Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Question: What Is Hardware?
Загружено:
Aneek KumarИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Question: What Is Hardware?
Загружено:
Aneek KumarАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Question: What is Hardware?
Answer: Physical component of a pc is known as hardware. Question: What is software? Answer: A set of instruction is called a Programme. A group of programme is software. Two types of software:1. Operating system software 2. Application software Question: How many type of O/S Installation? Answer: Three Type of installation:Attended (Clean Installation) Unattended (Upgrade) Remote installation Service. Question: What is Partition? Answer: A dedicated space on the hard disk is known as partition. Question: What is disk Partition? Answer: Disk partition is a way of dividing the physical disk so that each partion can work / function as a separate unit. Question: How many difference between NTFS & FAT file. Answer: NTFS provide file & folder level Security. FAT does not provide. NTFS provide Disk compression. (FAT- NA) NTFS provide file encryption & disk Quota. NTFS accept A.D. (FAT- NA) Question: How to change FAT32 to NTFS. Answer: Start- Run- cmd- convert drivename: /fs:ntfs. Question: What is Disk Quota? Answer: Disk quota is used the specific the disk space for particular user for a particular drive. Question: What is EFS? Answer: EFS is Encrypt file system we convert our data on a coded form due to security reason. Which is not accessible by the other users. Question: What is Remote Desktop program? Answer: Remote Desktop program is a program or an operation system feature that allows the user to convert to a computer in another location, see that computers desktop and interact with it as if it were local. Question: What is Remote Assistance? Answer: Computer users may have many problems and queries that the users find difficult to solve on their own remote Assistance enables the users to get help and assistance from their help desk professionals easily. Question: What is Sharing? Answer: Sharing is used to access the data from the network sharing of three types:Manually sharing. By default sharing. Published sharing. Question: What is hardware Profile? Answer: It is a setting of hardware device which is enable or disable any hardware threw which we can unable or disable any hardware devices. Question: How many type of users? Answer: Three type of Users Local user. Domain User. Built-in-user. (It is automatically created during installation) Local User: The user account to use for managing & maintaing the workgroup environment and limit the security within one machine. These User account decide in the computer security account manager. Domain User: Domain is a user in the server machine that can manage all the network resources security and environment variables from that server to all their client machine. Question: What is Group? Answer: Group is a collection of user and computers. If we have to set rights and permission of multiple users then create group and add users to this group and the set rights and permission on this group. Two type of group 1. Local Group. 2. Domain Group. Question: Local Security policy? Answer: Set of rules which is not directly link with user and group. It is implemented on entire machine.
(Run- secpol.msc)
Question: What is offline? Answer: It is used the access the data from the network when the network path breaks that is system is in offline. Question: What is Backup? Answer: Backup is a utility program if Microsoft windows network operating system. Which is used for the disaster recovery method. There are five types of backup threw which user can safe or secure own database in the local machine or network. Normal Backup. Incremental Backup. Differential Backup. Copy Backup. Daily Backup. Normal Backup:- It is used to selected files and folders. It clears the archive attributes. Incremental Backup:- It is used to backup of all selected files or folders which are created or modified after the last/ incremental backup. It also clear archive attributes. It takes less time to take backup and also less and takes more time to restore. Differential Backup:- It is used to backup of all selected files or folders which are created or modified after the last normal/ differential backup. It sets the archive attributes. It takes more time to take backup and also take more space and takes less time to restore. Copy Backup:- It is used to backup of all selected files and folders. It also sets the archive attributes after the backup. Daily Backup:- It is used to backup of all selected files and folders. It is also sets the archive attributes after the backup as daily backup. Question: IP V4? Answer: It is a 32 bit Binary address which is separate by 4 doted (.) decimal and use in the source address and destination address of IP packet. It is software address or logical address in IP network. It is communication of network or Host id. It is divided into classic the first bit of I.P address represents the classic. Question: Default Gatway? Answer: Directly connected on router part is known as default gatway generally the first I.P address of each I.P loops is known as default gatway address.
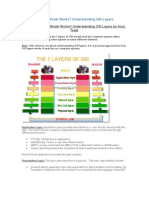
Question: OSI layer. Answer: Open System Interconnection (ISO International standard Org.) OSI DOD Application layer Presentation Layer Application Layer Session Layer Transport Layer Host to Host Network Layer Internet Data link Layer Physical Layer Network Access Physical Layer:- physical layer is the responsible for movement of indivial bits from one hope to node to the next. Connection type. Topology. Transmission mode. Bandwidth use. Multiplexing. Data rate. Synchronization of bits. Transmission media (LAN/WAN). Digital and Analog signals. Data link Layer:- Data link layer is responsible for moving frames from one hope to the next Framing. Physical addressing Flow control. Error control. Access control. Network Layer:- Network layer is responsible for delivery to individual packet from the source host to the destination hosts. Logical addressing. Switching. Routes discover. Routes selection. Transport Layer:- Transport layer is responsible for process to process delivery of the entire machine. Service point addressing.
End to End flow control. End to End error control. Address/ name resolution. Segmentation. Connection control. Session Layer:- (Network Dialog controller) Session layer is the network dialog controller session are control by mechanisms that established, synchronization and manage dialog between devices. Dialog control. Synchronization. Session administration Connection established. Data transfer. Connection release. Presentation Layer:- presentation layer is concerned with the cintex ans simentix of the information exchange between two systems. Translation. Encryption. Compression. Application Layer:- It enables the user, human or software to access the network it provide user into faces and support for services such as email (electronic mail) remote file access and transfer shared, data base management and other types of disturbed information services. File transfer, access manage. Mail server. Directory services.
DOD TCP/IP Protocol Application Layer(Application) SMTP FTP HTTP fw SNMP TFTP POP3 TELNET Host to Host (Transport) SCTP TCP UDP Internet (Network) ICMP ICMP IP DHCP BOOTP ARP RARP Network Access (Host to Host) physical layer Physical layerToken ring, Ethernet, PDDi.
(Application layer) SMTP:- Simple Mail Transfer Protocol is specify a standard for exchanging mail between work stations. It simply specify how the massage is passed from one host to another.
FTP:- File Transfer Protocol unables a user to move copies of files between two hosts. Ftp users virtual sercuite to established a reliable an account and password as verification or they can we configure for anyone access. HTTP:- Hyper Text Transfer Protocol provide a request/ method for accessing information on www and intranets. Using HTTP a client established a connection with a server and sends a request. The request indicates its purpose and provides simple search and retrieval functionly. DNS:- Domain Name system. SNMP:- Simple Network Management Protocol unables you to moniter network from a single work stations called an SNMP manager. TFTP:- Trival File Transfer Protocol it transfer a file between two systems without specific an account and password. TFTP does not require a reliables strums transport services. It runs on UDP or any other unreliable packet delivery system. POP3:- Post Office Protocol 3 is a standard mail server commonly used on the internet it provides a message store that holds incoming mail until user log on and download it all pending message and resptive attachments are download at the same time. POP3 is user the SMTP messaging protocol. TELNET:(Transport) UDP & TCP are transport level/layer protocols responsible for delivery of a massage from process to another. SCTP:- It provides support for newer applications such a voice over the internet. It is a transport layer protocol that combined trust feature of TCP & UDP. TCP:- Transmission control Protocol provide full transport layer services to application. Its accepts message of any lenth from a upper layer protocol and provides full duplex, acknowledge connection arrinted, full controlled transport to a TCP peer in a remote network station. TCP divides a stream of data into smaller units called segments. Each segment include a secure number for recording TCP is slow. UDP:- User Datagram Protocol is connectionless and does not acknowledge data received UDP accept and transport datagrams from a upper layer protocol & UDP is faster than TCP. (Network Layer) ICMP:- Internet Control Message Protocol is a machinzme used used by host and gateways to send notification of datagrams problems back to the senders ICMP works with IP to provide internet work error end other control information to TCP & upper layer protocols. An IP hosts sends ICMP message when:A packet cannot reach its destination. A packet TTLs expired. Buffer space is insufficient. It needs to determine if another host is up. If needs to determine which networks it is attached to. It needs to notify entire network of congested or failed link. Common ICMP message include the following:Time Exceeded. Destination unreachable. Echo request echo reply. IGMP:- Internet Group Message Protocol is used to the simultaneous transmission of a message to a group of recipients. IP:- Internet Working Protocol is the transpition mechanize used by the TCP/IP protocol. It is an unreliable and connection less protocol a best effort delivery service. The term best efforts means that IP provides no error checking or tracking IP transport data in packets called datagrams each of which is transpated separately. DHCP:- Dynamic Host Configure Protocol. BOOTP:- BOOTP working with RARP. ARP:- Address Resolution Protocol used to associate a logical with a physical address. Logical Address
Mac or Physical Address RARP:- The reverse address resolution protocol allows a host to discover its internet address when it knows only its physical address. It is used when a computer is connected to a network for the first or when a diskless computer is routed. Mac or Physical Address Logical Address (Physical Layer) Token Ring:Ethernet:PDDI:Others:Question: Describe managing printer. Answer: Local printer is used in the workgroup network which manage the print jobs and their properties including their security writes. Network Printer is used in the domain network that manage the centralized environment of printing which is know as print server. Question: What is RIS? Answer: Remote installation service is used to connect the NIC/LAN card that can configure their remote settings an on imaging server. This server can share their own operating system files through NIC/LAN cards and install the o/s in each and every client without any disc. Requirement:DNS service must be installed and configure properly. DHCP service must be installed and configure properly. Active directory must be installed. RIS and RIS image must be configure.
RIS service must be authorized in Active directory. Question: What's the difference between DDR1 and DDR2 RAM? Answer: It depends on the Motherboard weather it supports DDR1 or 2. older computers used DDR1. now all new pc's use DDR2 and DDR 3. The physical difference is that DDR ram memory is 184 pins long. DDR2 is 240 pins.
Question: What is the difference between WINS a nd DNS?
Answer: WINS and DNS are both name resolution services for TCP/IP networks. While WINS resolves names in the NetBIOS namespace, DNS resolves names in the DNS domain namespace. WINS primarily supports clients that run older versions of Windows and applications that use NetBIOS. Windows 2000, Windows XP, and Windows Server 2003 use DNS names in addition to NetBIOS names. Environments that include some computers that use NetBIOS names and other computers that use domain names must include both WINS servers and DNS servers. Question: What is Recovery Console? Answer: If our system is corrupt means some system files are corrupt when our system file or corrupt some application may be not working properly with the help of recovery console feature we recover a system files. Question: Booting Sequence. Answer: Windows Xp. POST (Power on self test) BSL (Boot Startup loader) Initial startup of configuration file. NTLDR NTDETECT.com MSdos.sys Io.sys Command.sys Page file.sys Logon process Question: Windows Server 2003 Edition. Answer: Win 2003 Standard Edition C.P.U 133 MHZ. 550 MHZ. RAM 128 MB 256 MB HDD 1.5 GB NA Win 2003 Enterprises Edition:C.P.U 133 MHZ. 550 MHZ. RAM 128 MB 256 MB HDD 1.5 GB 2.0 GB Win 2003 Data center Edition:C.P.U 400MHZ 733 MHZ RAM 512 MB 1GB HDD 1.5 GB 2.0 GB Win 2003 WEB Edition:C.P.U 133 MHZ 550MHZ RAM 1.5 GB NA HDD 128 MB 256 MB
Question: What is Active Directory? Answer: Active directory stores information about object on the network and makes this information easy for administrator and user to find and use. Function:Centralizes control of network resources. Centralizes and decentralizes resources management. Stores object securely in a logical structure. Optimizes network traffic. The Logical components of active directory structure include:Domain Organizational unit Tress Forest Domain controllers Schema Question: What is Schema in Active Directory? Answer: Active Directory Schema define objects that can be stored in Active Directory. Question: What is the name of Active Directory database and its location? Answer: c:\Windows\NTDS\ntds.dit. Question: What are the log file of Active Directory? Answer: There are three log file of Active Directory. Edb.log Res1.log Res2.log Question: What is ADC? Answer: Additional Domain Controller contains the read write copy of data base of parent root domain. It is used for fault tolerance when the server/parent domain down. Question: Parent Root Domain? Answer: The first domain controller in a network/ in a forest is knows a parent root domain Question: What is Global Catalog Server? Answer: Global catalog server contains the complete information of its own domain and partial information of the domain controller in a forest. By default first domain controller contain a copy of global catalog server in a forest. It is needed to maintain and prevent the duplexes of an active directory objects. Question: What is member server? Answer: win 2000/2003/2008 server o/s which is a part of active directory but does not contain active directory database. Question: What is FTP? Answer: FTP is an acronym for File Transfer Protocol. As the name suggests, FTP is used to transfer files between computers on a network. You can use FTP to exchange files between computer accounts, transfer files between an account and a desktop computer, or access online software archives. Question: What is Anonymous FTP? Answer: Through anonymous FTP account you can access a machine without having to have an account on that machine. Question: What is IIS? Answer: It is used to manage and maintain website and FTP sites in operating system. It is also known as web server that control their document with IIS. The system administrator can also authenticate the website in different port ID number that defines the websites then it will runs threw the SSL (Secure socket layer, port no. 443). Question: what is DNS? Answer: Domain name system is a naming convention. It is a logical hierarchical name space. It also knows as naming convention it resolves hosts names to IP address and vice versa. It uses FQDN to resolve I.P address to host name and vice versa. Two types of DNS:Forward lookup zone Host name to IP address (PTR Record). Reverse lookup zone IP Address to host name (A-Record). There are three parts of forward and Reverse lookup zone:Primary zone: Store the full read & write copy of all DNS resource record. Secondary zone. Stub zone. DNS Query: A Query is a request for name resolution to a DNS server. Two type of DNS Query:Recursive Query:- A recursive querie is a query made to a DNS server in which the DNS client asked the DNS server to provide a complete answer to query. Iterative Query:- DNS Client ask to DNS server to best answer with the help of further query use in WAN technologies. Root Hint: Root hints are DNS resource records stored on a DNS server that list the IP address for the DNS root servers. Forwarder: A forwarder is a DNS server designated by other internal DNS servers to forward queries for resolving external or offsite DNS domain names. Question: What is FQDN? Answer: Fully Qualified Domain Name which includes host name and domain name.
Question: What is the difference between Host name and FQDN? Answer: Host name is the name of the local indusial host and FQDN is the combination of Host name and domain name. Question: What are the different types of DNS Zones used in windows server 2003? Answer: DNS Zone types are following. Primary Zone Secondary Zone Active Directory Intregrated Zone Reverse Lookup Zone Stub Zone.
Question: What is DHCP? Answer: The basic function DHCP is provide IP address to the client side automatically on the behalf of client request. DHCP Lease: The amount of time that the DHCP server grants to the DHCP clients permission to use a particular IP address. DHCP Scope: A DHCP scope consists of a pool of IP address the DHCP server can assign or leave to DHCP client. Question: What is VPN? Answer: VPN is the feature threw which we can connect remote location client. VPN works on two protocols:LAN (Microsoft)- Point to point turning protocol (PPTP) WAN (Cisco)- Layer to point turning protocol (LPTP) Requirement:Two LAN card. Disabled windows firewall ICS. (Start programs - admin tools services windows firewall ICS service).
Question: What is difference between HUB and switch? Answer: HUB SWITCH Hub works on data link layer of the OSI model. Switch work on Network layer of the OSI model. HUB work on 10 mbps. Switch work on 100 mbps. User cant sent & receive packet data at a same time. User can sent & receive packet data on same time. We cant create VLAN. We can create VLAN on configuration switch. Question: What is a IP Address and MAC address? Answer: IP address is a logical protocol which is used to communication to other pcs. Mac address a physical address which is coded on the LAN card. IP Address MAC Address 32 bit Address. Its a logical address. Its a physical address. Its work on network layer. Its work on data link layer. Question: What is the difference between network LAN, WAN, and MAN. Answer: LAN WAN MAN
LAN: A Local Area Network (LAN) is a network that is confined to a relatively small area. It is generally limited to a geographic area such as a writing lab, school, or building. Rarely are LAN computers more than a mile apart.
WAN: Wide Area Networks connect larger geographic areas, such as india, the United States, or the world. MAN: (metropolitan area network) This is a larger network that connects computer users in a particular geographic area or region. Question: What is Network? Answer: The computers on a network may be linked through cables, telephone lines, radio waves, satellites, or infrared light beams. Question: What is networking? Answer: Networking is two more computer connected using a transmission media and use the shared resources.
Question: How to restore win xp in command mode? Answer: Restart your computer and press (F8) during the initial startup Select Safe mode. Select win XP O/S. Logon to your computer with an admin account. Start- Run- CMD- C:window\system32\restore\rstrui.exe.
Question: Difference between Standard and Enterprise Edition of Exchange Server 2003? Answer: Standard Edition:One storage group can be created on a server. Exchange clustering is not supported. Maximum 16 GB data base limit per data base. Enterprise Edition:Four Storage Group Five database per storage group Exchange clustering supported Question: What is a Network Topology?
Answer:
Network topology is the layout pattern of interconnections of the various elements (links, nodes, etc.) of a computer network. Question: What are windows XP system tools? Answer: Disk cleanup, Disk Defragmenter, system restore, Backup, System Information. Question: How to check a hardware device is properly installed or not. Answer: My computer- properties- hardware- device manager. Question: How to start a computer in Safe mode? Answer: Restart computer then press F8 key and select the option. Question: How to check shared folder in a computer? Answer: my computer- manage- shared folder. Question: How to enable & disable firewall? Answer: Run- firewall.cpl- ok- general- off. Question: How do you recover an object in Active directory which is accidentally deleted by you, with no backup? Answer: using ntdsutil.exe command we can restored the active directory object. Question: How to convert roaming user profile to mandatory user profile? Answer: Rename the Ntuser.dat to Ntuser.man. Question: Define IP Address classes and its subnet mask. Answer: Class A 1 to 126. Public 255.0.0.0 Subnet mask Class B 128 to 191 Public 255.255.0.0 Subnet mask Class C 192 to 223 Public 255.255.255.0 Subnet mask Question: What is IP Sec? Answer: IPSec (Internet Protocol Security) is a framework for a set of protocols for security at the network or packet processing layer of network communication. Question: What is Traee utility? Answer: Traee utility is a command line utility that you can use to check the path to the destination IP address that you want to reach. Question: What is a Bandwith? Answer: The volume of data that can be transferred across a network at a given time is called its bandwith. Question: A user application on their desktop is not working, explain what you would do to resolve this problem.
Answer: we need check when did the issue started like after installation any software or after performing any update. If you are not sure of the above information in a windows pc go to Event viewer and check if there any error information available. If available follow the step related to that. If not available kill the application in the task manager any try to open it. If it is still not working try restarting the pc reinstalling application. Question: How to improve virtual memory of pc? Answer: Just right click on my computer Select properties Go to advance- performance Settings- advanced Select virtual memory Select how much u want & Apply Question: What is PXE used for? What dependencies does it have to be useful? Answer: Preboot Execution Environment (PXE):- When we are trying to boot system from network we need to enable PXE boot device from BIOS. It is helpful to install operating system from network and it will pick IP address automatically. It is helpful in large network were we cannot install operating system manually. Question: What is outlook Express? Answer: Outlook express is a POP3 and IMAP-compatible mail client with a built-in news reader. It is available with internet explorer for windows XP or as a stand-alone client for MAC operating system 8.1 to 9x you can configure it to retrieve email from your account via pop or configure it as an IMAP client to access your mail on an IMAP mail server. Question: When was windows XP released? Answer: 25th Oct, 2001 (RTM 24th Aug, 2001) Question: How will you install operating system in more than 50 pc at a time when the all pc having same configuration? Answer: I would install operating system in 50 pc support of a remote installation or ghost installation. When we use the Remote Installation first we will see which pc we are using in network then we will see all the network card PXI Bootable. Question: What is APIPA? Answer: APIPA stands for Automatic Private IP Address. If DHCP server is not available APIPA will be assigned to the system. Question: What is Domain Local, Global and Universal Group? Answer: Domain Local:- Domain local groups assign access permissions to global domain groups for local domain resources. Global Group:- Global groups provide access to resources in other trusted domains. Universal Group:- Universal groups grant access to resources in all trusted domains. Question: Where are Group Policy Stored? Answer: %SystemRoot%System32\GroupPolicy Question: What are Exchange Services? Answer: There are nine exchange services. Microsoft Exchange Event Microsoft Exchange Management Microsoft Exchange Information Store Microsoft Exchange Site replication Microsoft Exchange MTA Stack Microsoft Exchange Routing Services Microsoft Exchange Mailbox store Microsoft Exchange POP3 Microsoft Exchange IMAP4 Question: Difference between Distribution Group and Security Group? Answer: Security Group:- allow you to manage user and computer access to shared resources. Distribution Group:- mainly used for distribution of emails.
Вам также может понравиться
- Lab1 1Документ4 страницыLab1 1Md. Tanvir Hasan 1812974042Оценок пока нет
- Week 1 TutorialДокумент12 страницWeek 1 TutorialRabindra PoudelОценок пока нет
- Cisco Interview QuestionsДокумент8 страницCisco Interview QuestionsssprudhviОценок пока нет
- Networking - 2 (B1 Jan'23 Batch)Документ9 страницNetworking - 2 (B1 Jan'23 Batch)divakara sОценок пока нет
- What Are The Difference Between Hub and SwitchДокумент10 страницWhat Are The Difference Between Hub and SwitchSameer HussainОценок пока нет
- These Interview Questions With Answers Will Test Your Basic Knowledge of PC and NetworkingДокумент4 страницыThese Interview Questions With Answers Will Test Your Basic Knowledge of PC and NetworkingAnonymous LYPs0TATwVОценок пока нет
- Different Networking Systems Advantages and DisadvantagesДокумент71 страницаDifferent Networking Systems Advantages and Disadvantagesshabir AhmadОценок пока нет
- Osi ModelДокумент11 страницOsi ModelMu Asif KhОценок пока нет
- Networking Question Answer InterviewДокумент10 страницNetworking Question Answer InterviewNavin KumarОценок пока нет
- Desktopinterviewqestionsanswer 121224011729 Phpapp01Документ5 страницDesktopinterviewqestionsanswer 121224011729 Phpapp01srinivas K100% (1)
- Networking Questions PDFДокумент38 страницNetworking Questions PDFAdam DanielОценок пока нет
- Course Code CIT 333Документ53 страницыCourse Code CIT 333M Shumraiz SharifОценок пока нет
- Network Operating SystemsДокумент32 страницыNetwork Operating SystemsRieri RiezaОценок пока нет
- Computer Networks (1) - 157-172Документ16 страницComputer Networks (1) - 157-172Harini VelrajОценок пока нет
- QuizДокумент9 страницQuizGeisler Jelo MangaranОценок пока нет
- Jimma University: Jimma Institute of Technology Faculty of ComputingДокумент7 страницJimma University: Jimma Institute of Technology Faculty of ComputingadmachewОценок пока нет
- Session 1 AnswerДокумент3 страницыSession 1 AnswerAdvait GarvОценок пока нет
- Interview QuestionДокумент9 страницInterview Questionsonupawar8883Оценок пока нет
- DCN286 Week 3 Lecture 1Документ4 страницыDCN286 Week 3 Lecture 1Vitor Fogaça TonioliОценок пока нет
- System File CheckerДокумент9 страницSystem File CheckeraaronОценок пока нет
- Install and Configure A NetworkДокумент29 страницInstall and Configure A Networkperweeng31Оценок пока нет
- Day-4 Active DirectoryДокумент3 страницыDay-4 Active DirectoryPrudhvikrishna GurramОценок пока нет
- Networking QuestionsДокумент32 страницыNetworking QuestionsRaghu RamanОценок пока нет
- Principles of Operating System All inДокумент5 страницPrinciples of Operating System All inMark JuarezОценок пока нет
- CCNAДокумент14 страницCCNAshripal singhОценок пока нет
- Osi Model NotesДокумент7 страницOsi Model NotesSuman KumarОценок пока нет
- Difference Between Outlook Express and MS Outlook?Документ7 страницDifference Between Outlook Express and MS Outlook?bigОценок пока нет
- Selective CourseДокумент51 страницаSelective CoursewilliamОценок пока нет
- Asiignment With SolutionДокумент56 страницAsiignment With SolutionmaulikОценок пока нет
- Command Line Troubleshooting Tools Reference GuideДокумент9 страницCommand Line Troubleshooting Tools Reference GuidedabaОценок пока нет
- What Is Ping Utility?Документ7 страницWhat Is Ping Utility?Sanjeev RajОценок пока нет
- Course 276 Exercise 2Документ70 страницCourse 276 Exercise 2Essaïd Fassy FehryОценок пока нет
- 4Документ64 страницы4ksant77Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 26: Remote Log-In, Electronic Mail and File TransferДокумент34 страницыChapter 26: Remote Log-In, Electronic Mail and File Transferedsheeran23170% (1)
- How OSI 7 Layer Model WorksДокумент9 страницHow OSI 7 Layer Model WorksRanjit SinghОценок пока нет
- System Network and AdministrationДокумент6 страницSystem Network and AdministrationDaddy's PicksОценок пока нет
- OSI ModelДокумент8 страницOSI ModelMuhammad RehanОценок пока нет
- FON Unit IV - IoTДокумент29 страницFON Unit IV - IoT21d41a0513Оценок пока нет
- Net 102 Prelim ModulesДокумент36 страницNet 102 Prelim ModulesNovy Airhris MianaОценок пока нет
- Network ProgrammingДокумент23 страницыNetwork ProgrammingDesi babaОценок пока нет
- Study Guide ExpandedДокумент7 страницStudy Guide ExpandedGabby ShearerОценок пока нет
- OSI ModelДокумент33 страницыOSI Modelhadirehman488Оценок пока нет
- Quizdocx 6 PDF FreeДокумент9 страницQuizdocx 6 PDF FreeJOSHUA JOSHUAОценок пока нет
- CSE 338 Lab Manual 1Документ3 страницыCSE 338 Lab Manual 1Russel PeterОценок пока нет
- Network Basics 1.1 What Is A Network?Документ115 страницNetwork Basics 1.1 What Is A Network?santhoshmayal_460311Оценок пока нет
- COS2626 Exam NotesДокумент77 страницCOS2626 Exam NotesNedeem HendricksОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Socket Programming-NBVДокумент289 страницIntroduction To Socket Programming-NBVvenkat_ritchОценок пока нет
- Osi and Tcp/Ip Model: DR - Tanuja S.DhopeДокумент36 страницOsi and Tcp/Ip Model: DR - Tanuja S.DhopeAnmol PatilОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Networking and The Osi ModelДокумент22 страницыIntroduction To Networking and The Osi ModelJerald Pacheco JoseОценок пока нет
- Used To Manage and Monitor The NetworkДокумент35 страницUsed To Manage and Monitor The NetworkFikru TesefayeОценок пока нет
- Microsoft Certified Systems Engineer: Types of NetworksДокумент163 страницыMicrosoft Certified Systems Engineer: Types of NetworksArun TiwariОценок пока нет
- # TCP/IP Protocol Layers:-1.application Layer: Protocols UsedДокумент8 страниц# TCP/IP Protocol Layers:-1.application Layer: Protocols UsedPRIYANSHU KUMARОценок пока нет
- Application Threats: Cyber Laws in Different CountriesДокумент30 страницApplication Threats: Cyber Laws in Different CountriesVariОценок пока нет
- FTP Server and ClientДокумент8 страницFTP Server and ClientMonika SharmaОценок пока нет
- Notes On Computer Networks Unit5Документ9 страницNotes On Computer Networks Unit5Rohit Chaudhary100% (2)
- Networking Interview QuestionДокумент9 страницNetworking Interview QuestionbobeluОценок пока нет
- Windows Admin QuestionsДокумент5 страницWindows Admin QuestionsNagendra Prasad TatikondaОценок пока нет
- Abstract On Socket ProgrammingДокумент33 страницыAbstract On Socket Programmingyogesh_yadav2012100% (2)
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1От EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- 3rd Floor ITДокумент1 страница3rd Floor ITAneek KumarОценок пока нет
- Activity Exemplar - Emails For The Release PlanДокумент4 страницыActivity Exemplar - Emails For The Release PlanMartinAlexisGonzálezVidal100% (1)
- Mutual FundsДокумент34 страницыMutual Fundsbijmadevi jaiswalОценок пока нет
- Offboarding Devices - JAMFДокумент10 страницOffboarding Devices - JAMFAneek KumarОценок пока нет
- Screencapture Documentation Meraki MS Stacking Switch Stacks 2022 12 16 16 - 28 - 27Документ14 страницScreencapture Documentation Meraki MS Stacking Switch Stacks 2022 12 16 16 - 28 - 27Aneek KumarОценок пока нет
- Activity Template - Email CoalitionДокумент2 страницыActivity Template - Email CoalitionAneek KumarОценок пока нет
- Business KnowingДокумент1 страницаBusiness KnowingAneek KumarОценок пока нет
- How Can Make Request and Report Issue in Service NowДокумент4 страницыHow Can Make Request and Report Issue in Service NowAneek KumarОценок пока нет
- TANCalculation SampleSolutionДокумент1 страницаTANCalculation SampleSolutionAneek KumarОценок пока нет
- AD-pradeep Script Error LogsДокумент1 страницаAD-pradeep Script Error LogsAneek KumarОценок пока нет
- Route Print, Ping Drops and Tracert LogsДокумент4 страницыRoute Print, Ping Drops and Tracert LogsAneek KumarОценок пока нет
- 004 Star BurnДокумент14 страниц004 Star BurnAneek KumarОценок пока нет
- Calculating RASДокумент2 страницыCalculating RASAneek KumarОценок пока нет
- Azure Enrollment IssueДокумент1 страницаAzure Enrollment IssueAneek KumarОценок пока нет
- 1296460382php ModuleДокумент199 страниц1296460382php ModuleKotireddy DeviОценок пока нет
- Running Fortios (Fortigate VM) in VmwareДокумент15 страницRunning Fortios (Fortigate VM) in VmwareAneek KumarОценок пока нет
- PDF ResizeДокумент1 страницаPDF ResizeAneek KumarОценок пока нет
- Chat HistoryДокумент191 страницаChat HistoryAneek KumarОценок пока нет
- Conversion Gate01Документ1 страницаConversion Gate01Aneek KumarОценок пока нет
- Panch Tara SongДокумент1 страницаPanch Tara SongAneek KumarОценок пока нет
- Linux ServerДокумент44 страницыLinux ServerJakub ObetkoОценок пока нет
- David Aaron Katz Health Singing: First, Get A Doctor's AdviceДокумент5 страницDavid Aaron Katz Health Singing: First, Get A Doctor's AdviceAneek KumarОценок пока нет
- Hindustani Sangeet BasicДокумент8 страницHindustani Sangeet BasicAneek KumarОценок пока нет
- Teri Befai TeДокумент1 страницаTeri Befai TeAneek KumarОценок пока нет
- Featured Snippet From The Web: Easily Add Closed Captioning - Get Camtasia® NowДокумент7 страницFeatured Snippet From The Web: Easily Add Closed Captioning - Get Camtasia® NowAneek KumarОценок пока нет
- !! Requires - Read Me !!Документ6 страниц!! Requires - Read Me !!Aneek KumarОценок пока нет
- What Is Mysql: RelationalДокумент5 страницWhat Is Mysql: RelationalAneek Kumar100% (2)
- Readme JsdksДокумент2 страницыReadme JsdksAneek KumarОценок пока нет
- !! Requires - Read Me !!Документ1 страница!! Requires - Read Me !!Aneek KumarОценок пока нет
- !! Requires - Read Me !!Документ1 страница!! Requires - Read Me !!Aneek KumarОценок пока нет
- Solved Objective Finalterm Mega Paper by Syeda 2Документ65 страницSolved Objective Finalterm Mega Paper by Syeda 2Irshad Ullah BaigОценок пока нет
- TR 3647Документ4 страницыTR 3647batungОценок пока нет
- Cabsat PDFДокумент43 страницыCabsat PDFBhARaT KaThAyATОценок пока нет
- CCNPv7 TSHOOT Lab4 2 Mixed Layer 2 3 Connectivity StudentДокумент13 страницCCNPv7 TSHOOT Lab4 2 Mixed Layer 2 3 Connectivity StudentPeter Ndungu0% (2)
- Digital Pakistan's JounneryДокумент4 страницыDigital Pakistan's JounnerysyedchangezafarОценок пока нет
- TR400 Tachometer ES400 Rev F 111813Документ2 страницыTR400 Tachometer ES400 Rev F 111813Juan GalvesОценок пока нет
- IoT Based Health Monitoring System@Документ17 страницIoT Based Health Monitoring System@atikpОценок пока нет
- Project Invention in ChsДокумент5 страницProject Invention in ChsMelanie Daclan AntepasadoОценок пока нет
- PHILIPS Laser MFDДокумент86 страницPHILIPS Laser MFDbladimir77Оценок пока нет
- 7.6 Branch and Bound Method: C 1 1 0 0 0 Basic Variables Basic Basic Variables X X S S S Coefficient Variables ValuesДокумент8 страниц7.6 Branch and Bound Method: C 1 1 0 0 0 Basic Variables Basic Basic Variables X X S S S Coefficient Variables ValuesKowsalyaОценок пока нет
- Pile Foundation Design Using Microsoft Excel: Computer Applications in Engineering Education January 2007Документ13 страницPile Foundation Design Using Microsoft Excel: Computer Applications in Engineering Education January 2007Aayush CharanОценок пока нет
- IPSXM3136 2 Installation ManualДокумент20 страницIPSXM3136 2 Installation ManualdreicouОценок пока нет
- Eaton VFDДокумент94 страницыEaton VFDsalimskaini1990Оценок пока нет
- GAMBAS Middleware - GAMBASДокумент5 страницGAMBAS Middleware - GAMBASSURYA PRAKASH PANDEYОценок пока нет
- Integrated XML Gateway Implementation GuideДокумент142 страницыIntegrated XML Gateway Implementation GuideManu K BhagavathОценок пока нет
- Hughes 9502 Upgrader User Instructions PC v3.5 0Документ7 страницHughes 9502 Upgrader User Instructions PC v3.5 0Derek RogerОценок пока нет
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 PM583 Di524 8 9 Ta521 Di524 PM583 Ta521 CM597 Ci522Документ1 страница1 2 3 4 5 6 7 PM583 Di524 8 9 Ta521 Di524 PM583 Ta521 CM597 Ci522mahmoud sheblОценок пока нет
- Harmony Xb7 Xb7nd21Документ6 страницHarmony Xb7 Xb7nd21Luthfi KurniawanОценок пока нет
- Arduino Uno Rev3 02 TH - SCHДокумент1 страницаArduino Uno Rev3 02 TH - SCHMatija Buden100% (1)
- 1.2D Viewing TransformationsДокумент127 страниц1.2D Viewing TransformationsAbhigyan HarshaОценок пока нет
- Handwritten Text Recognition Using Deep LearningДокумент13 страницHandwritten Text Recognition Using Deep LearningHarini MurugananthamОценок пока нет
- Evidence CasesДокумент79 страницEvidence Caseszyphora grace trillanesОценок пока нет
- What Is A Digital Strategy?: What Is It About, and How Can It Be Laid Out?Документ24 страницыWhat Is A Digital Strategy?: What Is It About, and How Can It Be Laid Out?api-290841500Оценок пока нет
- Tom Shanley x86 Instruction Set Architecture PDFДокумент1 567 страницTom Shanley x86 Instruction Set Architecture PDFCharles Kelly0% (1)
- Ebook Future Proofing Internal AuditДокумент22 страницыEbook Future Proofing Internal Auditgoyosito100% (1)
- Development of Value Stream Mapping From L'Oreal's Artwork Process PDFДокумент25 страницDevelopment of Value Stream Mapping From L'Oreal's Artwork Process PDFReuben AzavedoОценок пока нет
- Financial Intelligence Centre South AfricaДокумент1 страницаFinancial Intelligence Centre South AfricaShahab UllahОценок пока нет
- Jurnal Internasional XiaomiДокумент16 страницJurnal Internasional Xiaomipoppy hidayahОценок пока нет
- 4U Incline AccelerationДокумент4 страницы4U Incline AccelerationUshbah AsimОценок пока нет