas For 1950Shahzad AliОценок пока нет
- Ducati Monster 796 Service ManualДокумент685 страницDucati Monster 796 Service ManualShamaelBenShabbatai88% (8)
- CAT 320D CID CodeДокумент80 страницCAT 320D CID CodeZaw Phyo100% (1)
- HP1050Документ736 страницHP1050bowcoastieОценок пока нет
- Caterpillar Fault CodesДокумент6 страницCaterpillar Fault Codessystembyt100% (1)
- Turbocompounding TechnologyДокумент23 страницыTurbocompounding TechnologyPawan BeniwalОценок пока нет
- Ducati Panigale R Owner's ManualДокумент326 страницDucati Panigale R Owner's Manualfauzi ahmadОценок пока нет
- Caterpillar Fault Codes PDFДокумент21 страницаCaterpillar Fault Codes PDFElhadi Enp84% (56)
- G3306Документ4 страницыG3306carlucido247970100% (1)
- Aircraft Gas Turbine Tecnology by IRWINE TREAGER PDFДокумент684 страницыAircraft Gas Turbine Tecnology by IRWINE TREAGER PDFLorraine100% (3)
- MTUДокумент16 страницMTUWira Karya Diesel40% (5)
- Ducati 848 Workshop and Repair Manual - Manuale D'Officina Superbike 848 - EnGLISH - 2008Документ774 страницыDucati 848 Workshop and Repair Manual - Manuale D'Officina Superbike 848 - EnGLISH - 2008CapitanSalami100% (1)
- Pow Powertrain Products PDF enДокумент67 страницPow Powertrain Products PDF enJesse DavisОценок пока нет
- VR220, 330Документ180 страницVR220, 330denniscm3k3Оценок пока нет
- S590 Machine SpecsДокумент6 страницS590 Machine SpecsdilanОценок пока нет
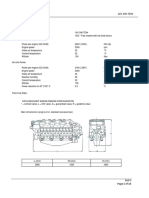
- 3-934584-65-9 VP44Документ4 страницы3-934584-65-9 VP44raddumocanuОценок пока нет
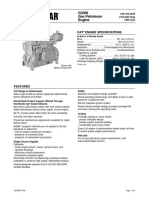
- 3516C 4160V 2250 KW Tier 4 PrimeДокумент6 страниц3516C 4160V 2250 KW Tier 4 PrimesprikitОценок пока нет
- Mechanical Engineering ContentДокумент1 страницаMechanical Engineering ContentMowaten MasryОценок пока нет
- Complete Dodge Cummins ISB fault code guideДокумент2 страницыComplete Dodge Cummins ISB fault code guideEduardo TorresОценок пока нет
- Nissan Almera n15 - Engine Control System PDFДокумент419 страницNissan Almera n15 - Engine Control System PDFRolfs Almonte Diaz83% (12)
- AEC Militant MkIII Recovery User Manual V1Документ78 страницAEC Militant MkIII Recovery User Manual V1David Kelly100% (3)
- MAN B&W Diesel A/S Electronically Controlled ME Engine DocumentationДокумент116 страницMAN B&W Diesel A/S Electronically Controlled ME Engine Documentationnicoletabytax100% (11)
- How a car works guideДокумент256 страницHow a car works guidealonsodiazherreraОценок пока нет
- Service Manual Sachs MadAss 50Документ107 страницService Manual Sachs MadAss 50Zabegan Eden100% (1)
- TAD941GE: Volvo Penta Industrial DieselДокумент2 страницыTAD941GE: Volvo Penta Industrial DieselroozbehxoxОценок пока нет
- Cat Engine Specifications 2.0 G/BHP-HR Nox (Nte)Документ4 страницыCat Engine Specifications 2.0 G/BHP-HR Nox (Nte)Oghale B. E. OmuaborОценок пока нет
- ISX Fault Code ListДокумент5 страницISX Fault Code ListSlV50% (2)
- 13644653116090HFU84 300 kVAДокумент2 страницы13644653116090HFU84 300 kVALeonardo Da Cao QuyОценок пока нет
- G3512 SpecДокумент4 страницыG3512 SpecnunkpОценок пока нет
- Marine Diesel Engines: Maintenance, Troubleshooting, and RepairОт EverandMarine Diesel Engines: Maintenance, Troubleshooting, and RepairРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (15)
- Automotive Air Conditioning and Climate Control SystemsОт EverandAutomotive Air Conditioning and Climate Control SystemsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (6)
- Plumbing and Piping Systems Inspection Notes: Up to CodeОт EverandPlumbing and Piping Systems Inspection Notes: Up to CodeРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (2)
- Hydroprocessing for Clean Energy: Design, Operation, and OptimizationОт EverandHydroprocessing for Clean Energy: Design, Operation, and OptimizationОценок пока нет
- Ho Chi Minh Was Noted For Success in Blending Nationalism and CommunismДокумент10 страницHo Chi Minh Was Noted For Success in Blending Nationalism and CommunismnguyenhongduongktdtОценок пока нет
- ISI Cancellation in 4G Wireless MobilesДокумент1 страницаISI Cancellation in 4G Wireless MobilesnguyenhongduongktdtОценок пока нет
- Operation and Main Aux GensetДокумент123 страницыOperation and Main Aux GensetMd Rodi BidinОценок пока нет
- OLTC FailureДокумент18 страницOLTC FailurevtpsОценок пока нет
- VianoBrochure 2015Документ60 страницVianoBrochure 2015Тимченко ИванОценок пока нет
- Modified Thick Thermal Barrier CoatingsДокумент86 страницModified Thick Thermal Barrier CoatingsAnonymous p0mg44xОценок пока нет
- AC70000Документ4 страницыAC70000Faruq. MechanicОценок пока нет
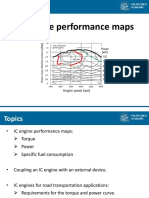
- Chapt1 - Torque & PowerДокумент42 страницыChapt1 - Torque & PowerpeterОценок пока нет
- Informe Isuzu Septiembre 2022Документ24 страницыInforme Isuzu Septiembre 2022Compania CuencanaОценок пока нет
- Skybridge Company InformationДокумент61 страницаSkybridge Company InformationbackinthesandtrapОценок пока нет
- Product WoodwardДокумент46 страницProduct WoodwardSuhendar Bin Husein HaimeedОценок пока нет
- EngineIzusu6BG1 TRA13forzx240 5GДокумент154 страницыEngineIzusu6BG1 TRA13forzx240 5GGarick Parialpalacio100% (2)
- Benefits of Electric Loaders Over DieselДокумент12 страницBenefits of Electric Loaders Over Dieselumut2000Оценок пока нет
- History of Rail TransportДокумент4 страницыHistory of Rail TransportAsif MalikОценок пока нет
- Catalogue of SimulatorДокумент9 страницCatalogue of Simulatorgire_3pich2005Оценок пока нет
- Man D2862 (800 - 1000 Kva)Документ4 страницыMan D2862 (800 - 1000 Kva)eriscano1100% (3)
- Proact™ Isc Integrated Speed Control: Product Manual 26246 (Revision U, 5/2017)Документ120 страницProact™ Isc Integrated Speed Control: Product Manual 26246 (Revision U, 5/2017)davonesОценок пока нет
- L554 452 0202 05-2000 enДокумент243 страницыL554 452 0202 05-2000 enЯрослав Валько75% (4)
- Syllabus of MVSIДокумент3 страницыSyllabus of MVSIKashan Khan0% (1)
- Assessment of Small Reciprocating Engine Manufacturers and Generator Set PackagersДокумент66 страницAssessment of Small Reciprocating Engine Manufacturers and Generator Set PackagersAnonymous zfmlsb2GjA100% (1)
- Processes 11 01199Документ21 страницаProcesses 11 01199Đại HảiОценок пока нет
- Prabhu T. - Automobile Engineering. Basic Fundamentals. Basic Fundamentals To Advanced Concepts of Automobile Engineering (2021, Nestfame Creations Pvt. LTD.) - Libgen - LiДокумент1 377 страницPrabhu T. - Automobile Engineering. Basic Fundamentals. Basic Fundamentals To Advanced Concepts of Automobile Engineering (2021, Nestfame Creations Pvt. LTD.) - Libgen - Livivek panchalОценок пока нет
- Allis Chalmers HD-5 Service ManualДокумент220 страницAllis Chalmers HD-5 Service Manualjeffreyguy1Оценок пока нет
- Diesel Engine ComponentsДокумент34 страницыDiesel Engine Componentsmohammad100% (1)
- Kubota v1505 Engine Repair ManualДокумент10 страницKubota v1505 Engine Repair Manualchristopher98% (51)
- Power Data Ambient Data: P-Wheel (KW)Документ1 страницаPower Data Ambient Data: P-Wheel (KW)Andreea NițoiuОценок пока нет
- Types: Piston Rings Cylinder Liners/finned Cylinders AssemblyДокумент3 страницыTypes: Piston Rings Cylinder Liners/finned Cylinders Assemblyeng_ebrahim_20000% (1)
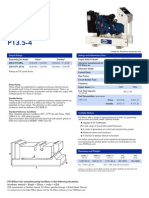
- FG Wilson P13.5-4 Generating Set Ratings and SpecsДокумент4 страницыFG Wilson P13.5-4 Generating Set Ratings and Specsscribdledee100% (1)
- Great-Wall-Wingle-5 2016 en Manual de Taller 76a3f09b84 (394-510)Документ117 страницGreat-Wall-Wingle-5 2016 en Manual de Taller 76a3f09b84 (394-510)Brändön LänfräncöОценок пока нет
- AFfpd1522582796 PDFДокумент8 страницAFfpd1522582796 PDFMexanik212Оценок пока нет
- Fire TruckДокумент4 страницыFire Truckchris0% (1)
- HeatEnginesVol 2Документ314 страницHeatEnginesVol 2luchoosorioОценок пока нет
- 01 4TNV98T-ZCSTY 规格参数表-英文Документ4 страницы01 4TNV98T-ZCSTY 规格参数表-英文Eric CОценок пока нет
- Genset PDFДокумент63 страницыGenset PDFkartik kapoorОценок пока нет