Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Risk Assessment
Загружено:
Anuj BhagatИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Risk Assessment
Загружено:
Anuj BhagatАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
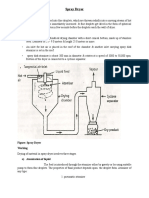
Risk Assessment: Risk Identification: What might be the risk?
isk? Risk Analysis: What is the probability of the occurrence of the risk? Risk Evaluation: What might be the impact of the risk identified and analyzed? Risk Control: Whether to reduce and/ or accept the risk? Reduce the risk to an acceptable level using analysis like benefit-cost analysis.
Risk management methodology Quality risk management supports a scientific and practical approach to decision-making. It provides documented, transparent and reproducible methods to accomplish steps of the quality risk management process based on current knowledge about assessing the probability, severity and sometimes detectability of the risk. Traditionally, risks to quality have been assessed and managed in a variety of informal ways (empirical and/ or internal procedures) based on, for example, compilation of observations, trends and other information. Such approaches continue to provide useful information that might support topics such as handling of complaints, quality defects, deviations and allocation of resources. Quality risk management can facilitate better and more informed decisions, can provide regulators with greater assurance of a companys ability to deal with risks, and might affect the extent and level of direct regulatory oversight. In addition, quality risk management can facilitate better use of resources by all parties.
Quality the degree to which a set of inherent properties of a product, system or process fulfils requirements (see ICH Q6a definition specifically for "quality" of drug substance and drug (medicinal) products.) Quality risk management a systematic process for the assessment, control, communication and review of risks to the quality of the drug (medicinal) product across the product lifecycle Risk the combination of the probability of occurrence of harm and the severity of that harm
Failure Mode Effects Analysis Failure Mode Effects and Criticality Analysis Fault Tree Analysis Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP)
Hazard Operability Analysis (HAZOP) Preliminary Hazard Analysis
Potential Applications of QRM: Documentation Training and Education Quality defects Risk Communication Auditing/ Inspection Periodic Review Change Management/ Control Continual Improvement Inspection and Assessment
Microsoft Office Project Task scheduling Task execution Assigning cost and resources Monitoring cost & schedule
Quality management is concerned with controlling activities with the aim of ensuring that products and services are fit for their purpose and meet the specifications. Producing products of the required quality does not happen by accident. There has to be a production process which is properly managed. Ensuring satisfactory quality is a vital part of the production process. Risk related considerations have also become increasingly important as companies strive to enhance their brand and protect the interests of their employee, customers and shareholders. Quality management can be defined as managing the entire organization so that it performs perfectly in all the dimensions of product and services that are important to the customer. The quality of a service or product determines whether a customer will remain a customer or will move to a competitor. Quality management therefore uses quality assurance and control of processes as well as products to achieve more consistent quality. Having a good quality system
in place will ensure that your products, services are of the highest standards, your customers are happy and the future of your organization is heading in the right direction.
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- My Son The Fanatic, Short StoryДокумент4 страницыMy Son The Fanatic, Short StoryScribdAddict100% (2)
- The Diary of Anne Frank PacketДокумент24 страницыThe Diary of Anne Frank Packetcnakazaki1957Оценок пока нет
- AppyДокумент18 страницAppyAnuj Bhagat0% (1)
- Horizontal Machining Centers: No.40 Spindle TaperДокумент8 страницHorizontal Machining Centers: No.40 Spindle TaperMax Litvin100% (1)
- Ace CorporationДокумент3 страницыAce CorporationAnuj BhagatОценок пока нет
- Infosys CSR ElabДокумент1 страницаInfosys CSR ElabAnuj BhagatОценок пока нет
- Indu SPMДокумент1 страницаIndu SPMAnuj BhagatОценок пока нет
- 5 Ways To Sell AnythingДокумент2 страницы5 Ways To Sell AnythingAnuj BhagatОценок пока нет
- Shipping Corporation of India: Project Report OnДокумент6 страницShipping Corporation of India: Project Report OnAnuj BhagatОценок пока нет
- Parle Products PVTДокумент51 страницаParle Products PVTrathod30100% (7)
- Socio-cultural influences on educationДокумент4 страницыSocio-cultural influences on educationofelia acostaОценок пока нет
- The Seven Kings of Revelation 17Документ9 страницThe Seven Kings of Revelation 17rojelio100% (1)
- Indian ChronologyДокумент467 страницIndian ChronologyModa Sattva100% (4)
- Elements of Ayurveda Daily Routine GuideДокумент1 страницаElements of Ayurveda Daily Routine GuideShivani GargОценок пока нет
- Financial Services : An OverviewДокумент15 страницFinancial Services : An OverviewAnirudh JainОценок пока нет
- Design of Self - Supporting Dome RoofsДокумент6 страницDesign of Self - Supporting Dome RoofszatenneОценок пока нет
- Dryers in Word FileДокумент5 страницDryers in Word FileHaroon RahimОценок пока нет
- New Japa Retreat NotebookДокумент48 страницNew Japa Retreat NotebookRob ElingsОценок пока нет
- Detailed Lesson Plan in MAPEH III I. ObjectivesДокумент19 страницDetailed Lesson Plan in MAPEH III I. ObjectivesJenna FriasОценок пока нет
- SCM PPT (Supply Chain Management)Документ19 страницSCM PPT (Supply Chain Management)Mairaj NaseemОценок пока нет
- Mini Centre CatalogДокумент26 страницMini Centre CatalogJohn EarleyОценок пока нет
- OM - Rieter - UNIMix A76Документ321 страницаOM - Rieter - UNIMix A76Phineas FerbОценок пока нет
- T Cells & Autoimmunity, s3Документ21 страницаT Cells & Autoimmunity, s3LiaAriestaОценок пока нет
- Clustering Social Network GraphsДокумент12 страницClustering Social Network GraphsRáhùl SréédhãrОценок пока нет
- Oxy AcetyleneДокумент43 страницыOxy Acetyleneregupathi100% (1)
- Ir Pc-1: Pre-Check (PC) Design Criteria For Freestanding Signs and Scoreboards: 2019 CBCДокумент15 страницIr Pc-1: Pre-Check (PC) Design Criteria For Freestanding Signs and Scoreboards: 2019 CBCAbrar AhmadОценок пока нет
- Product Manual 82434 (Revision C) : Generator Loading ControlДокумент26 страницProduct Manual 82434 (Revision C) : Generator Loading ControlAUGUSTA WIBI ARDIKTAОценок пока нет
- Statement Bank MBBДокумент11 страницStatement Bank MBBminyak bidara01Оценок пока нет
- Moment Influence Line LabsheetДокумент12 страницMoment Influence Line LabsheetZAXОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 - The Political SelfДокумент6 страницChapter 7 - The Political SelfJohn Rey A. TubieronОценок пока нет
- 740 (Q50, V40, Awa 4Документ10 страниц740 (Q50, V40, Awa 4rawat2583Оценок пока нет
- Quality Management - QuestionДокумент4 страницыQuality Management - QuestionLawzy Elsadig SeddigОценок пока нет
- Modesto Mabunga Vs PP (GR 142039)Документ3 страницыModesto Mabunga Vs PP (GR 142039)Ericha Joy GonadanОценок пока нет
- Biomérieux 21342 Vitek 2 GP: Intended UseДокумент19 страницBiomérieux 21342 Vitek 2 GP: Intended UserezaОценок пока нет
- F&B Data Analyst Portfolio ProjectДокумент12 страницF&B Data Analyst Portfolio ProjectTom HollandОценок пока нет
- Horizontal Vertical MarketДокумент4 страницыHorizontal Vertical MarketVikasОценок пока нет
- Ifatsea Atsep Brochure 2019 PDFДокумент4 страницыIfatsea Atsep Brochure 2019 PDFCondor GuatonОценок пока нет